*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NSG 6001 100% exam solution possible questions and answers 2020 (All)
NSG 6001 100% exam solution possible questions and answers 2020
Document Content and Description Below
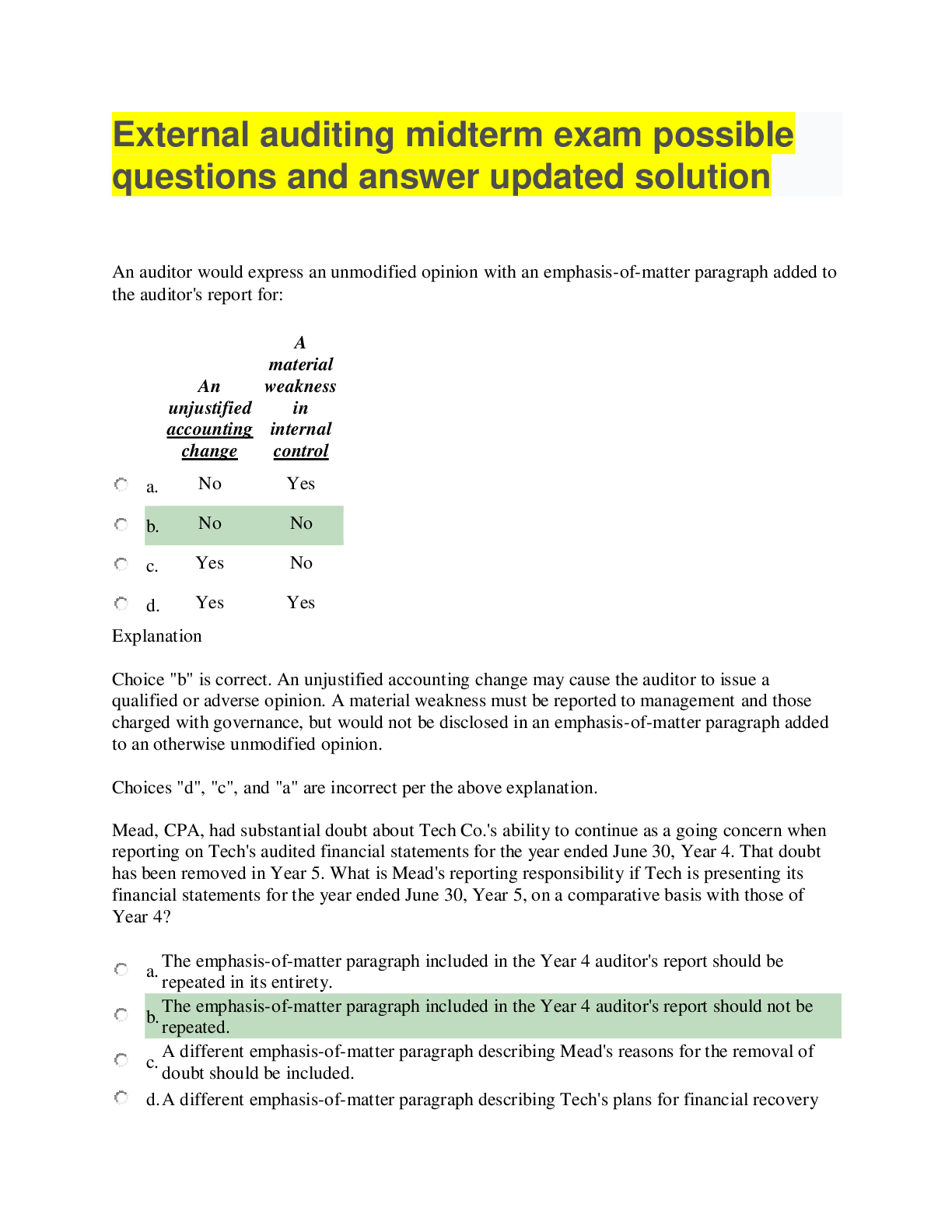
NSG 6001 100% exam solution possible questions and answers 2020 MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A patient is 66 inches in height, weighing 200 lbs, and newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). T... he A1c is 7.1%. What is the best initial treatment? A. No treatment at this time B. Diet and exercise C. Diet, exercise, and metformin D. Diet, exercise, and exogenous insulin 2. The clinician suspects that a patient seen in the office has hyperthyroidism. Which test should the clinician order on the initial visit? A. Sensitive thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) assay and T4 B. Free T4 and serum calcium C. Nuclear scintigraphy with radiolabeled iodine (123I) D. Magnetic resonance imaging 3. Which statement made by a patient with type 1 diabetes indicates successful teaching regarding general guidelines for exercise? A. “I will not exercise if my blood sugar is 315.” B. “I should just check my blood glucose after exercise.” C. “I should eat more carbohydrates if my blood glucose is less than 200.” D. “I will exercise when my urine ketones are positive but blood sugar is 260.” 4. A male patient with type 1 diabetes comes to the clinic complaining of feeling nervous and clammy. He states that he took his insulin this morning but was late for work and did not eat breakfast. Which action should the clinician take first? A. Administer glucagon subcutaneously. B. Have him drink 4 ounces of juice. C. Call 911. D. Ask him about his usual eating habits. 5. A patient with type 2 diabetes comes to the clinic after reading about metformin in a magazine. Which condition that the patient also has would be a contraindication to taking metformin? A. Ulcerative colitis B. Inflammatory bowel disease C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease D. Renal disease 6. A 25-year-old patient presents to the clinic with fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain, and constipation for the past 3 months. On physical examination, the clinician notices muscular stiffness; coarse, dry hair; and a delay in relaxation in deep tendon reflexes. Which test should be ordered next? A. Serum calcium B. Thyroid-stimulating hormone C. Electrolytes D. Urine specific gravity 7. The clinician has been doing diabetic teaching for a patient with type 1 diabetes with no retinopathy. Which statement by the patient would indicate that teaching has been effective? A. “As long as I don’t need glasses, I don’t have to worry about going blind.” B. “I know I need to have my eyes checked every 2 years.” C. “My primary doctor will check my eyes.” D. “I will see my eye doctor when my vision gets blurry.” 8. A 64-year-old man with type 2 diabetes presents to the clinic with the complaint of “my feet feel like they are on fire.” He has a loss of vibratory sense and +1 Achilles reflex. Which of the following would be an appropriate treatment? A. Tricyclic antidepressants B. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors C. Aspirin D. Insulin 9. After removing a tack from a type 2 diabetic’s heel and evaluating the site for infection, what is the best plan for this patient? A. Suggest the patient use a heating pad to improve circulation. B. Refer to a podiatrist for a foot-care treatment plan. C. Send the patient for acupuncture treatments. D. Recommend increased intake of vitamin B12. 10. Joyce is seen in the clinic complaining of vague symptoms of nervousness and irritability. She is also having problems sleeping at night. On physical examination, the clinician finds an irregular heartbeat and hyperactive reflexes. The differential diagnosis should include which condition? A. Myxedema B. Thyrotoxicosis C. Cushing’s syndrome D. Pan-hypopituitarism 11. The patient is prescribed radioactive iodine (RAI) and asks the clinician how this drug works. The clinician’s response should include which information? A. RAI prevents the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3. B. RAI binds free T4. C. RAI destroys thyroid tissue. D. RAI reduces freely circulating iodine. 12. A patient is diagnosed with hypothyroidism. Which electrocardiogram change should the clinician observe as a manifestation of the disease? A. Sinus bradycardia B. Atrial fibrillation C. Supraventricular tachycardia D. U waves 13. After 6 months of Synthroid therapy, the clinician should expect which result in the repeat thyroid-stimulating hormone studies? A. Elevated B. Normal C. Low D. Undetectable 14. Which laboratory finding should the clinician observe in a patient with untreated Graves’ disease? A. Elevated TSH B. Decreased T3 C. Decreased TSH receptor antibody test D. Elevated antithyroglobulin antibodies 15. The clinician prescribes glipizide (Glucotrol) for a diabetic patient. Which statement made by the patient would indicate teaching has been effective? A. “I’ll take my pill before breakfast.” B. “I know to take my Glucotrol at bedtime.” C. “It is important to take my medication right after I eat.” D. “Since I only like to eat two meals a day, I can take the pill between my meals.” 16. A male patient with diabetes asks the clinician why he needs to check his blood sugar at home even when he feels good. Which response by the clinician would be most appropriate? A. “Control of glucose will help postpone or delay complications.” B. “Regularly checking blood sugar will help you.” C. “Monitoring glucose will promote a sense of connectedness.” D. “Because you know it is the right thing to do for your disease.” 17. How often should the clinician examine the feet of a person with diabetes? A. Every year B. Every 6 months C. Every 3 months D. Every visit 18. The clinician sees a patient who has a body mass index (BMI) of 32.4 kg/m2. How would the clinician classify this patient? A. Overweight B. Obesity Class 1 C. Obesity Class 2 D. Obesity Class 3 19. Mr. S presents in the clinic with pain, tenderness, erythema, and swelling of his left great toe. The clinician suspects acute gout. Which of the following should the clinician expect in the initial test results for this patient? A. Elevated uric acid level B. Elevated blood urea nitrogen C. Decreased urine pH D. Decreased C-reactive protein 20. Which blood test would confirm a diagnosis of diabetes mellitus? A. A1c 5.5% B. Fasting plasma glucose level of 120 mg/dL C. Oral glucose tolerance test 250 mg/dL (2-hour level) D. Random plasma glucose level 175 mg/dL 21. Which test should the clinician order to confirm Charcot foot? A. Bone scan of lower extremities B. Computed tomography (CT) scan C. X-ray of the foot D. Culture of the foot ulcer 22. A vegetarian patient with gout asks the clinician about foods to avoid. The clinician should advise the patient to avoid which of the following foods? A. Rice B. Carrots C. Spinach D. Potatoes 23. The clinician should question the patient with suspected gout about use of which of these medications? A. Antihypertensives B. Thiazide diuretics C. Cardiac glycosides D. Potassium supplements 24. The clinician finds numerous nodules on the thyroid of a 65-year-old woman. The clinician suspects thyroid cancer. Which data would be most significant for this patient? A. A history of enlarged tonsils in the 1940s B. Recent exposure to mumps C. Vegetarian diet D. Allergy to iodine 25. Which of the following is essential for diagnosing thyroid cancer? A. Fine needle aspiration biopsy B. Thyroid ultrasound C. Computed tomography scan D. Magnetic resonance imaging 26. Which of the following is a common sign of type 2 DM? A. Anorexia B. Recurrent yeast infection C. Fluid overload D. Elevated high-density lipoprotein cholesterol 27. Which medication can cause hyperglycemia? A. Prednisolone (Omnipred) B. Metformin (Glucophage) C. Levothyroxine (Synthroid) D. Cephalexin (Keflex) 28. Which laboratory test result is diagnostic for hypoglycemia? A. A1c 7.0% B. Fasting blood sugar of 75 mg/dL C. Glucose level 43 mg/dL D. Random glucose level 64 mg/dL 29. Which medication for type 2 diabetes mellitus would be contraindicated during pregnancy? A. Insulin B. Metformin (Glucophage) C. Glipizide (Glucotrol) D. Acarbose (Precose) 30. A 35-year-old woman presents with symptoms of hypoglycemia. There is no history of diabetes mellitus. Which condition should be included in the differential diagnosis? A. Peripheral vascular disease B. Pheochromocytoma C. Cushing’s disease D. Acromegaly 31. Which action would the clinician take to elicit Chvostek’s sign? A. Check serum level of glucose after drinking a glass of juice. B. Tap the facial nerve below the zygomatic arch anterior to the earlobe. C. Press into the lower quadrant of the abdomen and release quickly. D. Pump a blood pressure cuff 20 mm Hg above the patient’s systolic pressure. 32. The clinician should examine which area for gynecomastia? A. Female’s vagina B. Male’s breast C. Male’s penis D. Female’s ovaries 33. Which slightly elevated laboratory result would the clinician observe in a patient with idiopathic hirsutism? A. Free testosterone B. Luteinizing hormone (LH)/follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) C. Serum calcium D. Albumin 34. The clinician is assessing for the most common cause of increased neck size. Which area would the clinician exam? A. Salivary glands B. Lymph nodes C. Thyroid D. Trachea 35. Which “P” is a component of “the 3 P’s” of diabetes mellitus? A. Pain B. Paresthesia C. Pallor D. Polyphagia 36. A woman presents with new-onset hoarseness with hemoptysis. For which condition should the clinician focus an examination? A. Hyperthyroidism B. Pheochromocytoma C. Cushing’s syndrome D. Thyroid cancer 37. Which statement by the patient would indicate teaching has been successful regarding management of Cushing’s syndrome at home? A. “I will take cortisone on an empty stomach.” B. “I will stay away from large crowds.” C. “I will maintain a low-protein diet.” D. “I will avoid foods high in potassium.” 38. The patient presents to the clinic with a “buffalo hump,” weight gain, easy bruising, and hyperpigmentation. Which initial diagnostic test should the clinician order? A. 1 mg overnight dexamethasone suppression test B. Abdominal computer tomography scan C. RAI uptake testing D. Early-morning salivary cortisol 39. The clinician suspects a patient has Addison’s disease. Which clinical manifestation would the clinician observe upon a physical examination? A. Moon face B. Central obesity C. Hyperpigmentation D. Myxedema coma 40. Which hydrocortisone dose would the clinician prescribe for a patient with Addison’s disease? A. 25 to 50 mg daily B. 0.5 to 0.2 mg daily C. 20 mg in the morning and 10 mg in early evening D. 2 to 4 mg in the morning and 1 to 2 mg in the evening 41. The patient with type 1 diabetes is exhibiting Kussmaul respirations, anorexia, fatigue, and increased thirst. Which condition should the clinician manage? A. Hypoglycemia B. Somogyi effect C. Diabetic ketoacidosis D. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome 42. The patient has hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome. Which laboratory findings would the clinician observe? A. Plasma bicarbonate 8 mEq/L B. Blood glucose level 40 mg/dL C. Serum osmolality 420 mOsm/kg D. Blood pH 7.20 43. Which question should the clinician ask to determine the most frequent cause of diabetic ketoacidosis? A. “How often are you taking the insulin?” B. “Which type of infection have you experienced recently?” C. “What type of diet have you been following?” D. “Is there any reason you don’t like taking your medications?” 44. A patient with type 1 diabetes has diabetic ketoacidosis. Which first-line treatment should the clinician prescribe? A. NPH insulin B. Regular insulin C. IV normal saline D. Thiazolidinedione 45. A nondiabetic patient has idiopathic hypoglycemia. Which dietary instruction should the clinician share with the patient? A. Follow a low-protein, high-carbohydrate diet B. Allow caffeine at each meal C. Avoid nuts and seeds D. Eat six small meals a day 46. The clinician is using the HALT acronym to help a patient identify overeating triggers. What does the “T” represent? A. Tired B. Tense C. Temper D. Threats 47. The patient weighs 350 lbs and is on a weight loss program. After 6 months, which ideal weight in pounds should the clinician observe? A. 335 B. 325 C. 315 D. 305 48. Which instruction should the clinician include in patient teaching regarding management of obesity? A. Occasionally skipping meals is acceptable. B. Try to use nonstick cookware when baking or frying. C. High-intensity physical activity is recommended. D. Exercise for about 100 minutes per week. 49. The patient has metabolic syndrome. The patient is at increased risk for which condition? A. Anxiety disorder B. Gallbladder disease C. Diabetes mellitus D. Hyperparathyroidism 50. A 45-year-old male presents with throbbing podagral pain and tophi in the ear pinnae. Which medication should the clinician prescribe for this acute attack? A. Colchicine (Colcrys) B. Probenecid (Benemid) C. Allopurinol (Zyloprim) D. Pegloticase (Krystexxa) [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 03, 2020
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 03, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
64