BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Test Bank Chapter Number: 6 questions with answers practice paper 2020 (All)
Test Bank Chapter Number: 6 questions with answers practice paper 2020
Document Content and Description Below
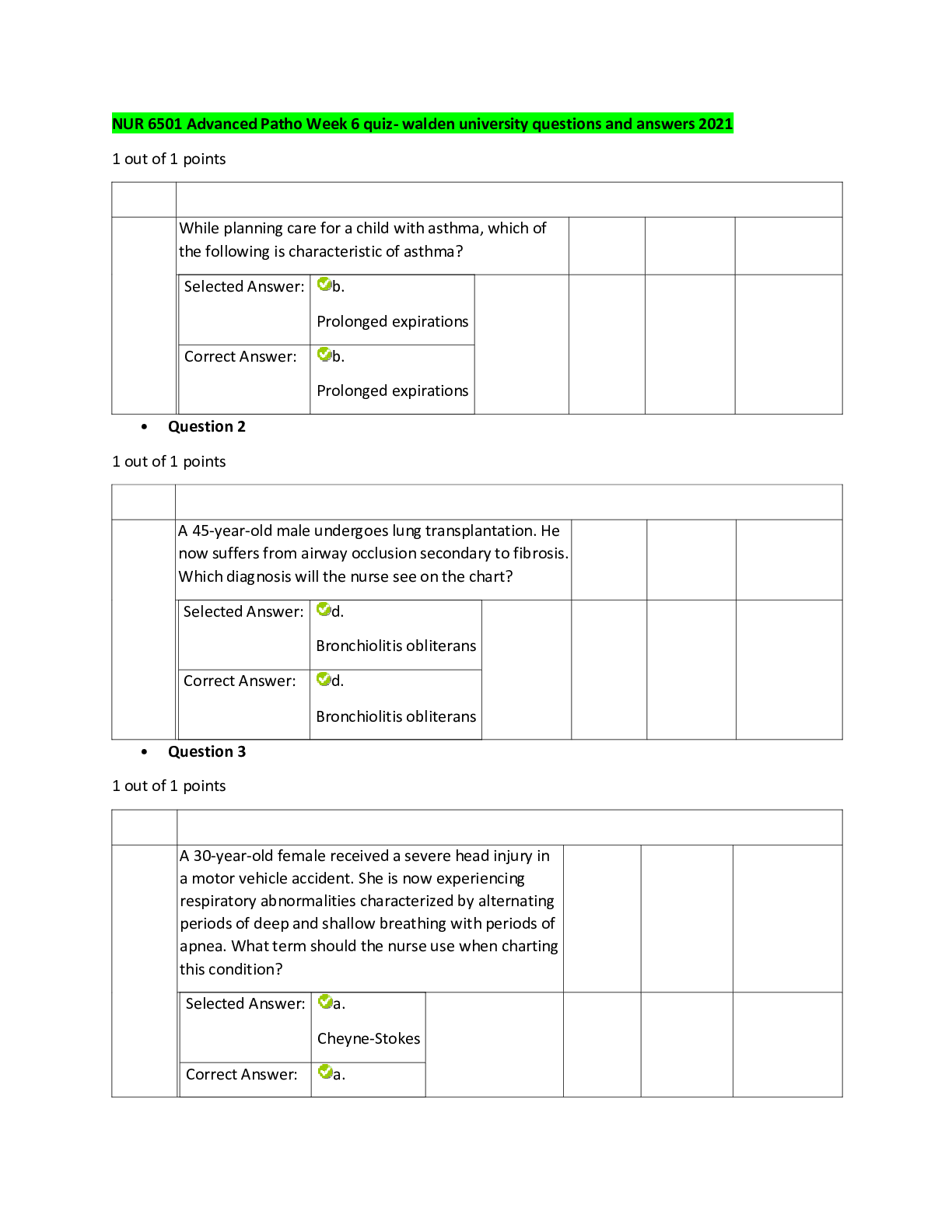
Test Bank Chapter Number: 6 questions with answers practice paper 2020 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Different enzymes that catalyze the same reaction are known as _____. A) transfera... ses B) isomerases C) allosteric enzymes D) holoenzymes E) isozymes 2) An uncatalyzed reaction has a rate of 4.2 x 10–7 sec–1. When an enzyme is added the rate is 3.2 x 104 sec–1. Calculate the rate enhancement caused by the enzyme. A) 7.6 x 1010 B) 3.2 x 104 C) 1.3 x 10–2 D) 7.4 x 10–3 E) cannot be determined 3) Which of the following is the most effective way to increase the rate of a biochemical reaction? A) increase the temperature B) increase the concentrations of the reactants C) increase or decrease the pH D) add a catalyst E) none of the above 4) Chymotrypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of a peptide bond and is therefore categorized as a _____. A) oxidoreductase B) transferase C) hydrolase D) lyase E) ligase 5) The ability for an enzyme to pick out one particular substrate from the myriad of molecules floating around its environment is an example of _____. A) natural selection B) specificity C) high affinity D) processivity E) none of the above 6) The highest point in a reaction coordinate diagram represents _____. A) an intermediate of the reaction pathway B) the reactants in an exergonic reaction C) the products in an endergonic reaction D) the transition state E) the overall G for the reaction 7) How does a catalyst affect the overall G of an endergonic reaction? A) it has no effect B) the reaction becomes more endergonic C) the reaction has a G of zero D) the reaction becomes exergonic E) none of the above 8) How does a catalyst increase the rate of a reaction? A) it makes the reaction more exergonic B) it increases the temperature of the reaction C) it allows reacting molecules to more easily form the transition state D) it causes a localized increase in the concentration of reactants E) none of the above 9) An organic molecule that is tightly bound to an enzyme and participates in an enzyme catalyzed reaction is specifically referred to as a _____. A) cofactor B) metal ion C) coenzyme D) cosubstrate E) prosthetic group 10) An enzyme that forms a covalent bond with its substrate during the course of a reaction is considered to undergo _____. A) acid-base catalysis B) covalent catalysis C) electrophilic catalysis D) metal ion catalysis E) none of the above 11) Which of the following amino acids would be most likely found in the active site of an enzyme that uses acid-base catalysis? A) Asn B) Ser C) Met D) His E) Trp 12) Which of the following is seen in a reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction that uses covalent catalysis? A) an intermediate B) two distinct transition states C) reactants that are lower in energy than an intermediate D) products that are lower in energy than an intermediate E) all of the above 13) In the enzyme catalyzed decarboxylation of acetoacetate, a Schiff base is formed between the ketone of acetoacetate and a _____ residue in the active site of the enzyme. A) Arg B) Asn C) Lys D) Glu E) Ser 14) Of the following ions, which would be most likely to participate in metal ion catalysis? A) Na+ B) Zn2+ C) Ag+ D) K+ E) Ba2+ 15) In an enzyme mechanism that generates a negative charge in the transition state, which of the following would be most effective to have in the active site of the enzyme? A) transition metal cation B) Asp residue C) Gln residue D) transition metal anion E) none of the above 16) What three amino acids are found in the catalytic triad of chymotrypsin? A) Glu, His, Thr B) Ser, Arg, Cys C) Asp, His, Ser D) Cys, Lys, Glu E) Asn, His, Thr 17) What amino acid performs the nucleophilic attack during the chymotrypsin mechanism? A) Ser B) His C) Lys D) Cys E) Thr 18) During the first half of the chymotrypsin mechanism where the acyl-enzyme intermediate is formed, what role does His play? A) general acid only B) general base only C) general acid then general base D) general base then general acid E) nucleophile 19) If the Asp in the chymotrypsin active site was mutated to another amino acid, which of the following would be considered an invisible mutation in that it is least likely to impact the function of the enzyme? A) Asp Asn B) Asp Glu C) Asp His D) Asp Ser E) Asp Lys 20) Of all the species that enzymes bind, they are thought to bind most tightly to _____. A) substrates B) products C) transition states D) intermediates E) all are bound very tightly 21) In the chymotrypsin mechanism, what is used to stabilize the negative charge on the carbonyl oxygen of the transition state? A) hydrogen bonding between the enzyme and the anion from the carbonyl oxygen B) electrostatic interaction of the positively charged His and carbonyl oxygen C) electrostatic interaction of the negatively charged Asp and carbonyl oxygen D) electrostatic interaction of the active site Zn2+ and carbonyl oxygen E) all of the above 22) If an enzyme rate increases 10-fold for every 5.7 kJ/mol decrease in the energy of activation, what rate increase would be observed if three H-bonds were stabilizing the transition state with each H-bond having a strength of 21 kJ/mol? A) 11-fold increase B) 37-fold increase C) 60-fold increase D) 100-fold increase E) 1011-fold increase 23) When the transition state is formed, what is the specific interaction observed between Asp and His that helps stabilize the transition state? A) dipole-dipole interaction B) electrostatic interaction C) hydrogen bond D) low-barrier hydrogen bond E) covalent bond 24) The ability for an enzyme to change its shape upon substrate binding represents the concept of _____. A) lock and key B) induced fit C) proximity and orientation effects D) covalent catalysis E) none of the above 25) The enzyme hexokinase catalyzes a reaction where its substrates are completely sequestered from the aqueous environment allowing for interactions to occur between enzyme and substrates that would not normally occur in an aqueous environment. What term describes this type of catalysis? A) electrostatic catalysis B) desolvation catalysis C) non-aqueous catalysis D) hydrogen-bonded catalysis E) closed-system catalysis 26) Chymotrypsin catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds adjacent to _____ residues in a peptide. A) neutral polar B) nonpolar C) negatively charged D) positively charged E) all of the above since chymotrypsin has little substrate specificity 27) What amino acid residue present in the specificity pocket allows trypsin to bind to peptides containing Arg or Lys? A) Ser B) His C) Lys D) Val E) Asp 28) Chymotrypsin has a large specificity pocket to bind the aromatic amino acids while elastase has a very small specificity pocket meant to bind Ala or Gly. Which of the following amino acid substitutions changes the specificity pocket of chymotrypsin to that of elastase? A) TrpSer B) LeuAla C) Gly Val D) Lys Asp E) Val Asn 29) The molecule chymotrypsinogen is known as a(n) _____. A) apoenzyme B) holoenzyme C) protease inhibitor D) zymogen E) none of the above 30) Which protein in the blood is responsible for converting fibrinogen to fibrin? A) thrombin B) factor X C) factor VII D) factorVIIa E) prothrombin 31) Conversion of factor X to factor Xa represents a(n) _____ form of activation; binding of antithrombin to thrombin represents a(n) _____ form of inhibition. A) reversible; reversible B) irreversible; reversible C) reversible; irreversible D) irreversible; irreversible E) none of the above since antithrombin is not an inhibitor of thrombin 32) Which of the following is true regarding heparin? A) it is an allosteric activator of antithrombin B) it is a sulfated polysaccharide C) it simultaneously binds to antithrombin and the target of antithrombin D) it is used clinically as an anticoagulant E) all of the above 33) Zymogens are not enzymatically active because _____. A) they do not contain the cofactors required for catalysis B) they are the product of mutated genes C) their active sites are distorted and incapable of enzymatic activity D) the pH of their environment is not optimal for activity E) none of the above 34) Which of the following is a feature of protease inhibitor specific for trypsin? A) contains a positive charge to mimic the charge of the substrate B) ability to interact with the Ser of the catalytic triad C) inability to form the tetrahedral intermediate D) high affinity for the enzyme active site E) all of the above [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 01, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 01, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
53