Management > EXAM > MGT 6203 FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS 2021 | Already Graaded A+ (All)
MGT 6203 FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS 2021 | Already Graaded A+
Document Content and Description Below
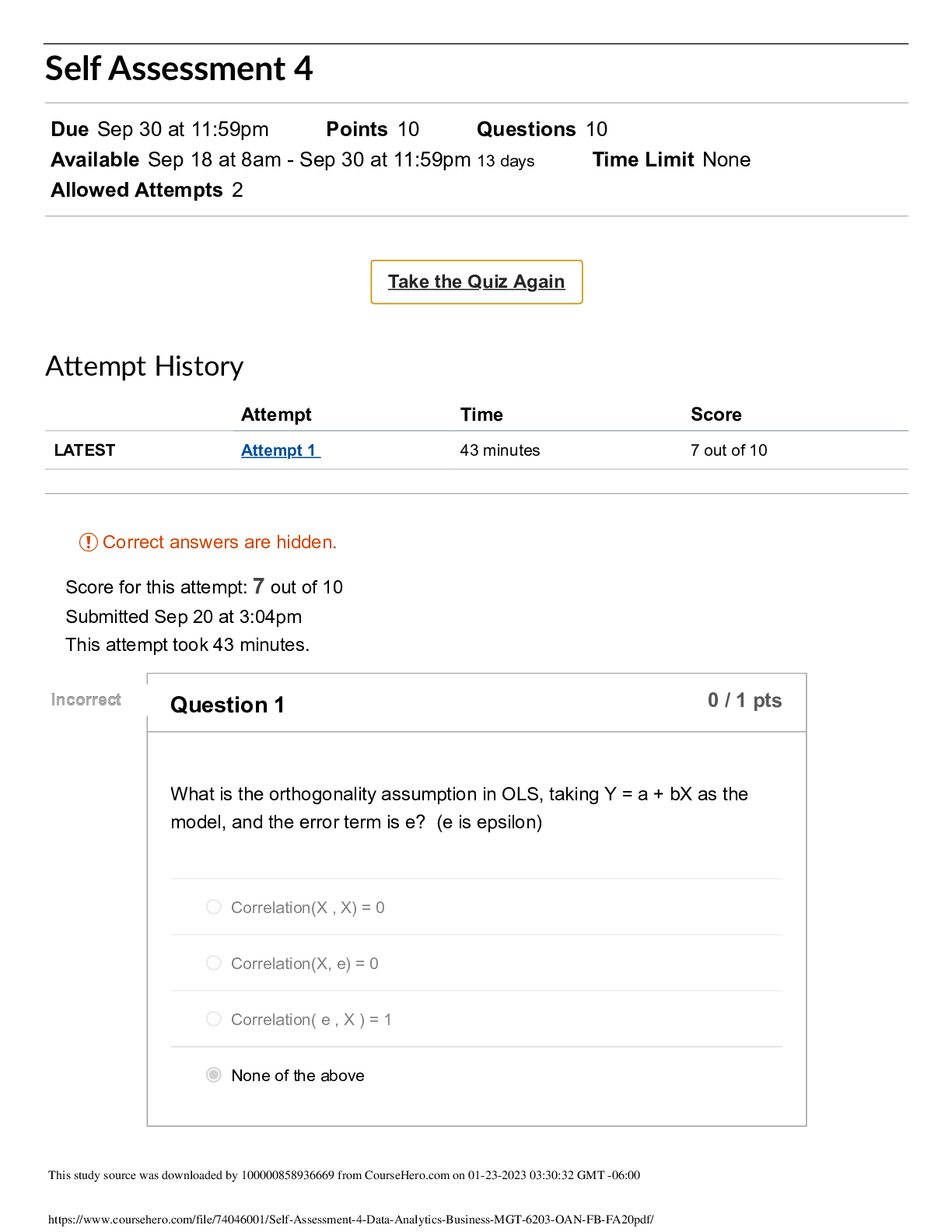
FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS 2021 Theory - 20 questions Week 1 Questions Q1. If the explained sum of squares is 35 and the total sum of squares is 49, what is the residual sum of squares? A. 10 B. ... 14 C. 12 D. 18 Solution: B Explanation: Total Sum of Squares = Explained Sum of Squares + Residual Sum of Squares SST = SSE + SSR SSR = SST – SSE = 49 – 35 = 14 Week 2 Questions Q2. Consider a regression model predicting the amount someone has spent (on some arbitrary product) based on their salary and age. To improve the model we have created an interaction variable between Salary and Age. Assume salary given in dollars, and age in years. b0 = 500 b1 = 0.35 b2 = 0.12 b3=0.21 AmountSpent = b0 + b1Salary + b2Age + b3SalaryAge How much more will a 30-year old person with a salary of $20,000 spend than a person who is 2 years older and earns $5000 less than him/her? a)17500 b)33249.54 c)26949.76 d)26950.24 Solution: (c) Week2 Lesson 4 DifInAmountSpent = b1 * (Dif in Salary) + b2*(Dif in Age) + b3* (Dif in (Salary*Age)) DifInAmountSpent = 0.35*(5000) +0.12*(-2) + 0.21 * (120,000) = 26949.76 Week 3 Questions Q3 Given the independent variable X and dependent variable Y, we regress Y on log(X) and get the following formula: Y = b1 * log(X) + b0 where b1 and b0 are the estimated coefficient and intercept respectively from OLS regression. How should we interpret it? A. As X increases by 1 unit, Y increases by b1 units B. As X increases by 1%, Y increases by 0.01 b1 units C. As X increases by 1 unit, Y increases by 100( eb1−1 )% D. As X increases by 1%, Y increases by 100( e0.01b1−1 )% Answer: B As X increases by 1%, log(X) becomes log(X) + 0.01 and y_new = b1 *(log(X) + 0.01) + b0 = y_old + 0.01 b1 Refer to Week 3 TA session notes Week 4 Questions Q4 Select the option from below which is TRUE regarding the False Positive Rate: A). A model with high Specificity will have a high False Positive Rate. B). A model with high Specificity will have a low False Positive Rate. C). The False Positive Rate of a model is not dependent on the number of True Negatives D). The False Positive Rate is given by the formula: False Positive / (True Negatives + True Positives) Answer: Option B. Lesson Slide: Page 26 False Positive Rate = 1 - Specificity Week 5 Questions Q5 What is the orthogonality assumption in OLS, taking Y = a + bX as the model, and error term is e? (A) Correlation(X, X) = 0 (B) Correlation(X, e) = 0 (C) Correlation(e, X) = 1 (D) None of the above Ans: (B) The orthogonality assumption in OLS is that the error terms and predictors are not related at all. (Week 5, Lesson 2) Week 7 Questions Q6 A speculative fund manager wants to take advantage of a mispricing in the market, where he sees a XYZ stock trading at $98.00 five minutes before the closing bell and decides to buy the stock. However, his order cannot be placed in time and the market closes with the XYZ stock price at $98.00. The next day once the market opens, he sees the best bid and offer prices of the stock XYZ (in $) as follows: What is the delay cost per share (in basis points) he will incur if he places a market order immediately? (rounded to the closest integer)? a) 102 bps b) 153 bps c) 51 bps d) There is no delay cost and the order will get executed at $98 Solution: b) If the speculator wants to buy a stock on a market order, it’ll be executed in the ask price, which is $99.50. Hence, delay cost of (99.50-98) = $1.50. Basis points = (1.5/98) *10^4 = 153.06 bps Q7 Marty had purchased the stock of ABC at $120 last year as ABC had announced a promising new product. The current stock price of ABC is at $110 and after the latest quarterly results the outlook for the stock Is not very good as the new product has failed to generate the expected sales and the stock price is expected to fall to lower levels. Marty is not willing to sell the stock as: 1) he does not want to book a loss and 2) in spite of the poor sales report he still believes his initial research cannot go wrong and the price will increase. Which behavioural biases is Marty exhibiting? a) Anchoring and Recency effect b) Recency effect and Anchoring c) Loss Aversion and Overconfidence d) Loss Aversion and Recency effect [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
MGT 6203 COMPLETE COURSE
MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct Week 10 Self Assessment 6_ Data Analytics Business - MGT-6203-OAN MGT 6203 Homework 3- Questions & Answers | All Answers Correct...
By d.occ 2 years ago
$36
18
Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 21, 2021
Number of pages
21
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 21, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
160























