Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIOLOGY 1113 Chapter 29 quizlet (GRADED A) /(Atom, Proton, Chemical bond, infection e) Questions and (All)
BIOLOGY 1113 Chapter 29 quizlet (GRADED A) /(Atom, Proton, Chemical bond, infection e) Questions and Answers | 100% GUARANTEED ACE.
Document Content and Description Below
BIOLOGY 1113 Chapter 29 quizlet Lymphatic tissue closely associated with the bloodstream as well as lymphatic circulation is found in the: a) tonsils. b) thymus. c) spleen. d) intestine. e) bo... ne marrow. c Antibodies are produced by plasma cells and regulatory T cells. True False true Cells that help initiate the adaptive immune response by placing microbial antigens on their surfaces are generally referred to as: a) helper T cells. b) regulatory T cells. c) B cells. d) mast cells. e) antigen-presenting cells. e Signaling proteins that alert the immune system an infection is present and that sometimes directly fight pathogens are the: a) complement proteins. b) antihistamines. c) antibodies. d) cytokines. e) histamines. d Which of the following would best be defined in part as an immune system overreaction? a) chronic disease b) cell-mediated response c) autoimmune disease d) cytotoxic T cell action e) allergies e Infected body cells can self-identify for destruction by the immune system by: a) releasing histamine. b) placing fragments of the infectious agent on their surfaces. c) reshaping their membranes into a pattern that B cells recognize. d) becoming dendritic cells. e) secreting hormones that stimulate macrophages. b B cells are the main cells of the cell-mediated pathway. True False false Therapy involving Toll-Like Receptors may be useful in treating some autoimmune disorders and cancers. True False true Macrophages and dendritic cells can both be antigen presenting cells. True False true Any substance that can cause an immune response is a/an: a) antibody. b) nonspecific defense. c) interferon. d) antigen. e) microbe. d Stomach acid is one of our natural defenses against bacteria in food. True False true CD4 and CD8 T cells are likely to become active when they: a) travel through the spleen. b) are attracted by the inflammatory response. c) travel through lymph nodes. d) interact with B-cells. e) dock with a dendritic cell with a matching antigen. e Smallpox vaccines used today are heat-killed cowpox viruses. True False false What is the explanation for why B cells come in so many different types that can produce so many different antibodies? a) B cells have gene fragments that can shuffle or recombine. b) B cells can recombine their genes with T cells. c) The genome of B cells is much larger than other body cells. d) B cells can regulate shape to match the antigen. e) B cells can recombine their genes with the pathogen. a Which of the following best describes the role of regulatory T cells? a) Regulatory T cells stabilize and support memory cells. b) Regulatory T cells are a kind of helper T cell that stimulates cytotoxic T cells. c) Regulatory T cells help limit the immune system response. d) Regulatory T cells are a kind of helper T cell that stimulates B cells. e) Regulatory T cells stimulate natural killer cells to attack tumors. c Which statement about the B cells' abilities to produce antibodies is most accurate? a) B cells wait to encounter an antigen and then copy it. b) There may be 100 million different B-cells, each producing a different antibody. c) Most B cells are capable of producing any kind of antibody. d) There are no B cells until an antigen is encountered. e) B cells don't produce antibodies until they develop in the thymus. b Why does producing a large "clone" of activated T cells also provide long-term immunity? a) Leftover antibodies last a long time. b) More cells are produced than necessary. c) Some of the T cells become memory cells. d) Some of the T cells can become B cells. e) The cloned cells are stronger than the original cells. c The lymphocyte group that includes both CD4 receptor "helper" and CD8 receptor "killer" cells would be the: a) macrophages. b) dendritic cells. c) mast cells. d) B-cells. e) T-cells. e A plasma cell is a cell that has differentiated from a: a) B cell. b) mast cell. c) dendritic cell. d) T cell. a Attaching an antibody to an antigen so that the antigen cannot attach to anything else is referred to as: a) antigen presentation. b) agglutination. c) neutralization. d) coagulation. c The natural killer (NK) cell specializes in attacking bacteria. True False false Antibodies may help phagocytes grab and ingest bacteria. True False true Which part of the innate response can sometimes kill bacteria outright but mainly speeds up metabolism, improving the immune response? a) fever b) histamine c) macrophage attack d) protective immunity e) fibrin a Helper T cells: 1. facilitate adaptive response 2. are B cells that make antibodies 3. limit the immune response 4. directly kill cells 5. are antigen-presenting cells1 Regulatory T cells: 1. facilitate adaptive response 2. are B cells that make antibodies 3. limit the immune response 4. directly kill cells 5. are antigen-presenting cells3 Cytotoxic T cells: 1. facilitate adaptive response 2. are B cells that make antibodies 3. limit the immune response 4. directly kill cells 5. are antigen-presenting cells4 Dendritic cells: 1. facilitate adaptive response 2. are B cells that make antibodies 3. limit the immune response 4. directly kill cells 5. are antigen-presenting cells5 Plasma cells: 1. facilitate adaptive response 2. are B cells that make antibodies 3. limit the immune response 4. directly kill cells 5. are antigen-presenting cells2 Lymph "glands" (nodes) swelling is a sign that an infection is present. True False true The response that targets specific (and only specific) pathogens is the: a) adaptive immune response. b) barrier to infection. c) innate response. d) phagocytosis response. e) inflammatory response. a Lymphocytes and other white blood cells are produced in the: a) lymph nodes. b) bone marrow. c) heart. d) thymus gland. b There are different Toll-Like Receptors for bacteria and viruses. True False true Complement proteins are antibodies produced by skin cells. True False false AIDS is an autoimmune disease. True False false What do many of the different kinds of allergies have in common? a) They result in high blood pressure. b) All allergens are living things. c) They cause histamine release. d) They contribute to autoimmune disorders. c Which part of the immune system does not target specific microbial invaders? a) antigens b) specific defense c) innate response d) antibodies c An antigen is any foreign substance that elicits an immune response. True False true Histamine causes which of the following? a) TLR production b) complement protein production c) increased permeability and dilation of blood vessels d) the anti-inflammatory response e) antibody production c Which of the following cells release histamine? a) lymphocytes b) dendritic cells c) eosinophils d) mast cells d Phagocytes can ingest pathogens, cells, and cell parts in the body. True False true Which of the following best describes the place adaptive immunity occupies in the animal kingdom? a) All animals except sponges have adaptive immunity. b) Only vertebrates, echinoderms, and mollusks have adaptive immunity. c) Only mammals have adaptive immunity. d) Only vertebrates have adaptive immunity. e) Only humans have adaptive immunity. d Once you have had a primary exposure to a specific antigen and encounter this antigen again, you will mount a rapid immune response due to: a) cytotoxic T cells. b) antibodies. c) memory cells. d) antigen-presenting cells. c Lymphocytes that become part of cell-mediated immunity arm of the adaptive immune response develop in the: a) spleen. b) intestine. c) bone marrow. d) lymph nodes. e) thymus. e Why may a transplanted organ be rejected by the immune system? a) The organ contains different T cells. b) The organ contains different B cells. c) The immune system produces a severe allergic response. d) The organ has non-self surface recognition molecules. e) The organ contains different blood antigens. d The virus HIV, which causes AIDS, infects: a) T cells. b) mast cells. c) B cells. d) phagocytes. a Which cells in the immune system produce memory cells? a) lymphocytes b) eosinophils c) mast cells d) dendritic cells a The skin serves as which type of defense against pathogens? a) innate response b) adaptive immunity c) complement d) protective immunity e) barrier to infection e Which of the following is an autoimmune disease that affects women in far greater numbers than men? a) lupus b) type 1 diabetes c) AIDS d) allergies a Which of the following is not true of antibodies? a) T cells produce antibodies. b) Antibodies are secreted by plasma cells. c) Vaccines can stimulate production of antibodies. d) There are many different kinds of antibodies. e) Antibodies bind to antigens. a Helpful bacteria that produce lactic acid would be a defense found in which part of the body? a) skin b) female reproductive tract c) respiratory tract d) urinary tract e) stomach a Dendritic cells are the histamine-producing cells of the immune system. True False false Immune therapy research with potential to work in alleviating both organ rejection and autoimmune disease involves: a) regulatory T cells. b) cytotoxic T cell action. c) vaccines. d) antibodies. a Which of the following would be best categorized as a phagocyte? a) dendritic cell b) mast cell c) eosinophil d) lymphocyte c B cell receptors are specific to only one antigen. True False true Cells in the body that have been infected by a virus or bacteria are specifically killed by: a) dendritic cells. b) mast cells. c) regulatory T cells. d) cytotoxic T cells. e) cytotoxic B cells. d What does it mean when we say a vaccine is based on an "attenuated" virus? a) The vaccine is a live virus that has been heat-killed. b) The vaccine is a live virus that has been chemically damaged. c) The vaccine isn't the virus at all, just similar-shaped chemicals. d) The vaccine is based on a virus that has been rendered harmless by lab-induced mutation. e) The vaccine is a similar species to the virus that isn't harmful (e.g., cowpox for smallpox). d Cytokines are molecules that cut holes in bacterial membranes. True False false Clumping of antibodies and antigens is referred to as: a) neutralization. b) agglutination. c) antigen presentation. d) coagulation. b Lymphocytes that become part of antibody-mediated immunity arm of the adaptive immune response develop in the: a) spleen. b) intestine. c) thymus. d) bone marrow. e) lymph nodes. d Which part of the innate response cuts holes in the cell membranes of pathogens? a) histamines b) complement proteins c) fibrin d) antibodies e) cytokines b Place the following in proper sequence regarding activation of the cell-mediated response: (1) dendritic cell migrates to lymph node, (2) T cells divide rapidly, (3) dendritic cell ingests pathogen, (4) CD4 and CD8 cells dock with dendritic cell, (5) dendritic cell presents antigen on its surface. a) 5, 3, 1, 2, 4 b) 3, 5, 1, 4, 2 c) 4, 3, 1, 5, 2 d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 e) 3, 1, 5, 2, 4 b The lymphocyte group that includes antibody-producing cells would be the: a) T-cells. b) mast cells. c) B-cells. d) dendritic cells. e) macrophages. c T cells develop in the thalamus. True False false AIDS has become a more manageable illness in developed countries in recent years due to: a) general resistance in the human population. b) declining disease rates in most areas of the world. c) vaccines. d) medications that keep HIV from copying itself. e) changes in the viral genome. d T cells are a type of lymphocyte. True False true In which type of response are Toll-Like Receptors (TLR's) important to pathogens? a) complement response b) barrier to infection c) adaptive immunity d) innate response e) protective immunity d We use the scientific method every day. Imagine your car doesn't start one morning before school. Which of these is a reasonable hypothesis regarding the problem? a) Add a quart of oil. b) I'm going to be late. c) I'm out of gas. d) Check to see whether your lights were left on all night. c The questions that can be answered by science are: a) without limit. b) limited by what is found in the living world. c) limited by religious doctrine. d) limited only be imagination. e) limited by what can be investigated using the scientific method. e Tissues are grouped together in functional units called: a) organelles. b) organs. c) cells. d) organisms. b It doesn't matter whether a hypothesis is correct or not when it is first stated. True False true A good hypothesis must: a) lead to a question. b) be falsifiable. c) be false. d) be theoretical. e) be true. b The physicist Freeman Dyson made which of the following predictions? a) Within 50 years, the human species would become extinct. b) Within 50 years, the energy crisis would be solved. c) Within 50 years, global warming would make the Earth unlivable. d) Within 50 years, gardeners would be able to design their own roses and orchids. d Which of the following is the most complex level of organization? a) a water molecule b) a rainforest c) the circulatory system d) a heart b The difference between a theory and a hypothesis is that: a) a theory must be proven beyond a shadow of a doubt. b) a hypothesis must be supported by evidence. c) a hypothesis must be proven beyond a shadow of a doubt. d) a theory must be supported by evidence. d Which of the following could be considered a scientific principle? a) The height of Americans has been steadily increasing over the past 30 years. b) Leaves bend toward the light because they sense light is needed to grow. c) Radioactive isotopes can be used as tracers in medicine because radioactive isotopes behave the same as other isotopes. d) Biology is a more exact science than chemistry. c Which scientist proved that the theory of spontaneous generation is untrue? a) Watson b) Einstein c) Pasteur d) Crick e) Pauling c The study of the physical functioning of plants and animals is called . physiology A unifying principle of biology states that there is a gradual modification of populations of living things over time that sometimes results in new species. This principle is called . evolution Observation of a natural event by more than one human or scientific instrument is the basis of the scientific method. True False true Choose the answer that best describes the sequence of the scientific method. a) guess, hypothesis, experiment, conclusion b) hypothesis, experiment, observation, conclusion c) observation, hypothesis, experiment, absolute fact d) experiment, observation, hypothesis, conclusion e) observation, hypothesis, experiment, conclusion e How living organisms relate to each other and to their physical environment 1. the functioning of plants and animals 2. molecular biology 3. ecology 3 Physiology 1. the functioning of plants and animals 2. molecular biology 3. ecology 1 Studying how molecules affect living beings 1. the functioning of plants and animals 2. molecular biology 3. ecology 2 Which of the following is true? a) A scientific fact and a scientific theory carry the same weight in the scientific community. b) A scientific theory is a hunch about a natural event. c) A scientific theory is the final answer to a question about a natural event. d) A scientific theory explains what we know to this date about a natural event. d Organelles are: a) compartments within cells. b) cells. c) organisms. d) a group of cells that serve a common function. e) proteins. a The development of the physical sciences differed from development of biological sciences in that: a) physical sciences offer the potential to find underlying principles, but such a goal is virtually impossible in biological sciences. b) physical sciences aimed to find underlying principles after this approach was taken in biological sciences. c) physical sciences aimed to find underlying principles before this approach was taken in biological sciences. d) physical sciences developed much more slowly than biological sciences. e) physical sciences developed more slowly than biological sciences because physical sciences are more difficult than biological science. c Which one of the following is true about scientific knowledge? a) Scientific knowledge is acquired though teachings passed on by great scientists. b) Scientific knowledge is derived from careful thinking about the way things must work based on application of a few fundamental principles. c) When based on many experiments, scientific knowledge is absolutely true. d) Scientific knowledge is derived from the strongest arguments made by the brightest scientists. e) Scientific knowledge is not absolute, because the possibility is always held open that new experiments may one day prove it wrong. e Which of the following is evidence that global warming is occurring? a) The intensity of hurricanes has been decreasing in recent years. b) The intensity of hurricanes has been increasing in recent years. c) The number of hurricanes has been increasing in recent years. d) The number of hurricanes has been decreasing in recent years. b The scientist who demonstrated that the Earth moves around the sun was . Copernicus The students in a classroom could be considered which of the following? a) a population b) an organism c) a niche d) a community e) a biosphere a When Pasteur tested the hypothesis of spontaneous generation, he compared the ability of a sterilized growth medium (meat broth) to produce a population of bacteria in two different types of flasks. One had a simple neck open to the outside, and the other had a "goose neck" bend that also was open to the environment. Pasteur expected that bacteria would appear in the flask with the standard neck. In this experiment, the standard neck flask served as: a) a variable. b) an observation. c) a statistic. d) a control. e) a hypothesis. d Living things inherit information from their parents encoded in: a) DNA. b) proteins. c) molecules. d) atoms. a Scientific observations: a) are limited to available equipment used to record a natural phenomenon. b) can be made directly by humans. c) can be made by instrumentation. d) all of the above d Which of the following is an example of statistics that were used to demonstrate that smoking causes lung cancer? a) A mathematical analysis of a large number of people with lung cancer demonstrated that far more people who smoked developed lung cancer. b) A woman who smoked developed lung cancer. c) A doctor notices that most of her lung cancer patients smoked. a Which of the following is an example of homeostasis? An organism that can: a) evolve from other living things. b) reproduce. c) respond to the environment. d) maintain a relatively constant internal environment. e) assimilate and use energy. d Which of the following is an example of how living things assimilate energy? a) solving a mathematics problem b) producing a new generation of children c) eating a meal d) blinking at a bright light c Which animals have had human genes inserted into their makeup to produce milk with human proteins? a) camels b) cattle c) goats d) horses c Which of the following is true of smoking? a) Lung cancer rates have been shown to rise and fall with smoking rates. b) Scientists knew in 1940 that smoking causes lung cancer. c) Before smoking became popular in the 1920s, lung cancer was common. a A theory must be supported by evidence. True False true If a sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilizes a mother's egg, which of the following will be true? a) A sperm can't carry a Y chromosome; only the egg can. b) A baby boy will develop. c) A baby girl will develop. d) Nothing will happen. b A scientific explanation that is tentative and that requires more investigation is termed a/an: a) theory. b) fact. c) control. d) observation. e) hypothesis. e All of the kinds of living things in a given area are called a . community The experiments of Louis Pasteur to disprove spontaneous generation illustrate the process of the scientific method. True False true If a sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilizes a mother's egg, which of the following will be true? a) A sperm can't carry an X chromosome; only the egg can. b) Nothing will happen. c) A baby boy will develop. d) A baby girl will develop. d Currently there is a controversy over whether which of the following organisms is a direct descendant of the dinosaurs? a) frogs b) birds c) lizards d) snakes e) crocodiles b Imagine you're a biology instructor lecturing to a group of students interested in ecology, the branch of biology that studies interactions between organisms and their environments. They complain bitterly that they're not interested in atoms and molecules because these are irrelevant to their interests. As a responsible instructor aiming to provide a complete and meaningful education, you would state: a) "You need to study atoms and molecules because all biologists, regardless of their specific interests, should know about them." b) "You need to study atoms and molecules because it's in the book." c) "You need to study atoms and molecules because the organization of life is hierarchical; this implies that to understand the complex (ecology), you first need to understand the simpler underlying levels." d) "Ok, have it your way." e) "You to need to study atoms and molecules because they're important for many things." c Genetically altered salmon are grown to eating weight in half the normal time. True False true If you flip the light switch in your living room and nothing happens, what might be a good hypothesis to explain the absence of light? a) You might have made too many telephone calls this month, thereby reducing the amount of electricity in your lines. b) The air conditioner is also running upstairs, and it might be using all of the electricity available in your house at the moment. c) The circuit breaker for the living room might be the "off" position. d) Electricity sometimes flows backward in a wire, preventing the light from shining. c A hypothesis must be supported by evidence. True False false Tissues are: a) cells. b) compartments within cells. c) organisms. d) proteins e) a group of cells that serve a common function. e Which of the following is the correct order of complexity, going from least to most complex? a) organ, tissue, cell, organelle, atom, molecule b) molecule, atom, organ, tissue, cell, organelle c) organ, tissue, cell, organelle, molecule atom d) atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ e) atom, molecule, organelle, cell, organ, tissue d Which of the following is a theory? a) There is molecular and biochemical evidence that all organisms are related. b) Many people claim that the Earth is only 6,000 years old. c) Many people believe echinacea cures their colds. d) A boy finds a chipped rock he believes is an arrowhead. a Isotopes have been used to: a) determine the age of fossils. b) detect bone cancer. c) create new elements. d) A and B e) A, B, and C d The mass of matter is proportional to the: a) density of matter. b) weight of matter. c) volume of matter. d) number of electrons. e) number of protons. b If an atom has an atomic number of 11, which of the electron shells are filled? a) the first shell b) the first, second, third, and fourth shell c) the first, second, and third shell d) the first and second shell d When you put sugar into your morning coffee or tea, the sugar is the , and the tea or coffee is the . a) solution, solute b) solute, solvent c) solvent, solution d) solute, solution e) solvent, solute b Cigarette smoking and exposure to sunlight the production of free radicals by our bodies. increase You have a substance and begin a set of experiments in which you break it down into other substances through chemical reactions. After a few successive reactions, you discover a set of products that can't be broken down further, no matter what type of chemical reaction you attempt. These substances are: a) electrons. b) elements. c) protons. d) isotopes. e) neutrons. b Acids release hydrogen ions into aqueous solutions. True False true If the atomic number is 18, then: a) the outermost energy level is full. b) this atom would be considered reactive. c) there are seven electrons in the outermost shell. d) the atom has 18 electrons in the nucleus. a An atom whose atomic number is 10 has how many electrons in its outermost energy level? a) two b) five c) ten d) three e) eight e Hydrogen bonds may form between oxygen of one water molecule and of another water molecule. hydrogen Which of the following is not a compound? a) methane b) a protein c) nitrogen d) glucose e) table salt c Nonpolar molecules develop when: a) one atom is much more electronegative than the other. b) electrons transfer from one atom to another. c) both atoms have similar electronegativity. d) shared electrons are not shared equally. b Potassium has one electron in its fourth shell, and chloride has seven electrons in its third shell. Which of the following is most likely to be true? a) The two atoms will share the electron unequally in a polar bond. b) The two atoms will share an electron equally in a covalent nonpolar bond. c) Potassium will give an electron to chloride to form an ionic bond. d) Chloride will give an electron to potassium to form an ionic bond. c Anything that occupies space is energy. True False false Atoms are electrically neutral. True False true proton: 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 1 Keeps most electrons from escaping the nucleus of an atom 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 8 Explains the attraction of water molecules for each other 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 6 Would be the least affected by the presence of water 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 7 neutrons 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 2 electrons 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 3 Results from an unequal sharing of shared electrons 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 5 Results from electrons being transferred between atoms 1. positive charge 2. no charge 3. negative charge 4. ionic bond 5. polar covalent bond 6. hydrogen bond 7. nonpolar covalent bond 8. electron-proton interaction 4 Sodium chloride (NaCl) crystals (table salt) form as a result of: a) chemical unreactivity. b) the attraction of oppositely charged particles for each other. c) covalent bonding. d) the lack of chemical attraction. b Nitrogen has seven protons, and hydrogen has one proton. Based on your knowledge of the rules of covalent bonding, which of the following molecules will form from the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen? a) NH3 b) NH c) NH4 d) NH2 e) NH5a Two hydrogen atoms (atomic number 1) form a covalent bond. Which of the following is true? a) Both hydrogen atoms now have two protons in their outer shell. b) Both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their outer shell. c) One hydrogen atom now has zero protons in its outer shell, and the other has two. d) Each hydrogen atom still has one electron in its outer shell. e) One hydrogen atom now has zero electrons in its outer shell, and the other has two. b The component of an atom or molecule that is most important in determining its chemical bonding properties is the: a) nucleus. b) electron. c) proton. d) neutron. e) isotope. b Atoms form bonds to: a) fill their outer shells with electrons. b) obtain an equal number or protons and electrons. c) fill their outer shells with neutrons. d) obtain an equal number of protons and neutrons. e) fill their outer shells with protons. a Which type of bonding occurs between molecules and not within molecules? a) hydrogen b) polar covalent c) covalent d) ionic d Which of the following are found in the nucleus of an atom? a) neutrons b) protons c) electrons d) A and B e) A, B, and C d Hydrophobic molecules tend to be by water. a) repelled b) absorbed c) attracted d) mixed a Which of the following results from the making of a bond? a) Electrons are destroyed. b) Molecules are broken down. c) Atoms become more stable. d) Atoms become more reactive. c The electrons of an atom contribute significantly to the mass of an atom. True False false Covalent bonds form when one atom its with another atom. a) gives up; electrons b) gives up; protons c) gives up; neutrons d) shares; electrons e) shares; protons d An atom always contains the same number of protons as neutrons. True False false Water molecules are uncharged and . polar A single covalent chemical bond represents a sharing of electrons between two atoms. two The subatomic particles with the most mass are: a) protons. b) electrons. c) neutrons. d) both A and C d Chemical reactions that occur within living things change the nucleus of atoms. True False false Which of the following is true of chemical bonds? a) They cannot occur between two identical atoms. b) One atom can give up a proton to another to form bonds. c) Atoms can achieve a higher energy state and less stability by forming bonds. d) Two atoms can share an electron unequally, with one drawing it more toward itself. d When an electron passes from one atom to another: a) attraction occurs between two atoms based on opposite charges. b) the identity of the atom changes. c) a proton is also lost from the nucleus. d) the electron travels in orbitals around both the donor and recipient atom. b As an acid mixes in water: a) The solution will cool down. b) the number of hydrogen ions will increase. c) The pH remains at 7. d) the number of hydroxide ions will increase. b In what ways are hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds similar? a) Both are based on attraction between two atoms that each carry a negative charge. b) Both are based on attraction between two atoms that each carry a positive charge. c) Both are based on repulsion between atoms that carry differences in electrical charge. d) Both involve an even sharing of electrons between atoms. e) Both are based on attraction between atoms that carry differences in electrical charge. e What is it about carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14 that makes them all carbon? a) They all have the number of neutrons that is characteristic of carbon. b) They all have the number of protons that is characteristic of carbon. c) They all have the number of protons plus neutrons that is characteristic of carbon. d) All are radioactive. e) All are elements. b Enzymes are proteins that catalyze specific reactions within a cell. For catalysis to occur, they require a starting substance to bind directly to the enzyme. What must be true for this binding to happen correctly? a) Both the enzyme and the starting substance must be hydrophilic. b) The starting substance must be larger than the enzyme. c) Both the enzyme and the starting substance need to have matching shapes. d) The enzyme must be acidic, and the starting substance must be basic. c You mix sugar in water and stir until it's completely dissolved. In this system, the water is the , the sugar is the , and the end result is a . a) solution; solvent; solute b) solvent; solution; solute c) solute; solvent; solution d) solvent; solute; solution e) solute; solution; solvent d Protons move at very fast speeds around the outside of the nucleus of an atom. True False false Hydrogen bonds are very important in the functional shape of: a) proteins. b) sugars. c) fats. d) nucleic aids. e) Both A and D are true e An element can't be broken down into another form of pure matter. True False true Oxygen has six electrons in its second outer shell. How many covalent bonds is oxygen likely to make with hydrogen, which has one electron in its first outer shell? a) one b) eight c) two d) three e) six c An element with 22 protons, 22 neutrons, and 22 electrons would have an atomic number of: a) 44. b) 22. c) 11. d) 66. b Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in their: a) ionic charge. b) number of protons. c) number of electrons. d) number of neutrons. d A(n) has a higher pH than a(n) . base; acid The subatomic particles that play the greatest role in cellular chemical reactions are: a) neutrons. b) protons. c) isotopes. d) electrons. d Which of the following is not a component of atoms? a) neutrons b) molecules c) protons d) electrons b A signal will to a receptor if the molecules shape match, similar to a key in a lock. bind An atom will react with other atoms only until: a) all of its outermost orbitals have been filled. b) it has achieved maximum stability. c) it has completely filled its outmost energy level. d) All of the above are true. d Ionic bonds occur through a sharing of electrons. True False false Neutrons are negatively charged. True False false The symbol 3CO2 represents: a) three carbon atoms and one molecule of oxygen. b) one atom of carbon and three atoms of oxygen. c) three molecules of carbon dioxide. d) one atom of oxygen and three of carbon. c The naturally occurring helium atom is chemically inert because: a) it has all of the shared electrons it could ever have. b) its outermost shell is filled with electrons. c) it has the most protons that it could ever carry. d) its nucleus is filled with two neutrons. b orbit around the nucleus of an atom. Electrons H2S is an example of a: a) structural formula. b) space-filling model. c) ball-and-stick formula. d) molecular formula. e) none of the above d The mass within an atom comes from: a) protons and neutrons. b) protons only. c) electrons only. d) protons, neutrons, and electrons. a Chlorine has an atomic number of 17, and argon has an atomic number of 18. From this information alone, you can predict that: a) chlorine is more chemically reactive than argon. b) argon will more readily ionize than chlorine. c) argon has more neutrons than chlorine. d) chlorine has more neutrons than argon. e) argon is more chemically reactive than chlorine. a The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom gives it a unique chemical nature. True False false For an atom to be considered an ion: a) neutrons can outnumber protons. b) protons can outnumber neutrons. c) protons can outnumber electrons. d) protons equal electrons. c In a bottle of water, hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen of one atom and: a) an oxygen atom in a different molecule. b) a hydrogen atom in a different molecule. c) an oxygen atom in the same water molecule. d) a hydrogen atom in the same molecule. a Isotopes differ from each other in the number of protons that they possess. True False false When atoms form bonds, they share or exchange: a) electrons. b) neutrons. c) protons. d) A and B e) A, B, and C a Water is a polar molecule because: a) oxygen has more electrons than hydrogen. b) oxygen has more neutrons than hydrogen. c) hydrogen has more neutrons than oxygen. d) hydrogen is more electronegative than oxygen. e) oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. e Which of the following would form the fewest covalent bonds? a) hydrogen (one electron it the first shell) b) neon (eight electrons in the second shell) c) oxygen (six electrons in the second shell) d) carbon (four electrons in the second shell) b An atom becomes an ion when: a) hydrogen ions are shared. b) it gains or loses neutrons. c) it gains or loses electrons. d) it forms a covalent bond. e) it gains or loses protons. c The skeleton from which steroids hormones are made is . cholesterol May serve as either enzymes or antibodies 1. DNA 2. polysaccharide 3. glycoproteins 4. globular proteins 4 Is composed of functional units call genes 1. DNA 2. polysaccharide 3. glycoproteins 4. globular proteins 1 Serve as cell surface receptors 1. DNA 2. polysaccharide 3. glycoproteins 4. globular proteins 3 A carbohydrate polymer 1. DNA 2. polysaccharide 3. glycoproteins 4. globular proteins 2 Wax is a lipid. True False true Keratin is an example of a protein. structural Ribosomes are made up of . RNA Which of the following is an organic molecule? a) H2O b) C4H10 c) O2 d) NH3 b An example of an important organic molecule that may contain the —NH2 group is: a) an enzymes. b) steroids. c) a starch. d) a glucose molecule. e) a triglyceride. a What do polysaccharides, such as cellulose; nucleic acids, such as DNA; and proteins, such as keratin, have in common? a) They are all amino acids. b) They are all lipids. c) They are all built of chemically linked monomers. d) They are all carbohydrates. e) They are all nonpolar. c Which of the following is the indigestible (at least for humans) glucose polysaccharide that is found in plants? a) glycogen b) starch c) chitin d) cellulose d Which of the following are composed of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen? a) phospholipids b) amino acids c) DNA d) glucose d Before DNA was established as the genetic material, proteins were considered the most likely molecules to serve this role. In part this belief was based on the fact that there are 20 building blocks (20 different kinds of amino acids) for proteins versus four building blocks (four different nucleotides) for DNA. If proteins stored a code, there would be a far greater number of code words possible for a protein of a given number of amino acids than for a DNA molecule of the same number of nucleotides. For example, there are 16 different sequences (4 4) possible for a DNA two nucleotides, long and 400 (20 20) different sequences possible for a protein two amino acids long. For a sequence three nucleotides or three amino acids in length, the number of distinct DNA sequences is , and the number of distinct protein sequences is . a) 800; 8,000 b) 64; 8,000 c) 20; 240 d) 64; 800 e) 30; 800 b Monosaccharides are determined by which of the following groups? a) a molecule of three to six carbon atoms b) a carboxyl group c) the presence of glycerol and fatty acids d) carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of 1:2:1 e) the presence of carbon and hydrogen in a ratio of 1:2 d Proteins may function as: a) structural building materials. b) transport molecules. c) hormones. d) enzymes. e) all of the above e Refer to the chemical reaction below then answer the question that follows. Glucose + fructose 1 → sucrose + water ← 2 Which molecule is the disaccharide? a) glucose b) sucrose c) fatty acids d) water b Sugar is an organic molecule because it contains: a) water. b) carbon and hydrogen. c) carbon and oxygen. d) carbon dioxide. e) carbon and nitrogen. b Lipids: a) are a component of proteins. b) include cartilage and chitin. c) include fats that are broken down into one fatty acid molecule and three glycerol molecules. d) serve as long-term energy reserves in many organisms. d Polypeptides differ in their and of amino acids. number; kinds Your muscles contract using contractile proteins to produce movement. True False true You eat a steak. This meal contains mostly of: a) protein. b) nucleic acids. c) starch. d) glucose. a Glycogen is used to store in the . a) glucose, spleen b) glucose, liver c) protein, muscle d) protein, liver e) nucleic acids, liver b What do wax and testosterone have in common? a) They are both hormones. b) They are both steroids. c) They are both lipids. d) They are both proteins. c All hormones are steroids. True False false Oil doesn't dissolve in water because it isn't a molecule. polar Butter, which is made from milk fat, tends to be harder at room temperature than most margarines. If you wanted to make a "softer" butter at cool room temperature, you should consider: a) creating more double bonds in the fatty acid chains. b) adding more than three fatty acid chains to the triglycerides. c) making the fatty acid chains longer. d) making fatty acid chains with fewer kinks. e) saturating the fatty acid chains. a Which of the following lipids is the primary component in cell membranes? a) glycerol b) phospholipids c) triglycerides d) steroids b The structural backbone of any membranous structure in a cell is the: a) membrane-bound proteins. b) glycoproteins. c) the phospholipid bilayer. d) glycolipids. e) steroids. c Carbon is such an important molecule for life because: a) it can form chemical bonds with a maximum of four other atoms. b) it can hydrogen bond to so many molecules. c) it is part of the water molecule. d) it can be bonded ionically. e) it can form isomers. a Glycogen is the carbohydrate found in plant cell walls. True False false It is recommended to include fish as part of a healthy diet because it contains , which lead to a reduction in LDL. a) monounsaturated fats b) trans fats c) polyunsaturated fats d) omega-3 fatty acidsd Both men and women make testosterone. True False true You love to eat potato chips, but you realize they contain many trans fats. Eating too many potato chips will negatively effect your health because it can: a) cause you to have more HDL than LDL. b) cause you to have more LDL than HDL. c) cause you to have no LDL. d) cause you to have no HDL. b A triglyceride contains fatty acid chains, whereas a phospholipid contains fatty acid chains. a) four; two b) two; three c) two; four d) three;two d Only those proteins that are composed of more than one polypeptide when they are functional are said to have structure. Refer to the figure above for help. a) tertiary b) secondary c) quaternary d) primary c Hydroxyl groups are found on all amino acids. True False false The monomers of a neutral fat (triglyceride) are: a) amino acids. b) sugars. c) glycerol and fatty acids. d) carboxyl acids. e) nucleotides. c Lipids with double bonds become solids at lower temperatures than do saturated fats. True False false Oxygen is an organic molecule. True False false It is better to have HDLs than LDLs in your blood. more The difference between one amino acid and another is: a) the type of peptide bond that each contains. b) the type of sugar that each contains. c) the type of base groups it contains. d) the type of R-group that it may contain. e) whether or not it is saturated. d In plants, glucose is stored primarily as: a) glycogen. b) chitin. c) cellulose. d) starch. d Which of the following is not a monosaccharide? a) fructose b) deoxyribose c) cellulose d) glucose c A nucleotide is a polymer of nucleic acids. True False false The active site of an enzyme is a product of its . three-dimensional shape (conformation) Some proteins can be toxic. True False true A kilocalorie is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1,000 grams of water 1 degree Celsius (the "calories" given for energy in foods are actually kilocalories). If you applied 1 kilocalorie of heat energy to 1,000 grams of vegetable oil, how much do you think its temperature would increase? a) to the boiling point b) more than one degree Celsius c) less than one degree Celsius d) one degree Celsius e) none at all b If you boil an egg for lunch, the egg white becomes hard, white, and opaque because the protein in it has been . denatured Some proteins function as enzymes, but others don't. True False true In some vintage science fiction movies, space travelers find themselves on a planet orbiting a distant star in which there are curious forms of life based on silicon instead of carbon. Although the story clearly is sci-fi, there is an aura of plausibility in the choice of silicon, an atom with 14 protons, in place of carbon as this alien life-form's central atom. The reason is that silicon: a) is heavier than carbon. b) has one more proton than carbon so is very similar to it. c) is lighter than carbon. d) has four electrons in its outermost shell. e) is an isotope of carbon. d The polymer of amino acids that makes up a protein is called a . polypeptide You notice that water is running off the feathers of a bird in the rain. The reason is probably that the bird has coated the feathers with , which keeps the water out of them. a) proteins b) nucleic acids c) polysaccarides d) lipids d Saturated fats are usually found in: a) a beef steak. b) canola oil. c) safflower oil. d) cocounut oil. e) both A and D e Your cousin eats only rice. Her diet will be very high in which of the following types of biological molecules? a) fat b) cholesterol c) glucose d) protein c You isolate a protein that is actually made up of three separate polypeptides. This is an example of: a) quaternary structure. b) primary structure. c) secondary structure. d) tertiary structure. a The chitin that makes up the exoskeleton of insects is made of a polymer of amino acids. True False false Which of the following is true of cellulose? a) Plants store amino acids as cellulose. b) Animals store glucose as cellulose. c) Plants' cell walls are made up of cellulose. d) Plants store glucose as cellulose. c Which of the following is a type of lipid? a) steroids b) triglycerides c) oils d) all of the above d DNA is made up of: a) nucleotides. b) proteins. c) sugars. d) amino acids. e) steroids. a Water is an organic molecule. True False false Amino acids contain both amine and carboxyl functional groups. True False true Which of the following is/are true of steroids? a) If people inject male steroid hormones, they can build muscle mass, but they can have side effects. b) Cholesterol is a steroid. c) They exist naturally in humans as hormones. d) A and B are true. e) A, B, and C are true. e Proteins are made up of: a) sugars. b) nucleotides. c) amino acids. d) steroids. e) lipids. c Glycogen is a polysaccharide used for energy storage by: a) animals. b) plants. c) fungi. d) monera. a ATP is an energy-carrying modified . nucleotide Chitin and cellulose are polymers of: a) fats. b) nucleic acids. c) amino acids. d) glucose. d Polysaccharides are made up of: a) lipids. b) amino acids. c) sugars. d) nucleotides. e) steroids. c Unique chemical groups that are added to carbon compounds are called: a) functional groups. b) lipids. c) amino acids. d) monomers. a Which of the following is the correct order for the flow of information in the cell? a) RNA codes for DNA, which codes for protein. b) DNA codes for protein, which codes for RNA. c) DNA codes for RNA, which codes for protein. d) Proteins code for DNA, which codes for RNA. c Nucleotides are the building blocks for: a) disaccharides. b) proteins. c) lipids. d) ATP and RNA. e) steroids. d are the very heart of life, allowing cells to do such things as build structures, speed chemical reactions, and move. a) Carbohydrates b) Lipids c) Sterols d) Nucleic acids e) Proteins e Which of the following is an organic molecule? a) lipid b) protein c) monosaccharide d) nucleic e) all of above e You have a defect in catalyzing the reaction to make the amino acid tryptophan. The reason is that you lack the gene in your , which causes you to lack the that allows you to catalyze this reaction. DNA; enzyme What determines whether a protein will be produced on a "free ribosome" or on one attached to the endoplasmic reticulum? a) The mRNA of certain proteins moves directly to ribosomes already attached to the ER. b) Every ribosome will migrate to the ER. c) a chemical signal on the protein being produced d) Microtubules attach randomly to ribosomes and move a fraction of them to the ER. c Cells can increase the number or size of some organelles in response to new demands. The amount of one organelle often is increased dramatically in the livers of alcoholics. Based on what you know of organelle function, this organelle is the: a) nucleus. b) ribosome. c) Glogi apparatus. d) mitochondrion. e) smooth endoplasmic reticulum e The nucleolus protects the DNA inside the nucleus while it is being copied into RNA. True False false You isolate a cell with the following characteristics: (1) no nucleus, (2) no requirement for oxygen, and (3) 2 μm in size. This cell could be: a) an animal cell. b) a bacterium. c) a plant cell. d) A or B e) A, B, or C b A secretory protein that exits from the ER within a vesicle will head directly to: a) the plasma membrane. b) the nucleus. c) the mitochondria. d) the cytosol. e) the Glogi complex. e The cytoskeleton is composed of: a) microfilaments, mitochondria, and intermediate filaments. b) microfilaments, cilia, and intermediate filaments. c) microtubules, intermediate filaments, and cilia. d) microfilaments, microtubules, and lysosomes. e) microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. e One of the main structural ingredients of the eukaryotic plant cell wall is: a) cellulose. b) granola. c) mitochondria. d) glucose. e) protein. a The cytoskeleton of animal cells really is a bit like the skeleton of the whole animal in the way it provides structure to cells. But the cytoskeleton is also like another important part of animals. This is the: a) muscular system. b) immune system. c) nervous system. d) digestive system. a Which of the following describes a prokaryotic cell? a) It would not have a nucleus. b) A plant cells is an example. c) It would have mitochondria. d) A human cells are an example. e) It would contain endoplasmic reticulum. a Gap junctions are found in plant cells. True False false Mitochondria and chloroplasts are similar to one another in that: a) both capture the energy of the sun during photosynthesis and store it as sugar. b) both convert the energy of the sugar into ATP for use by the cell. c) both have their own DNA and are surrounded by a double membrane. d) both are present in all eukaryotic cells. c The central vacuole is used for nutrient storage and photosynthesis in plant cells. True False false The function of ribosomes is to synthesize: a) RNA. b) proteins. c) lipids. d) DNA. e) polysaccharides. b Which of the following is an example of a eukaryotic cell? a) a bacterium b) a plant cell c) an archaea d) a virus b Two organelles that are believed to be remnants of unicellular bacteria are: a) mitochondria and chloroplasts. b) mitochondria and ER. c) ribosomes and chloroplasts. d) flagella and ribosomes. e) ER and flagella. a You are a physician treating a child with a genetic disorder in which the child does not secrete an enzyme for lipid metabolism. What organelle would be dysfunctional and prohibit this enzyme's secretion? the Golgi complex Lysosomes produce within a cell. True False false The large central vacuole of plants: a) allows the plant to produce its own food. b) may make up as much as 90 percent of the internal volume of the cell. c) produces proteins. d) replaces the nucleus. b Animal cells need oxygen most directly to: a) producte protein. b) secrete enzymes. c) produce ATP. d) produce DNA. c The most common form of cystic fibrosis, a fatal genetic disease, occurs when a protein destined for the plasma membrane of the cell is destroyed. The protein is destroyed by one of the cell's organelles because the protein is not shaped correctly. Which organelle recognizes the misshaped protein? a) Golgi apparatus b) lysosome c) ribosome d) nucleus e) endoplasmic reticulum e Who was the first person to refer to a single unit within a living organism as a "cell"? a) Robert Downy b) Anton van Leeunwenhoek c) James Watson d) Robert Hooke d A nanometer is larger than a micrometer. True False false The relationship between surface and volume (the surface-to-volume ratio) of cubes of two different sizes has a lot to do with explaining why cells are small. Cells are small so that they maintain a: a) low surface-to-volume ratio. b) high surface-to-volume ratio. c) constant volume. d) nucleus and cytomembrane system. e) constant surface area. a You isolate a cell with a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole. This cell is most likely a cell.plant mRNA carries a code from the to make a particular polypeptide.DNA The rough endoplasmic reticulum is the site where lipid synthesis occurs in an animal cell. True False false The cytoskeleton is an internal scaffolding used for cellular movement. True False true Indicate which of the following choices correctly ranks the given objects in size, from smallest to largest. a) protein, virus, bacterium, frog egg, animal cell b) protein, virus, bacterium, animal cell, frog egg c) protein, bacterium, virus, animal cell, frog egg d) virus, protein, bacterium, animal cell, frog egg e) bacterium, virus, protein, animal cell, frog egg b Vesicles that contain digestive enzymes are called lysosomes. True False true Prokaryotic cells lack: a) DNA. b) ribosomes. c) proteins. d) internal compartmentalization. d Which of the following is found in plant cells but not in animal cells? a) chloroplast b) mitochondria c) nucleus d) lysosomes e) ribosomes a Smoker's cough results from damage to the external structure of lung cells by tobacco smoke. What part of the cell would you predict is damaged? a) plasmodesmata b) cilia c) the mitochondria d) the Golgi appartatus e) the lysosome b People with oxidative phosphorylation disorders suffer a lack of energy due to diminished function of nerve and muscle cells. The organelle most likely to be altered in oxidative phosphorylation disorders is the: a) rough endoplasmic reticulum. b) cytoskeleton. c) cell wall. d) chloroplast. e) mitochondrion. e Ribosomes are found only with eukaryotic cells. True False false Plant cells often contain large central vacuoles and chloroplasts. True False true Without photosynthesis, humans could not survive. True False true You have isolated a new organism that is 0.5 micrometers in size. This organism is most likely: a) a virus. b) a plant cell. c) a bacterium. d) This organism could be any of the above. e) an animal cell. c Which of the following is a characteristic of plant cells and not animal cells? a) lysosome b) microtubule c) mitochondrion d) a central vacuole d Plasmodesmata allow plant cells to actually be connected to each other. True False true Eukaryotic animal cells contain centrioles and chloroplasts. True False false Within the cisternae of the RER: a) proteins get fatty acids added to them. b) proteins get phospholipids added to them. c) proteins get a side-chain of carbohydrate added to them. d) proteins assume their tertiary structure. e) proteins are synthesized from nucleotides. c Which of the following explains why cells are so small? a) They can only produce a limited amount of cell membrane components. b) As cell surface area increases, cell volume increases faster. c) As cell surface area increases, cell volume decreases. d) As cell volume increases, surface area decreases. e) As cell volume increases, surface area increases faster. b Mitochondria require which of the following in order to function? a) ATP b) oxygen c) carbon dioxide d) Water b Insulin is a protein made in large amounts in cells of the pancreas. These cells secrete insulin into the blood, where it controls the uptake of sugar by body cells. How is insulin transported from the ER to the surface of the cell? a) It moves along tracks of cytoskeleton proteins. b) It is sent through the cavities (lumen) of the endoplasmic reticulum that attach directly to the plasma membrane. c) It is carried by lysosomes that empty their contents outside the cell. d) It is carried in small sacs of membrane (vesicles) that move from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus and then to the plasma membrane. e) It moves through plasmodesmata to the surface of the cell. d You owe your very life to chloroplasts. The reason is that: a) chloroplasts produce all the water and carbon dioxide essential for life. b) when we eat plants, it is the chloroplasts that are the nutritious part of plant cells. c) chloroplasts supply all the ATP needed by living organisms. d) like the ancestors of mitochondria, the ancestors of chloroplasts were once bacteria taken up by a eukaryotic cell. e) chloroplasts produce the oxygen we breathe and ultimately are the source of most nutrients we consume. e Which of the following is not involved in transport of materials within a eukaryotic cell? a) the rought endoplasmic reticulum b) lysosome c) mitochondrion d) the Golgi complex c Both cilia and flagella are involved in which of the following functions? a) production of proteins b) expelling waste c) movement of materials d) energy production e) division of the cell c Which of the following are associated with matter and energy transfers in eukaryotic cells? a) mitochondria and smooth ER b) lysosomes and Golgi complex c) chloroplasts and mitochondria d) mitochondria and rough ER e) chloroplasts and the cell wall c The part of a prokaryotic cell that contains the cellular DNA is called the . nucleoid Which of the following pairs is correctly matched? a) endomembrane system - cilia b) microfilaments - permanent c) microtubules - tubulin d) intermediate filaments - actin c The function of the nucleus is to: a) contain and replicate the DNA. b) add sugars to proteins. c) produce proteins. d) organize the cytoskeleton. e) contain the cytoplasm. a The boundary of a cell is the: a) cell membrane. b) cytoskeleton. c) cytosol. d) nucleus. a Most animal cells are between 10 and 100 μm. True False true The basic building compartments of life on this planet are called: a) proteins. b) energy. c) phospholipids. d) cells. e) organelles. d Only eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles. True False true Which of the following expresses an accurate difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? a) Prokaryotes have organelles, but eukaryotes do not. b) Prokaryotic cells are larger than eukaryotes. c) Eukaryotes have a nucleus, but prokaryotes do not. d) Prokaryotes are can be multicellular, but eukaryotes cannot. c Eukaryotic animal cells are surrounded by a cell wall. True False false Which of the following is not considered an organelle? a) a lysosome b) a ribosome c) a mitochondrion d) DNA d The surface-to-volume ratio of a cube 1 centimeter on a side is 6 (the cube has a surface area of 6 square centimeters, a volume of 1 cubic centimeter). What would be the surface-to-volume ratio of a cube 2 centimeters on a side? a) 1 b) 1/2 c) 6 d) 3 e) 20 d Which cell type can produce proteins? a) both prokaryotes and eukaryotes b) neither prokaryotes nor eukaryotes c) eukaryotes only d) prokaryotes only b The compartment that holds most of a eukaryotic cell's DNA is the . nucleus Actin and myosin are called . microfilaments Tiny holes that are channels between animal cells are called gap junctions. True False true An important by-product of photosynthesis is: a) glucose. b) water. c) protein. d) starch. e) oxygen. e Which of the following is the correct order of events in a cell? a) RNA makes DNA; DNA makes protein. b) DNA makes RNA; RNA makes protein. c) RNA makes protein; protein makes DNA. d) Protein makes DNA; DNA makes RNA. e) DNA makes protein; protein makes RNA. b What maintains cell shape, anchors organelles in place, and moves materials within a cell? a) cytoskeleton b) Golgi complex c) cilia d) hydrogen bonds a Which of the following is evidence that mitochondria may have at one time been independently living bacteria? a) The sequence of mitochondrial DNA is very similar to that of bacterial DNA. b) Mitochondria can live and reproduce outside cells in the laboratory. c) Bacteria, like mitochondria, have internal membranes. d) Mitochondria can produce their own food. a The protein structures that support cilia and flagella of eukaryotic cells are called . microtubules Which of the following is a function of nuclear pores? a) to allow DNA to leave the nucleus to go to the cytoplasm b) to allow newly synthesized protein to leave the nucleus to go to the cytoplasm c) to allow RNA to enter the nucleus from the cytoplasm d) to allow DNA to enter the nucleus from the cytoplasm e) to allow RNA to leave the nucleus to go to the cytoplasm e Which choice below correctly matches organelle with function? a) smooth endoplasmic reticulum — lipid production b) lysosome — energy generation c) cytoskeleton — recycling of materials d) mitochondria — food generation a Many antibiotics work by blocking the function of ribosomes. Therefore, these antibiotics will: a) block DNA synthesis. b) block RNA synthesis. c) block protein synthesis. d) prevent the movement of proteins through nuclear pores. e) make the two nuclear membranes fuse into one. c The protein actin is found in the: a) nucleus. b) thin filaments. c) thick filaments. d) membrane. b May have "ground substance" 1. Connective tissue 2. Muscle tissue 3. Nervous tissue 4. Epithelial 1 "Smooth" is one type 1. Connective tissue 2. Muscle tissue 3. Nervous tissue 4. Epithelial 2 Inclueds glial cells 1. Connective tissue 2. Muscle tissue 3. Nervous tissue 4. Epithelial 3 Covers surfaces and forms linings 1. Connective tissue 2. Muscle tissue 3. Nervous tissue 4. Epithelial 4 A sweat gland is a type of exocrine gland. True False true The discipline dealing with the study of how parts of the body work is: a) endocrinology. b) anatomy. c) mechanics. d) physiology. b In the textbook, the stomach was given as an example of an organ. Which of the following is a valid description of the work of one of its tissues? a) Its nervous tissue communicates directly with the intestines to coordinate digestion. b) Its epithelial tissue secretes substances that help with digestion. c) Its muscle tissue forces secretions out of glands and into the stomach. d) Its connective tissue helps drain the stomach contents. b Groups of cells with a common function make up a/an: a) organ. b) gland. c) tissue. d) limb. e) organ system. c A prescription medication lists a rare side effect of impairing the movement of smooth muscle. This medication could potentially affect the: a) heart. b) walls of the small intestine. c) muscles that move the eyeballs. d) muscles that move your arms and legs. b Which of the following typically connects a bone to another bone? a) ligaments b) cartilage c) tendons d) marrow a A function of connective tissue is to: a) move the muscles of the body. b) protect and cover the body. c) form glands. d) stabilize and support the body. d Which part of the muscle cell actually does the work of contraction by attaching, pivoting, and pulling? a) calcium ions b) neurotransmitter molecules c) myosin heads d) actin filaments c Smooth muscle may be moved by either voluntary or involuntary control depending on location in the body. True False false The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are separated by the: a) lungs. b) rib cage. c) diaphragm. d) vertebral column. c Keratinized cells near the surface of the epidermis are: a) derived from nervous tissue. b) found in a single layer. c) about one month old. d) mostly dead and water resistant. d Blood vessels and nerves are found in which part of compact bone? a) in central canals b) only in the marrow cavity c) only on the outside surface d) in osteoblasts a In humans, the heart and lungs are found in the: a) cranial cavity. b) thoracic cavity. c) abdominopelvic cavity. d) spinal cavity. b Which of the following is characteristic of cardiac muscle? a) It is not striated. b) It is most similar in appearance to smooth muscle. c) It contracts under the control of its pacemaker cells. d) It is found only in the heart and blood vessels. c Subcutaneous fat tissue in humans is located mainly in the dermis. True False false Structures such as hair and nails are part of the: a) endocrine system. b) lymphatic system. c) muscular system. d) integumentary system. e) skeletal system. d Which human body system would be best described as playing roles in both waste disposal and conservation? a) nervous b) cardiovascular c) respiratory d) urinary e) lymphatic d Hair color (or lack of it) is mostly due to: a) a colored version of keratin. b) sweat gland pigments. c) activity of melanocytes. d) sebaceous gland pigments. c The function of epithelial tissue is to: a) form the immune system. b) protect and cover the body. c) support the body. d) allow for movement of the body. b Muscle tissue has a specialized ability to: a) protect the body. b) provide an internal framework for the body. c) shorten or contract. d) form the glands. e) support the body. c Structures of the skeletal system include all of the following except: a) nails. b) cartilage. c) bone. d) ligaments. a Acne is caused by problems with the: a) sweat glands. b) sebaceous glands. c) hair follicles. d) endocrine glands. b Homeostasis is maintained mostly by positive feedback. True False false Glial cells are cells found in which type of tissue? a) connective b) muscle c) nervous d) epithelial c Bone, cartilage, adipose tissue, and blood are all examples of: a) epithelial tissue. b) nervous tissue. c) connective tissue. d) small organ systems. e) muscle tissue. c The dermis is mostly made up of connective tissue. True False true The abdominopelvic cavity is part of the larger ventral body cavity. True False true Which of the following is the study of the body's structure? a) zoology b) homeostasis c) anatomy d) endocrinology e) physiology c Keratin in the skin is produced mainly by the cells in the epidermis. True False true The brain is responsible for essentially all homeostasis. True False false Which of the following statements best describes epithelial tissue? a) It covers internal and external surfaces. b) It is found only in the skin. c) It only covers surfaces exposed to the internal environment. d) It produces blood cells. e) It is always at least several layers thick. a Groups of tissues that perform a specific body function make up: a) an organ system. b) a tissue. c) an organ. d) the integument. e) a gland. c Which of the following is part of the axial skeleton? a) pelvic girdle bones such as the os coxa b) arm bones such as the humerus c) thoracic cage bones such as the ribs d) leg bones such as the femur c Which of the following is true concerning homeostasis? a) Homeostasis allows for major fluctuations in body conditions. b) Homeostasis is the maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment. c) Homeostasis is the maintenance of a rigid internal environment with no variation. d) The maintenance of homeostasis relies mainly on positive feedback. b Which of the following best describes "spongy bone"? a) bone tissue found only in the skull b) soft bone tissue c) contains blood-cell-producing red marrow d) very similar to compact bone but more flexible c Which of the following systems are involved in coordination and regulation? a) digestive and cardiovascular b) lymphatic and respiratory c) nervous and endocrine d) urinary and cardiovascular c Connective tissue is different from epithelial tissue in that connective tissue: a) has a structure called basement membrane. b) is not made up of cells. c) is found only in joints. d) has cells that are usually separated and scattered in an extracellular material. d What unusual feature do you find in connective tissues? a) extracellular material called the ground substance b) cells with the ability to contract c) conductive cells d) glandular secretions a In the levels of organization, the tissue level is between the cellular and organ levels. True False true In a muscle cell, sarcomeres are the: a) fundamental units of muscle contraction. b) thin filaments. c) thick filaments. d) myofibrils that run the length of the cell. a The heart is in the thoracic cavity. True False true Groups of cells that secrete substances are called: a) organ systems. b) glands. c) hormones. d) tissues. b Which of the two systems listed work together to bring oxygen into your body and deliver it to your cells? a) urinary and cardiovascular b) lymphatic and endocrine c) respiratory and cardiovascular d) respiratory and digestive c In oxygen homeostasis, the kidney that releases EPO, prompting increased red blood cell production is the: a) response. b) reactant. c) product. d) stimulus. a Glands found primarily in the groin and armpit areas are the: a) endocrine glands. b) merocrine sweat glands. c) apocrine glands. d) sebaceous glands. c The inner layer of the skin, the dermis, is mostly: a) epithelial tissue. b) keratin. c) connective tissue. d) muscle tissue. e) nervous tissue. c The two main divisions of the skeletal system are: a) cranial and axial. b) appendicular and cranial. c) vertebral and appendicular. d) axial and articular. e) appendicular and axial. e The spinal cavity and cranial cavity are the two parts of the: a) ventral cavity. b) abdominopelvic cavity. c) dorsal cavity. d) skeletal system. c Which of the following systems are involved in bringing nutrients into the body and to its cells? a) respiratory and cardiovascular b) urinary and cardiovascular c) digestive and cardiovascular d) lymphatic and respiratory c The type of muscle tissue that can be under our conscious control is: a) skeletal and smooth. b) smooth and cardiac. c) smooth. d) cardiac. e) skeletal. e Which human body system includes lymphatic organs of the lymphatic network, such as the tonsils and lymph notes? a) urinary b) cardiovascular c) endocrine d) immune e) nervous d A stimulus producing a response that reduces the stimulus describes: a) breakdown of homeostasis. b) negative feedback. c) all stimulus-response chains. d) positive feedback. b The four types of body tissues are: a) connective, cardiac, nervous, and adipose. b) epithelial, glandular, muscle, and nervous. c) connective, epithelial, nervous, and muscle. d) connective, neuronal, muscle, and epithelial. e) epithelial, hormonal, cellular, and bone. c Because they form linings or coverings, epithelial tissues always face an open area or an exterior environment. True False true A paper cut that draws blood must have cut down into at least which layer of the skin? a) epidermis b) adipose layer c) subcutaneous layer d) dermis d Routine activities and energy conservation are controlled by the: a) peripheral nervous system. b) parasympathetic division. c) thalamus. d) sympathetic division. b The parts of the central nervous system are the: a) nerves and receptors. b) afferent and efferent. c) autonomic and somatic. d) brain and spinal cord. d Which of the following best describes sensory receptors? a) Sensory receptors translate stimulation into action potentials. b) Sensory receptors interpret sensation. c) Sensory receptors translate action potentials into stimuli. d) Sensory receptors work through efferent pathways. a Which part of the human eye detects colored light? a) rhodopsin molecules b) cones c) enzymes in ganglion cells d) aqueous humor e) cornea b If the left side of the body is paralyzed by a stroke or other brain injury, the damage occurred on the left side of the brain. True False false How do hair cells of the cochlea translate vibration into nervous impulses? a) Pulling hairs trigger an action potential. b) Bending cilia lead to ion flow and neurotransmitter release. c) Moving cilia break molecules at their bases. d) Vibrating hairs open voltage sensitive channels. b Different parts of the tongue are responsive to different tastes. True False false Nerves would be best described as: a) bundles of dendrites in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). b) collections of motor neuron dendrites and cell bodies. c) collections of sensory neuron dendrites and cell bodies. d) bundles of axons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS). d Which part of your brain processes the information in this question and, you hope, retrieves the information necessary to answer it? a) pons b) hypothalamus c) cerebral cortex d) midbrain e) cerebellum c Proprioceptors provide us with: a) hearing. b) the sense of touch. c) information about the position of the joints. d) sight. c The cochlea is part of the: a) eye. b) brain. c) outer ear. d) inner ear. d Damage to the medulla oblongata in the brain could interfere with breathing. True False true The basic taste sensations are different in that each sensation works through: a) a different chemical reaction route in a taste cell. b) different taste nerves. c) a similar chemical reaction route in a taste cell. d) different ciliated receptor varieties, just like smell receptors. a The neuron being stimulated by a neurotransmitter comes after the synaptic cleft. True False true Inrushing sodium ions trigger the opening of nearby channels and movement of sodium inward at that neighboring section of the membrane. What is occurring? a) protein movement b) an action potential c) normal resting potential d) neurotransmitter release b Pons 1. regulation of drives 2. the "bridge" to the cerebrum 3. motor control and balance 4. regulates breathing and blood pressure 5. reasoning and memory 2 Medulla oblongata 1. regulation of drives 2. the "bridge" to the cerebrum 3. motor control and balance 4. regulates breathing and blood pressure 5. reasoning and memory 4 Cerebrum 1. regulation of drives 2. the "bridge" to the cerebrum 3. motor control and balance 4. regulates breathing and blood pressure 5. reasoning and memory 5 Hypothalamus 1. regulation of drives 2. the "bridge" to the cerebrum 3. motor control and balance 4. regulates breathing and blood pressure 5. reasoning and memory 1 Cerebellum 1. regulation of drives 2. the "bridge" to the cerebrum 3. motor control and balance 4. regulates breathing and blood pressure 5. reasoning and memory 3 The cilia that respond to sounds in the cochlea have "trapdoor" channels for K+ ions. True False true Part of the reason for the charge difference inside and outside a neuron's membrane is: a) negatively charged proteins inside the membrane. b) positively charged proteins inside the membrane. c) excess potassium outside the membrane. d) positively charged proteins outside the membrane. e) excess sodium inside the membrane. a Spinal nerves emerging from the spinal cord are named for: a) the organ they supply. b) the portion of the vertebral column around them. c) their basic function. d) strictly the number sequence 1—30. b Any collection of nerve cell bodies in the PNS is called a: a) efferent nerve. b) dendrite. c) ganglion. d) afferent nerve. c The action potential moves across the synaptic cleft as an electrical signal. True False false You are giving first aid to a semiconscious person who (before your arrival) told a bystander something about taking a drug overdose. The person has dilated pupils and a dry mouth. You recall reading that many drugs "mimic" the effects of nervous system functions, and you quickly size up which part of the nervous system is being mimicked here. The bystander is calling 911. In order to save time and best advise the emergency dispatcher about the treatment EMTs should be prepared to begin when they arrive, you tell the bystander to tell the 911 operator that the drug taken probably mimics which nervous system division? a) sympathetic b) parasympathetic c) sfferent d) somatic a Which statement about the sense of smell in humans is most accurate? a) Smell is about equally as strong as taste. b) One hundred different receptor varieties allow us to discern about 100 scents. c) Ciliated cells rapidly move scent molecules to the brain for rapid analysis. d) Combinations of over 300 receptors allow us to discern thousands of scents. d The iris of the human eye is composed partly of: a) nervous tissue. b) rods. c) smooth muscle. d) empty space. e) connective tissue. c Which of the following best describes the structural aspect of the cerebral cortex? a) a cap of white matter over the spinal cord, made mostly of the thalamus b) a thin band of gray matter making the outer layer of the cerebrum c) a core of fast, myelinated axons in the interior of the brain d) a thick band of white matter making the outer layer of the cerebru, b The autonomic nervous system is a part of the: a) appendicular nervous system. b) central nervous system. c) peripheral nervous system. d) somatic nervous system. c A section of a neuron's membrane becomes temporarily positive on the inside when: a) negatively charged proteins exit the cell. b) ion channels open and sodium ions rush in. c) ion channels open and potassium ions rush in. d) neurotransmitters enter the cell. b When light enters the eye, it is bent, or refracted, first by the: a) vitreous body. b) cornea. c) lens. d) retina. b In a reflex such as the "knee jerk" or patellar reflex, the efferent signal travels through the: a) interneuron. b) motor neuron. c) spinal cord. d) sensory neuron. b Most sensory information is routed through which structure before arriving in the cerebrum? a) medulla oblongata b) pons c) thalamus d) hypothalamus e) midbrain c An organ or group of cells that responds to a motor neuron is a/an: a) glial cell. b) receptor. c) effector. d) sensory organ. c Which statement best describes how one neuron stimulates another? a) Sodium ions jump across to the next neuron's membrane. b) The neurons are physically connected, so the action potential continues movement. c) Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synapse. d) Calcium ions diffuse across the synapse. c A nerve is larger than a neuron. True False true The human body has more sensory input to the CNS than the traditional "five senses." True False true Voluntary movement of the legs is controlled by the somatic nervous system. True False true Nerve 1. bundle of axons 2. mostly neuron cell bodies 3. carries signals to the CNS 4. carries signals away from the CNS 5. glial membrane wrapping 1 Efferent neuron 1. bundle of axons 2. mostly neuron cell bodies 3. carries signals to the CNS 4. carries signals away from the CNS 5. glial membrane wrapping 4 Myelin 1. bundle of axons 2. mostly neuron cell bodies 3. carries signals to the CNS 4. carries signals away from the CNS 5. glial membrane wrapping 5 Afferent neuron 1. bundle of axons 2. mostly neuron cell bodies 3. carries signals to the CNS 4. carries signals away from the CNS 5. glial membrane wrapping 3 Gray matter 1. bundle of axons 2. mostly neuron cell bodies 3. carries signals to the CNS 4. carries signals away from the CNS 5. glial membrane wrapping 2 The cells of the nervous system that transmit nervous system messages are the: a) glial cells. b) neurons. c) dendrites. d) synapses. b The brain and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS). True False true Any nerve that carries messages from the brain and spinal cord is an afferent division of the PNS. True False false Which of the following would send a signal to the central nervous system that you had touched a hot object? a) motor neuron b) sensory neuron c) glial cell d) interneuron b When a neuron is at its "resting potential," which of the following is true about the concentration of sodium ions? a) The sodium concentration is the same outside and inside the neuron's cell membrane. b) Sodium ions have a greater concentration inside the neuron's cell membrane. c) Sodium ions have a greater concentration outside the neuron's cell membrane. c Axons of motor neurons first leave the spinal cord through the: a) dorsal root ganglion. b) dorsal roots. c) spinal nerve. d) ventral roots. d Cells in the central nervous system that are important for functions such as memory are the: a) motor neurons. b) interneurons. c) glial cells. d) sensory neurons. b The Pacinian corpuscle is important to: a) the sense of touch. b) information about the position of the joints. c) sight. d) hearing. a Which of the following would be a function of the sympathetic division? a) stimulate the gallbladder b) accelerate heart rate c) constrict the pupils d) stimulate the stomach b Accelerates heart 1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division 3. somatic division 1 Inhibits digestion 1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division 3. somatic division 1 Stimulates salivation 1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division 3. somatic division 2 Constricts pupils 1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division 3. somatic division 2 Stimulates skeletal muscles 1. sympathetic division 2. parasympathetic division 3. somatic division 3 A drug that causes potassium to leak out of the neuron would: a) cause the inside of the neuron to become more positive. b) make it harder to trigger action potentials in the neuron. c) make it easier to trigger action potentials in the neuron. d) cause the outside of the neuron to become more negative. b The value of the three small bones of the middle ear is that they: a) translate solid vibration into internal liquid vibration. b) translate vibration into nerve impulses. c) connect the eardrum to the nerves of hearing. d) amplify vibrations by concentrating them into a smaller area. d White matter areas of the nervous system mostly contain: a) ganglia. b) cerebrospinal fluid. c) neuron cell bodies. d) myelinated axons. d Our "oldest" sense, which works in a very similar way in insects, is the sense of: a) touch. b) smell. c) vision. d) hearing. b The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system would be key in preserving an individual who is escaping from a dangerous situation. True False false A person is blindfolded and then given a piece of apple to eat while the scent of pineapple is wafted around his or her nose. The person would most likely guess that he or she is eating a/an: a) new type of fruit. b) apple. c) pineapple. d) 50-50 mixture of apple and pineapple. c The portion of the nervous system that most directly controls skeletal muscles is the: a) parasympathetic. b) somatic. c) afferent. d) autonomic. e) sympathetic. b Neurons are not true cells because they aren't spherical in shape. True False false Which of the following does the central nervous system use for the action of pulling your hand away from a hot object? a) sensory neurons b) receptors c) motor neurons d) glial cells c The term "brain dead" may refer to the fact that all brain centers have ceased to function except the: a) hypothalamus. b) cerebellum. c) medulla oblongata. d) thalamus. e) cerebrum. c When a neuron is resting, it has a higher concentration of Na+ ions inside the cell membrane than outside. True False false Our visual system creates images as well as perceiving them. True False true Follicle-stimulating hormone 1. stimulates contraction of the uterus 2. stimulates estrogen production and egg development in females 3. increases blood calcium levels 4. increases heart rate and blood pressure 5. increases metabolic rate 2 Parathyroid hormone 1. stimulates contraction of the uterus 2. stimulates estrogen production and egg development in females 3. increases blood calcium levels 4. increases heart rate and blood pressure 5. increases metabolic rate 3 Oxytocin 1. stimulates contraction of the uterus 2. stimulates estrogen production and egg development in females 3. increases blood calcium levels 4. increases heart rate and blood pressure 5. increases metabolic rate 1 Epinephrine 1. stimulates contraction of the uterus 2. stimulates estrogen production and egg development in females 3. increases blood calcium levels 4. increases heart rate and blood pressure 5. increases metabolic rate 4 T3 and T4 1. stimulates contraction of the uterus 2. stimulates estrogen production and egg development in females 3. increases blood calcium levels 4. increases heart rate and blood pressure 5. increases metabolic rate 5 Peptide hormones generally work by: a) attaching to membrane receptors and triggering chemical reactions. b) passing into the cell and attaching to receptors inside. c) triggering an influx of potassium ions. d) triggering an action potential in the cell. e) stimulating endocytosis of hormones and receptors. a Which of the following is a steroid hormone? a) T4 from the thyroid b) adrenaline c) melatonin d) estrogen e) glucagon d Release of most hormones is controlled by: a) the cerebrum. b) DNA. c) negative feedback. d) internal enzyme levels. e) positive feedback. c Steroid hormones generally work by: a) stimulating endocytosis of hormones and receptors. b) attaching to membrane receptors and triggering chemical reactions. c) passing into the cell and attaching to receptors inside. d) triggering an influx of potassium ions. e) triggering an action potential in the cell. c The structure that is at the center of control for endocrine activity, particularly as it relates to homeostasis, is the: a) cerebral cortex. b) posterior pituitary gland. c) hypothalamus. d) thyroid gland. e) brain stem. c Hypothalamic neurons directly control the anterior pituitary with neural stimuli at a synapse. True False false The hypothalamus makes the hormones that are released from the posterior pituitary. True False true A consequence of the way hormones, as compared to neurotransmitters, get to their target cells is that hormones: a) must be larger molecules. b) would be slower to act. c) cannot maintain homeostasis. d) must be proteins. e) can be lipids. b In order to maintain homeostasis, parathyroid hormone would stimulate what response to low blood calcium levels? a) prompt bones to store calcium b) prompt bones to release stored calcium c) stimulate the hunger drive d) reduce urine production at the kidneys e) stimulate the thirst drive b Oxytocin 1. thyroid 2. adrenal cortex 3. anterior pituitary 4. pancreas 5. posterior putuitary 5 Glucocorticoids 1. thyroid 2. adrenal cortex 3. anterior pituitary 4. pancreas 5. posterior putuitary 2 Prolactin 1. thyroid 2. adrenal cortex 3. anterior pituitary 4. pancreas 5. posterior putuitary 3 Insulin 1. thyroid 2. adrenal cortex 3. anterior pituitary 4. pancreas 5. posterior putuitary 4 Calcitonin 1. thyroid 2. adrenal cortex 3. anterior pituitary 4. pancreas 5. posterior putuitary 1 Hormones made from variations on the cholesterol molecule are: a) peptide hormones. b) glycoprotein hormones. c) steroid hormones. d) protein hormones. e) glycolipid hormones. c A bunch of hormone molecules travel by one cell and have no effect but quickly stimulate the next cell. What did the second cell have that the first did not? a) larger size b) receptors for the hormone c) greater need for the hormone d) dendrites e) a homeostatic response b Receptors inside cell 1. steroid hormone 2. amino-acid-based hormone 3. peptide hormone 4. steroid hormone 4 Growth hormone 1. steroid hormone 2. amino-acid-based hormone 3. peptide hormone 4. steroid hormone 2 Adrenaline 1. steroid hormone 2. amino-acid-based hormone 3. peptide hormone 4. steroid hormone 3 Estrogen 1. steroid hormone 2. amino-acid-based hormone 3. peptide hormone 4. steroid hormone 1 Which of the following is a peptide hormone? a) progesterone b) adrenaline c) glucagon d) estrogen e) melatonin c When blood sugar levels are running low, the body would produce more: a) insulin than cortisol. b) glucagon than insulin. c) insulin than adrenaline. d) insulin than glucagon. e) glycogen than insulin. b Most of the hormones of the anterior pituitary control other endocrine glands. True False true Cortisol is part of the body's stress response. True False true The adrenal glands are located close to the heart. True False false Hormones that are released by the posterior pituitary were made in the: a) anterior pituitary. b) hypothalamus. c) brain stem. d) adrenal glands. e) thalamus. b Small amounts of testosterone are made in the ovaries and adrenal glands of females. True False true Most peptide hormones enter the target cell through large channels. True False false The endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis through positive feedback. True False false Hormones differ from other chemical messengers such as neurotransmitters in that hormones: a) are all in the lipid chemical family. b) cross a synapse. c) always suppress rather than stimulate a response. d) travel through the bloodstream. e) are released through ducts. d Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates thyroid gland follicles to produce T4. True False false Hormones made from chains of amino acids are: a) glycolipid hormones. b) steroid hormones. c) protein hormones. d) peptide hormones. e) glycoprotein hormones. d Through nervous stimulation, the hypothalamus controls the release of which hormone? a) growth hormone b) follicle-stimulating hormone c) adrenaline d) thyroid-stimulating hormone e) glucagon c Which hormone controls water retention by the kidneys and is also known as antidiuretic hormone? a) vasopressin b) T4 c) luteinizing hormone d) oxytocin e) parathyroid hormone a Release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary is inhibited when: a) T3 and T4 levels are high. b) the metabolic rate of cells decreases. c) blood sugar levels are high. d) blood sugar levels are low. e) T3 and T4 levels are low. a Insulin and glucagon are produced by a: a) large proportion of the cells in the pancreas. b) small proportion of the cells in the pancreas. c) large proportion of the cells in the adrenal glands. d) small proportion of the cells in the pituitary. b Which hormone causes glucose to be produced from the breakdown of protein and fat? a) oxytocin b) insulin c) cortisol d) growth hormone e) glucagon c "Releasing hormones" and "inhibiting hormones" produced by the hypothalamus target the: a) adrenal glands. b) digestive organs. c) ovaries and testes. d) anterior pituitary. e) posterior pituitary. d Alpha cells of the pancreas make insulin. True False false Insulin stimulates liver cells to store glucose in the form of glycogen. True False true Some hormones may take up to several hours to work. True False true Which organ that is a target of insulin plays the most significant role in regulating sugar levels in circulation? a) pituitary b) stomach c) kidneys d) liver e) adrenal glands d Capillaries are essentially water-tight vessels, so nutrients and gases diffuse in and out, but water stays put. True False true Which is the best description of the function of the respiratory system? a) delivers carbon dioxide to the blood b) facilitates gas exchange between the environment and body cells c) fills the lungs with air d) delivers oxygen to the blood b What relationship between LDLs and HDLs is the healthiest? a) low levels of both HDLs and LDLs b) high levels of both HDLs and LDLs c) high levels of LDLs and low levels of HDLs d) low levels of LDLs and high levels of HDLs d When the thoracic cavity gets smaller, the pressure inside the lungs increases. True False true The blood consists entirely of blood cells and water. True False false The formed elements account for about what percentage of the total volume of blood? a) 75 percent b) 45 percent c) 100 percent d) 10 percent b The trachea branches into left and right bronchioles. True False false When a doctor uses a stethoscope to listen to your heart and hears the lub-dub sound, she is actually listening to the: a) blood surging through the arteries. b) contraction of the cardiac muscle in the ventricles. c) electrical signals that control heartbeat. d) valves in the heart closing. d Which factor contributes to plaque formation in coronary arteries? a) fat cells clogging the interior b) inflammation of the lining where LDLs have attached c) inflammation of the lining where HDLs have attached d) protein deposits in the interior b Blood flow from the heart, to the lungs, and back to the heart is known as the: a) coronary circulation. b) pulmonary circulation. c) pericardial circulation. d) systemic circulation. b Which vein in the body carries oxygenated blood? a) superior vena cava b) coronary vein c) inferior vena cava d) Veins never carry oxygenated blood. e) pulmonary vein e Why do new red blood cells survive for only a few months? a) The oxygen that red blood cells carry damages their organelles. b) The heart pumps red blood cells so often that their membranes deteriorate. c) Red blood cells do not have most organelles or a nucleus. d) The hemoglobin that red blood cells carry is toxic. c The human cardiovascular system is comparable in some ways to a car's: a) transmission system. b) cooling system. c) electrical system. d) engine. b When the diaphragm contracts, the thoracic cavity , and you . a) gets larger; exhale b) gets larger; inhale c) gets smaller; exhale d) gets smaller; inhale b Contraction of the diaphragm causes exhalation to occur. True False false Some of the fluid that leaks out of the capillaries is pulled back nearer to the end of the capillary bed by: a) higher blood pressure in the capillaries. b) low interstitial fluid pressure. c) suction from valves. d) higher osmotic pressure in the capillaries. d The combination of large numbers and small size collectively gives alveoli what characteristic that is essential to their function? a) easy inflatability b) low air resistance c) high surface area d) low surface area c Which of the following usually drain blood from a capillary bed? a) veins b) venules c) arteries d) arterioles b The coronary arteries that bring blood to the heart branch off from the: a) pulmonary vein. b) pulmonary artery. c) vena cava. d) aorta. d Blockage of the aorta is the most common fatal heart attack. True False false Some proteins are too large to leave the capillaries. True False true Which blood component is made of fragments of cells rather than a complete cell? a) white blood cells b) red blood cells c) plasma d) platelets d Right ventricle 1. receives blood from the superior vena cava 2. pumps blood to the pulmonary arteries 3. receives blood from the pulmonary veins 4. pumps blood to the aorta 2 Left atrium 1. receives blood from the superior vena cava 2. pumps blood to the pulmonary arteries 3. receives blood from the pulmonary veins 4. pumps blood to the aorta 3 Right atrium 1. receives blood from the superior vena cava 2. pumps blood to the pulmonary arteries 3. receives blood from the pulmonary veins 4. pumps blood to the aorta 1 Left ventricle 1. receives blood from the superior vena cava 2. pumps blood to the pulmonary arteries 3. receives blood from the pulmonary veins 4. pumps blood to the aorta 4 Most of the oxygen in human blood is: a) dissolved in the plasma. b) carried in hemoglobin. c) carried on albumin. d) carried in the plasma membrane of red blood cells. b Formed elements in the blood consist of all the parts below except: a) white blood cells. b) red blood cells. c) platelets. d) plasma proteins. d Because they are cell fragments, not cells, platelets are a component of plasma, not a formed element. True False false Which of the following best describes fibrinogen? a) Fibrinogen is a plasma protein involved in clotting. b) Fibrinogen is the connective tissue in the wall of an artery. c) Fibrinogen is a lipid found in platelets. d) Fibrinogen is a transport lipoprotein that carries cholesterol. e) Fibrinogen is the protein portion of the hemoglobin molecule. a Arteries always carry blood that is oxygen rich. True False false The tiny air sacs of the lungs are called: a) bronchioles. b) trachea. c) alveoli. d) bronchi. c The left ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary artery. True False false Alveoli 1. tiny air sacs 2. "upper throat" 3. small air passageways 4. "windpipe" 5. "voicebox" 1 Bronchioles 1. tiny air sacs 2. "upper throat" 3. small air passageways 4. "windpipe" 5. "voicebox" 3 Larynx 1. tiny air sacs 2. "upper throat" 3. small air passageways 4. "windpipe" 5. "voicebox" 5 Pharynx 1. tiny air sacs 2. "upper throat" 3. small air passageways 4. "windpipe" 5. "voicebox" 2 Trachea 1. tiny air sacs 2. "upper throat" 3. small air passageways 4. "windpipe" 5. "voicebox" 4 Which structure contains deoxygenated blood? a) pulmonary vein b) left atrium c) left ventricle d) pulmonary artery e) aorta d If someone has an iron deficiency in the diet, which part of the blood would this mainly impact? a) red blood cells b) white blood cells c) plasma proteins d) platelets a Many people regularly donate plasma. Which of the following substances is not given when the plasma is donated? a) red blood cells b) electrolytes c) water d) antibodies a Veins always carry blood: a) toward the capillaries. b) away from the heart. c) toward the heart. d) away from the lungs. c Which of the following will raise HDL and lower LDL levels? a) drinking more milk b) exercise c) stopping the use of anti-inflammatory medications d) replacing unsaturated fat in the diet with saturated fat b Which of the following may be found in blood plasma? a) water, proteins, nutrients, and ions b) water, proteins, and ions c) water d) water and proteins a In an area that has been "set up" for a heart attack by plaque formation, what is the most direct final trigger likely to be? a) eating a fatty meal b) blood clot formation in the swollen area c) a sudden drop in LDL levels d) thinning of the blood e) a sudden rise in HDL levels b Water and plasma proteins make up about 99 percent of blood plasma. True False true The movement of air in and out of the lungs is called: a) external respiration. b) cellular respiration. c) ventilation. d) internal respiration. c What force is most important in returning blood back to the heart in the veins? a) osmotic pressure of proteins in the blood b) contraction of the ventricles on the heart c) gravity d) contraction of the skeletal muscles in the body d Which chamber of the heart receives blood from the lungs? a) left atrium b) left ventricle c) right atrium d) right ventricle a If a person is unable to clot blood properly, which of the following might be lacking? a) platelets b) white blood cells c) red blood cells d) ions a Nerve-like muscle cells that function as the heart's pacemaker are found in the: a) sinoatrial node. b) left ventricle. c) atrioventricular valves. d) right ventricle. e) coronary arteries. a Veins are smaller blood vessels than capillaries. True False false What is the relationship of bone marrow to the cardiovascular system? a) Bone marrow helps keep the blood moving through the body. b) Bone marrow produces chemicals that help carry carbon dioxide in the blood. c) Bone marrow produces red blood cells. d) Bone marrow breaks down old blood cells. c Valves in veins are important features that help keep blood moving back toward the heart. True False true Inflammation is a typical part of the initial process that can result in a heart attack. True False true Ions in plasma are also known as electrolytes. True False true The outer layer of an artery or vein is composed of: a) cartilage. b) connective tissue. c) smooth muscle. d) Epithelium. b Which vessels are structurally suited for the central purpose of allowing substances to pass in and out of them through their entire lengths? a) capillaries b) arteries c) arterioles d) veins e) semilunar valves a Which of the following is true of the relationship of red blood cells to the other formed elements? a) Red blood cells are the only formed element without a plasma membrane. b) Red blood cells make up about half of the formed elements. c) Red blood cells make up over 99 percent of the formed elements. d) Red blood cells are the most important formed element involved in blood clotting. e) Red blood cells are the only formed element not made in bone marrow. c During gas exchange, oxygen and carbon dioxide always move: a) into the alveoli. b) down their concentration gradients. c) into the blood. d) out of the blood. b Which of the following best describes High-Density Lipoproteins (HDLs)? a) HDLs are critical components to the oxygen-carrying ability of red blood cells. b) HDLs are large versions of the cholesterol molecule. c) HDLs are transport proteins that carry lipids from the liver to tissues. d) HDLs are transport proteins that carry lipids from tissues to the liver. d Which chamber of the heart is connected to the aorta? a) right atrium b) left ventricle c) right ventricle d) left atrium b What happens when the diameter of an artery decreases? a) Its semilunar valves open. b) The heart rate decreases. c) The blood pressure decreases. d) Its epithelial cells stretch. e) The blood pressure increases. e Blood in the pulmonary arteries is moving toward the heart. True False false The stimuli for contraction of the heart come from within the heart rather than from the nervous system. True False true A heart murmur would be associated with the malfunction of which structure? a) pacemaker b) heart epithelial tissue c) atrioventricular valves d) heart muscle e) aorta c Erythrocyte is another term for: a) red blood cell. b) plasma protein. c) white blood cell. d) platelet. a Why is the left side of the heart stronger than the right side of the heart? a) The right side pumps blood only to the brain, and the left side pumps blood around the whole body. b) The left side receives more oxygen from the lungs. c) The left side pumps blood to the right side of the body, which has more muscle mass. d) The right side pumps only to the lungs, and the left side pumps blood around the whole body. d Pulmonary ventilation occurs because of pressure differences between the lungs and the external environment. True False true People with high blood pressure often take medication to lower blood pressure. Some of these medications might do this by: a) opening the valves in the veins. b) relaxing the smooth muscles in the arteries. c) increasing the number of platelets in the blood. d) increasing the blood volume. b Most of the absorption of digested food takes place in the: a) stomach. b) small intestine. c) large intestine. d) esophagus. b Why does alcohol ingestion increase urine output? a) The alcohol suppresses ADH production. b) The alcohol is converted to excess water by the liver. c) The alcohol stimulates ADH production. d) The alcohol increases blood pressure. e) The alcohol redirects blood flow away from the skin and to the kidneys. a The appendix is attached to which portion of the large intestine? a) the ileocecal valve b) the colon c) the cecum d) the rectum c Which type of muscle is involved in peristalsis in the intestine? a) smooth b) voluntary c) skeletal d) cardiac a In what way are the essential amino acids different from nonessential amino acids? a) Essential amino acids are the ones exclusively used to make enzymes. b) Essential amino acids cannot be made and must be obtained from food. c) Nonessential amino acids are not necessary for any proteins we make. d) Nonessential amino acids are not absorbed by the digestive tract. b Which of the following is a complex carbohydrate that cannot be digested? a) high fructose corn syrup b) fibers c) starches d) disaccharides b Which of the following is an example of a nutrient that helps to regulate bodily processes? a) lipid b) protein c) water d) potassium d Minerals are always chemical elements, not compounds. True False true Gallstones are a problem when they: a) block the cystic duct or common bile duct. b) break and release cholesterol. c) break and release enzymes. d) get stuck in the folds of the small intestine. a How does food move from the pharynx to the stomach? a) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the esophagus. b) Gravity alone pushes food through the esophagus. c) Gravity alone pushes food through the trachea. d) Peristalsis and gravity push food through the trachea. a Which category of nutrient would be best described as compounds needed in small amounts in the diet to facilitate chemical reactions in the body? a) enzymes b) trace minerals c) lipids d) Vitamins d Which of the following is a trace mineral? a) sodium b) phosphorus c) sulfur d) iodine d How would blockage of the pancreatic duct affect the digestive system? a) The stomach would be unable to function. b) The food in the small intestine would be more basic (alkaline). c) The small intestine would contain acidic, mostly undigested chyme. d) It would have little effect because liver enzymes would take over. c How do fats leave the digestive system and enter the bloodstream? a) in the veins b) in the arteries c) in the capillaries d) in the lymphatic vessels d Most digestion occurs in the: a) small intestine. b) mouth. c) stomach. d) large intestine. a What problem might result from damage to the epiglottis? a) A person would no longer be able to swallow. b) Food would be able to enter the respiratory passageway. c) Food would not be digested properly. d) A person would no longer be able to taste food. b The urethra is different lengths in men and women. True False true Fiber is defined as a complex carbohydrate that is digestible. True False false Large intestine 1. turns food to chyme 2. water and vitamin K absorbed 3. transport of food only 4. secretes enzymes and chemical buffers 5. most digestion and absorption 2 Esophagus 1. turns food to chyme 2. water and vitamin K absorbed 3. transport of food only 4. secretes enzymes and chemical buffers 5. most digestion and absorption 3 Small intestine 1. turns food to chyme 2. water and vitamin K absorbed 3. transport of food only 4. secretes enzymes and chemical buffers 5. most digestion and absorption 5 Stomach 1. turns food to chyme 2. water and vitamin K absorbed 3. transport of food only 4. secretes enzymes and chemical buffers 5. most digestion and absorption 1 Pancreas 1. turns food to chyme 2. water and vitamin K absorbed 3. transport of food only 4. secretes enzymes and chemical buffers 5. most digestion and absorption 4 Deficiency of which nutrient can cause muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, or paralysis? a) sulfur b) iron c) potassium d) copper c Urethra 1. carries urine from the bladder out of the body 2. carries urine to the bladder 3. contraction forces urine out the body 4. tube sensitive to ADH 1 Urinary bladder 1. carries urine from the bladder out of the body 2. carries urine to the bladder 3. contraction forces urine out the body 4. tube sensitive to ADH 3 Ureter 1. carries urine from the bladder out of the body 2. carries urine to the bladder 3. contraction forces urine out the body 4. tube sensitive to ADH 2 Collecting duct 1. carries urine from the bladder out of the body 2. carries urine to the bladder 3. contraction forces urine out the body 4. tube sensitive to ADH 4 Chemical digestion begins in the: a) mouth. b) large intestine. c) small intestine. d) stomach. a In a traditional food pyramid, which type of food would be closest to the base? a) vegetables b) whole grain foods c) fruits d) fish and poultry e) dairy products b Which of the following best describes the stomach's role in absorption? a) The stomach absorbs mostly large proteins. b) The stomach absorbs most nutrients. c) The stomach absorbs some drugs and alcohol but few nutrients. d) The stomach absorbs acids. c Voluntary control of urination is accomplished by: a) an internal sphincter of smooth muscle. b) contraction of the ureters. c) an external sphincter made of skeletal muscle. d) the skeletal muscle of the bladder. c Why are large amounts of red meat and butter not healthy choices in the diet? a) Most people cannot digest them. b) They contain excessive amounts of fiber. c) They contain a lot of saturated fat. d) They contain too much protein. c The tube leading from the bladder that carries urine out of the body is the ureter. True False false What is the difference between fats and oils? a) Fats are mostly made of unsaturated fat. b) Oils are mostly made of saturated fat. c) Fats are always healthier as long as they are mostly saturated. d) Oils are liquids and fats are solid at room temperature. d Digestion is a process of mechanical and chemical breakdown of larger food molecules into smaller ones that can be absorbed. True False true Which organ is central to the body's metabolism of nutrients? a) the kidneys b) the liver c) the small intestine d) the stomach b Place the following in order of the movement of urine through the urinary system: (1) urethra, (2) ureter, (3) kidney, (4) urinary bladder. a) 3, 4, 1, 2 b) 2, 3, 4, 1 c) 1, 2, 3, 4 d) 3, 2, 4, 1 e) 1, 3, 2, 4 d Which of the following has the most stored energy per gram? a) carbohydrates b) minerals c) proteins d) lipids d Calories are a measure of the: a) amount of energy the food contains. b) amount of minerals and vitamins a food contains. c) weight of the food. d) nutritional value of food. a Roughly how long is the small intestine? a) 20 feet b) 14 feet c) 6 feet d) 30 feet a The knot of capillaries in a nephron, where filtration of blood occurs, is the: a) collecting duct. b) bowman's capsule. c) glomerulus. d) distal tubule. e) proximal tubule. c What affect does ADH secretion have on the kidneys? a) Blood pressure to the kidneys decreases. b) Water stays trapped in the kidney tubules. c) Urine output increases. d) The filtration rate increases. e) Water moves out of the kidney tubules. e Why are saturated fats considered a less healthy nutrient? a) Saturated fats cannot be used for energy as the other fats can. b) Saturated fats raise HDL levels, which contributes to heart disease. c) Saturated fats raise LDL levels, which contributes to heart disease. d) Because saturated fats are from animal sources, they can produce allergic reactions. c The upper throat may be referred to as the: a) trachea. b) epiglottis. c) larynx. d) pharynx. d The measure of how blood glucose levels are affected by a given amount of carbohydrate is: a) monosaccharide ratio. b) insulin index. c) sugar input. d) glycemic load. d Which of the following is an accessory organ in the digestive system? a) the skin b) the pancreas c) the kidneys d) the lungs b What is the main function of the colon? a) to digest and absorb carbohydrates b) to absorb water and vitamin K c) to control nutrients it will send to the rest of the body d) to complete the digestion of lipids b A "nutritional" calorie is actually 1,000 of the energy unit calories. True False true What is the first part of the small intestine that receives food from the stomach? a) jejunum b) duodenum c) ileum d) cecum b Blood carries most nutrients straight from the small intestine to which organ? a) the stomach b) the kidneys c) the pancreas d) the heart e) the liver e Why doesn't the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach digest its own lining cells? a) The cells make chemicals that quickly neutralize all the acid. b) Lining cells produce a protective mucus layer. c) The acid is specific to proteins, not cells. d) The stomach has a dense connective tissue lining.b Which is the main organic molecule that is digested by the secretions of the stomach? a) protein b) nucleic acid c) carbohydrate d) lipida About 99 percent of the fluid the kidney processes is recycled back into the body. True False true Which layer of the digestive tract is actually in contact with the food? a) submucosa b) serosa c) muscularis externa d) mucosa d What is unusual about soy protein as opposed to other plant protein sources? a) Soy protein has all essential amino acids in the proper proportions. b) Soy protein has only one-tenth the energy per gram of other proteins. c) Soy protein has more energy per gram than lipids. d) Soy protein has the same saturated fat levels as animal fat. a Digestion of which organic molecule takes a somewhat more complicated route than most nutrients? a) nucleic acid b) carbohydrate c) protein d) fat d In addition to breaking down food, what other valuable function does stomach acid perform? a) Stomach acid kills bacteria and other pathogens in food. b) Stomach acid recycles chlorine. c) Stomach acid converts waste molecules into bile. d) Stomach acid activates enzymes in the small intestine. a Most of the blood vessels and nerves in the digestive tract are located in the layer of: a) mucosa. b) serosa. c) muscularis externa. d) submucosa. d What is the function of the rugae, or folds in the stomach? a) The rugae neutralize excess acid. b) The rugae allow the stomach to expand when food enters. c) The rugae push food down toward the intestine. d) The rugae manufacture bile. b Sodium is a nutrient because it provides us with energy. True False false The outermost layer of the digestive tract is the: a) mucosa. b) submucosa. c) serosa. d) muscularis externa. c Which structure regulates the passage of food from the stomach into the small intestine? a) the epiglottis b) the stomach submucosa c) the pharynx d) the pyloric sphincter d Soy protein and nearly all animal protein sources provide all the essential amino acids needed in the diet. True False true Which of the following types of fat are the least healthy? a) trans fat b) monounsaturated fat c) polyunsaturated fat d) saturated fata The main function of the gallbladder is to: a) store and concentrate bile. b) store and concentrate digestive enzymes. c) make bile. d) make gallstones. a In the digestive system, the villi are: a) blood vessels that pick up nutrients from the digestive system. b) muscles in the digestive system that push the food along. c) finger-like projections of the mucosa. d) glands that release digestive enzymes. c Most digested food is absorbed into the blood by the villi of the small intestine. True False true The mixture of food and digestive juices that leaves the stomach is called: a) trypsin. b) chyme. c) cud. d) pepsin. b An egg implants in the uterus and awaits sperm for fertilization. True False false Which of the following statements concerning sperm and fertilization is correct? a) Several sperm must contribute their DNA to the egg for fertilization to occur. b) Many sperm release their enzymes before one can get through. c) The first sperm that approaches the egg is the one to fertilize the egg. d) The first capacitated sperm fertilizes the egg. b Acrosome 1. sperm storage 2. becomes the fetal portion of the placenta 3. sperm stem cell 4. makes female hormones 5. enzyme storage 5 Corpus luteum 1. sperm storage 2. becomes the fetal portion of the placenta 3. sperm stem cell 4. makes female hormones 5. enzyme storage 4 Spermatogonia 1. sperm storage 2. becomes the fetal portion of the placenta 3. sperm stem cell 4. makes female hormones 5. enzyme storage 3 Epididymis 1. sperm storage 2. becomes the fetal portion of the placenta 3. sperm stem cell 4. makes female hormones 5. enzyme storage 1 Trophoblast 1. sperm storage 2. becomes the fetal portion of the placenta 3. sperm stem cell 4. makes female hormones 5. enzyme storage 2 In humans, females contribute more resources to reproduction and development than males. True False true How much does the cervix ultimately dilate during labor? a) 3 centimeters b) 1 centimeters c) 10 centimeters d) 5 centimeters c Which of the following is a structure in which sperm mature and are stored? a) testis b) epididymis c) vas deferens d) accessory glands b Immature versions of all the major organ systems have formed by about what point in pregnancy? a) 12 weeks b) 16 days c) 3 weeks d) not until at least 30 weeks a Semen is the mixture of sperm and secretions from male reproductive glands. True False true Sperm development begins in the: a) epididymis. b) seminiferous tubules. c) prostate gland. d) vas deferens. b An ovarian follicle is a developing oocyte and the follicular cells surrounding it. True False true Implantation occurs in the: a) uterine tube. b) ovary. c) uterus. d) vagina. c The normal position of the fetus at the start of labor is "upside down." True False true Fallopian tube is another name for the uterine tube. True False true Sperm develop in the seminal vesicles. True False false Sperm are made in the: a) ovary. b) vas deferens. c) testes. d) epididymis c Human embryos do not go through a morula stage of development as do most other animals. True False false The stages of follicle development are: a) primary follicle, secondary follicle, tertiary follicle, corpus luteum. b) ovarian follicle, mature follicle, oocyte. c) corpus luteum, tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle. d) tertiary follicle, secondary follicle, primary follicle, corpus luteum. a As sperm are made, they travel through the vas deferens and are stored in the seminal vesicles until ejaculation. True False false Human pregnancy lasts an average of about 38 weeks. True False true Why is it useful for accessory glands to produce alkaline substances to accompany sperm? a) Alkaline substances neutralize the acidic environment of the vagina. b) Alkaline substances produce a pH optimum for nutrient absorption. c) Alkaline substances function as enzymes needed for swimming. d) Alkaline substances are mainly fats used for energy. a Which of the following is considered a gamete? a) zygote b) oocyte c) child d) embryo b Why does a female have millions of ovarian follicles as a fetus but has perhaps just over a thousand in her early fifties? a) Several thousand follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate. b) Natural degeneration of follicles speeds up in later years. c) Production of new follicles from stem cells slows in her fifties. d) Several hundred follicles ovulate per monthly cycle and deplete the follicle supply at a steady rate. b Through what structure does an oocyte travel on its way to the uterus? a) vagina b) ovary c) cervix d) uterine tube d Why is production of lung surfactant important for a baby? a) Without lung surfactant, the baby's lungs do not develop properly. b) Lung surfactant keeps the lungs from sticking to the diaphragm. c) Lung surfactant may block the placenta from exchanging oxygen. d) Lung surfactant keeps the lung sacs from collapsing. d Ovulation refers to growth of the primary follicle. True False false It generally takes the enzymes from dozens of sperm for one sperm to gain access to the oocyte membrane. True False true Which of the following best describes the period during which the developing offspring is considered a fetus? a) from fertilization to eight weeks b) the third trimester only c) the first trimester only d) from fertilization to three weeks e) from nine weeks until birth e Sperm are fully mature when they reach the epididymis. True False false What is the "afterbirth" associated with the birth process? a) the process of cutting the umbilical cord b) the blood lost from the uterus in the weeks after birth c) the placenta d) the amniotic fluid c What prevents multiple sperm from fertilizing one egg? a) phagocytosis by accessory cells once one sperm contacts the membrane b) atresia c) egg immediately divides and becomes impervious to sperm d) release of granules that harden the membrane outside of the oocyte d When does the fetus achieve about 15 percent of its birth weight and start kicking? a) in the third trimester b) in the second trimester c) at the end of embryonic phase d) in the first trimester e) at the start of organogenesis b Women produce oocytes from stem cells from puberty all throughout life. True False false On average, about how often does ovulation occur? a) every 6 months b) every 14 days c) every day d) every 28 days d A woman begins puberty with about 400,000 follicles. True False true The sequence of development of sperm is: a) primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, tertiary spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm. b) immature sperm, mature sperm, secondary sperm, spermatocyte. c) primary spermatocyte, spermatogonia, sperm. d) spermatogonia, spermatocyte, spermatid, sperm. d The portion of a sperm that carries enzymes needed for fertilization is the: a) mitochondrion. b) tail. c) nucleus. d) acrosome. d Ejaculation initially deposits the sperm in the uterus. True False false Which statement concerning gamete production is correct? a) The number of sperm a man can produce is essentially unlimited, whereas the number of eggs a woman can potentially produce is limited. b) Sperm cells can be produced only at certain points in the reproductive cycle. c) A man is born with all of the sperm he will need for the rest of his life. d) Progestins stimulate development of new follicles. a The specialized tissue of the uterus where implantation occurs is the: a) cervix. b) vagina. c) uterine tube. d) endometrium. d When a spermatogonium divides, it produces one primary spermatocyte and: a) two secondary spermatocytes. b) one spermatid. c) one spermatogonium. d) one nurse cell. c Development of sperm occurs from the: a) inside of the seminiferous tubule toward the outside. b) outside of the seminiferous tubule toward the inside. c) middle of the penis toward the prostate gland. d) outside of the epididymis toward the inside. b Menstruation refers to the later life cessation of the monthly ovarian cycle. True False false Fraternal twins develop when: a) two eggs are fertilized by one sperm. b) multiple ovulations occur, and two eggs are fertilized. c) one egg is fertilized by two sperm. d) one egg is fertilized by one sperm, but the resulting cells separate from one another and continue development. b An ectopic pregnancy is: a) another name for identical twins. b) attachment of an embryo outside the uterus. c) another name for fraternal twins. d) implantation of the embryo in the uterus. b Corpus luteum translates as "yellow body." True False true In the human birth process, what does labor refer to? a) the period between the first contraction and dilation of the cervix b) regular contractions of uterine muscles c) the last part of the process when the fetus is expelled from the vagina d) the period between birth and expulsion of the placenta b Spermatids are produced by: a) sertiary spermatocytes. b) spermatogonia. c) secondary spermatocytes. d) primary spermatocytes. c Sperm development takes about: a) 1 month. b) 28 days. c) 2.5 months. d) 6 months. c Which structure would be best described as helping to prepare the female tract for pregnancy and maintain it during the early phases of pregnancy? a) vagina b) corpus luteum c) uterine tube d) oocyte b From which structure does the corpus luteum develop? a) primary follicle b) secondary follicle c) tertiary follicle d) oocyte c A man has been experiencing reduced urine flow problems. After examination by his doctor, the diagnosis is an enlarged prostate gland. What is the connection between prostate enlargement and reduced urine flow? a) The prostate is located where the ureters enter the bladder. b) An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the kidneys. c) The prostate surrounds the urethra, the tube that transmits sperm and urine. d) An enlarged prostate is a sign of cancer that affects the bladder. c Sperm cells do not need a nucleus and expel it during development as a weight-saving tactic. True False false An egg is not a gamete. True False false If a chemical were to destroy all oocytes: a) sperm would not form. b) eggs would form but have no chromosomes. c) sperm would form but have no chromosomes. d) eggs would not form. d A fertility doctor is trying to determine why a couple is infertile. It has been determined that the woman is fertile, so the problem may be with the man. In analyzing his semen, the doctor notices adequate sperm production, but the sperm are largely inactive. He concludes that the semen may be lacking in proper nutrients for the sperm. Which structure would be the most likely candidate for the source of the problem? a) seminal vesicles b) vas deferens c) seminiferous tubules d) urethra a The male stem cells in sperm production are the spermatogonia. True False true The developing organism is referred to as a fetus during its first eight weeks. True False false Three weeks after conception, which of the following has happened in an embryo? a) organ formation b) primitive eye formation c) limb bud formation d) neural tube formation d What changes occur in the endometrium as the time of possible fertilization approaches? a) The endometrium secretes estrogen. b) The endometrium enters the secretory phase. c) The endometrium enters the proliferative phase. d) Menstruation occurs. b The vas deferens ducts empty sperm into the: a) seminal vesicles. b) uterus. c) urethra. d) epididymis. c Which hormone stimulates the muscular contractions associated with birth of a child? a) estrogen b) luteinizing hormone c) oxytocin d) progesterone c Which of these becomes the baby? a) outer cell mass b) placenta c) inner cell mass d) trophoblast c Which of these is not a supporting gland in males? a) seminal vesicle b) bulbourethral gland c) prostate gland d) epididymis d Normally, anywhere from one to four sperm fertilize the egg. True False false Sperm development requires temperatures somewhat cooler than found in the rest of the body. True False true How many sperm participate in the formation of fraternal twins? a) four b) two c) three d) one b There is an epididymis adjacent to each testis. True False true [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 79 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 23, 2021
Number of pages
79
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 23, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
44


 And LETRS Unit 8 Final Assessment Test.png)






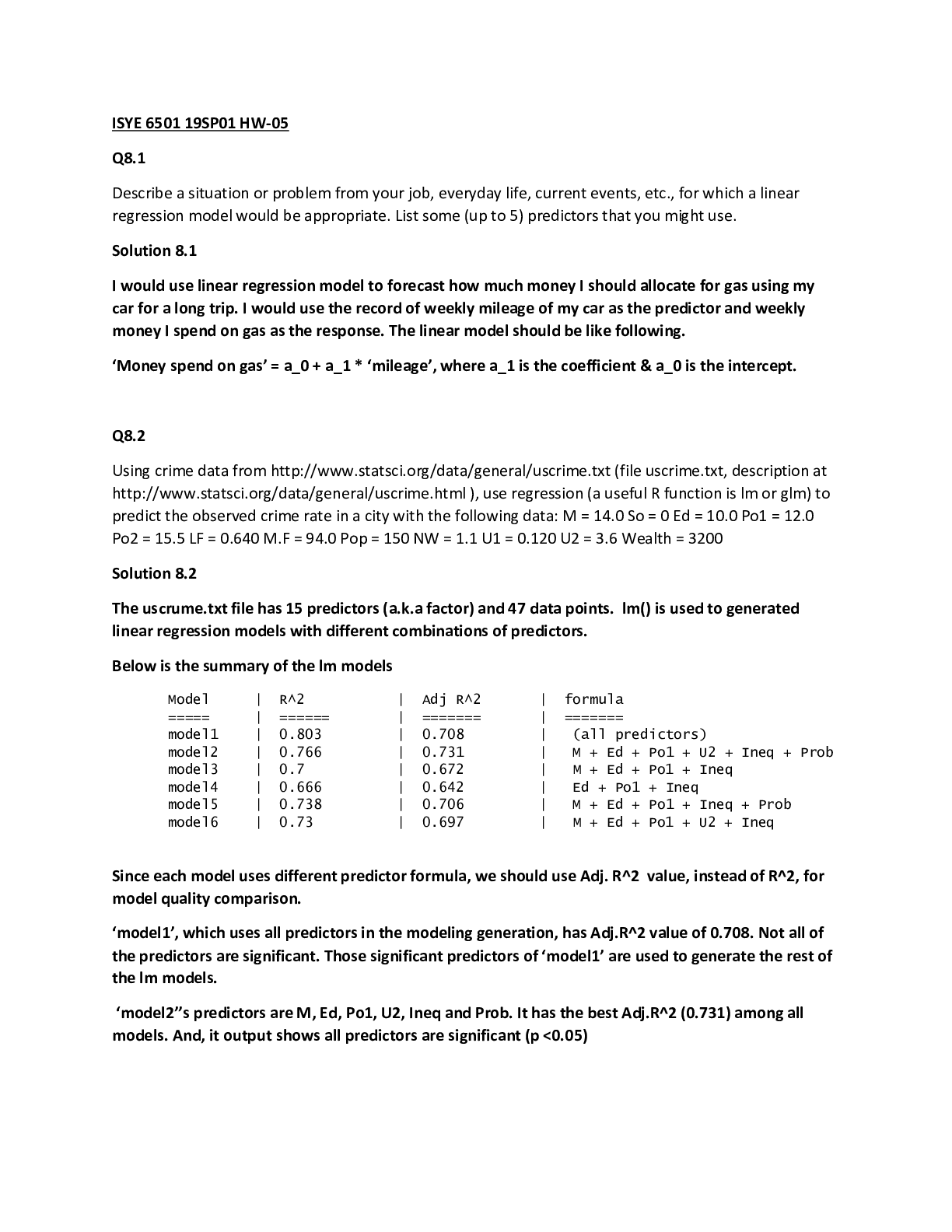










.png)