Search for
Filter By
Rating
Price in $
Search Results 'Findings'
Showing All results
Sort by
*NURSING > TEST BANK > TEST BANK FOR ADVANCED ASSESSMENT: INTERPRETING FINDINGS AND FORMULATING DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES 4th Edition, Mary Jo Goolsby, Laurie Grubbs (All)
Health Care > TEST BANK > Test Bank for Advanced Assessment Interpreting Findings differential_diagnoses_4th_edition_goolsby (All)
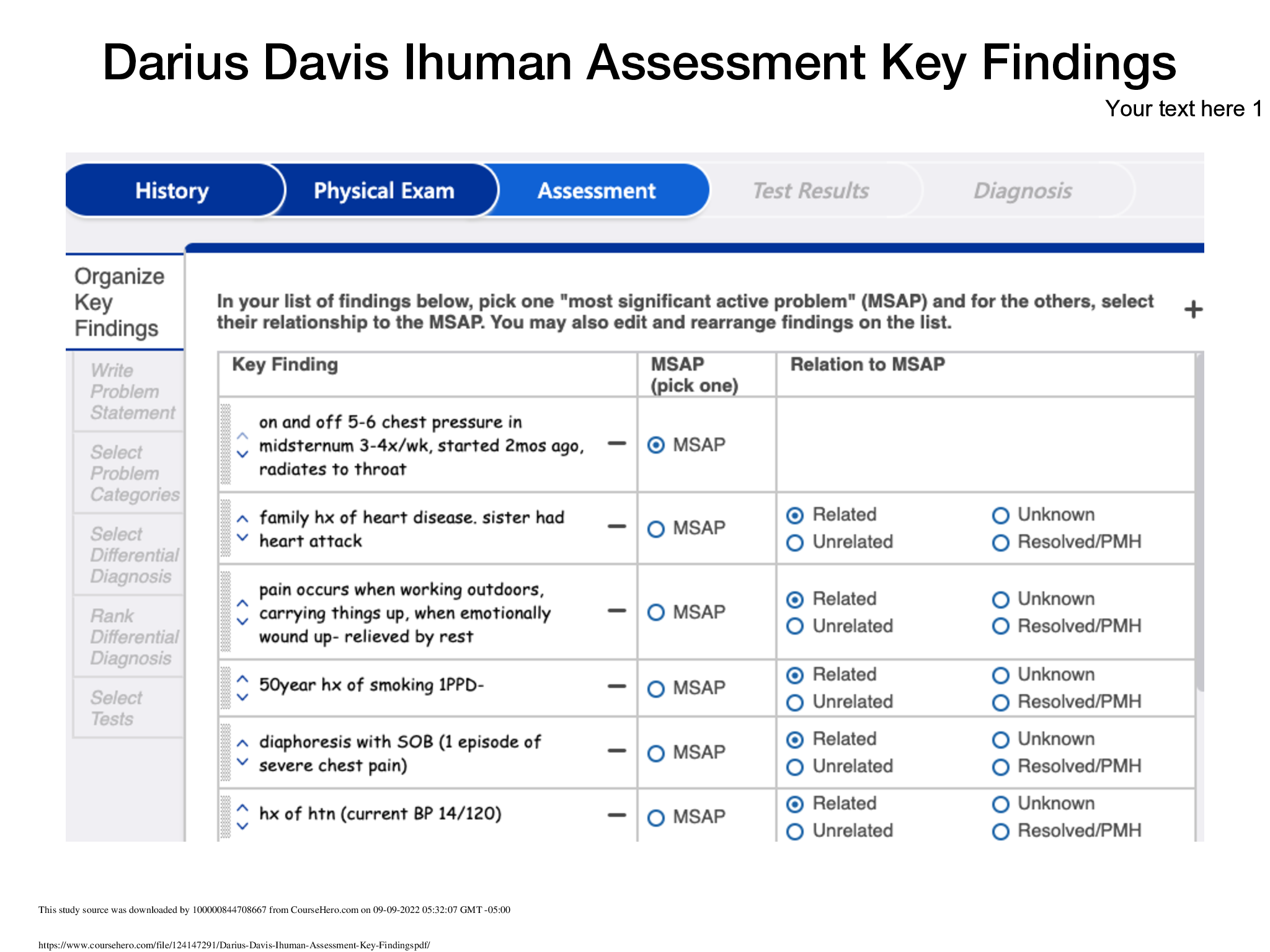
*NURSING > iHuman > Darius Davis Ihuman Assessment Key Findings (All)
*NURSING > TEST BANK > Chapter 2. Genomic Assessment: Interpreting Findings and Formulating Differential Diagnosis MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The first step in the genomic assessment of a patient is obtaining information regarding: A. Family history B. Environmental exposures C. Lifestyle and behaviors D. Current medications 2. An affected individual who manifests symptoms of a particular condition through whom a family with a genetic disorder is ascertained is called a(n): A. Consultand B. Consulband C. Index patient D. Proband 3. An autosomal dominant (AD) disorder involves the: A. X chromosome B. Y chromosome C. Mitochondrial DNA D. Non-sex chromosomes 4. To illustrate a union between two second cousin family members in a pedigree: A. Arrows are drawn pointing to the male and female B. Brackets are drawn around the male and female C. Double horizontal lines are drawn between the male and female D. Circles are drawn around the male and female 5. To illustrate two family members in an adoptive relationship in a pedigree: A. Arrows are drawn pointing to the male and female B. Brackets are drawn around the male and female C. Double horizontal lines are drawn between the male and female D. Circles are drawn around the male and female 6. When analyzing the pedigree for autosomal dominant (AD) disorders, it is common to see: A. Several generations of affected members B. Many consanguineous relationships C. More members of the maternal lineage affected than the paternal D. More members of the paternal lineage affected than the maternal (All)
*NURSING > CASE STUDY > NRNP 6531 Victoria Lewis All History Questions and Key Findings (All)
Health Care > EXAM > TEST BANK FOR ADVANCED ASSESSMENT: INTERPRETING FINDINGS AND FORMULATING DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES 4th Edition, Mary Jo Goolsby, Laurie Grubbs (All)
Business > INSTRUCTOR MANUALS > Leadership Research Findings, Practice, and Skills 10th Edition by Andrew DuBrin (Instructor Manual All Chapters, 100% original verified, A+ Grade) (All)
*NURSING > EXAM > NRNP 6531-Darius Davis Ihuman Assessment Key Findings (All)
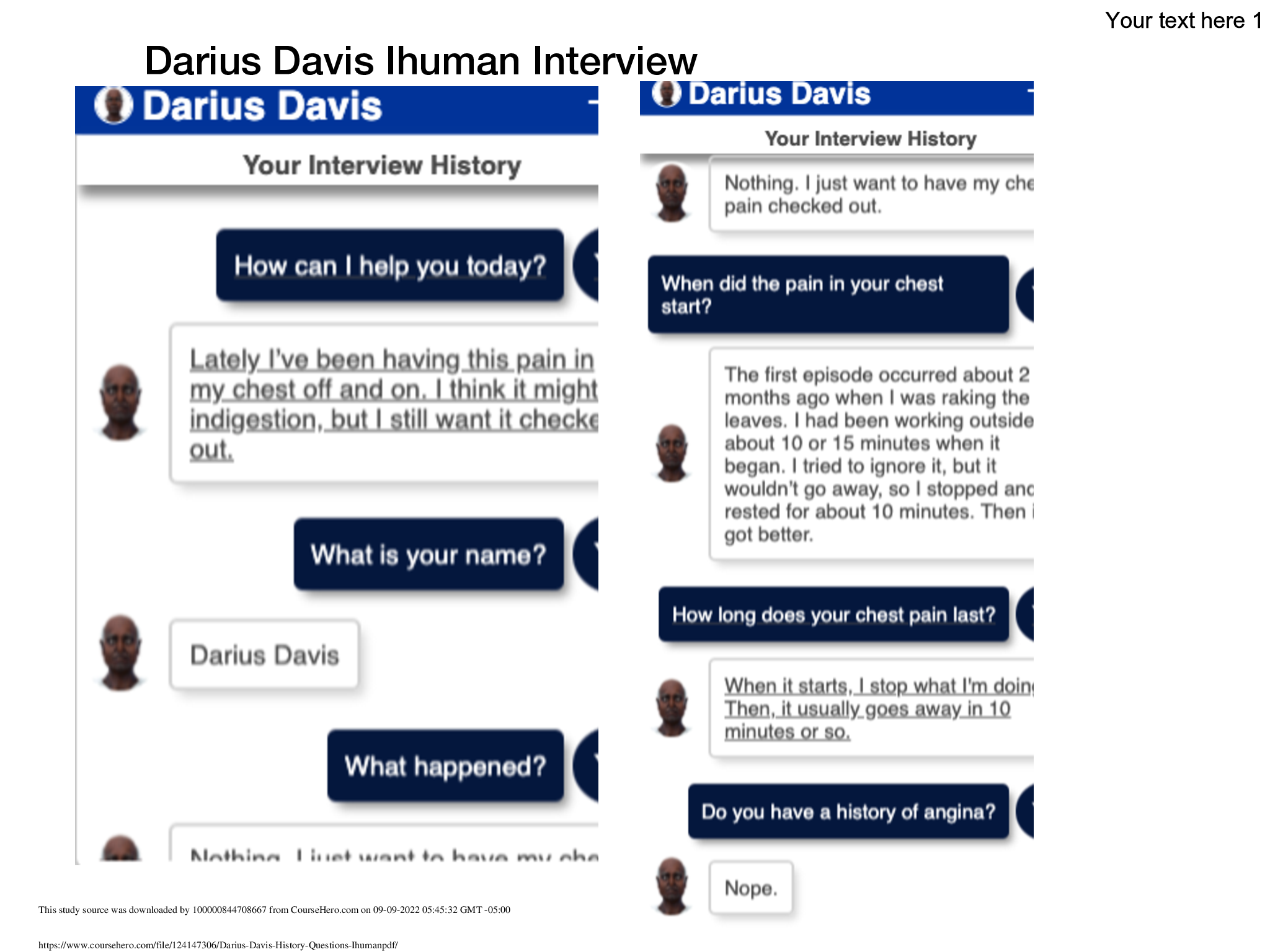
Health Care > iHuman > Darius Davis History new Interview /Darius Davis Ihuman Assessment new Key Findings (All)
*NURSING > TEST BANK > Advanced Assessment, Interpreting Findings and Formulating Differential Diagnoses, 4th Edition by Goolsby Test Bank (All)