*NURSING > HESI MED SURG > Abraham Baldwin Agricultural CollegeNURS 2208Medsurg Hesi Topics (All)
Abraham Baldwin Agricultural CollegeNURS 2208Medsurg Hesi Topics
Document Content and Description Below
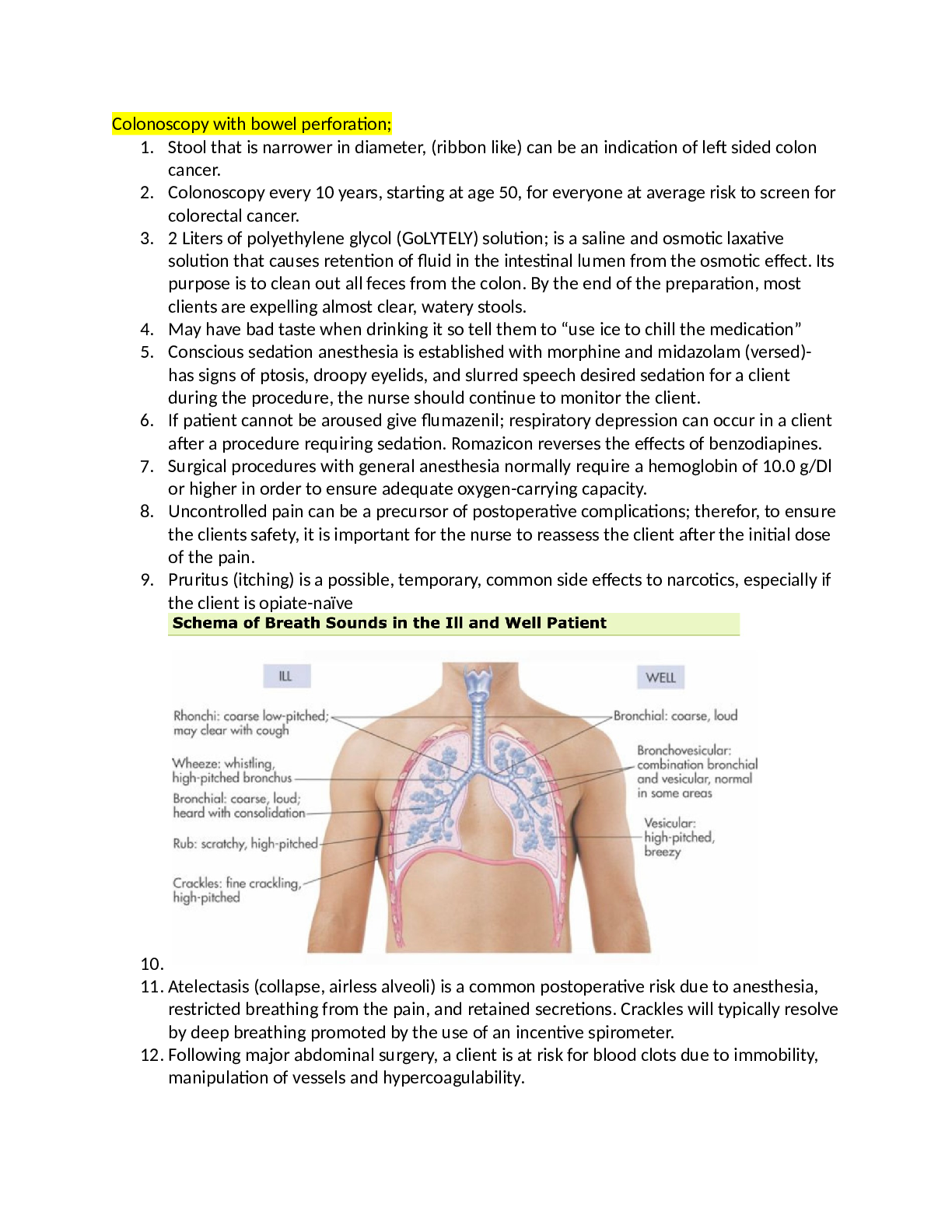
1. Nursing process-Stroke TIA: Med-Surg book p930-945 lot of pages just hitting the highlights.........TIA = Transient ischemic attack. TEMPORAY neurologic dysfunction resulting from a brief interru... ption in cerebral blood flow. Typically resolves in 30 to 60 min. Treatment focuses on preventing another TIA or stroke: Reducing high BP, the most common risk factor for stroke, by adding or adjusting drugs to lower BPTaking aspirin or another antiplatelet drug to prevent strokes (Plavix) Controlling diabetes and keeping blood sugar levels in a target range, typically 100-180mg/dl Promoting lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, eating heart-healthy foods, and being more active Ensure that the pt taking antiplatelet drugs is aware of precautions and actions to take if bleeding occurs. A Stroke - Is a medical emergency, and it should be treated immediately to reduce permanent disability. It is caused by an interruption of perfusion to any part of the brain. Recommend a diet high in fruits and veggies and low in saturated fats. Light to moderate alcohol consumption may reduce the risk for stroke, but a higher consumption may increase it. NCLEX purple book p225, 937-939 1.In clients with hemorrhagic strokes, the head of the bed is usually elevated to 30 degrees to reduce intracranial pressure and to facilitate venous drainage. 2.For clients with ischemic strokes, the head of the bed is usually kept flat 3.Maintain the head in a midline, neutral position to facilitate venous drainage from the head. 4.Avoid extreme hip and neck flexion; extreme hip flexion may increase intrathoracic pressure, whereas extreme neck flexion prohibits venous drainage from the brain ALERT! A critical factor in the early intervention and treatment of stroke is the accurate identification of stroke manifestations and establishing the onset of the manifestations. Stroke screening scales may be used to quickly identify stroke manifestations. Box 66-17 Neurological Assessment in Stroke: Changes in level of consciousness Signs of increasing intracranial pressure Assessment of cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X and XII Cranial nerve V: Difficulty with chewing Cranial nerve VII: Facial paralysis or paresis Cranial nerve IX and X: Dysphagia Cranial nerve IX: Absent gag reflex Cranial nerve XII: Impaired tongue movement Review box 66-18 Assessmnet findings in a stroke HESI green book p 144-146HESI HINT– CNS involvement related to cause of stroke: Hemorrhagic: caused by a slow or fast hemorrhage into the brain tissue; often related to HTN Emoblic: Caused by a clot that has broken away from a vessel and has lodged in one of the arteries of the brain, blocking the blood supply. It is often related to atherosclerosis (so it may occur again). HESI HINT– Atrial flutter and fibrillation produce a high incidence of thrombus formation following dysrhythmia caused by turbulence of blood flow through all valves and heart chambers. HESI HINT– A woman who had a stroke 2 days earlier has left-sided paralysis. She has begun to regain some movement in her left side. What can the nurse tell the family about the client’s recovery period? The quicker movement is recovered, the better the prognosis is for full or improved recovery. She will need patience and understanding from her family as she tried to cope with the stroke. Mood swings can be expected during the recovery period, and bouts of depression and tearfulness are likely.See table 4-35 Location of disruption in the brain p145 HESI HINT– Words that describe losses in strokes: 1.Apraxia: inability to perform purposeful movements in the absence of motor problems 2.Dysarthria: difficulty articulating 3.Dysphasia: impairment of speech and verbal comprehension 4.Aphasia: loss of the ability to speak 5.Agraphia: loss of the ability to write 6.Alexia: loss of the ability to read 7.Dysphagia: dysfunctional swallowing HESI HINT– Steroids are administered after a stroke to decrease cerebral edema and retard permanent disability. H2 inhibitors are administered to prevent peptic ulcers [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 23, 2021
Number of pages
24
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 23, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
65













 Test Bank.png)



.png)







 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
.png)


 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)

