Financial Accounting > EXAM REVIEW > University of Memphis: ACCT 3120 Intermediate Acct II Exam 3 help. 118 Pages of Questions, Worked S (All)
University of Memphis: ACCT 3120 Intermediate Acct II Exam 3 help. 118 Pages of Questions, Worked Solutions and Explantions. 100%.
Document Content and Description Below
ACCT 3120 Intermediate Acct II Exam 3 help 1. Blanton Plastics, a household plastic product manufacturer, borrowed $9 million cash on October 1, 2018, to provide working capital for year-end prod... uction. Blanton issued a four-month, 15% promissory note to L&T Bank under a prearranged short-term line of credit. Interest on the note was payable at maturity. Each firm’s fiscal period is the calendar year. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record (a) the issuance of the note by Blanton Plastics and (b) L&T Bank’s receivable on October 1, 2018. 2. Prepare journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the note through 31/01/2019 3. Suppose the face amount of the note was adjusted to include interest (a noninterest-bearing note) and 15% is the bank’s stated discount rate. (a) Prepare the journal entries to record the issuance of the noninterest-bearing note by Blanton Plastics on October 1, 2018, the adjusting entry at December 31, and payment of the note at maturity. (b) What would be the effective interest rate? Req 1 Prepare the journal entries to record (a) the issuance of the note by Blanton Plastics and (b) L&T Bank’s receivable on October 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 2 Prepare the journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the note through January 31, 2019. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 3A Suppose the face amount of the note was adjusted to include interest (a noninterest-bearing note) and 15% is the bank’s stated discount rate. (a) Prepare the journal entries to record the issuance of the noninterest-bearing note by Blanton Plastics on October 1, 2018, the adjusting entry at December 31, and payment of the note at maturity. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Show less (b) • Req 3B Suppose the face amount of the note was adjusted to include interest (a noninterest-bearing note) and 15% is the bank’s stated discount rate. (b) What would be the effective interest rate? (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your final answer to 1 decimal place.) 2.Camden Biotechnology began operations in September 2018. The following selected transactions relate to liabilities of the company for September 2018 through March 2019. Camden’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Its financial statements are issued in April. 2018 a. On September 5, opened checking accounts at Second Commercial Bank and negotiated a short-term line of credit of up to $20,000,000 at the bank’s prime rate (9.5% at the time). The company will pay no commitment fees. b. On October 1, borrowed $17 million cash from Second Commercial Bank under the line of credit and issued a five-month promissory note. Interest at the prime rate of 9% was payable at maturity. Management planned to issue 10-year bonds in February to repay the note. c. Received $3,100 of refundable deposits in December for reusable containers used to transport and store chemical-based products. d. For the September–December period, sales on account totaled $4,190,000. The state sales tax rate is 3% and the local sales tax rate is 3%. (This is a summary journal entry for the many individual sales transactions for the period.) e. Recorded the adjusting entry for accrued interest. 2019 f. In February, issued $12.8 million of 10-year bonds at face value and paid the bank loan on the March 1 due date. g. Half of the storage containers covered by refundable deposits were returned in March. The remaining containers are expected to be returned during the next six months. Required: 1. Prepare the appropriate journal entries for 2018 and 2019 transactions. 2. Prepare the current and long-term liability sections of the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. Trade accounts payable on that date were $283,000. • Required 1 Prepare the appropriate journal entries for 2018 and 2019 transactions. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 2 Prepare the current and long-term liability sections of the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. Trade accounts payable on that date were $283,000. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation 3. The balance sheet at December 31, 2018, for Nevada Harvester Corporation includes the liabilities listed below: a. 12% bonds with a face amount of $48 million were issued for $48 million on October 31, 2009. The bonds mature on October 31, 2029. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on October 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $48 million. Market conditions are such that the call is not expected to be exercised. b. Management intended to refinance $11.1 million of its 12% notes that mature in May 2019. In early March, prior to the actual issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Nevada Harvester negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $6.6 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. c. Noncallable 14% bonds with a face amount of $33.0 million were issued for $33.0 million on September 30, 1996. The bonds mature on September 30, 2019. Sufficient cash is expected to be available to retire the bonds at maturity. d. A $23 million 11% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Nevada Harvester’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.7 to 1 and remains so for six months. That ratio was 1.45 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in inventory levels. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the first quarter of 2019. Required: 1. For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? 2. Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $14 million. • Required 1 For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? (Enter your answers in millions (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) • Required 2 Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $14 million. (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place, (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) 4. The unadjusted trial balance of the Manufacturing Equitable at December 31, 2018, the end of its fiscal year, included the following account balances. Manufacturing’s 2018 financial statements were issued on April 1, 2019. Other information: a. The bank notes, issued August 1, 2018, are due on July 31, 2019, and pay interest at a rate of 15%, payable at maturity. b. The mortgage note is due on March 1, 2019. Interest at 14% has been paid up to December 31 (assume 14% is a realistic rate). Manufacturing intended at December 31, 2018, to refinance the note on its due date with a new 10-year mortgage note. In fact, on March 1, Manufacturing paid $477,500 in cash on the principal balance and refinanced the remaining $982,500. c. Included in the accounts receivable balance at December 31, 2018, were two subsidiary accounts that had been overpaid and had credit balances totaling $18,850. The accounts were of two major customers who were expected to order more merchandise from Manufacturing and apply the overpayments to those future purchases. d. On November 1, 2018, Manufacturing rented a portion of its factory to a tenant for $36,600 per year, payable in advance. The payment for the 12 months ended October 31, 2019, was received as required and was credited to rent revenue. Required: 1. Prepare any necessary adjusting journal entries at December 31, 2018, pertaining to each item of other information (a–d). 2. Prepare the current and long-term liability sections of the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. • Required 1 o RePrepare any necessary adjusting journal entries at December 31, 2018, pertaining to each item of other information (a–d). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation • Required 2 Prepare the current and long-term liability sections of the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. 5. Sometimes compensation packages include bonuses designed to provide performance incentives to employees. The difficulty a bonus can cause accountants is not an accounting problem, but a math problem. The complication is that the bonus formula sometimes specifies that the calculation of the bonus is based in part on the bonus itself. This occurs anytime the bonus is a percentage of income because expenses are components of income, and the bonus is an expense. Regalia Fashions has an incentive compensation plan through which a division manager receives a bonus equal to 6% of the division’s net income. Division income in 2018 before the bonus and income tax was $320,000. The tax rate is 30%. Required: 2. Calculate the amount of the bonus. 3. Prepare the adjusting entry to record the bonus compensation. 4. Bonus arrangements take many forms. Suppose the bonus specifies that the bonus is 6% of the division’s income before tax, but after the bonus itself. Calculate the amount of the bonus. • Required 2 Calculate the amount of the bonus. (Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) Explanation • Required 3 Prepare the adjusting entry to record the bonus compensation. (Do not round intermediate calculations. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) No Event General Journal Debit Credit 1 1 Bonus compensation expense +/-0.5%12,898 Accrued bonus compensation payable +/-0.5 • Required 4 Bonus arrangements take many forms. Suppose the bonus specifies that the bonus is 6% of the division’s income before tax, but after the bonus itself. Calculate the amount of the bonus. (Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.) 4. The approach is the same in any case: (1) express the bonus formula as one or more algebraic equation(s), (2) use algebra to solve for the amount of the bonus. For example, the bonus might specify that the bonus is 6% of the division’s income before tax, but after the bonus itself: B = 0.06 ($320,000 – B) B = $19,200 – 0.06B 1.06B = $19,200 B = $18,113 6. Eastern Manufacturing is involved with several situations that possibly involve contingencies. Each is described below. Eastern’s fiscal year ends December 31, and the 2018 financial statements are issued on March 15, 2019. a. Eastern is involved in a lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a supplier. On February 3, 2019, judgment was rendered against Eastern in the amount of $115 million plus interest, a total of $130 million. Eastern plans to appeal the judgment and is unable to predict its outcome though it is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the company. b. In November 2017, the State of Nevada filed suit against Eastern, seeking civil penalties and injunctive relief for violations of environmental laws regulating hazardous waste. On January 12, 2019, Eastern reached a settlement with state authorities. Based upon discussions with legal counsel, the Company feels it is probable that $148 million will be required to cover the cost of violations. Eastern believes that the ultimate settlement of this claim will not have a material adverse effect on the company. c. Eastern is the plaintiff in a $208 million lawsuit filed against United Steel for damages due to lost profits from rejected contracts and for unpaid receivables. The case is in final appeal and legal counsel advises that it is probable that Eastern will prevail and be awarded $140 million. d. At March 15, 2019, Eastern knows a competitor has threatened litigation due to patent infringement. The competitor has not yet filed a lawsuit. Management believes a lawsuit is reasonably possible, and if a lawsuit is filed, management believes damages of up to $41 million are reasonably possible. Required: 1. Determine the appropriate means of reporting each situation. 2. Prepare the appropriate journal entries for these situations. • Required 1 Determine the appropriate means of reporting each situation. • Required 2 Prepare the appropriate journal entries for these situations. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation Required: 1. For each item, indicate how treatment of the amount would differ between U.S. GAAP and IFRS. 2. Consider the total effect of items a–d. If HW’s goal is to show the lowest total liabilities, which set of standards, U.S. GAAP or IFRS, best helps it meet that goal? • Required 1 For each item, indicate how treatment of the amount would differ between U.S. GAAP and IFRS. Explanation • Required 2 Consider the total effect of items a–d. If HW’s goal is to show the lowest total liabilities, which set of standards, U.S. GAAP or IFRS, best helps it meet that goal? 8.The Heinrich Tire Company recalled a tire in its subcompact line in December 2018. Costs associated with the recall were originally thought to approximate $47 million. Now, though, while management feels it is probable the company will incur substantial costs, all discussions indicate that $47 million is an excessive amount. Based on prior recalls in the industry, management has provided the following probability distribution for the potential loss: (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) An arrangement with a consortium of distributors requires that all recall costs be settled at the end of 2019. The risk-free rate of interest is 5%. Required: 1. & 2. By the traditional approach to measuring loss contingencies, what amount would Heinrich record at the end of 2018 for the loss and contingent liability? For the remainder of this problem, apply the expected cash flow approach of SFAC No. 7.Estimate Heinrich’s liability at the end of the 2018 fiscal year. 3. to 5. Prepare the necessary journal entries. • Req 1 and 2 By the traditional approach to measuring loss contingencies, what amount would Heinrich record at the end of 2018 for the loss and contingent liability? For the remainder of this problem, apply the expected cash flow approach of SFAC No. 7.Estimate Heinrich’s liability at the end of the 2018 fiscal year. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation • Req 3 to 5 Prepare the necessary journal entries. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Van Rushing Hunting Goods’ fiscal year ends on December 31. At the end of the 2018 fiscal year, the company had notes payable of $18.0 million due on February 8, 2019. Rushing sold 3.5 million shares of its $0.25 par, common stock on February 3, 2019, for $14.0 million. The proceeds from that sale along with $4.0 million from the maturation of some 3-month CDs were used to pay the notes payable on February 8. Through his attorney, one of Rushing’s construction workers notified management on January 5, 2019, that he planned to sue the company for $1 million related to a work-site injury on December 20, 2018. As of December 31, 2018, management had been unaware of the injury, but reached an agreement on February 23, 2019, to settle the matter by paying the employee’s medical bills of $77,000. Rushing’s financial statements were finalized on March 3, 2019. Required: 1. What amount(s) if any, related to the situations described should Rushing report among current liabilities in its balance sheet at December 31, 2018? 2. What amount(s) if any, related to the situations described should Rushing report among long-term liabilities in its balance sheet at December 31, 2018? 3. What amount(s) if any, related to the situations described should Rushing report among current liabilities and long-term liabilities in its balance sheet at December 31, 2018 if the settlement agreement had occurred on March 15, 2019, instead? 4. What amount(s) if any, related to the situations described should Rushing report among current liabilities and long-term liabilities in its balance sheet at December 31, 2018 if the work-site injury had occurred on January 3, 2019, instead? (For all requirements, enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation 1. 10. Transit Airlines provides regional jet service in the Mid-South. The following is information on liabilities of Transit at December 31, 2018. Transit’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Its annual financial statements are issued in April. 1. Transit has outstanding 6.6% bonds with a face amount of $75 million. The bonds mature on July 31, 2027. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on July 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $75 million. Market conditions are such that the call option is not expected to be exercised. 2. A $25 million 8% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Transit’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.9 to 1 and remains so for 6 months. That ratio was 1.75 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in parts inventories. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the sixth week of 2019. 3. Transit management intended to refinance $40 million of 4% notes that mature in May of 2019. In late February 2019, prior to the issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Transit negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $35 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. 4. Transit is involved in a lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a food caterer. On February 13, 2019, judgment was rendered against Transit in the amount of $59 million plus interest, a total of $60 million. Transit plans to appeal the judgment and is unable to predict its outcome though it is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the company. Required: 1. How should the 6.6% bonds be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 2. How should the 8% bank loan be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 3. How should the 4% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 4. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? 5. Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $44 million. • Req 1 to 4 How should the 6.6% bonds, 8% bank loan and 4% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? (Enter your answers in millions.) Explanation The lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a food caterer should not be accrued. The suit is in appeal and it is not deemed probable that that Transit will lose the appeal. Note disclosure is required. • Req 5 Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $44 million. (Enter your answers in millions.) 5.11.Alamar Petroleum Company offers its employees the option of contributing retirement funds up to 5% of their wages or salaries, with the contribution being matched by Alamar. The company also pays 80% of medical and life insurance premiums. Deductions relating to these plans and other payroll information for the first biweekly payroll period of February are listed as follows: Wages and salaries $ 2,500,000 Employee contribution to voluntary retirement plan 89,000 Medical insurance premiums 47,000 Life insurance premiums 9,500 Federal income taxes to be withheld 450,000 Local income taxes to be withheld 58,000 Payroll taxes: Federal unemployment tax rate 0.60 % State unemployment tax rate (after FUTA deduction) 5.40 % Social Security tax rate 6.20 % Medicare tax rate 1.45 % ________________________________________ Required: Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record salaries and wages expense and payroll tax expense for the biweekly pay period. Assume that no employee’s cumulative wages exceed the relevant wage bases for Social Security, and that all employees’ cumulative wages do exceed the relevant unemployment wage bases. Salaries are not yet paid. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation 12. On November 1, 2018, Quantum Technology, a geothermal energy supplier, borrowed $22 million cash to fund a geological survey. The loan was made by Nevada BancCorp under a noncommitted short-term line of credit arrangement. Quantum issued a nine-month, 9% promissory note. Interest was payable at maturity. Quantum’s fiscal period is the calendar year. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry for the issuance of the note by Quantum Technology. 2. & 3. Prepare the appropriate adjusting entry for the note by Quantum on December 31, 2018 and journal entry for the payment of the note at maturity. (For all requirements, if no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation 3. On July 1, 2018, Ross-Livermore Industries issued nine-month notes in the amount of $600 million. Interest is payable at maturity. Required: Determine the amount of interest expense that should be recorded in a year-end adjusting entry under each of the following independent assumptions: (Enter your answers in millions (10,000,000 should be entered as 10) 14. The following selected transactions relate to liabilities of United Insulation Corporation. United’s fiscal year ends on December 31. 2018 Jan. 13 Negotiated a revolving credit agreement with Parish Bank that can be renewed annually upon bank approval. The amount available under the line of credit is $30.0 million at the bank’s prime rate. Feb. 1 Arranged a three-month bank loan of $8.4 million with Parish Bank under the line of credit agreement. Interest at the prime rate of 10% was payable at maturity. May 1 Paid the 10% note at maturity. Dec. 1 Supported by the credit line, issued $18.3 million of commercial paper on a nine-month note. Interest was discounted at issuance at a 9% discount rate. 31 Recorded any necessary adjusting entry(s). 2019 Sept. 1 Paid the commercial paper at maturity. Required: Prepare the appropriate journal entries through the maturity of each liability 2018 and 2019. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation 15. Bavarian Bar and Grill opened for business in November 2018. During its first two months of operation, the restaurant sold gift certificates in various amounts totaling $8,800, mostly as Christmas presents. They are redeemable for meals within two years of the purchase date, although experience within the industry indicates that 90% of gift certificates are redeemed within one year. Certificates totaling $3,100 were presented for redemption during 2018 for meals having a total price of $3,500. The sales tax rate on restaurant sales is 4%, assessed at the time meals (not gift certificates) are purchased. Sales taxes will be remitted in January. Required: 1. Prepare the appropriate journal entries (in summary form) for the gift certificates sold during 2018 (keeping in mind that, in actuality, each sale of a gift certificate or a meal would be recorded individually). 2. Determine the liability for gift certificates to be reported on the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. 3. What is the appropriate amount for each classification (current or noncurrent) of the liabilities at December 31, 2018? • Required 1 o Prepare the appropriate journal entries (in summary form) for the gift certificates sold during 2018 (keeping in mind that, in actuality, each sale of a gift certificate or a meal would be recorded individually). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation • Required 2 Determine the liability for gift certificates to be reported on the December 31, 2018, balance sheet. 2. • Required 3 What is the appropriate amount for each classification (current or noncurrent) of the liabilities at December 31, 2018? 3 16. At December 31, 2018, Newman Engineering’s liabilities include the following: 1. $28 million of 10% bonds were issued for $28 million on May 31, 1999. The bonds mature on May 31, 2029, but bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on May 31, 2019. However, the option to call is not expected to be exercised, given prevailing market conditions. 2. $32 million of 9% notes are due on May 31, 2022. A debt covenant requires Newman to maintain current assets at least equal to 193% of its current liabilities. On December 31, 2018, Newman is in violation of this covenant. Newman obtained a waiver from National City Bank until June 2019, having convinced the bank that the company’s normal 2 to 1 ratio of current assets to current liabilities will be reestablished during the first half of 2019. 3. $25 million of 12% bonds were issued for $25 million on August 1, 1989. The bonds mature on July 31, 2019. Sufficient cash is expected to be available to retire the bonds at maturity. Required: Classify the above mentioned debts as current liabilities or noncurrent liabilities. Also, provide corresponding value for the same. (Enter your answer in millions (i.e., 10,000,000 should be entered as 10) Explanation 17. Cupola Awning Corporation introduced a new line of commercial awnings in 2018 that carry a two-year warranty against manufacturer’s defects. Based on their experience with previous product introductions, warranty costs are expected to approximate 3% of sales. Sales and actual warranty expenditures for the first year of selling the product were: Required: 1. Does this situation represent a loss contingency? 2. Prepare journal entries that summarize sales of the awnings (assume all credit sales) and any aspects of the warranty that should be recorded during 2018. 3. What amount should Cupola report as a liability at December 31, 2018? • Required 1 Does this situation represent a loss contingency? • Required 2 Prepare journal entries that summarize sales of the awnings (assume all credit sales) and any aspects of the warranty that should be recorded during 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 2. Accrued liability and expense: Warranty expense (3% × $5,050,000) = $151,500. • Required 3 What amount should Cupola report as a liability at December 31, 2018? 18. Sound Audio manufactures and sells audio equipment for automobiles. Engineers notified management in December 2018 of a circuit flaw in an amplifier that poses a potential fire hazard. An intense investigation indicated that a product recall is virtually certain, estimated to cost the company $2.0 million. The fiscal year ends on December 31. Required: 1. Should this loss contingency be accrued & disclosed, only disclosed, or neither? 2. What loss, if any, should Sound Audio report in its 2018 income statement? 3. What liability, if any, should Sound Audio report in its 2018 balance sheet? 4. Prepare any journal entry needed. • Req 1 to 3 Should this loss contingency be accrued & disclosed, only disclosed, or neither? What loss and liability, if any, should Sound Audio report in its 2018 income statement and balance sheet respectively? (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) Explanation 1. This is a loss contingency. A liability is accrued if it is both probable that the confirming event will occur and the amount can be at least reasonably estimated. If one or both of these criteria is not met, but there is at least a reasonable possibility that the loss will occur, a disclosure note should describe the contingency. In this case, a liability is accruedsince both of these criteria are met. • Req 4 Prepare any journal entry needed. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) 19. The Manda Panda Company uses the allowance method to account for bad debts. At the beginning of 2018, the allowance account had a credit balance of $77,900. Credit sales for 2018 totaled $2,460,000 and the year-end accounts receivable balance was $520,000. During this year, $75,500 in receivables were determined to be uncollectible. Manda Panda anticipates that 4% of all credit sales will ultimately become uncollectible. The fiscal year ends on December 31. Required: 1. Does this situation describe a loss contingency? 2. What is the bad debt expense that Manda Panda should report in its 2018 income statement? 3. Prepare the appropriate journal entry to record the contingency. 4. Complete the table below to calculate the net realizable value Manda Panda should report in its 2018 balance sheet? • Required 1 Does this situation describe a loss contingency? Explanation 2. Bad debt expense: 4% × $2,460,000 = $98,400. • Required 3 Prepare the appropriate journal entry to record the contingency. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Required 4 Complete the table below to calculate the net realizable value Manda Panda should report in its 2018 balance sheet. 4. Allowance for uncollectible accounts: 20. The following selected transactions relate to contingencies of Classical Tool Makers, Inc., which began operations in July 2018. Classical’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Financial statements are issued in April 2019. 1. Classical's products carry a one-year warranty against manufacturer’s defects. Based on previous experience, warranty costs are expected to approximate 2% of sales. Sales were $3.5 million (all credit) for 2018. Actual warranty expenditures were $25,800 and were recorded as warranty expense when incurred. 2. Although no customer accounts have been shown to be uncollectible, Classical estimates that 2% of credit sales will eventually prove uncollectible. 3. In December 2018, the state of Tennessee filed suit against Classical, seeking penalties for violations of clean air laws. On January 23, 2019, Classical reached a settlement with state authorities to pay $3.0 million in penalties. 4. Classical is the plaintiff in a $5.5 million lawsuit filed against a supplier. The suit is in final appeal and attorneys advise that it is virtually certain that Classical will win the case and be awarded $4.0 million. 5. In November 2018, Classical became aware of a design flaw in an industrial saw that poses a potential electrical hazard. A product recall appears unavoidable. Such an action would likely cost the company $650,000. 6. Classical offered $25 cash rebates on a new model of jigsaw. Customers must mail in a proof-of-purchase seal from the package plus the cash register receipt to receive the rebate. Experience suggests that 70% of the rebates will be claimed. Eleven thousand and five hundred of the jigsaws were sold in 2018. Total rebates to customers in 2018 were $120,000 and were recorded as promotional expense when paid. Required: 1-a Prepare the year-end entries for any amounts that should be recorded as a result of each of the above contingencies. 1-b Indicate whether a disclosure note is needed for the above transactions. • Required a Prepare the year-end entries for any amounts that should be recorded as a result of each of the above contingencies. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required B Indicate whether a disclosure note is needed for the above transactions. 21. Woodmier Lawn Products introduced a new line of commercial sprinklers in 2017 that carry a one-year warranty against manufacturer's defects. Because this was the first product for which the company offered a warranty, trade publications were consulted to determine the experience of others in the industry. Based on that experience, warranty costs were expected to approximate 2% of sales. Sales of the sprinklers in 2017 were $3.1 million. Accordingly, the following entries relating to the contingency for warranty costs were recorded during the first year of selling the product: General Journal Debit Credit Accrued liability and expense Warranty expense (2% × $3,100,000) 62,000 Estimated warranty liability 62,000 Actual expenditures (summary entry) Estimated warranty liability 27,000 Cash, wages payable, parts and supplies, etc. 27,000 ________________________________________ In late 2018, the company's claims experience was evaluated and it was determined that claims were far more than expected—3% of sales rather than 2%. Required: 1. Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $4.2 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $94,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. 2. Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. • Required 1 Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $4.2 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $94,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 2 Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 2. Estimated warranty liability: ($62,000 – $27,000) = $35,000 Loss on product warranty: ([3% – 2%] × $3,100,000) = $31,000 Cash, wages payable, parts and supplies, etc: (3% × $3,100,000) – $27,000 = $66,000 22. The Commonwealth of Virginia filed suit in October 2016 against Northern Timber Corporation, seeking civil penalties and injunctive relief for violations of environmental laws regulating forest conservation. When the 2017 financial statements were issued in 2018, Northern had not reached a settlement with state authorities, but legal counsel advised Northern Timber that it was probable the ultimate settlement would be $1,232,000 in penalties. The following entry was recorded: General Journal Debit Credit Loss—litigation 1,232,000 Liability—litigation 1,232,000 ________________________________________ Late in 2018, a settlement was reached with state authorities to pay a total of $734,000 to cover the cost of violations. Required: 1. Prepare any journal entries related to the change. 2. Would a disclosure note be required for the change in estimate? • Required 1 Prepare any journal entries related to the change. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation • Required 2 Would a disclosure note be required for the change in estimate? Explanation 23. The Dune Chemical Company provides chemical, plastic, and agricultural products and services to various consumer markets. The following excerpt is taken from the disclosure notes of Dune’s 2015 annual report: In total, the Company’s accrued liability for probable environmental remediation and restoration costs was $738 million at December 31, 2015, compared with $770 million at the end of 2014. This is management’s best estimate of the costs for remediation and restoration with respect to environmental matters for which the Company has accrued liabilities, although it is reasonably possible that the ultimate cost with respect to these particular matters could range up to approximately two and a half times that amount. Required: Does the excerpt describe a loss contingency? Under what conditions would Dune accrue such a contingency? What journal entry would Dune use to record this amount of provision (loss)? • Disclosure Does the excerpt describe a loss contingency? Under what conditions would Dune accrue such a contingency? • General Journal What journal entry would Dune use to record this amount of provision (loss)? (Enter your answers in millions. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 24. Lee Financial Services pays employees monthly. Payroll information is listed below for January 2018, the first month of Lee's fiscal year. Assume that none of the employees exceeded any relevant wage base. Salaries $ 430,000 Federal income taxes to be withheld 86,000 Federal unemployment tax rate 0.60 % State unemployment tax rate (after FUTA deduction) 5.40 % Social security tax rate 6.20 % Medicare tax rate 1.45 % ________________________________________ Required: Calculate the income and payroll taxes for the January 2018 pay period. Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record salaries and wages expense (not paid) and payroll tax expense for the January 2018 pay period. • Payroll Tax o Calculate the income and payroll taxes for the January 2018 pay period. • General Journal Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record salaries and wages expense (not paid) and payroll tax expense for the January 2018 pay period. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 1. In 2018, Cap City Inc. introduced a new line of televisions that carry a two-year warranty against manufacturer's defects. Based on past experience with similar products, warranty costs are expected to be approximately 1% of sales during the first year of the warranty and approximately an additional 3% of sales during the second year of the warranty. Sales were $5,800,000 for the first year of the product's life and actual warranty expenditures were $27,000. Assume that all sales are on credit. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to summarize the sales and any aspects of the warranty for 2018. 2. What amount should Cap City report as a liability at December 31, 2018? • Required 1 o Prepare journal entries to summarize the sales and any aspects of the warranty for 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Required 2 What amount should Cap City report as a liability at December 31, 2018? Explanation : 3. On July 1, 2018, Ross-Livermore Industries issued nine-month notes in the amount of $600 million. Interest is payable at maturity. Required: Determine the amount of interest expense that should be recorded in a year-end adjusting entry under each of the following independent assumptions: (Enter your answers in millions (i.e., 10,000,000 should be entered as 10).) 4. The following selected circumstances relate to pending lawsuits for Erismus, Inc. Erismus’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Financial statements are issued in March 2019. Erismus prepares its financial statements according to U.S. GAAP. Required: Indicate the amount Erismus would record as an asset, liability, or not accrued in the following circumstances. 1. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes the company has a slightly worse than 50/50 chance of eventually prevailing in court, and that if it loses, the judgment will be $1,430,000. 2. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company will lose in court. If it loses, management believes that damages could fall anywhere in the range of $2,830,000 to $5,660,000, with any damage in that range equally likely. 3. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company will lose in court. If it loses, management believes that damages will eventually be $5,650,000, with a present value of $3,955,000. 4. Erismus is a plaintiff in a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company eventually will prevail in court, and that if it prevails, the judgment will be $1,430,000. 5. Erismus is a plaintiff in a lawsuit. Erismus’s management believes it is virtually certain that the company eventually will prevail in court, and that if it prevails, the judgment will be $602,000. Explanation 5 ) Woodmier Lawn Products introduced a new line of commercial sprinklers in 2017 that carry a one-year warranty against manufacturer's defects. Because this was the first product for which the company offered a warranty, trade publications were consulted to determine the experience of others in the industry. Based on that experience, warranty costs were expected to approximate 1% of sales. Sales of the sprinklers in 2017 were $4.4 million. Accordingly, the following entries relating to the contingency for warranty costs were recorded during the first year of selling the product: General Journal Debit Credit Accrued liability and expense Warranty expense (1% × $4,400,000) 44,000 Estimated warranty liability 44,000 Actual expenditures (summary entry) Estimated warranty liability 26,000 Cash, wages payable, parts and supplies, etc. 26,000 ________________________________________ In late 2018, the company's claims experience was evaluated and it was determined that claims were far more than expected—2% of sales rather than 1%. Required: 1. Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $5.5 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $107,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. 2. Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. • Required 1 Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $5.5 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $107,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 2 Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) The balance sheet at December 31, 2018, for Nevada Harvester Corporation includes the liabilities listed below: a. 10% bonds with a face amount of $35 million were issued for $35 million on October 31, 2009. The bonds mature on October 31, 2029. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on October 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $35 million. Market conditions are such that the call is not expected to be exercised. b. Management intended to refinance $9.0 million of its 7% notes that mature in May 2019. In early March, prior to the actual issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Nevada Harvester negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $4.0 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. c. Noncallable 10% bonds with a face amount of $16.0 million were issued for $16.0 million on September 30, 1996. The bonds mature on September 30, 2019. Sufficient cash is expected to be available to retire the bonds at maturity. d. A $27 million 6% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Nevada Harvester’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.7 to 1 and remains so for six months. That ratio was 1.45 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in inventory levels. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the first quarter of 2019. Required: 1. For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? 2. Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $16 million. • Required 1 For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? (Enter your answers in millions (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) • Required 2 o Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $16 million. (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place, (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) a. The requirement to classify currently maturing debt as a current liability includes debt that is callable by the creditor in the upcoming year—even if the debt is not expected to be called. So, the entire $35.0 million debt is a current liability. b. $4.0 million can be reported as long term, but $5.0 million must be reported as a current liability. Short-term obligations that are expected to be refinanced with long-term obligations can be reported as noncurrent liabilities only if the firm (a) intends to refinance on a long-term basis and (b) actually has demonstrated the ability to do so. Ability to refinance on a long-term basis can be demonstrated by either an existing refinancing agreement or by actual financing prior to the issuance of the financial statements. The refinancing agreement in this case limits the ability to refinance to $4.0 million of the notes. In the absence of other evidence of ability to refinance, the remaining $5.0 million cannot be reported as long term. c. The entire $16.0 million maturity amount should be reported as a current liability because that amount is payable in the upcoming year and it will not be refinanced with long-term obligations. d. The entire $27.0 million loan should be reported as a long-term liability because that amount is payable in 2024 and it will not be refinanced with long-term obligations. The current liability classification includes (a) situations in which the creditor has the right to demand payment because an existing violation of a provision of the debt agreement makes it callable and (b) situations in which debt is not yet callable, but will be callable within the year if an existing violation is not corrected within a specified grace period—unless it's probable the violation will be corrected within the grace period. Here, the existing violation is expected to be corrected within six months (actually three months in this case). 7. Transit Airlines provides regional jet service in the Mid-South. The following is information on liabilities of Transit at December 31, 2018. Transit’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Its annual financial statements are issued in April. 1. Transit has outstanding 5.6% bonds with a face amount of $61 million. The bonds mature on July 31, 2027. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on July 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $61 million. Market conditions are such that the call option is not expected to be exercised. 2. A $50 million 5% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Transit’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.9 to 1 and remains so for 6 months. That ratio was 1.75 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in parts inventories. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the sixth week of 2019. 3. Transit management intended to refinance $25 million of 5% notes that mature in May of 2019. In late February 2019, prior to the issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Transit negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $20 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. 4. Transit is involved in a lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a food caterer. On February 13, 2019, judgment was rendered against Transit in the amount of $38 million plus interest, a total of $39 million. Transit plans to appeal the judgment and is unable to predict its outcome though it is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the company. Required: 1. How should the 5.6% bonds be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 2. How should the 5% bank loan be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 3. How should the 5% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 4. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? 5. Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $59 million. • Req 1 to 4 How should the 5.6% bonds, 5% bank loan and 5% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? (Enter your answers in millions.) • Req 5 Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $59 million. (Enter your answers in millions.) Explanation 8. Branch Corporation issued $8 million of commercial paper on March 1 on a nine-month note. Interest was discounted at issuance at a 12% discount rate. Prepare the journal entry for the issuance of the commercial paper and its repayment at maturity. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 1. On January 1, 2018, Instaform, Inc., issued 10% bonds with a face amount of $52 million, dated January 1. The bonds mature in 2037 (20 years). The market yield for bonds of similar risk and maturity is 12%. Interest is paid semiannually. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1-a. Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. 1-b. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by Instaform. 2-a. Assume the market rate was 9%. Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. 2-b. Assume the market rate was 9%. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by Instaform. 3. Assume Broadcourt Electronics purchased the entire issue in a private placement of the bonds. Using the data in requirement 2, prepare the journal entry to record the purchase by Broadcourt. • Req 1A Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. (Enter your answer in whole dollars.) • Req 1B Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by Instaform. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 2A Assume the market rate was 9%. Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. (Enter your answer in whole dollars.) • Req 2B Assume the market rate was 9%. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by Instaform. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 3 Assume Broadcourt Electronics purchased the entire issue in a private placement of the bonds. Using the data in requirement 2, prepare the journal entry to record the purchase by Broadcourt. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 2. On January 1, 2018, Baddour, Inc., issued 10% bonds with a face amount of $180 million. The bonds were priced at $158.0 million to yield 12%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Baddour’s fiscal year ends September 30. Required: 1. What amount(s) related to the bonds would Baddour report in its balance sheet at September 30, 2018? 2. What amount(s) related to the bonds would Baddour report in its income statement for the year ended September 30, 2018? 3. What amount(s) related to the bonds would Baddour report in its statement of cash flows for the year ended September 30, 2018? In which section(s) should the amount(s) appear? (For all requirements, Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 3. On January 1, 2018, Bradley Recreational Products issued $120,000, 8%, four-year bonds. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. The bonds were issued at $112,244 to yield an annual return of 10%. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Prepare an amortization schedule that determines interest at the effective interest rate. 2. Prepare an amortization schedule by the straight-line method. 3. Prepare the journal entries to record interest expense on June 30, 2020, by each of the two approaches. 5. Assuming the market rate is still 10%, what price would a second investor pay the first investor on June 30, 2020, for $12,000 of the bonds? 3. Prepare the journal entries to record interest expense on June 30, 2020, by each of the two approaches. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 5. Assuming the market rate is still 10%, what price would a second investor pay the first investor on June 30, 2020, for $12,000 of the bonds? (Round your intermediate calculation and final answer to whole dollars.) 4.On January 1, 2018, Tennessee Harvester Corporation issued debenture bonds that pay interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Portions of the bond amortization schedule appear below: Required: 1. What is the face amount of the bonds? 2. What is the initial selling price of the bonds? 3. What is the term to maturity in years? 4. Interest is determined by what approach? 5. What is the stated annual interest rate? 6. What is the effective annual interest rate? 7. What is the total cash interest paid over the term to maturity? 8. What is the total effective interest expense recorded over the term to maturity? 5. On February 1, 2018, Cromley Motor Products issued 6% bonds, dated February 1, with a face amount of $95 million. The bonds mature on January 31, 2022 (4 years). The market yield for bonds of similar risk and maturity was 8%. Interest is paid semiannually on July 31 and January 31. Barnwell Industries acquired $95,000 of the bonds as a long-term investment. The fiscal years of both firms end December 31. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Determine the price of the bonds issued on February 1, 2018. 2-a. Prepare amortization schedules that indicate Cromley’s effective interest expense for each interest period during the term to maturity. 2-b. Prepare amortization schedules that indicate Barnwell’s effective interest revenue for each interest period during the term to maturity. 3. Prepare the journal entries to record the issuance of the bonds by Cromley and Barnwell’s investment on February 1, 2018. 4. Prepare the journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through January 31, 2020. • Req 1 Determine the price of the bonds issued on February 1, 2018. (Enter your answer in whole dollars.) Explanation • Req 2A Prepare amortization schedules that indicate Cromley’s effective interest expense for each interest period during the term to maturity. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 2-a. • Req 2B Prepare amortization schedules that indicate Barnwell’s effective interest revenue for each interest period during the term to maturity. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 2-b. • Req 3 Prepare the journal entries to record the issuance of the bonds by Cromley and Barnwell’s investment on February 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 4 Cromley Prepare the journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through January 31, 2020. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Req 4 Barnwell Prepare the journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through January 31, 2020. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 4. 6.On April 1, 2018, Western Communications, Inc., issued 12% bonds, dated March 1, 2018, with face amount of $47 million. The bonds sold for $46.3 million and mature on February 28, 2021. Interest is paid semiannually on August 31 and February 28. Stillworth Corporation acquired $47,000 of the bonds as a long-term investment. The fiscal years of both firms end December 31, and both firms use the straight-line method. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries to record (a) issuance of the bonds by Western and (b) Stillworth’s investment on April 1, 2018. 2. Prepare the journal entries by both firms to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through maturity. • Req 1 Prepare the journal entries to record (a) issuance of the bonds by Western and (b) Stillworth’s investment on April 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation • Req 2 Western Prepare the journal entries for Western Communications, Inc., to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through maturity. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" • Req 2 Stillworth Prepare the journal entries for Stillworth Corporation to record all subsequent events related to the bonds through maturity. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 2. The original maturity of the bonds was 3 years, or 36 months. But since the bonds weren’t sold until one month after they were dated, they are outstanding for only 35 months. Straight-line amortization, then, is $700,000 ÷ 35 months = $20,000 per month for Western (and $700 ÷ 35 months = $20 per month for Stillworth’s investment). 7. McWherter Instruments sold $400 million of 10% bonds, dated January 1, on January 1, 2018. The bonds mature on December 31, 2037 (20 years). For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield was 12%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Blanton Technologies, Inc., purchased $400,000 of the bonds as a long-term investment. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Determine the price of the bonds issued on January 1, 2018. 2. Prepare the journal entries to record (a) their issuance by McWherter and (b) Blanton's investment on January 1, 2018. 3. Prepare the journal entries by (a) McWherter and (b) Blanton to record interest on June 30, 2018 (at the effective rate). 4. Prepare the journal entries by (a) McWherter and (b) Blanton to record interest on December 31, 2018 (at the effective rate). • Required 2 Prepare the journal entries to record (a) their issuance by McWherter and (b) Blanton's investment on January 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 3. Interest expense (6% × $339,814,000) = $20,388,840 Cash (5% × $400,000,000) = $20,000,000 Cash (5% × $400,000) = $20,000 Interest revenue (6% × $339,814) = $20,389 Prepare the journal entries by (a) McWherter and (b) Blanton to record interest on June 30, 2018 (at the effective rate). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 4. Interest expense (6% × [$339,814,000 + $388,840]) = $20,412,170 Cash (5% × $400,000,000) = $20,000,000 Cash (5% × $400,000) = $20,000 Interest revenue (6% × [$339,814 + $389]) = $20,412 Prepare the journal entries by (a) McWherter and (b) Blanton to record interest on December 31, 2018 (at the effective rate). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 8. The fiscal year ends December 31 for Lake Hamilton Development. To provide funding for its Moonlight Bay project, LHD issued 9% bonds with a face amount of $520,000 on November 1, 2018. The bonds sold for $475,389, a price to yield the market rate of 10%. The bonds mature October 31, 2038 (20 years). Interest is paid semiannually on April 30 and October 31 and is determined using the effective interest method. Required: 1. What amount of interest expense related to the bonds will LHD report in its income statement for the year ending December 31, 2018? 2. What amount(s) related to the bonds will LHD report in its balance sheet at December 31, 2018? 3. What amount of interest expense related to the bonds will LHD report in its income statement for the year ending December 31, 2019? 4. What amount(s) related to the bonds will LHD report in its balance sheet at December 31, 2019? (For all requirements, Do not round your intermediate calculation. Enter your answer in whole dollars.) 9. On January 1, 2018, Darnell Window and Pane issued $18.7 million of 10-year, zero-coupon bonds for $7,209,660. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 2. Determine the effective rate of interest. 1. & 3. to 5. Prepare the necessary journal entries. • Interest rate Determine the effective rate of interest. • General Journal Prepare the necessary journal entries. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your intermedaite calculation and final answers to nearest whole dollar.) 10. At the beginning of the year, Lambert Motors issued the three notes described below. Interest is paid at year-end. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) A. The company issued a two-year, 12%, $770,000 note in exchange for a tract of land. The current market rate of interest is 12%. B. Lambert acquired some office equipment with a fair value of $174,143 by issuing a one-year, $184,000 note. The stated interest on the note is 6%. C. The company purchased a building by issuing a four-year installment note. The note is to be repaid in equal installments of $1 million per year beginning one year hence. The current market rate of interest is 12%. Required: Prepare the journal entries to record each of the three transactions and the interest expense at the end of the first year for each. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Do not round intermediate calculations. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 11.At January 1, 2018, Brant Cargo acquired equipment by issuing a four-year, $175,000 (payable at maturity), 6% note. The market rate of interest for notes of similar risk is 12%. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. to 3. Prepare the necessary journal entries for Brant Cargo. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar) 12.At the beginning of 2018, VHF Industries acquired a equipment with a fair value of $6,760,200 by issuing a two-year, noninterest-bearing note in the face amount of $8 million. The note is payable in two annual installments of $4 million at the end of each year. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required:1. What is the effective rate of interest implicit in the agreement? 2. to 4. Prepare the necessary journal entry. 5. Suppose the market value of the equipment was unknown at the time of purchase, but the market rate of interest for notes of similar risk was 11%. Prepare the journal entry to record the purchase of the equipment. • Required 1 What is the effective rate of interest implicit in the agreement? • Required 2 to 4 Prepare the necessary journal entry. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollar.) 3.Interest expense (12% × outstanding balance) = $811,224 4.Interest expense (12% × [$6,760,200 – $3,188,776]) = $428,571 • Required 5 Suppose the market value of the equipment was unknown at the time of purchase, but the market rate of interest for notes of similar risk was 11%. Prepare the journal entry to record the purchase of the equipment. 13. Braxton Technologies, Inc., constructed a conveyor for A&G Warehousers that was completed and ready for use on January 1, 2018. A&G paid for the conveyor by issuing a $100,000, four-year note that specified 4% interest to be paid on December 31 of each year, and the note is to be repaid at the end of four years. The conveyor was custom-built for A&G, so its cash price was unknown. By comparison with similar transactions it was determined that a reasonable interest rate was 10%. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s purchase of the conveyor on January 1, 2018. 2. Prepare an amortization schedule for the four-year term of the note. 3. Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s third interest payment on December 31, 2020. 4. If A&G’s note had been an installment note to be paid in four equal payments at the end of each year beginning December 31, 2018, what would be the amount of each installment? 5. By considering the installment payment of required 4. Prepare an amortization schedule for the four-year term of the installment note. 6. Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s third installment payment on December 31, 2020. • Required 1 Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s purchase of the conveyor on January 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) ¥4% × $100,000 *Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 4, i = 10% (PVA of $1) **Present value of $1: n = 4, i = 10% (PV of $1) • Required 2 Prepare an amortization schedule for the four-year term of the note. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 1 • Required 3 Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s third interest payment on December 31, 2020. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Re • Required 4 If A&G’s note had been an installment note to be paid in four equal payments at the end of each year beginning December 31, 2018, what would be the amount of each installment? (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 4 • Required 5 By considering the installment payment of required 4. Prepare an amortization schedule for the four-year term of the installment note. (Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 6 Prepare the journal entry for A&G’s third installment payment on December 31, 2020. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 14. Three years ago American Insulation Corporation issued 10 percent, $830,000, 10-year bonds for $785,000. American Insulation exercised its call privilege and retired the bonds for $820,000. The corporation uses the straight-line method to determine interest. Required: Prepare the journal entry to record the call of the bonds. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 15. The long-term liability section of Twin Digital Corporation’s balance sheet as of December 31, 2017, included 12% bonds having a face amount of $35 million and a remaining discount of $1 million. Disclosure notes indicate the bonds were issued to yield 14%. Interest expense is recorded at the effective interest rate and paid on January 1 and July 1 of each year. On July 1, 2018, Twin Digital retired the bonds at 104 ($36.4 million) before their scheduled maturity. Required: 1. & 2. Prepare the necessary journal entries for Twin Digital on July 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollar.) Explanation 1. Interest expense (7% × $34,000,000) = $2,380,000 Cash (6% × $35,000,000) = $2,100,000 2. Discount on bonds payable ($1,000,000 – $280,000) = $720,000 16.Cupola Fan Corporation issued 10%, $510,000, 10-year bonds for $489,000 on June 30, 2018. Debt issue costs were $2,600. Interest is paid semiannually on December 31 and June 30. One year from the issue date (July 1, 2019), the corporation exercised its call privilege and retired the bonds for $495,000. The corporation uses the straight-line method both to determine interest expense and to amortize debt issue costs. Required: 1. to 4. Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of the bonds, the payment of interest and amortization of debt issue costs on December 31, 2018 & 2019, and the call of the bonds. (If no 4-Call of the bonds Discount and debt issue costs (9/10 x [$510,000 – $489,000 + $2,600]) = $21,240 17. The long-term liability section of Eastern Post Corporation’s balance sheet as of January 1, 2018, included 11% bonds having a face amount of $41.2 million and a remaining premium of $6.3 million. On January 1, 2018, Eastern Post retired some of the bonds before their scheduled maturity. Required: Prepare the journal entry by Eastern Post to record the redemption of the bonds under each of the independent circumstances below: 1. Eastern Post called half the bonds at the call price of 102 (102% of face amount). 2. Eastern Post repurchased $10.3 million of the bonds on the open market at their market price of $10.8 million. • Required 1 o Eastern Post called half the bonds at the call price of 102 (102% of face amount). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 2 Eastern Post repurchased $10.3 million of the bonds on the open market at their market price of $10.8 million. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 18.Bradley-Link’s December 31, 2018, balance sheet included the following items: Long-Term Liabilities ($ in millions) 9.0% convertible bonds, callable at 103 beginning in 2019, due 2022 (net of unamortized discount of $2) [note 8] $148 11.0% registered bonds callable at 106 beginning in 2028, due 2032 (net of unamortized discount of $1) [note 8] 69 Shareholders’ Equity 5 Equity—stock warrants Note 8: Bonds (in part) The 9.0% bonds were issued in 2005 at 98.0 to yield 10%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Each $1,000 bond is convertible into 40 shares of the Company’s no par common stock. The 11.0% bonds were issued in 2009 at 104 to yield 10%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. Each $1,000 bond was issued with 40 detachable stock warrants, each of which entitles the holder to purchase one share of the Company’s no par common stock for $20, beginning 2019. On January 3, 2019, when Bradley-Link’s common stock had a market price of $27 per share, Bradley-Link called the convertible bonds to force conversion. 90% were converted; the remainder were acquired at the call price. When the common stock price reached an all-time high of $32 in December of 2019, 40% of the warrants were exercised. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries that were recorded when each of the two bond issues was originally sold in 2005 and 2009. 2. Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019 and the retirement of the remainder. 3. Assume Bradley-Link induced conversion by offering $150 cash for each bond converted. Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019. 4. Assume Bradley-Link induced conversion by modifying the conversion ratio to exchange 45 shares for each bond rather than the 40 shares provided in the contract. Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019. 5. Prepare the journal entry to record the exercise of the warrants in December 2019. • Required 1 Prepare the journal entries that were recorded when each of the two bond issues was originally sold in 2005 and 2009. • Required 2 Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019 and the retirement of the remainder. 2. • Required 3 Assume Bradley-Link induced conversion by offering $150 cash for each bond converted. Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019. 3. • Required 4 Assume Bradley-Link induced conversion by modifying the conversion ratio to exchange 45 shares for each bond rather than the 40 shares provided in the contract. Prepare the journal entry to record (book value method) the conversion of 90% of the convertible bonds in January 2019. • Required 5 Prepare the journal entry to record the exercise of the warrants in December 2019. 19.On January 1, 2018, NFB Visual Aids issued $600,000 of its 20-year, 6% bonds. The bonds were priced to yield 8%. Interest is payable semiannually on June 30 and December 31. NFB Visual Aids records interest expense at the effective rate and elected the option to report these bonds at their fair value. On December 31, 2018, the fair value of the bonds was $492,000 as determined by their market value in the over-the-counter market. General (risk-free) interest rates did not change during 2021. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of 1) Required: 1-a. Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. 1-b to 4. Prepare the necessary Journal entries. • Req 1A Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. (Round final answer to the nearest whole dollars.) 1. Interest $ 18,000 × 19.79277 * = $ 356,270 Principal $ 600,000 × 0.20829 ** = 124,974 $ 481,244 ________________________________________ 3% × $600,000 = $18,000 *Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 40, i = 4% (PVA of $1) **Present value of $1: n = 40, i = 4% (PV of $1) • Req 1B to 4 Prepare the necessary Journal entries. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round final answers to the nearest whole dollars.) 1. Interest expense (4% × $481,244) = $19,250 Cash (3% × $600,000) = $18,000 2. Interest expense (4% × [$481,244 + 1,250]) = $19,300 Cash (3% × $600,000) = $18,000 3. The interest entries increased the book value from $481,244 to $483,794. To increase the book value to $492,000, NFB needed the following adjustment: Fair value adjustment ($492,000 – $483,794) = $8,206 20. At January 1, 2018, Rothschild Chair Company, Inc., was indebted to First Lincoln Bank under a $31 million, 10% unsecured note. The note was signed January 1, 2015, and was due December 31, 2021. Annual interest was last paid on December 31, 2016. Rothschild Chair Company was experiencing severe financial difficulties and negotiated a restructuring of the terms of the debt agreement. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: Prepare all journal entries by Rothschild Chair Company, Inc., to record the restructuring and any remaining transactions relating to the debt under each of the independent circumstances below: 1. First Lincoln Bank agreed to settle the debt in exchange for land having a fair value of $27 million but carried on Rothschild Chair Company’s books at $22.9 million. 2. First Lincoln Bank agreed to (a) forgive the interest accrued from last year, (b) reduce the remaining four interest payments to $1 million each, and (c) reduce the principal to $24.9 million. 3. First Lincoln Bank agreed to defer all payments (including accrued interest) until the maturity date and accept $43,051,000 at that time in settlement of the debt. • Required 1 First Lincoln Bank agreed to settle the debt in exchange for land having a fair value of $27 million but carried on Rothschild Chair Company’s books at $22.9 million. (Enter your answers in millions. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your answers to 1 decimal place.) • Required 2 First Lincoln Bank agreed to (a) forgive the interest accrued from last year, (b) reduce the remaining four interest payments to $1 million each, and (c) reduce the principal to $24.9 million. (Enter your answer in millions.If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round your answers to 1 decimal place.) 2.bNote: No interest expense should be recorded after the restructuring. All subsequent cash payments result in reductions of principal. • Required 3 First Lincoln Bank agreed to defer all payments (including accrued interest) until the maturity date and accept $43,051,000 at that time in settlement of the debt. • Required 2 3. Calculation of the new effective interest rate: 21.Your investment department has researched possible investments in corporate debt securities. Among the available investments are the following $100 million bond issues, each dated January 1, 2018. Prices were determined by underwriters at different times during the last few weeks. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Each of the bond issues matures on December 31, 2037, and pays interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield at January 1, 2018, is 14%. Required: Other things being equal, which of the bond issues offers the most attractive investment opportunity if it can be purchased at the prices stated? The least attractive? DD Corp. bonds: Note: The result differs from $100,000,000 only because the present value factors in any present value table are rounded. Because the stated rate and the market rate are the same, the true present value is $100,000,000. ¥ [14 ÷ 2] % × $100,000,000 * Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 40, i = 7% (PVA of $1) ** Present value of $1: n = 40, i = 7% (PV of $1) GG Corp. bonds: 22. The Bradford Company issued 14% bonds, dated January 1, with a face amount of $89 million on January 1, 2018. The bonds mature on December 31, 2027 (10 years). For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield is 16%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. 2. to 4. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Bradford Company on January 1, 2018, interest on June 30, 2018 and interest on December 31, 2018 (at the effective rate). • Req 1 Determine the price of the bonds at January 1, 2018. (Enter your answers whole dollars.) 1. Price of the bonds at January 1, 2018 Interest $ 6,230,000 ¥ × 9.81815 * = $ 61,167,074 Principal $ 89,000,000 × 0.21455 ** = 19,094,950 Present value (price) of the bonds $ 80,262,024 ________________________________________ ¥ 7% × $89,000,000 * Present value of an ordinary annuity of $1: n = 20, i = 8% (PVA of $1) ** Present value of $1: n = 20, i = 8% (PV of $1) • Req 2 to 4 Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Bradford Company on January 1, 2018, interest on June 30, 2018 and interest on December 31, 2018 (at the effective rate) 3. 23. The Gorman Group issued $820,000 of 13% bonds on June 30, 2018, for $881,688. The bonds were dated on June 30 and mature on June 30, 2038 (20 years). The market yield for bonds of similar risk and maturity is 12%. Interest is paid semiannually on December 31 and June 30. Required: Complete the below table to record the company's journal entry. 1. to 3. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Gorman Group on June 30, 2018, interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on June 30, 2019 (at the effective rate). • Calculation o Complete the below table to record the company's journal entry.(Round intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar. interest rate to 1 decimal place. (0.123 should be entered as 12.3) • Req 1 to 3 Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Gorman Group on June 30, 2018, interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on June 30, 2019 (at the effective rate). Explanation 24. On February 1, 2018, Strauss-Lombardi issued 10% bonds, dated February 1, with a face amount of $810,000. The bonds sold for $745,010 and mature on January 31, 2038 (20 years). The market yield for bonds of similar risk and maturity was 11%. Interest is paid semiannually on July 31 and January 31. Strauss-Lombardi’s fiscal year ends December 31. Required: 1. to 4. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by Strauss-Lombardi on February 1, 2018, interest on July 31, 2018 (at the effective rate), adjusting entry to accrue interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on January 31, 2019. 25. At the end of 2017, Majors Furniture Company failed to accrue $73,000 of interest expense that accrued during the last five months of 2017 on bonds payable. The bonds mature in 2031. The discount on the bonds is amortized by the straight-line method. The following entry was recorded on February 1, 2018, when the semiannual interest was paid: Required: Prepare any journal entry necessary to correct the errors as of February 2, 2018, when the errors were discovered. Also, prepare any adjusting entry at December 31, 2018, related to the situation described. (Ignore income taxes.) 1. In 2018, Cap City Inc. introduced a new line of televisions that carry a two-year warranty against manufacturer's defects. Based on past experience with similar products, warranty costs are expected to be approximately 1% of sales during the first year of the warranty and approximately an additional 3% of sales during the second year of the warranty. Sales were $5,800,000 for the first year of the product's life and actual warranty expenditures were $27,000. Assume that all sales are on credit. Required: 1. Prepare journal entries to summarize the sales and any aspects of the warranty for 2018. 2. What amount should Cap City report as a liability at December 31, 2018? • Required 1 o Prepare journal entries to summarize the sales and any aspects of the warranty for 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Required 2 What amount should Cap City report as a liability at December 31, 2018? 2. Albertson Corporation began a special promotion in July 2018 in an attempt to increase sales. A coupon was provided at various grocery stores upon checkout. Customers could send in five coupons to receive $2.70. Albertson's management estimated that 75% of the coupons would be redeemed. For the six months ended December 31, 2018, the following information is available: 3. On July 1, 2018, Ross-Livermore Industries issued nine-month notes in the amount of $600 million. Interest is payable at maturity. Required: Determine the amount of interest expense that should be recorded in a year-end adjusting entry under each of the following independent assumptions: (Enter your answers in millions (i.e., 10,000,000 should be entered as 10).) 4. The following selected circumstances relate to pending lawsuits for Erismus, Inc. Erismus’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Financial statements are issued in March 2019. Erismus prepares its financial statements according to U.S. GAAP. Required: Indicate the amount Erismus would record as an asset, liability, or not accrued in the following circumstances. 1. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes the company has a slightly worse than 50/50 chance of eventually prevailing in court, and that if it loses, the judgment will be $1,430,000. 2. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company will lose in court. If it loses, management believes that damages could fall anywhere in the range of $2,830,000 to $5,660,000, with any damage in that range equally likely. 3. Erismus is defending against a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company will lose in court. If it loses, management believes that damages will eventually be $5,650,000, with a present value of $3,955,000. 4. Erismus is a plaintiff in a lawsuit. Erismus's management believes it is probable that the company eventually will prevail in court, and that if it prevails, the judgment will be $1,430,000. 5. Erismus is a plaintiff in a lawsuit. Erismus’s management believes it is virtually certain that the company eventually will prevail in court, and that if it prevails, the judgment will be $602,000. 5 ) Woodmier Lawn Products introduced a new line of commercial sprinklers in 2017 that carry a one-year warranty against manufacturer's defects. Because this was the first product for which the company offered a warranty, trade publications were consulted to determine the experience of others in the industry. Based on that experience, warranty costs were expected to approximate 1% of sales. Sales of the sprinklers in 2017 were $4.4 million. Accordingly, the following entries relating to the contingency for warranty costs were recorded during the first year of selling the product: In late 2018, the company's claims experience was evaluated and it was determined that claims were far more than expected—2% of sales rather than 1%. Required: 1. Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $5.5 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $107,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. 2. Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. • Required 1 Assuming sales of the sprinklers in 2018 were $5.5 million and warranty expenditures in 2018 totaled $107,000, prepare any journal entries related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) • Required 2 Assuming sales of the sprinklers were discontinued after 2017, prepare any journal entry(s) in 2018 related to the warranty. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) The balance sheet at December 31, 2018, for Nevada Harvester Corporation includes the liabilities listed below: e. 10% bonds with a face amount of $35 million were issued for $35 million on October 31, 2009. The bonds mature on October 31, 2029. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on October 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $35 million. Market conditions are such that the call is not expected to be exercised. f. Management intended to refinance $9.0 million of its 7% notes that mature in May 2019. In early March, prior to the actual issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Nevada Harvester negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $4.0 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. g. Noncallable 10% bonds with a face amount of $16.0 million were issued for $16.0 million on September 30, 1996. The bonds mature on September 30, 2019. Sufficient cash is expected to be available to retire the bonds at maturity. h. A $27 million 6% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Nevada Harvester’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.7 to 1 and remains so for six months. That ratio was 1.45 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in inventory levels. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the first quarter of 2019. Required: 1. For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? 2. Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $16 million. • Required 1 For each liability listed above, what amount will be reported as a current liability on the December 31, 2018 balance sheet? (Enter your answers in millions (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) • Required 2 o Prepare the liability section of a classified balance sheet for Nevada Harvester at December 31, 2018. Accounts payable and accruals are $16 million. (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place, (i.e., 5,500,000 should be entered as 5.5).) Transit Airlines provides regional jet service in the Mid-South. The following is information on liabilities of Transit at December 31, 2018. Transit’s fiscal year ends on December 31. Its annual financial statements are issued in April. 5. Transit has outstanding 5.6% bonds with a face amount of $61 million. The bonds mature on July 31, 2027. Bondholders have the option of calling (demanding payment on) the bonds on July 31, 2019, at a redemption price of $61 million. Market conditions are such that the call option is not expected to be exercised. 6. A $50 million 5% bank loan is payable on October 31, 2024. The bank has the right to demand payment after any fiscal year-end in which Transit’s ratio of current assets to current liabilities falls below a contractual minimum of 1.9 to 1 and remains so for 6 months. That ratio was 1.75 on December 31, 2018, due primarily to an intentional temporary decline in parts inventories. Normal inventory levels will be reestablished during the sixth week of 2019. 7. Transit management intended to refinance $25 million of 5% notes that mature in May of 2019. In late February 2019, prior to the issuance of the 2018 financial statements, Transit negotiated a line of credit with a commercial bank for up to $20 million any time during 2019. Any borrowings will mature two years from the date of borrowing. 8. Transit is involved in a lawsuit resulting from a dispute with a food caterer. On February 13, 2019, judgment was rendered against Transit in the amount of $38 million plus interest, a total of $39 million. Transit plans to appeal the judgment and is unable to predict its outcome though it is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the company. Required: 1. How should the 5.6% bonds be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 2. How should the 5% bank loan be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 3. How should the 5% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet? 4. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? 5. Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $59 million. • Req 1 to 4 How should the 5.6% bonds, 5% bank loan and 5% notes be classified by Transit among liabilities in its balance sheet. How should the lawsuit be reported by Transit? (Enter your answers in millions.) • Req 5 Calculate the total current liabilities, total long-term liabilities, and total liabilities of a classified balance sheet for Transit Airlines at December 31, 2018. Transit's accounts payable and accruals were $59 million. (Enter your answers in millions.) 8. Branch Corporation issued $8 million of commercial paper on March 1 on a nine-month note. Interest was discounted at issuance at a 12% discount rate. Prepare the journal entry for the issuance of the commercial paper and its repayment at maturity. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) 1. Your investment department has researched possible investments in corporate debt securities. Among the available investments are the following $100 million bond issues, each dated January 1, 2018. Prices were determined by underwriters at different times during the last few weeks. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Each of the bond issues matures on December 31, 2037, and pays interest semiannually on June 30 and December 31. For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield at January 1, 2018, is 10%. Required: Other things being equal, which of the bond issues offers the most attractive investment opportunity if it can be purchased at the prices stated? The least attractive? 2. The Bradford Company issued 8% bonds, dated January 1, with a face amount of $75 million on January 1, 2018 to Saxton-Bose Corporation. The bonds mature on December 31, 2022 (5 years). For bonds of similar risk and maturity, the market yield is 10%. Interest is paid semiannually on June 30 and December 31. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.): Required: 1. to 3. Prepare the journal entry to record the purchase of the bonds by Saxton-Bose on January 1, 2018, interest revenue on June 30, 2018 and interest revenue on December 31, 2018 (at the effective rate). (Enter your answers in whole dollars. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) 3.December 31, 2018 Cash (4% × $75,000,000) = $3,000,000 Interest revenue (5% × [$69,208,440 + $460,422]) = $3,483,443 3. The Gorman Group issued $930,000 of 11% bonds on June 30, 2018, for $1,009,794. The bonds were dated on June 30 and mature on June 30, 2038 (20 years). The market yield for bonds of similar risk and maturity is 10%. Interest is paid semiannually on December 31 and June 30. Required: Complete the below table to record the company's journal entry. 1. to 3. Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Gorman Group on June 30, 2018, interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on June 30, 2019 (at the effective rate). • Calculation Complete the below table to record the company's journal entry. (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar. Enter interest rate to 1 decimal place. (i.e. 0.123 should be entered as 12.3).) • Req 1 to 3 Prepare the journal entry to record their issuance by The Gorman Group on June 30, 2018, interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on June 30, 2019 (at the effective rate). (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Round intermediate calculations and final answers to the nearest whole dollar.) . On March 1, 2018, Stratford Lighting issued 10% bonds, dated March 1, with a face amount of $420,000. The bonds sold for $414,000 and mature on February 28, 2038 (20 years). Interest is paid semiannually on August 31 and February 28. Stratford uses the straight-line method and its fiscal year ends December 31. Required: 1. to 4. Prepare the journal entry to record the issuance of the bonds by Stratford Lighting on March 1, 2018, interest on August 31, 2018, interest on December 31, 2018 and interest on February 28, 2019. (Do not round your intermediate calculations. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation New Securities Issues Corporate National Equipment Transfer Corporation —$209 million bonds via lead managers Second Tennessee Bank N.A. and Morgan, Dunavant & Co., according to a syndicate official. Terms: maturity, Dec. 15, 2024; coupon 7.55%; issue price, par; yield, 7.55%; noncallable, debt ratings: Ba-1 (Moody's Investors Service, Inc.), BBB + (Standard & Poor's). IgWig Inc. —$359 million of notes via lead manager Stanley Brothers, Inc., according to a syndicate official. Terms: maturity, Dec. 1, 2026; coupon, 6.3%; Issue price, 99; yield, 6.4%; call date, NC; debt ratings: Baa-1 (Moody's Investors Service, Inc.), A (Standard & Poor's). Required: 1. Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record the sale of both issues to underwriters. Ignore share issue costs and assume no accrued interest. 2. Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record the first semiannual interest payment for both issues. • Required 1 Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record the sale of both issues to underwriters. Ignore share issue costs and assume no accrued interest. • Required 2 Prepare the appropriate journal entries to record the first semiannual interest payment for both issues. Explanation Wilkins Food Products, Inc., acquired a packaging machine from Lawrence Specialists Corporation. Lawrence completed construction of the machine on January 1, 2016. In payment for the machine Wilkins issued a three-year installment note to be paid in three equal payments at the end of each year. The payments include interest at the rate of 9%. Lawrence made a conceptual error in preparing the amortization schedule, which Wilkins failed to discover until 2018. The error had caused Wilkins to understate interest expense by $50,000 in 2016 and $45,000 in 2017. Required: 1. Determine which accounts are incorrect as a result of these errors at January 1, 2018, before any adjustments. (Ignore income taxes) (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty the box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.) 2. Prepare a journal entry to correct the error. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Explanation 7.LCD Industries purchased a supply of electronic components from Entel Corporation on November 1, 2018. In payment for the $25.5 million purchase, LCD issued a 1-year installment note to be paid in equal monthly payments at the end of each month. The payments include interest at the rate of 12%. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) (Use appropriate factor(s) from the tables provided.) Required: 1. & 2. Prepare the journal entry for LCD’s purchase of the components on November 1, 2018 and the first installment payment on November 30, 2018. 3. What is the amount of interest expense that LCD will report in its income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018? • Req 1 and 2 Prepare the journal entry for LCD’s purchase of the components on November 1, 2018 and the first installment payment on November 30, 2018. (Enter your answers in whole dollars. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Req 3 What is the amount of interest expense that LCD will report in its income statement for the year ended December 31, 2018? (Enter your answer in whole dollars.) Explanation 8. The balance sheet of Indian River Electronics Corporation as of December 31, 2017, included 12.75% bonds having a face amount of $91.9 million. The bonds had been issued in 2010 and had a remaining discount of $4.9 million at December 31, 2017. On January 1, 2018, Indian River Electronics called the bonds before their scheduled maturity at the call price of 102. Required: Prepare the journal entry by Indian River Electronics to record the redemption of the bonds at January 1, 2018. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field. Enter your answers in whole dollars.) Explanation 9. On January 1, 2018, Gless Textiles issued $11 million of 8%, 20-year convertible bonds at 101. The bonds pay interest on June 30 and December 31. Each $1,000 bond is convertible into 40 shares of Gless’s no par common stock. Bonds that are similar in all respects, except that they are nonconvertible, currently are selling at 99 (that is, 99% of face amount). Century Services purchased 20% of the issue as an investment. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entries for the issuance of the bonds by Gless and the purchase of the bond investment by Century. 2. Prepare the journal entries for the June 30, 2022, interest payment by both Gless and Century assuming both use the straight-line method. 3. On July 1, 2023, when Gless’s common stock had a market price of $33 per share, Century converted the bonds it held. Prepare the journal entries by both Gless and Century for the conversion of the bonds (book value method). • Required 1 Prepare the journal entries for the issuance of the bonds by Gless and the purchase of the bond investment by Century. (Enter your answers in whole dollars. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Required 2 Prepare the journal entries for the June 30, 2022, interest payment by both Gless and Century assuming both use the straight-line method. (Enter your answers in whole dollars. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) • Required 3 On July 1, 2023, when Gless’s common stock had a market price of $33 per share, Century converted the bonds it held. Prepare the journal entries by both Gless and Century for the conversion of the bonds (book value method). (Enter your answers in whole dollars. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) Show less Explanation [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 118 pages
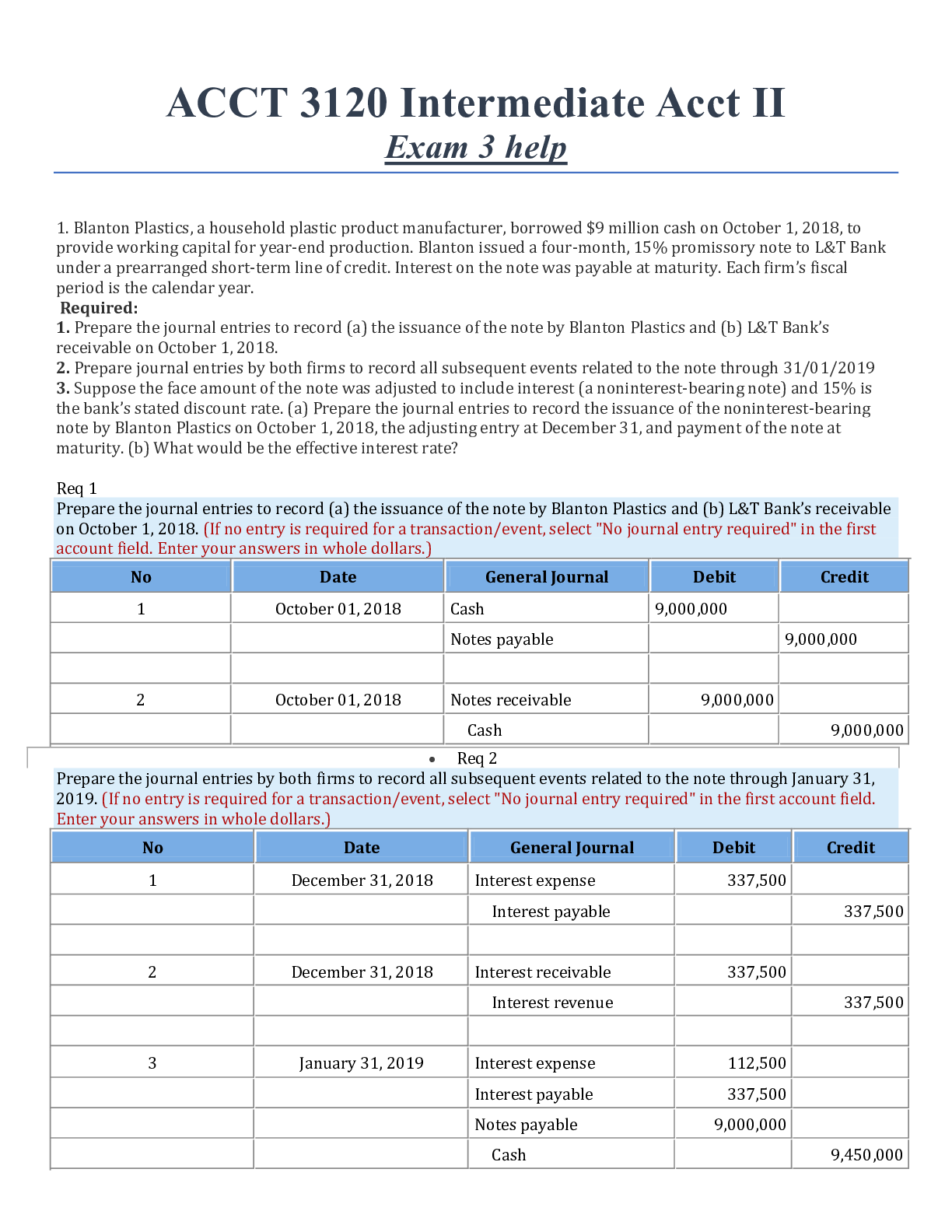
Reviews( 0 )
Recommended For You
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > NUR 2459 / NUR2459 Mental and Behavioral Health Nursing Exam 3 Review | Rated A | Latest 2021 / 2022 | Rasmussen College (All)

NUR 2459 / NUR2459 Mental and Behavioral Health Nursing Exam 3 Review | Rated A | Latest 2021 / 2022 | Rasmussen College
NUR 2459 / NUR2459 Mental and Behavioral Health Nursing Exam 3 Review | Rated A | Latest 2021 / 2022 | Rasmussen College 1. Kids Death & Dying: - 10-12yo: they understand that death is final 2....
By nurse_steph , Uploaded: Aug 20, 2021
$10
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > NUR 2790 PN3 Exam 3 Review (All)

NUR 2790 PN3 Exam 3 Review
NUR 2790 PN3 Exam 3 Review
By ACADEMICTUTORIAL , Uploaded: May 20, 2022
$3
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > HIMA 240 Exam 3 Principles of Healthcare Reimbursement Exam Elaborations Questions and Answers (All)

HIMA 240 Exam 3 Principles of Healthcare Reimbursement Exam Elaborations Questions and Answers
HIMA 240 Exam 3 Principles of Healthcare Reimbursement Exam Elaborations Questions and Answers
By Nursing By Chelsea , Uploaded: Aug 02, 2022
$20
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > PATHO Exam 3 Focus Points- Chapters 6,7,9,17 2022/2023 (All)

PATHO Exam 3 Focus Points- Chapters 6,7,9,17 2022/2023
PATHO Exam 3 Focus Points- Chapters 6,7,9,17 2022/2023
By STUDY-GUIDENOTES , Uploaded: Jun 24, 2022
$7
Pathophysiology> EXAM REVIEW > NR 283 Concept Review Exam 3 patho (Best for Revision) (All)
.png)
NR 283 Concept Review Exam 3 patho (Best for Revision)
NR 283 Concept Review Exam 3 **Please be sure to study etiology, clinical manifestations and complications, pathophysiology of the following topics: Hematology RBC-function- Erythrocytes (or RBC’s)...
By A+ Solutions , Uploaded: Jun 21, 2022
$12.5
Pathophysiology> EXAM REVIEW > NURS 3366: EXAM 3 REVIEW: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, Renal, Genitourinary (All)

NURS 3366: EXAM 3 REVIEW: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, Renal, Genitourinary
NURS 3366: EXAM 3 REVIEW: Cardiovascular, Pulmonary, Renal, Genitourinary
By quizprof , Uploaded: Jun 16, 2022
$10
Pharmacology> EXAM REVIEW > NUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEW (All)

NUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEW
NUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNUR 2474 EXAM 3 REVIEWNU...
By DOCTOR BEN , Uploaded: Jun 13, 2022
$16
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > NUR2356 MDC Exam 3 Review Completed A 2022/2023 (All)

NUR2356 MDC Exam 3 Review Completed A 2022/2023
NUR2356 MDC Exam 3 Review 1. Appropriate nursing actions: Nicole a) When a client falls 1st priority – check on patient for any injuries Before that, guide the patient to the floor. b) Position...
By Bobweiss , Uploaded: Jan 27, 2021
$9.5
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > NUR 2356 Multidimensional Care EXAM 3 REVIEW | MDC EXAM 3 REVIEW (Graded A) (All)

NUR 2356 Multidimensional Care EXAM 3 REVIEW | MDC EXAM 3 REVIEW (Graded A)
MDC Final Exam Review 1. Appropriate nursing actions: Nicole a) When a client falls 1 st priority – check on patient for any injuries Before that, guide the patient to the floor. b) Positionin...
By jimmydarts , Uploaded: Apr 16, 2022
$9
*NURSING> EXAM REVIEW > NUR2755 / NUR 2755 Multidimensional Care IV / MDC 4 Exam 3 Review (Latest 2021 / 2022) Rasmussen (All)

NUR2755 / NUR 2755 Multidimensional Care IV / MDC 4 Exam 3 Review (Latest 2021 / 2022) Rasmussen
NUR2755 / NUR 2755 Multidimensional Care IV / MDC 4 Exam 3 Review (Latest 2021 / 2022) Rasmussen 1. 2. 3. muscle weakness increase uncordination confusion apathy incoherence decreased clott...
By walli , Uploaded: Apr 12, 2022
$8.5
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 13, 2020
Number of pages
118
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 13, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
469






