Pathophysiology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > OUR LADY OF LAKE UNIVERSITY, PATHO 2410 Ch 2 Pathophysiology Test Bank. GRADED A (All)
OUR LADY OF LAKE UNIVERSITY, PATHO 2410 Ch 2 Pathophysiology Test Bank. GRADED A
Document Content and Description Below
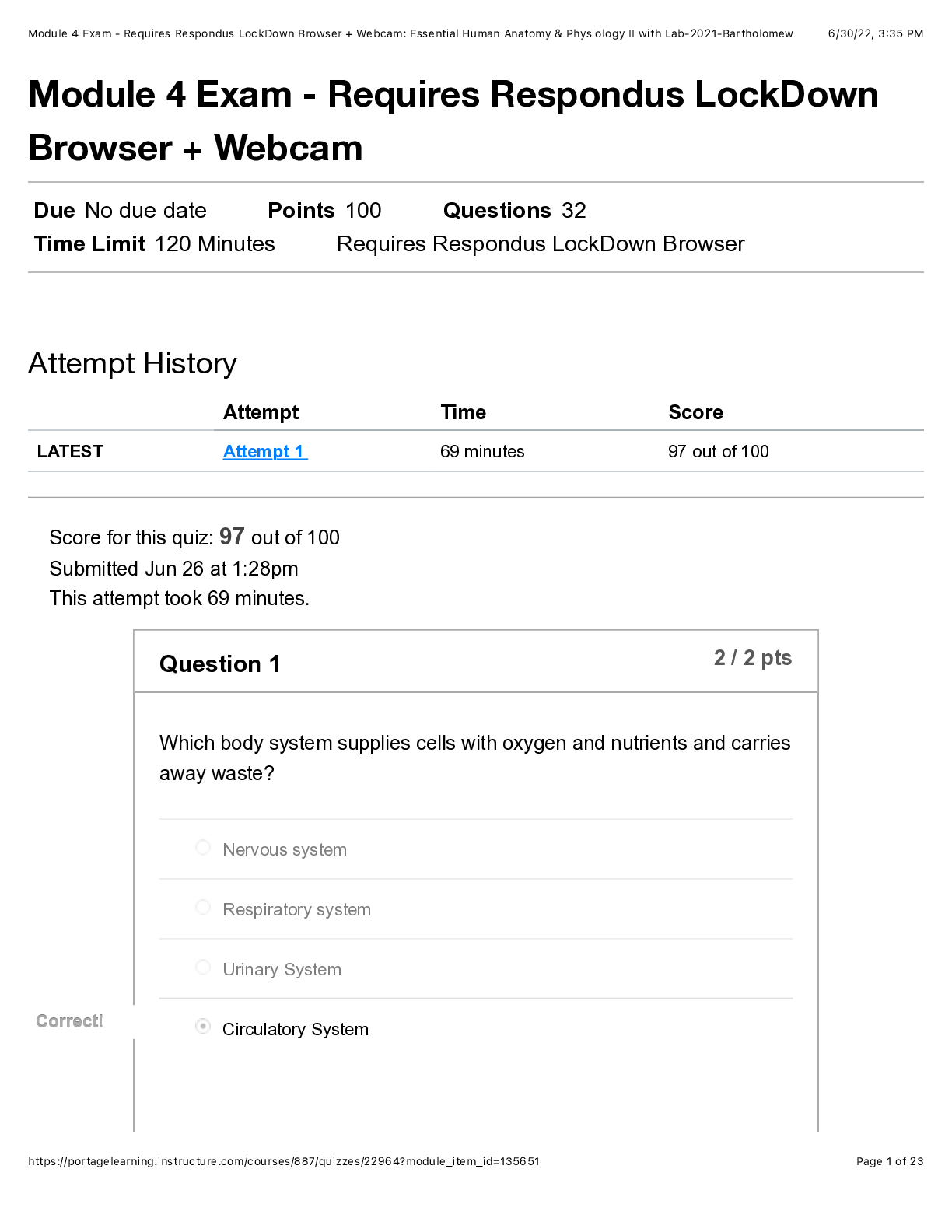
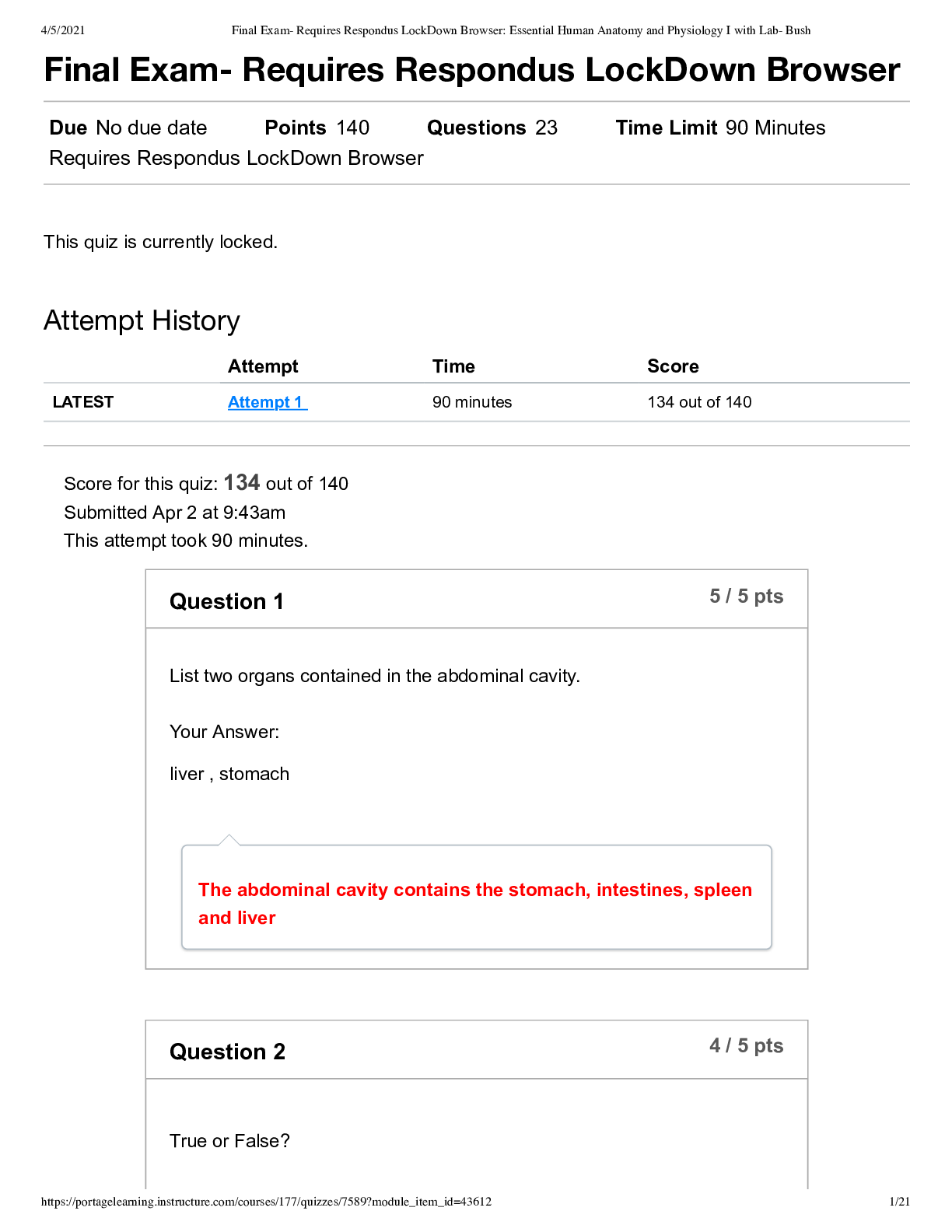
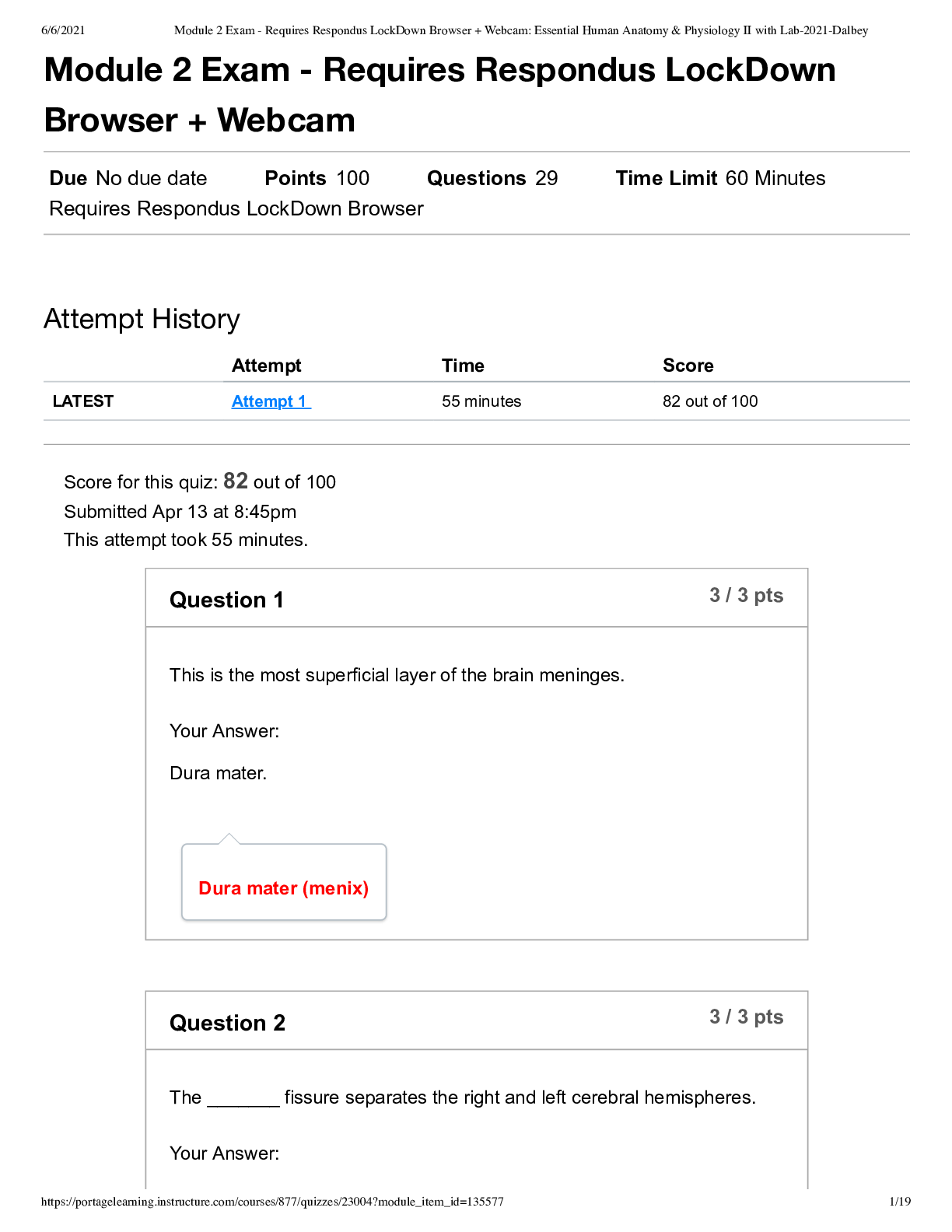
ch 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Choose the correct proportion of water to body weight to be expected in a healthy male ad... ult’s body: a. 30% b. 45% c. 60% d. 70% ____ 2. Choose the correct proportion of blood (to body weight) in an adult male’s body: a. 30% b. 20% c. 10% d. 4% ____ 3. Insensible fluid loss refers to water lost through: a. perspiration only. b. feces only. c. perspiration and expiration. d. urine and feces. ____ 4. When the osmotic pressure of the blood is elevated above normal, water would shift from the: a. blood into the cells. b. interstitial compartment into the cells. c. interstitial compartment into the blood. d. cells into the interstitial compartment. ____ 5. Which of the following would result from a deficit of plasma proteins? a. Increased osmotic pressure b. Decreased osmotic pressure c. Increased hydrostatic pressure d. Decreased hydrostatic pressure ____ 6. Which of the following would cause edema? a. Decreased capillary hydrostatic pressure b. Increased capillary osmotic pressure c. Decreased capillary permeability d. Increased capillary permeability ____ 7. Which of the following would likely be related to an elevated hematocrit reading? a. Fluid excess b. Fluid deficit c. Increased sodium level d. Decreased erythrocytes This study source was downloaded by 100000773243632 from CourseHero.com on 03-25-2022 03:07:31 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/17566289/Ch-2-Pathophysiology-Test-Bank/ ____ 8. Which of the following is a typical sign of dehydration? a. Rapid, strong pulse b. Low hematocrit c. Increased urine output d. Rough oral mucosa ____ 9. Which of the following terms refers to a combination of decreased circulating blood volume combined with excess fluid in a body cavity? a. Dehydration b. Third-spacing c. Hypovolemia d. Water retention ____ 10. Which of the following is the primary cation in the extracellular fluid? a. Sodium b. Potassium c. Calcium d. Iron ____ 11. Which of the following is a common cause of hyponatremia? a. Loss of the thirst mechanism b. Excessive sweating c. Excessive aldosterone secretion d. Prolonged period of rapid, deep respirations ____ 12. Which of the following is a common effect of both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia? a. Skeletal muscle twitch and cramps b. Oliguria c. Elevated serum pH d. Cardiac arrhythmias ____ 13. Choose the correct effect of increased parathyroid hormone. a. Increased movement of calcium ions into the bones b. Increased activation of vitamin D c. Increased absorption of calcium from the digestive tract d. Decreased reabsorption of calcium in the kidneys ____ 14. Which of the following results from hypocalcemia? 1. Low serum phosphate levels 2. Nausea and constipation 3. Skeletal muscle twitch and spasms 4. Weak cardiac contractions a. 1, 2 b. 1, 4 c. 2, 3 d. 3, 4 This study source was downloaded by 100000773243632 from CourseHero.com on 03-25-2022 03:07:31 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/17566289/Ch-2-Pathophysiology-Test-Bank/ ____ 15. Which of the following causes tetany? a. Increased permeability of nerve membranes due to low serum calcium b. Excess calcium ions in skeletal muscle due to excess parathyroid hormone (PTH) c. Excess calcium ions inside somatic nerves as a result of neoplasms d. Increased stimulation of the nerves in the cerebral cortex ____ 16. In which of the following processes is phosphate ion NOT a major component? a. Bone metabolism b. Metabolic processes involving adenosine triphosphate (ATP) c. Blood clotting d. Acid-base balance ____ 17. Which of the following would be considered normal serum pH? a. 4.5-8 b. 7.0 c. 7.4 d. 8 ____ 18. When many excess hydrogen ions accumulate in the blood, what happens to serum pH? The pH: a. decreases. b. increases. c. remains constant. d. varies based on metabolism. ____ 19. What is the slowest but most effective control for acid-base balance? a. Respiratory system b. Buffer systems in the blood c. Kidneys d. Brain ____ 20. Which of the following is essential in order to maintain serum pH within normal range? a. Carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion must be present in equal quantities. b. All excess carbonic acid must be excreted by the kidneys. c. The concentration of bicarbonate ion must remain constant. d. The ratio of carbonic acid to bicarbonate ion must be 1:20. ____ 21. Which is the correct effect on the body of abnormally slow respirations? a. Increased carbonic acid b. Decreased carbonic acid c. Increased bicarbonate ion d. Decreased bicarbonate ion ____ 22. Which condition is likely to cause metabolic acidosis? a. Slow, shallow respirations b. Prolonged diarrhea c. Mild vomiting d. Excessive fluid in the body This study source was downloaded by 100000773243632 from CourseHero.com on 03-25-2022 03:07:31 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/17566289/Ch-2-Pathophysiology-Test-Bank/ ____ 23. What would a serum pH of 7.33 in a patient with kidney disease indicate? a. Metabolic alkalosis b. Metabolic acidosis c. Respiratory alkalosis d. Respiratory acidosis ____ 24. Which serum value indicates decompensated metabolic acidosis? a. pH is below normal range b. pH is above normal range c. Bicarbonate level decreases d. Bicarbonate level increases ____ 25. What is the effect on blood serum when excessive lactic acid accumulates in the body? a. Bicarbonate ion levels decrease b. Bicarbonate ion levels increase c. Carbonic acid levels increase d. pH increases ____ 26. The direct effects of acidosis are manifested primarily in the functioning of the: a. Digestive system b. Urinary system c. Nervous system d. Respiratory system ____ 27. Compensation mechanisms in the body for dehydration would include: a. increased antidiuretic hormone (ADH). b. decreased aldosterone. c. slow, strong heart contraction. d. peripheral vasodilation. ____ 28. Which acid-base imbalance results from impaired expiration due to emphysema? a. Metabolic acidosis b. Metabolic alkalosis c. Respiratory acidosis d. Respiratory alkalosis ____ 29. In patients with impaired expiration associated with emphysema, effective compensation for the acid-base imbalance would be: a. increased rate and depth of respiration. b. decreased rate and depth of respiration. c. increased urine pH and decreased serum bicarbonate. d. decreased urine pH and increased s [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Instant download
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 25, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 25, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
36

.png)






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)



