Search for
Filter By
Rating
Price in $
Search Results 'Star'
Showing All results
Sort by
English > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Algoma University ENGL ENGL 1802 Choose the method of prewriting that works best for you (mind-mapping, lists, writing), and start brainstorming ideas for your essay. At the end of...
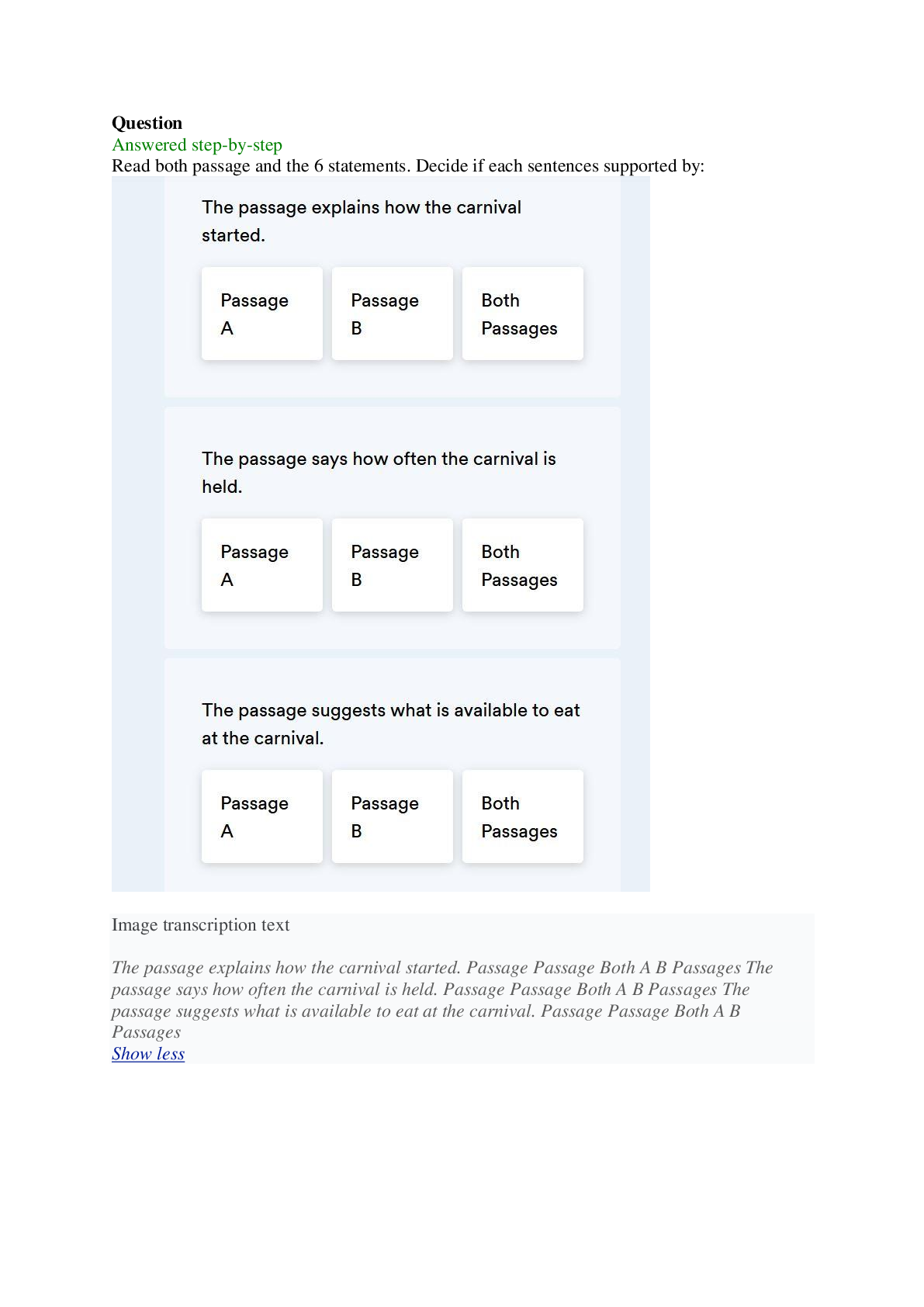
Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Elon University ECO ECO 22472 The passage explains how the carnival started. Passage Passage Both A B Passages The passage says how often the carnival is held. Passage Passage...
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Navigate 2 o Did I say use your test preps to study Medical Emergencies? This is a great resource written by the same publisher that created many of the test questions. Terminology and Medical Conditions o Ascites, jaundice, atelectasis, pleuritis, Biots respirations, agonal respirations, Cheyne Stokes respirations, hyperventilation, Internal Respiration, nocturnal dyspnea, erythropoiesis, Prinzmetal’s angina, Starlings Law, Preload vs. Afterload, Infarct, Ischemia, break through seizure, glycolysis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogen, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, DKA, Insulin Shock, Diabetic Coma, polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria, tolerance (as related to substance abuse), active listening, reflective listening, definitive listening, orthostatic hypotension, hypermetabolic state, angioedema, colic pain, hemipharesis, hemoglobin. Patient Assessment o It would be very difficult to give a specific review on this without giving a specific question. With that said, Know your patient assessment well and every little specific about it. History Taking Questioning patients during your assessment. Appropriate questions to ask based on the condition. SAMPLE and OPQRST Physical Exams DCAP BTLS Determining whether a medical patient is high or low priority Start memorizing vital signs in all age groups (page 440). Neurological assessments, GCS Scale
Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CHESSON Practice Questions with correct answer starred
Pharmacology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NURS 406PHARMACOLOGY ASSESSMENT 1 y 2 (1) (document rated 5 star)
Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BUS 339 BUS339 WEEK 1 rated 5 star
Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Lone Star College System ECON 1301 Answer_Key_Macro_Topic_3.8A-_Fiscal_Policy
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NUR 4290 Chapter 01: Mental Health and Mental IllnessHalter: Varcarolis’ Foundations of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: A Clinical Approach, 8th Edition(Lately updated and Rated 5 Star complete Solutions)
Pathophysiology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PATHO 2410;Protection/Adaptation Test Bank Best 2021 Rated 5 star with complete Solutions.100%(Chapter 1,5,6,7,20 & 21 each with 30 and more Questions) MORE THAN 180 Q & A.
Financial Accounting > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ACCOUNTING MISC - Exam_Q_and_A_5 STAR RATED WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION REFERENCES AND NOTES.ALL TOGETHER!







.png)


