NR 446 Exam 2 -Chapters 7, 8, 9, 10,12, 13, and 14 100% Pass
Document Content and Description Below
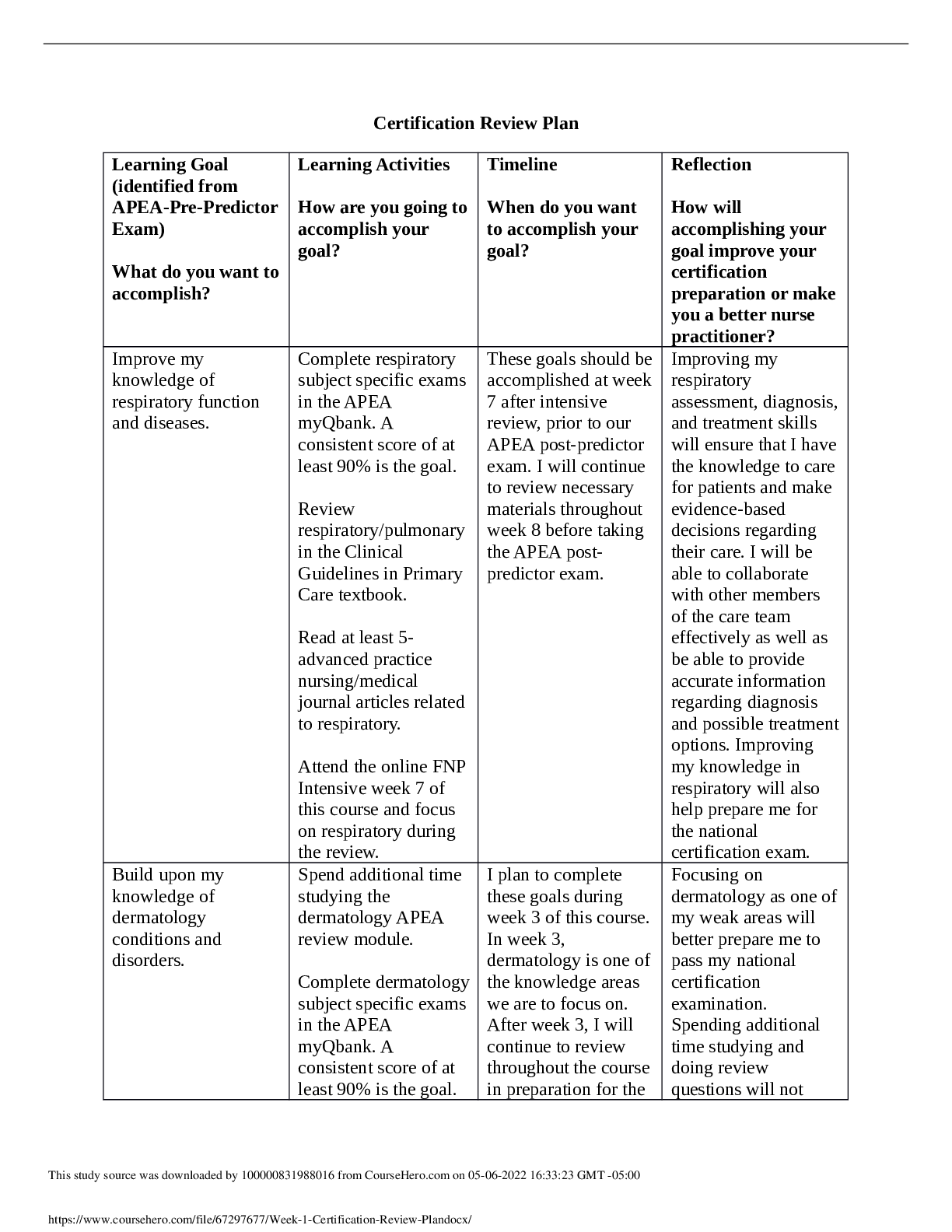
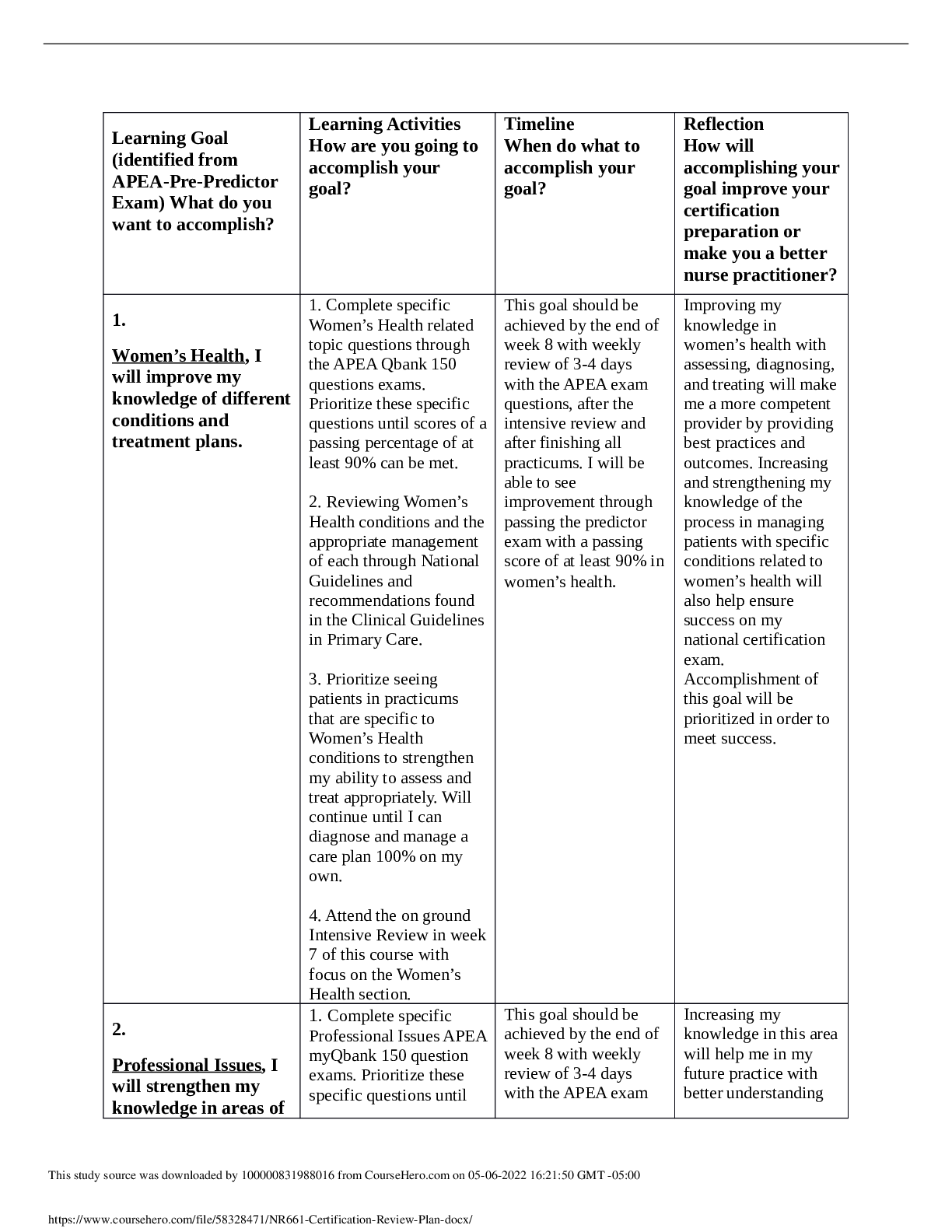
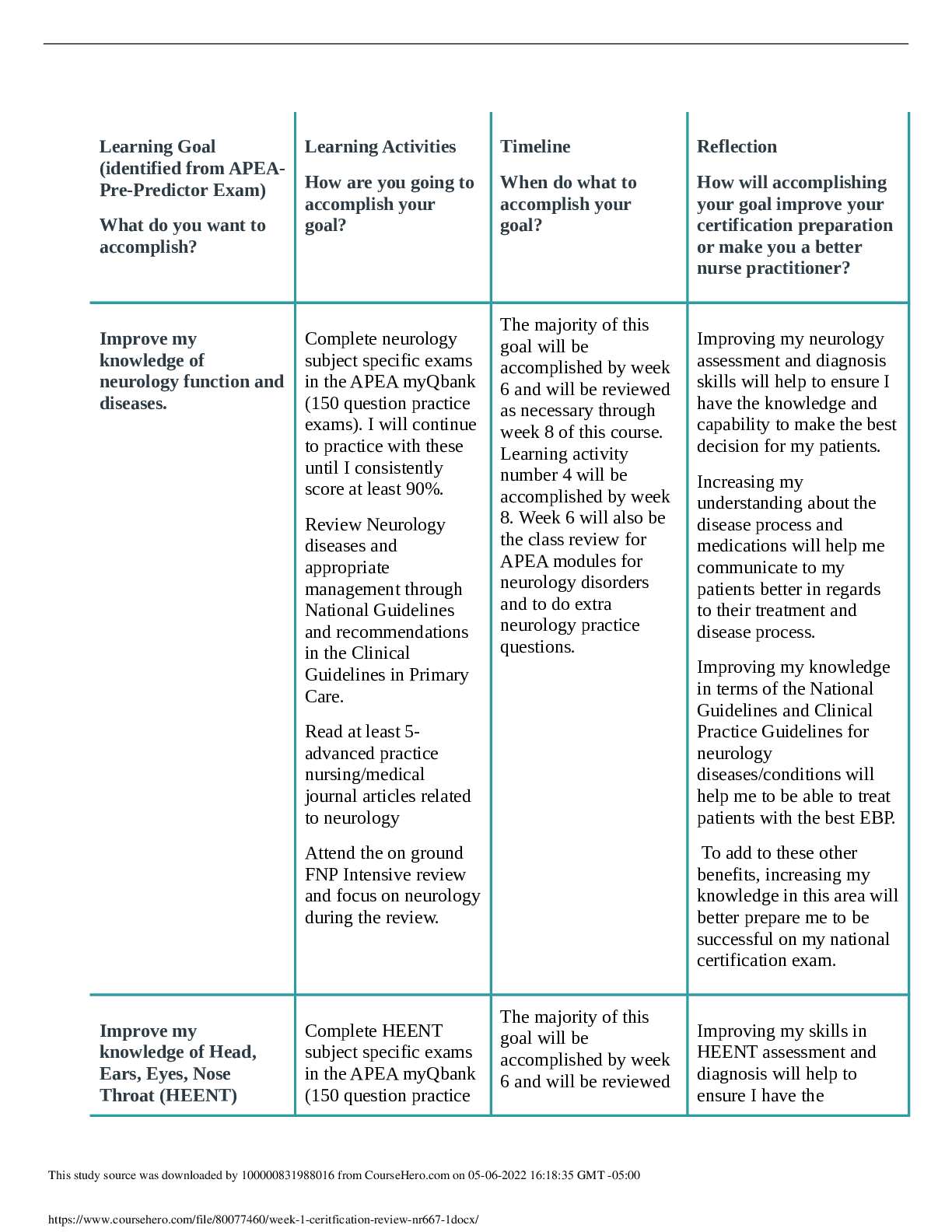
NR 446 Exam 2 Chapters 7, 8, 9, 10,12, 13, and 14 page 1 of 3 Blue Print Helpful hints to study. Please review the chapters covered. Questions are generally application of knowledge (critical think... ing to answer the questions). To do this you need to have a basic understanding of content to be able to answer the questions. Chapter 7 Rules, policies, procedures, plans, goals • Rules: are plans that define specific action or nonaction. Generally included in part of a policy and procedure statement. They describe situations that allow only for one choice of action. They are fairly inflexiable so the fewer rules, the better. • Policies: are plans reduced to statements or instructions that direct organizations in their decision making. They are derived from the organizations philosophy, goals and objectives. They explain how goals will be met and guide the general course and scope of activities. There are two types, implied and expressed. Implied policies are neither written nor expressed verbally, have usually developed over time and follow a precedent. Expressed policies are delineated verbally or in writing • Procedures: are plans that establish customary or acceptable ways of accomplishing a specific task and delineate a sequence of steps of required action. Established procedures save staff time, facilitate in delegation, reduce cost, increase productivity and provide a means of control. • Plans: • Goals: defined as the desired result toward which effort is directed. It is the aim of the philosophy. Goals should be measurable and ambitious but realistic. Goals should clearly delineate the desired end product. Factors that can influence future of healthcare and planning long term needs SWOT • Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat • Used in step 3 of the decision making process Organizational culture • Is the total of an organizations values, language, traditions, customs and sacred cows. It contributes to the unique social and psychological environment of an organization. Mission, Vision, and Philosophy statement • Mission Statement: is a brief statement, usually no longer than 4 sentences, identifying the reasons the organization exists. It identifies the organizations constituency and addresses its position regarding ethics, principles and standards of practice. A well written mission statement will identify what is unique about the organization. vision • Philosophy Statement: delineates the set of vaules and beliefs that guide all the actions of the organization. It is the basic foundation that directs all further planning toward that mission. Chapter 8 Aging organization ways to change, implications of not responding to change Three phases of change; unfreezing, movement, refreezing • Unfreezing: occurs when the change agent convinces members of the group to change or when guilt, anxiety or concern can be elicited. • Movement: the change agent identifies, plans and implements appropriate strategies ensuring that driving forces exceed restraining forces. • Refreezing: the change agent assists in stabilizing the system change so that it becomes integrated into the status quo. Rational-empirical, normative-reeducative, and power-coercive strategies • Rational-empirical strategies: the change agent assumes that resistance to change comes from a lack of knowledge and that humans are rational begins who will change when given factual information. • Normative-reducative strategies: these strategies uses group norms and peer pressure to socialize and influence people so that change will occur. The change agent assumes that humans are social creatures, more easily influenced by others than by facts. • Power-coercive strategies: these strategies include influencing the enactment of new laws and using group power for strikes and or sit- ins. Using authority inherent an individual position to effect change. These strategies assume that people often are set in their ways and will change only when rewarded for the change or when they are forced by some power-coercive method. Planned change as a collaborative process • Often begins with a few people who meet to discuss their dissatisfaction with the status quo • As a rule anyone who will be affected by a change should be included in planning it Factors effecting successful change, acceptance and resistance Chapter 9 Basic steps to time management • Take time to plan and establish priorities • Complete the highest priority task whenever possible, and finish one task before starting another • Reprioritize based on the remaining tasks and on new information that may have been received Time wasters • Technology, Socializing, etc. Time management process Three categories of prioritization • Don’t do • Do later • Do now Chapter 10 PPACA • Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act • Provided the first real hope for American of significant reductions in numbers of uninsured, greater access to coverage for those with preexisting conditions, and mandated health-care insurance provision by employers. Types of expenses; fixed, variable, controllable, non-controllable • Fixed: Do not vary with volume • Variable: do vary with volume • Controllable: can be controlled or varied by the manager • Non-controllable: cannot be controlled or varied Critical pathways • Are a strategy for assessing, implementing and evaluating the cost effectiveness of patient care. • Reflect relatively standardized predictions of patients progress for a specific diagnosis or procedure. Operating budget • Is the second area of expenditure that involves all managers. The operating budget reflects expenses that change in response to the volume of service, such as the cost of electricity, repairs, maintenance and supplies. Cost effective/containment • Cost containment: refers to effective and efficient delivery of services while generating needed revenues for continued organizational productivity. • Cost effective: producing good results for the amount of money spent. Managed care movement • Is a system that attempts to intergrate efficiency of care, access and cost of care. • Primary care providers as the “gate keeper” (MCO) • Utilization Review: is a process used by insurance companies to assess the need for medical care and to assure that payment will be received for the care. This study source w•as doTwynploeadsedobfym10a00n0a0g81e7d11c31a1r7efroomrgCaonuri szeHat ei roo.cnosmionnc0l9u-1d4e-20H21M07O:34a:3n3dGMMTC-05O:00 Capital budget • Plan for the purchase of buildings or major equipment, which includes equipment that has a long life, is not used in everyday operations and is more expensive than operating supplies. Chapter 12 Organizational charts; pros and cons • Pros: maps lines of decision-making authority, helps people understand their assignments and those of their coworkers, reveals to managers and new personnel how they fit in an organization, contributes to sound organizational structure, shows formal lines of communication. • Cons: shows only formal relationships, does not indicate degree of authority, are difficult to keep current, may show things as they are suppose to be used to rather than as they are, may define role to narrowly, possibility exists of confusing authority with status. Organizing Committees • Committees are use widely to facilitate upward communication • Assisting in management functions • Seek new ways to revamp old burearucratic structures • Increased staff performance Centralized verses decentralized organizational structure • Centralized: a few managers at the top of the hierarchy make decisions and the emphasis is on top-down control • Decentralized: diffuses decision making throughout the organization and allows problems to be solved by the lowest practical managerial level. Often this means that problems can be solved at the level they occurred. Organizational culture and climate • Culture: the values and behaviors that contribute to the unique social and psychological environment • Climate: how employees perceive an organization [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 29, 2021
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 29, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
66