Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Middle Tennessee State University MBAE 6865 Economic Decisions for Managers. CHAPTER 12 - KW. All An (All)
Middle Tennessee State University MBAE 6865 Economic Decisions for Managers. CHAPTER 12 - KW. All Answers Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
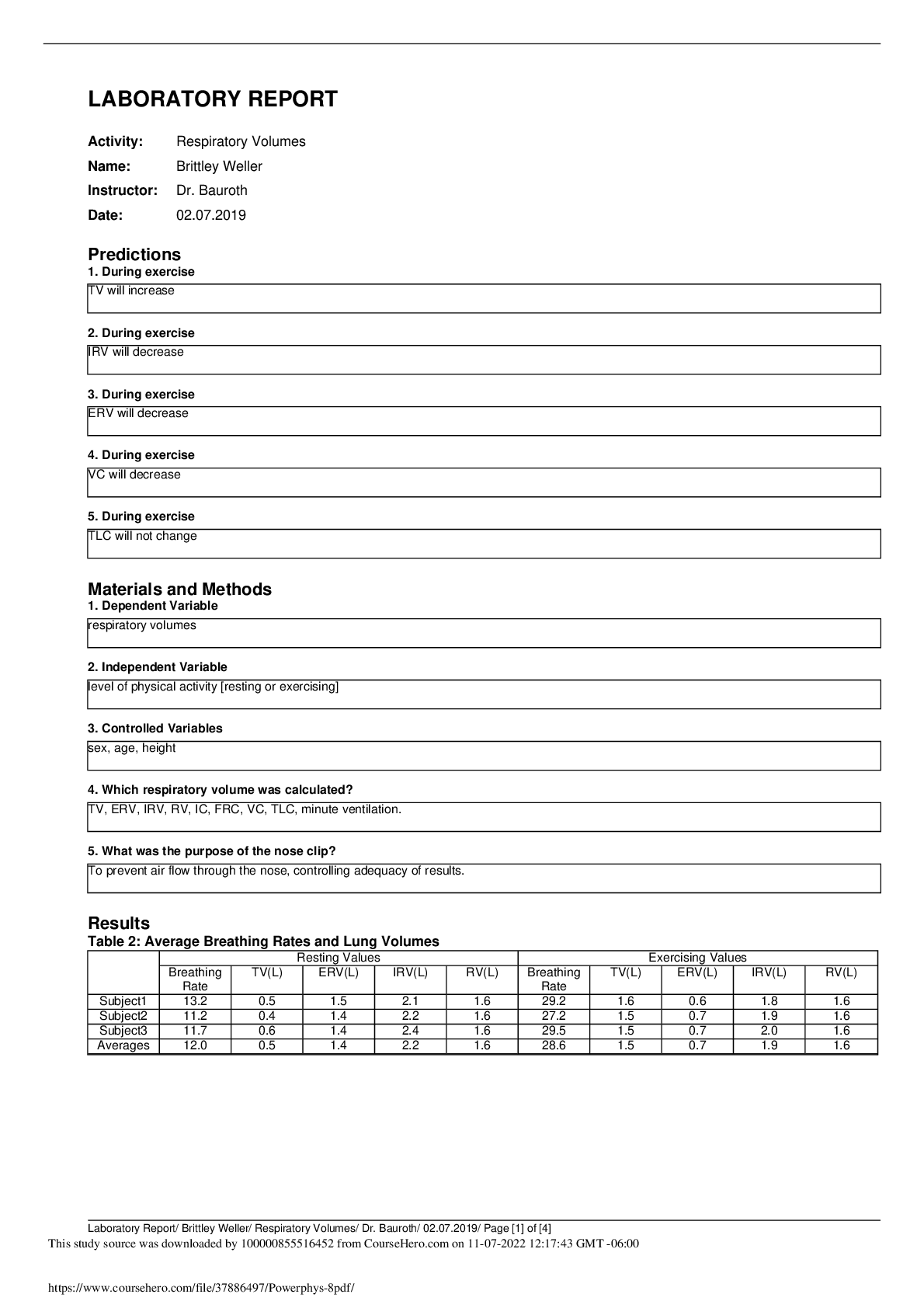
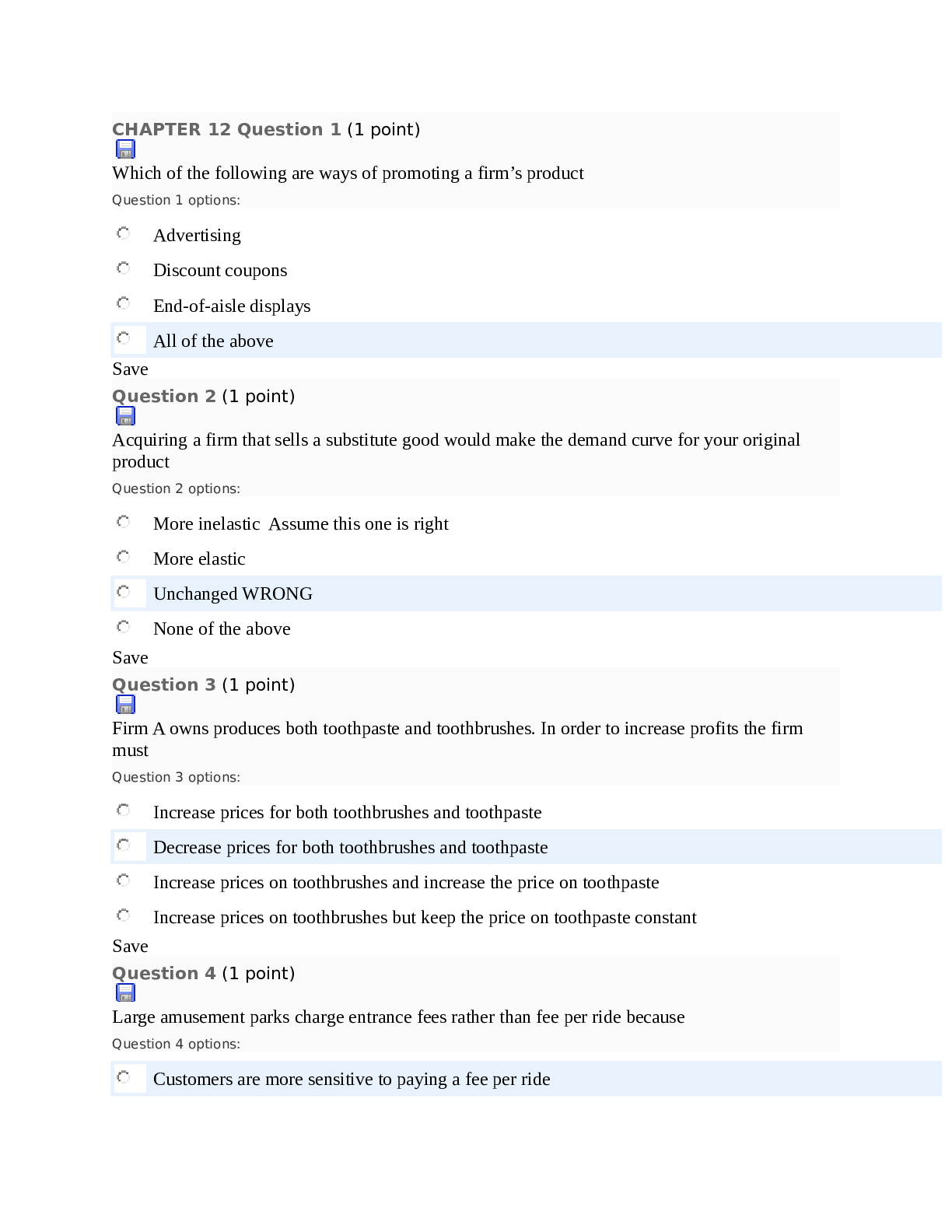
CHAPTER 12 Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following are ways of promoting a firm’s product Question 1 options: Advertising Discount coupons End-of-aisle displays All of the above Save Que... stion 2 (1 point) Acquiring a firm that sells a substitute good would make the demand curve for your original product Question 2 options: More inelastic Assume this one is right More elastic Unchanged WRONG None of the above Save Question 3 (1 point) Firm A owns produces both toothpaste and toothbrushes. In order to increase profits the firm must Question 3 options: Increase prices for both toothbrushes and toothpaste Decrease prices for both toothbrushes and toothpaste Increase prices on toothbrushes and increase the price on toothpaste Increase prices on toothbrushes but keep the price on toothpaste constant Save Question 4 (1 point) Large amusement parks charge entrance fees rather than fee per ride because Question 4 options: Customers are more sensitive to paying a fee per rideCustomers are less sensitive to paying a fee per ride Customers view paying per ride as a smaller cost None of the above Save Question 5 (1 point) Which of the following is FALSE? Question 5 options: To reduce cannibalization among products, reposition a product so that it does not directly compete with the other After acquiring a substitute product, raise prices on both the products After acquiring a complementary product, raise prices on both the products All of the above Save Question 6 (1 point) By focusing the customers on the price of a product, you make Question 6 options: The demand for the product more inelastic The customers less price sensitive to the product Both A & B None of the above Save Question 7 (1 point) The general rule to increase profits when two close complementary brands are jointly owned is Question 7 options: Increase prices for both brands Decrease prices for both brands Increase prices on one brand, decreasing it for the other Increase prices on one brand, keeping the prices of the second brand constant Save Question 8 (1 point)Prospect theory implies that consumers are motivated by Question 8 options: The actual price level The distance of the price from the reference price All of the above None of the above Save Question 9 (1 point) Which of the following is true? Question 9 options: To reduce cannibalization among products, reposition a product so that it does not directly compete with the other After acquiring a substitute product, raise prices on both the products After acquiring a complementary product, lower prices on both the products All of the above Save Question 10 (1 point) The general rule to increase profits when two close substitute brands are jointly owned is Question 10 options: Increase prices for both brands Decrease prices for both brands Increase prices on one brand, decreasing it for the other Increase prices on one brand, keeping the prices of the second brand constant Save Question 11 (1 point) By focusing the customers on the price of a product, you Question 11 options: Increase your chances of engaging in a price war with your competitors Make the customers more price sensitive to the product Make the demand for the product more elasticAll of the above Save Question 12 (1 point) The pricing rule MR=MC holds for Question 12 options: All firms Single product firms Multiple product firms None of the above Save Question 13 (1 point) In order to increase sales the firm can Question 13 options: Increase the reference price for the product Decrease prices Differentiate their product All of the above Save Question 14 (1 point) Which of the following is FALSE? Question 14 options: To reduce cannibalization among products, make the products more homogenous After acquiring a substitute product, raise prices on both the products After acquiring a complementary product, lower prices on both the products All of the above Save Question 15 (1 point) Firm X owns both a grocery store and the parking lot outside the grocery store. In order to increase the traffic at the store it must Question 15 options:Decrease the prices on the goods sold in the store Decrease the parking rates All of the above None of the above Save Question 16 (1 point) Given that you observe nothing but the high price of the product, you are more likely to infer that Question 16 options: The product is low quality The product is high quality The product is the lowest quality possible The product is defective Save Question 17 (1 point) A Swiss watch company advertises its history of superior craftsmanship. The company thinks that this would Question 17 options: Make the demand for the product less elastic Make the customers less sensitive to the price Assist them with differentiating their product All of the above Save Question 18 (1 point) After firm A acquired firm B, it lowered the prices for the goods produced by both firms. This can increase profits if the goods are Question 18 options: Substitutes Complements Not relatedNone of the above Save Question 19 (1 point) An airline wants to introduce a charge for snacks on flights. Why would it not be such a good idea? Question 19 options: Passengers would be less likely to buy snacks Passengers would be more likely to carry their own snacks onboard Passengers would feel nickel-and-dimed and would switch airlines WRONG All of the above ASSUME this one is right Save Question 20 (1 point) Firms tend to raise the price of their goods after acquiring a firm that sells a substitute because Question 20 options: They lose market power There is an increase in the overall demand for their products The bundle has a more elastic demand than individual goods The bundle has a more inelastic demand than individual goods SaveQuiz CH 13 & 14 Note: It is recommended that you save your response as you complete each question. Question 1 (1 point) A supermarket sells you a pound of coffee on the condition that you buy a gallon of milk. This is an example of Question 1 options: Bundling Tie in Sale Price Discounting Both a and b Save Question 2 (1 point) An important lesson about pricing is Question 2 options: Do not bargain with the customer When bargaining with the customer, do not bargain over the bundled price, bargain over unit price When bargaining with the customer, do not bargain over the unit price, bargain over the bundled price Bargain with the customer over everything Save Question 3 (1 point) Metering isQuestion 3 options: A form of indirect price discrimination A form of direct price discrimination An evaluation of a product An example of bundling Save Question 4 (1 point) For direct price discrimination to work, Question 4 options: The firm need not be able to identify members of the low-value group The firm must charge a single price to all its customers The firm need not worry about any arbitrage since all its customers are charged the same price None of the above Save Question 5 (1 point) The practice of buying a firm’s good in one market at a low price and selling it in another market for a higher price in order to profit from the price difference is known as Question 5 options: Predatory pricing Price collusionArbitrage Mark-up pricing Save Question 6 (1 point) Which of the following is FALSE about indirect price discrimination Question 6 options: The firm is able to identify each customer’s willingness to pay The firm is able to charge different prices to the different value customers The firm is be able to prevent arbitrage Assume this is correct All of the above WRONG Save Question 7 (1 point) Which of the following is an example of a “metering” strategy Question 7 options: A supermarket offers free parking space but charges higher for grocery A television reseller spends time making sure that the picture quality of the bargain priced sets is fuzzy Razors are sold at unit cost while razor blades have large profit margins All of the above Save Question 8 (1 point)A firm practicing direct price discrimination will charge lower prices to Question 8 options: Consumers with an elastic demand All consumers Consumers known to have an inelastic demand Consumers known to have a unitary elastic demand Save Question 9 (1 point) For a retailer buying from a wholesaler, volume discounts do not violate the Robinson-Patman act because Question 9 options: To sell larger volumes, the retailer himself has to offer discounts To sell larger volumes, the retailer has to incur costs in promoting the item To sell larger volumes, the retailer has to hold the items in inventory longer All of the above Save Question 10 (1 point) With no price discrimination, Question 10 options: A firm sells every unit at different prices A firm sells every unit at same pricesLow-value groups pay a lower price than the high-value groups Low-value groups pay a higher price than the high-value groups Save Question 11 (1 point) The consequences of price discrimination are Question 11 options: Consummate more transactions Extract more consumer surplus Increase producer surplus All of the above Save Question 12 (1 point) For direct price discrimination to work, the firm Question 12 options: Must be able to identify members of the low value group Charge the low-value group lower prices than the rest Prevent the low-value group from reselling their low priced goods to higher-valued group All of the above Save Question 13 (1 point)Which of the following is an example of a “damaged goods” strategy Question 13 options: A supermarket offers free parking space but charges higher for groceries A television reseller spends time making sure that the picture quality of the bargain priced sets is fuzzy A gift store hikes up the prices on gift wrapping services during its seasonal sale All of the above Save Question 14 (1 point) The strategy of sorting customers into high or low value based on the amount of sales made is known as the Question 14 options: Damaged goods strategy The willy-nilly strategy The Metering Strategy All of the above Save Question 15 (1 point) Amusement parks often offer discounts to locals with IDs. This is an example of Question 15 options: A direct discrimination scheme An indirect discrimination schemeDiminishing marginal returns Vertical integration Save Question 16 (1 point) Cooking Wok Value to home users Value to professional Chefs No-name brand $50 $60 High-end professional series $70 $100 Given that the firm offers both the products, what prices can it offer to motivate the two groups to profitably self-sort into buying the correct brand Question 16 options: No-name $60; High-end $100 No-name $50; High-end $100 No-name $50; High-end $90 No-name $60; High-end $90 Save Question 17 (1 point) Public transit offers discounted monthly passes to students, which can only be bought and used with valid student IDs. The transit system is using Question 17 options: A direct discrimination schemeAn indirect discrimination scheme The Robinson-Patman act None of the above Save Question 18 (1 point) Cooking Wok Value to home users Value to professional Chefs No-name brand $50 $60 High-end professional series $70 $100 Given an equal amount of users, if the firm can only set one price, how should the firm price the noname brand wok? Question 18 options: Price low and sell to both the users Price high and sell only to the professional chefs Price low and sell only to the home users All of the above Save Question 19 (1 point) Cooking Wok Value to home users Value to professional Chefs No-name brand $50 $60High-end professional series $70 $100 Given that the firm decides to only offer the high-end wok, what is the highest price it can charge the chefs? Question 19 options: $70 $80 $90 $100 Save Question 20 (1 point) Amusement Park / Cola Tie-in The Six Flags Over Texas amusement part in the middle of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex has a tie-in marketing campaign with Coca-Cola during the summer. In local grocery stores, some Coke cans offer $5 off admission to the park. Why does Six Flags limit these cans so that none are sold further than 20 miles from the park? Question 20 options: They limit this because it allows them to perform direct price discrimination targeting locals. This allows them to offer a lower price to people who live close by and thus have more elastic demand. Those outside the 20 mile radius have less elastic demand and therefore can be charged a higher price. Save [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 15, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 15, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
60