Biology > LAB QUIZ > LAB_ QUIZ BIO 201L_ MUSCLES MODULE 8|UPDATED 2022/2023| ALL QUIZ EXAMINABLE (All)
LAB_ QUIZ BIO 201L_ MUSCLES MODULE 8|UPDATED 2022/2023| ALL QUIZ EXAMINABLE
Document Content and Description Below
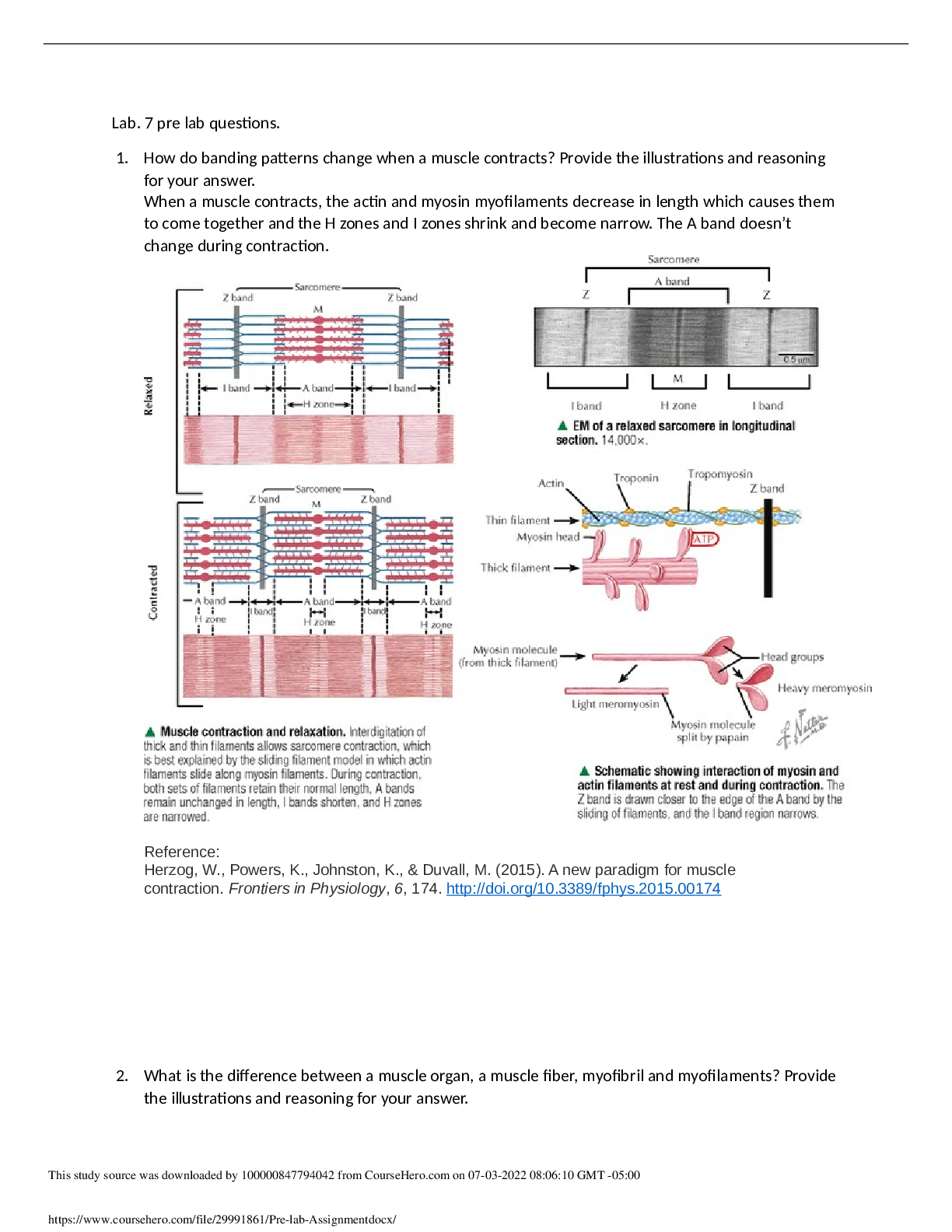
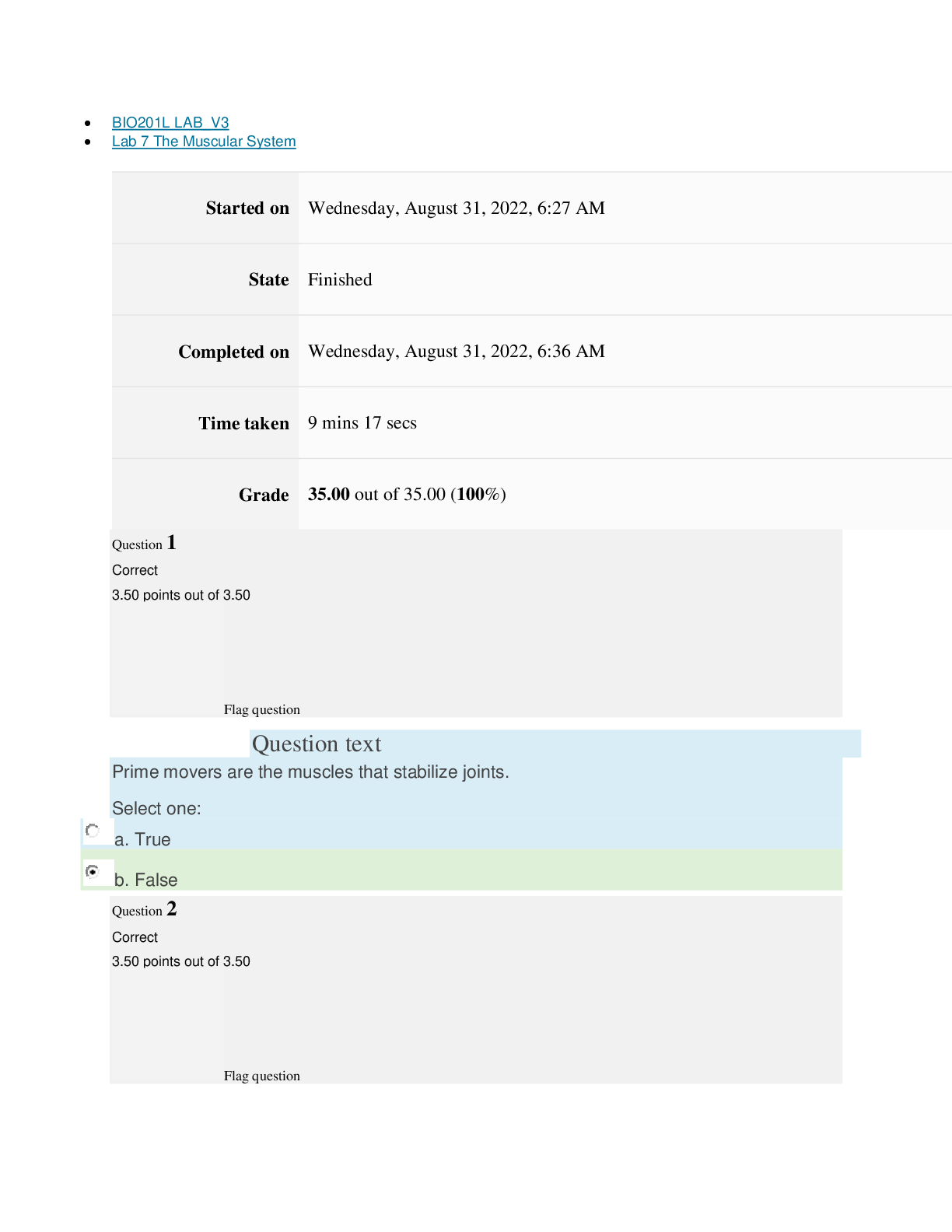
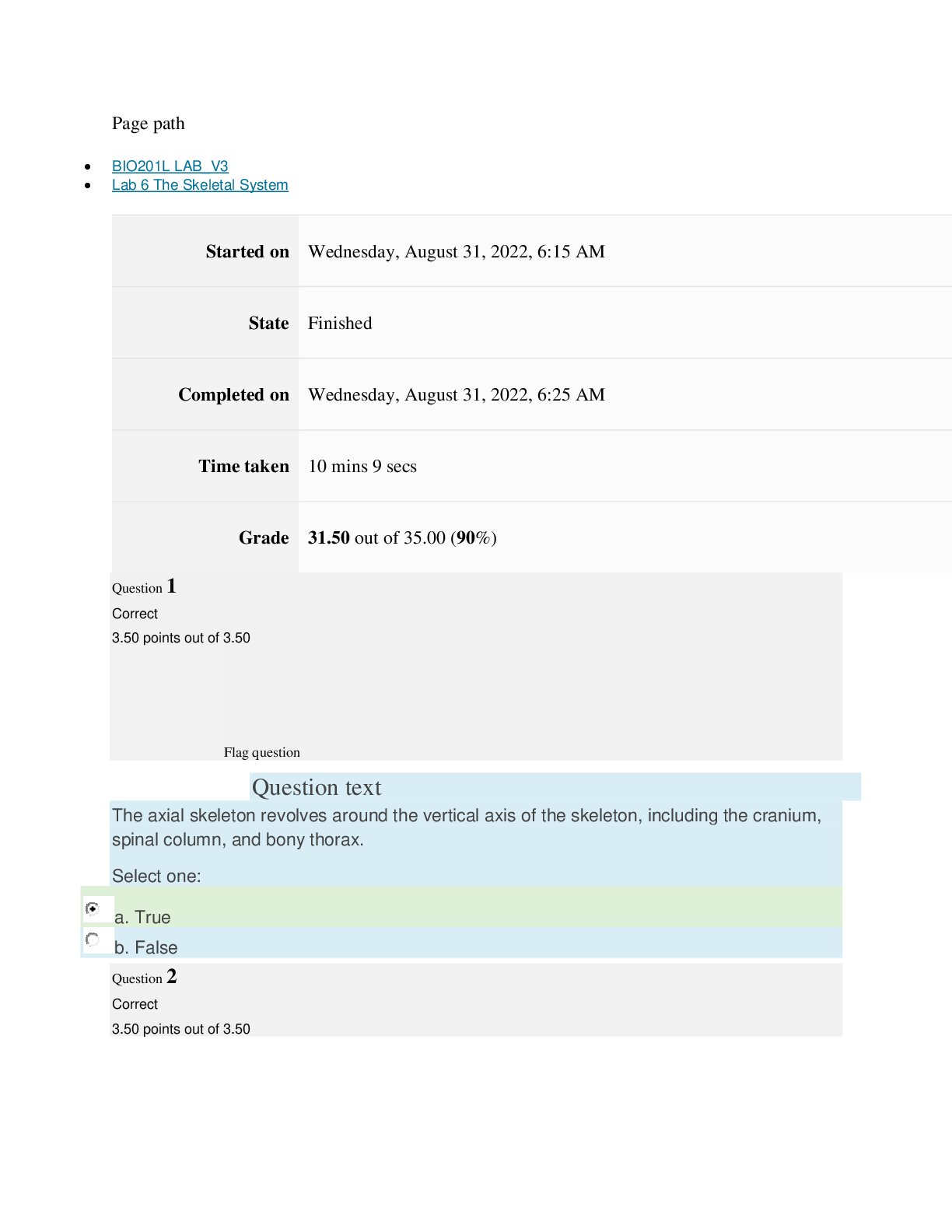
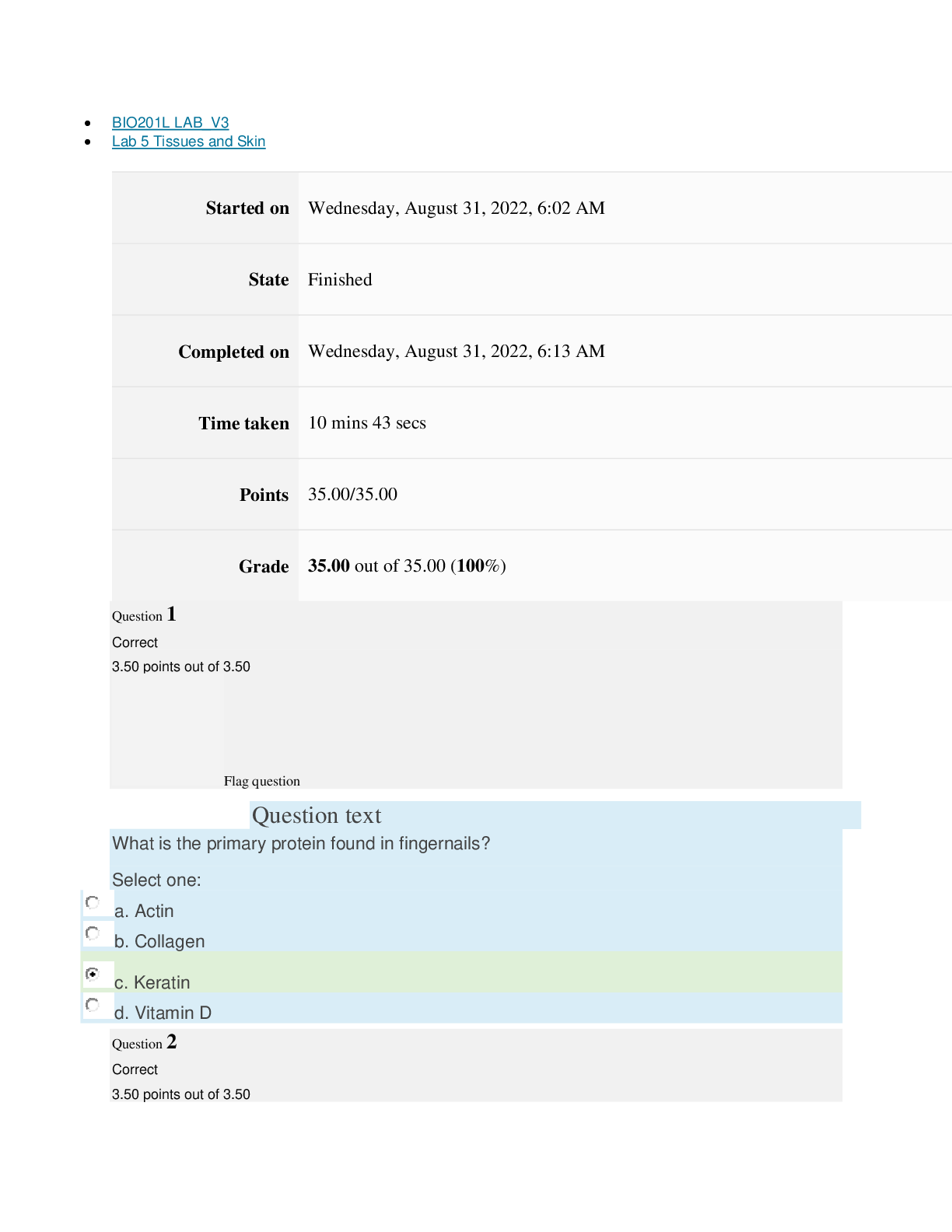
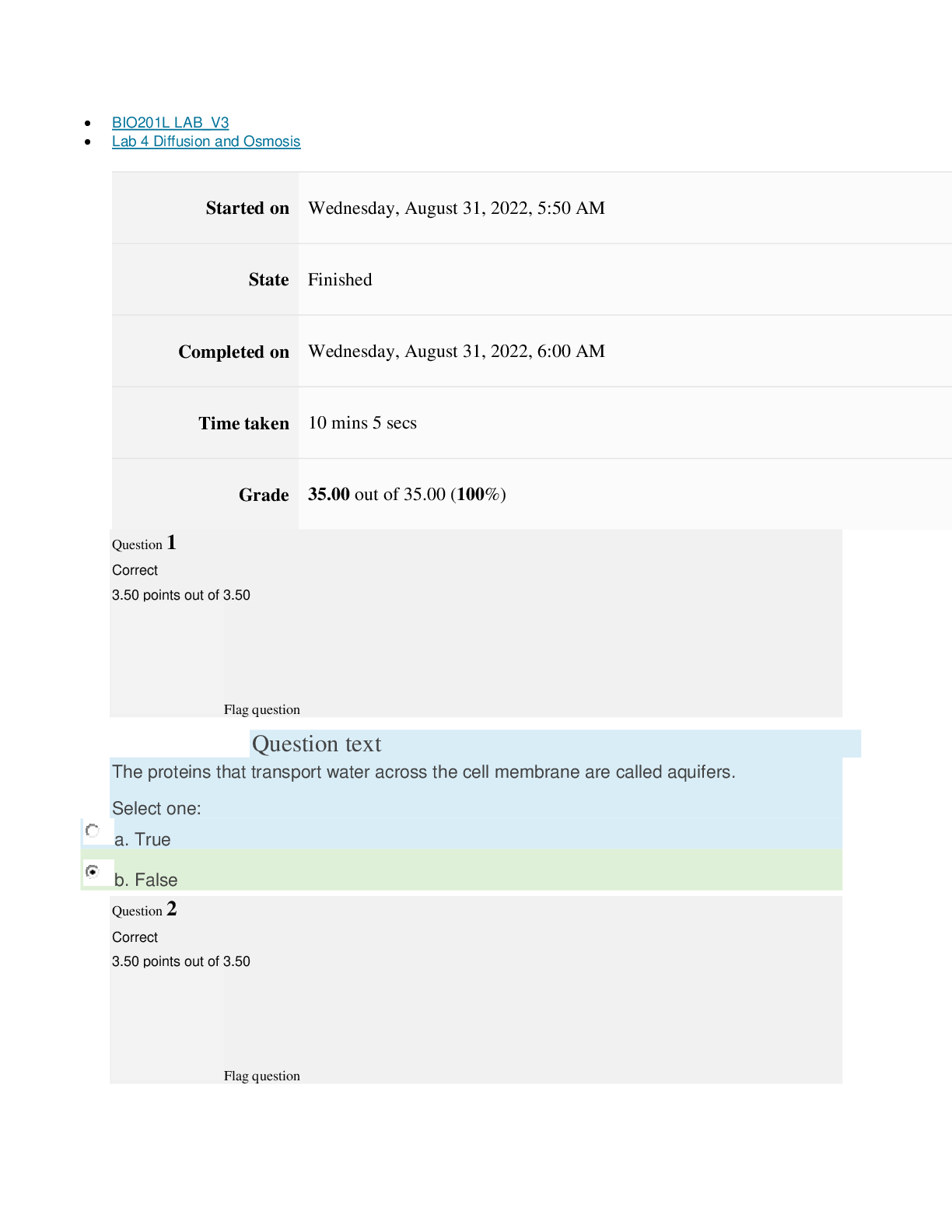
Pre-Lab Questions ”1. How do banding patterns change when a muscle contracts?” The actin and myosin myofilaments become smaller in length. The H and I zones also become smaller and narrower. T... he A band does not change during contractions. ”2. What is the difference between a muscle organ, a muscle fiber, myofibril and a myofilament? ” The muscular system is an organ with the main purpose of movement. There are three muscle types which are: skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. Muscle fibers are the cells that make up the muscles themselves. Myofibrils are long threadlike structures that contain actin and myosin myofilaments. These myofilaments are arranged into units called sarcomeres, which connect to form the myofibrils. ”3. Outline the molecular mechanism for skeletal muscle contraction. At what point is ATP used and why? ” ATP is essential to begin the cycle necessary for muscle contraction. ATP supplies the chemical energy that is then converted into movement of the muscles. First, ATP binds to myosin. Then, myosin ATPases hydrolyze ATP into ADP and Pi. These are bound to the myosin head. Intracellular Ca2+ binds with troponin, which causes a change to the position of tropomyosin. The tropomyosin moves and exposes myosin binding sites on the actin filaments. This allows myosin heads to attach, which forms a cross-bridge between myosin heads and actin filaments. After this ADP and Pi are released and this alters that shape of the myosin head. This shape movement is a sliding motion resulting in a power stroke. The cycle ends when Ca2+ is pumped back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. ”4. Explain why rigor mortis occurs. ” Rigor mortis occurs when ATP production stops and the levels begin to decrease after death. This causes active transport of Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum to stop, and Ca2+ leaks into the sarcoplasm. These Ca2+ levels increase over time and cross-bridges form. Without enough ATP to bind to the myosin molecules, the cross-bridges are unable to release and reform in a usual cycle. This causes the muscles to become very stiff and remain in that state until the muscle tissue begins to degenerate. Experiment 1: Tendons and Ligaments Post-Lab Questions ”1. Label the arrows in the slide images below based on your observations from the experiment. ” A- Chondrocytes B- Collagen C- Collagen Fibers D- Skeletal Muscle Fiber E- Nuclei F- Collagen Fibers Lab 7 The Muscular System BIO201L Lab 7 The Muscular System BIO201L ”2. How does the extra cellular matrix of connective tissues contribute to its function? ” The extra cellular matrix of connective tissues is made of proteins and proteoglycans. These substances fill the space between the cells within the tissue. The composition of these substances determines the function of the connective tissue. ”3. Why are tendons and ligament tissues difficult to heal? ” Tendons and ligaments are made of fibrous connective tissue. This tissue does not have an abundant blood supply like other tissues in the body. This lack of blood supply causes the healing process to be very slow compared to other body tissues. ”4. What difference do you see between the tendon – muscle insertion image and the tendon image? ” The tendon-muscle insertion image shows dense irregular muscle, and the tendon image shows smooth muscle tissue. ”5. What differences do you see between the tendon and ligament sections? ” The ligament section shows skeletal muscle fibers, which are very striated. The tendon slide appears much smoother with no striation. Lab 7 The Muscular System BIO201L Experiment 2: The Neuromuscular Junction Post-Lab Questions ”1. Are there few or many nuclei at the end plate? ” There are many nuclei at the end plate. ”2. What is a motor unit? ” A motor unit is made of a motor neuron and skeletal muscle fibers. Many motor units work together to create muscle contractions. ”3. How is a greater force generated (in terms or motor unit recruitment)? ” The more motor units are activated the stronger the muscle contraction will be, causing a greater force to be generated. ”4. What types of sensors are present within the muscle to identify how much force is generated? ” The sensors that detect how much force is generated within a muscle are called Proprioceptors. These include muscle spindles that sense muscle length, Pacinian corpuscles that detect changes in pressure, and Golgi tendon organs that can sense changes in muscle tension. Experiment 3: Muscle Fatigue Table 1: Experimental Counts Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5 Predicted Value 50 30 30 25 25 Actual Value 44 39 28 24 21 Post-Lab Questions ”1. How did the predicted results compare to the actual results? ” The actual results were lower than my predicted values. ”2. Did you notice any changes in the number of repetitions you could perform, or how your hand felt after each of the trials? ” With each subsequent trial it was harder and harder to move the rubber band. The muscles felt sore and fatigued. The number of repetitions continued to decrease after each trial. ”3. Explain the actions that were occurring at the cellular level to produce this movement. Include sources of energy and any possible effect of muscle fatigue. ” ATP is what allows muscle contractions to occur. After prolonged use of a muscle during a continuous movement, like during the experiment above, APT becomes depleted. Lactate builds while pH drops. The muscles experience oxidative stress and localized inflammatory reactions, which all cause the muscles to fatigue. Lab 7 The Muscular System BIO201L ”4. Hypothesize what would happen if blood flow was restricted to the hand when this experiment is performed. ” If blood flow was restricted from the hand during this experiment it would be even more difficult to move the rubber band and it would eventually come to a point when the muscles would no long [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 05, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 05, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
270









.png)



