Biology > EXAM > APUS_ERSC181_WEEK_8_FINAL_EXAM 50 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS _96% (All)
APUS_ERSC181_WEEK_8_FINAL_EXAM 50 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS _96%
Document Content and Description Below
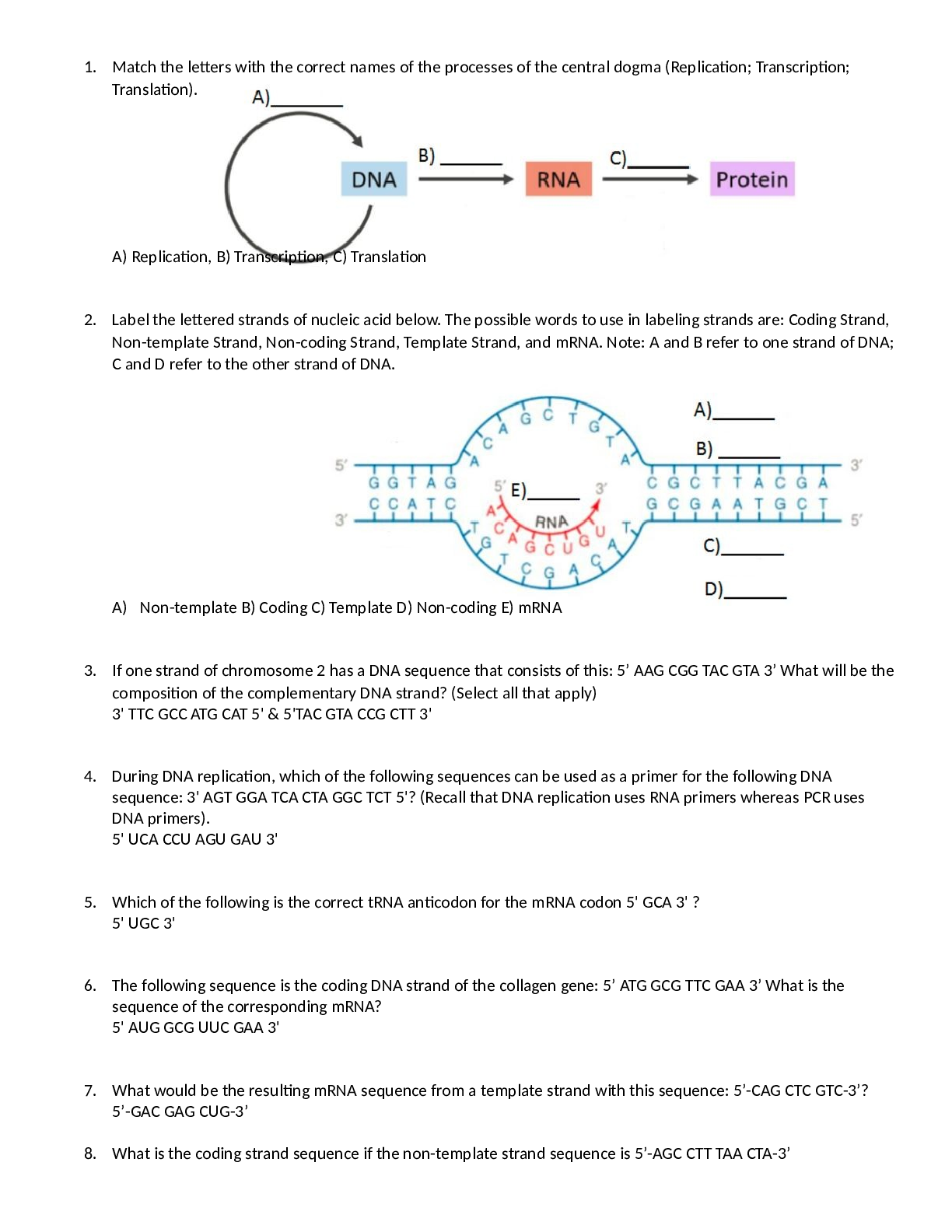
Week 8 Final Exam (timed and single access) Overall Grade (highest attempt): 96 / 100 - 96 % Question 1 2/2 points Pyroclastic flows are more associated with __________. ocean hot spots stratovol... canoes shield volcanoes flood basalts cinder cones Question 2 2/2 points In the rock cycle, what processes directly link igneous rocks to metamorphic rocks? compaction and cementation melting and crystallization deposition and lithification recrystallization by high heat and pressure weathering and erosion Question 3 2/2 points The primary basis for classifying detrital (clastic) rocks is _______, whereas the primary basis for classifying chemical rocks is ________. particle size ; mineral composition rock type ; rounding sorting ; density particle shape ; trace elements crystalline structure ; sorting Question 4 2/2 points The Precambrian Era is the time before abundant multicellular life with hard parts evolved. This time interval represents what percentage of earth's history? 99% 12% 88% 1% 50% Question 5 2/2 points When the radiometric clock starts ticking in zircon minerals, there is only 100% of the unstable radiometric parent isotope X and 0% of the stable daughter isotope Y. After testing in a lab millions of years later, there is 25% of the parent radiometric isotope and 75% of the daughter isotope. How many half lives have elapsed? 1 0.25 3 2 0.5 Question 6 2/2 points In the scientific method, a hypothesis is _______, and a theory is _________. an educated guess ; a law that has been universally accepted by the scientific community an objective observation ; an idea that hasn't been proven an educated guess ; a tentative untested explanation a tentative untested explanation ; well tested and widely accepted explanation a tentative untested explanation ; a law that has been universally accepted by the scientific community Question 7 2/2 points In terms of groundwater resources, what properties make the best aquifer? High porosity and low permeability Low porosity and low permeability High porosity and no permeability Low porosity and high permeability High porosity and high permeability Question 8 2/2 points James Hutton's statement that "the present is the key to the past" (uniformitarianism) is demonstrated by ________. ancient sedimentary rocks formed by similar processes as are observed today the fact that our human ancestors hunted dinosaurs for millennia the volcano that erupted last year on August 15 will occur every 10 years on that date the Earth's landscapes are fixed and have not changed gravity being a recent phenomenon and not changing metamorphic rocks in the past Question 9 2/2 points Applying the principles of relative age-dating to the diagram, which of the following is TRUE. Explanation of the diagram: "A" represents an unconformity (erosional surface), "B" is a basaltic dike, "C" is a shale formation, "D" is a sandstone formation, "E" is a limestone formation, "F" represents a thrust fault. D is YOUNGER than C F is YOUNGER than A A is YOUNGER than C B is OLDER than F E is OLDER than B Question 10 2/2 points Which of the following surficial processes results in the most poorly sorted sediments? wind deep marine glaciers ocean waves rivers Question 11 2/2 points The map below shows continental land as green and brown, the depth of the ocean floor in blue, and tectonic plate boundaries as colored lines. Evaluate this geologic evidence to determine which location would most likely require adequate tsunami preparedness. D A B C Question 12 2/2 points Where is the top of the asthenosphere closest to the earth's surface? Underneath a collision zone Next to a subduction zone In the center of continental plates (craton) Underneath a mid-ocean ridge Underneath a transform fault Question 13 2/2 points The number one factor causing landslides is (are) _____. earthquakes freeze-thaw cycles precipitation volcanic eruptions glaciation Question 14 2/2 points What evidence did Alfred Wegener use for his hypothesis of continental drift? similar rocks and fossils on distant continents earthquake patterns and GPS measurements paleomagnetic patterns on either side of the mid-oceanic ridge trenches and subduction zones mid-oceanic ridges and the age marine rocks Question 15 2/2 points Scientific conclusions are based on _____________. polling of experts public consensus subjective evidence and ancient books objective evidence and experiments only quantitative data Question 16 2/2 points Folds like anticlines and synclines are most associated with _______. Tectonic compression Tectonic shear Tectonic extension Volcanism Erosion Question 17 2/2 points Shield volcanoes consist of _________. Explosive pyroclastic material and low viscosity lava flows. Alternating layers of cinders and ash embedded in silica-rich lava flows. A combination of granitic lava and pyroclastic material with some rhyolite. Mostly low viscosity basalt flows with a lower silica content. Alternating layers of silica-rich rocks and intrusive igneous rocks such as basalt. Question 18 2/2 points Which best explains the processes at the mid-oceanic ridge? Plates converge creating new crust Plates diverge creating new crust Plates diverge destroying old crust Plates converge destroying old crust Plates slide past each other destroying old crust Question 19 2/2 points Where would you expect both shallow and deep earthquakes in which the deeper earthquakes are located farther inland? At a divergent plate boundary in the middle of a continental plate such as Africa's Great Rift Valley. At a divergent plate boundary in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. At a convergent plate boundary such as along the west coast of South America. At a transform boundary along the San Andreas fault in California. At a transform plate boundary anywhere in the world. Question 20 2/2 points Which type of faulting is most dangerous in Utah? Normal Strike-slip Thrust Reverse Transform Question 21 2/2 points When going from a magnitude 5 to a magnitude 6 earthquake on the Richter magnitude scale, what is the increase in seismic wave amplitude? 10 100 2 0.5 1 Question 22 2/2 points Refer to the image of a meandering stream shown here. At which site along the stream would stream erosion be the most active? D and B A and C B and C C and D A and E Question 23 2/2 points Which of the following is the most significant natural cause of climate change in the last 2 million years? Photosynthesis Burning of fossil fuels Solar flares Volcanic eruptions Milankovitch cycles Question 24 2/2 points A coarse-grained (phaneritic texture) igneous rock formed _________________. by immense direct pressure and heat on the surface of the earth in an explosive eruption on the surface of the earth in a quiet (effusive) eruption due to erosion, frost wedging, and weathering deep under the surface of the earth Question 25 2/2 points What information is needed to determine the distance from the epicenter of an earthquake to a seismic receiving station? The time interval between the P and S waves The difference between the amplitude of the seismic waves The amplitude of the seismic waves on a seismogram The magnitude of the earthquake The transverse nature of the s-wave Question 26 2/2 points Where do we generally find the most quantity of explosive volcanic eruptions? Divergent plate boundary Mid-oceanic ridges Subduction zone boundary Transform plate boundary Ocean island hotspots Question 27 2/2 points Which mineral property is essentially a measure of how tight the atoms are packed together? Hardness Color Magnetism Luster Streak Question 28 2/2 points Which is always the next step in the rock cycle after cooling magma? Crystallization Weathering Heat and pressure Deposition Erosion Question 29 2/2 points Which is the process that CREATES sediments from previously formed rocks? Erosion Cementation Deposition Compaction Weathering Question 30 2/2 points When comparing the protolith to the metamorphic rock that was formed after metamorphism, the chemical composition of the protolith is usually ______________ when compared to the metamorphic rock. lower in carbonate higher in carbonate about the same lower in silica higher in silica Question 31 2/2 points Which step in the rock cycle always has to be directly before sedimentary rocks in order for them to form? Melting Heat and pressure Crystallization Deposition Cooling Question 32 2/2 points As a subduction zone closes, destroys, and puts an end to an ocean basin, which plate tectonic boundary is likely to develop at the location of a former subduction zone? Hot spot Continental Collision Continental rift Mid-ocean ridge Transform fault Question 33 2/2 points Which type of magma produces slow-moving lava flows, explosive eruptions, steep-sided volcanoes, and typically granitic rocks? High pressure Shallow-forming High temperature Deep-forming High silica Question 34 2/2 points As a continental rift continues to open wider and wider, which plate tectonic boundary is likely to develop at that location? Subduction zone Transform fault Continental collision Hot spot Mid-ocean ridge Question 35 2/2 points Mafic minerals, as a group, are known for what property? Lacking cleavage Low density High hardness Pearly luster Dark color Question 36 2/2 points Metamorphic rocks are formed by ___________. heat and pressure weathering and erosion uplift and burial melting and crystallization compaction and cementation Question 37 2/2 points What element is the building block of the majority of minerals, especially the common rock-forming minerals? Hydrogen Carbon Calcium Sulfer Silicon Question 38 2/2 points Which is the process that glues sediments together, helping them turn into rocks? Weathering Erosion Cementation Compaction Deposition Question 39 2/2 points What two things are you usually trying to figure out when looking at metamorphic facies and a series of index minerals in a metamorphic rock? Protolith and temperature Pressure and cooling history Temperature and pressure of formation Speed of heating and protolith Fluid composition and protolith Question 40 2/2 points At subduction zones, magma is generated by _________________, while most other environments (e.g. hot spots, divergent) produce magma by __________________. adding volatiles ; decompression melting decompression melting ; adding volatiles decompression melting ; adding volatiles compression melting ; decompression melting adding volatiles ; compression melting Question 41 2/2 points Which fossil fuel is typically composed of higher alkanes such as methane? swamp gas oil coal natural gas Question 42 2/2 points Hydrothermal processes are most likely involved in the formation of which set of resources? coal and petroleum zinc, lithium, and tantalum. zinc, gold, and chromite zinc, salt, and gold Question 43 0/2 points Oil, gas, and coal are fossil fuels that provide over 90% of our energy needs in the United States. What makes these resources different from others such as nickel, iron, salt, or gypsum? They are more scarce than any other resource. They take millions of years to form. They form from hydrothermal processes They form from previous life forms like plants or microscopic organisms. Question 44 2/2 points Which of the following set of resources would be the least sustainable? solar, wind, and hydro solar, nuclear, and natural gas oil, coal, and nuclear oil, natural gas, and coal Question 45 2/2 points Buried and decomposed terrestrial plant life are more likely to become ________. future natural gas reserves. future coal reserves. future oil reserves. future uranium reserves Question 46 0/2 points Which of the following is a hypothesis for the formation of life on Earth? Brought to Earth from Mars Atmospheric processes around volcanoes Atmospheric processes around seawater Atmospheric processes around lightning Evaporation around seawater Question 47 2/2 points This time period is known for: first hard parts, a huge evolutionary explosion of diversification, first chordates. The abundance of fossils starting here is so different from older rocks, that the older rocks are all lumped together. What is the name of this time period? Cambrian Permian Jurassic Anthropocene Question 48 2/2 points What age are most of the Earth's cratons? Archean Mesozoic Proterozoic Paleozoic Question 49 2/2 points What was the definitive event that killed the dinosaurs? Meteorite impact in Mexico Volcanic eruptions in India Cold and glaciers in Gondwana Lowering sea level worldwide Question 50 2/2 points What important evolutionary advance did NOT occur in the Paleozoic? First trees First shells First mammals First jaws [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 03, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 03, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
85








.png)
.png)










