*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PN1 Exam 2 Review -Questions and Answers-Rasmussen College. 2022/2023 update (All)
PN1 Exam 2 Review -Questions and Answers-Rasmussen College. 2022/2023 update
Document Content and Description Below
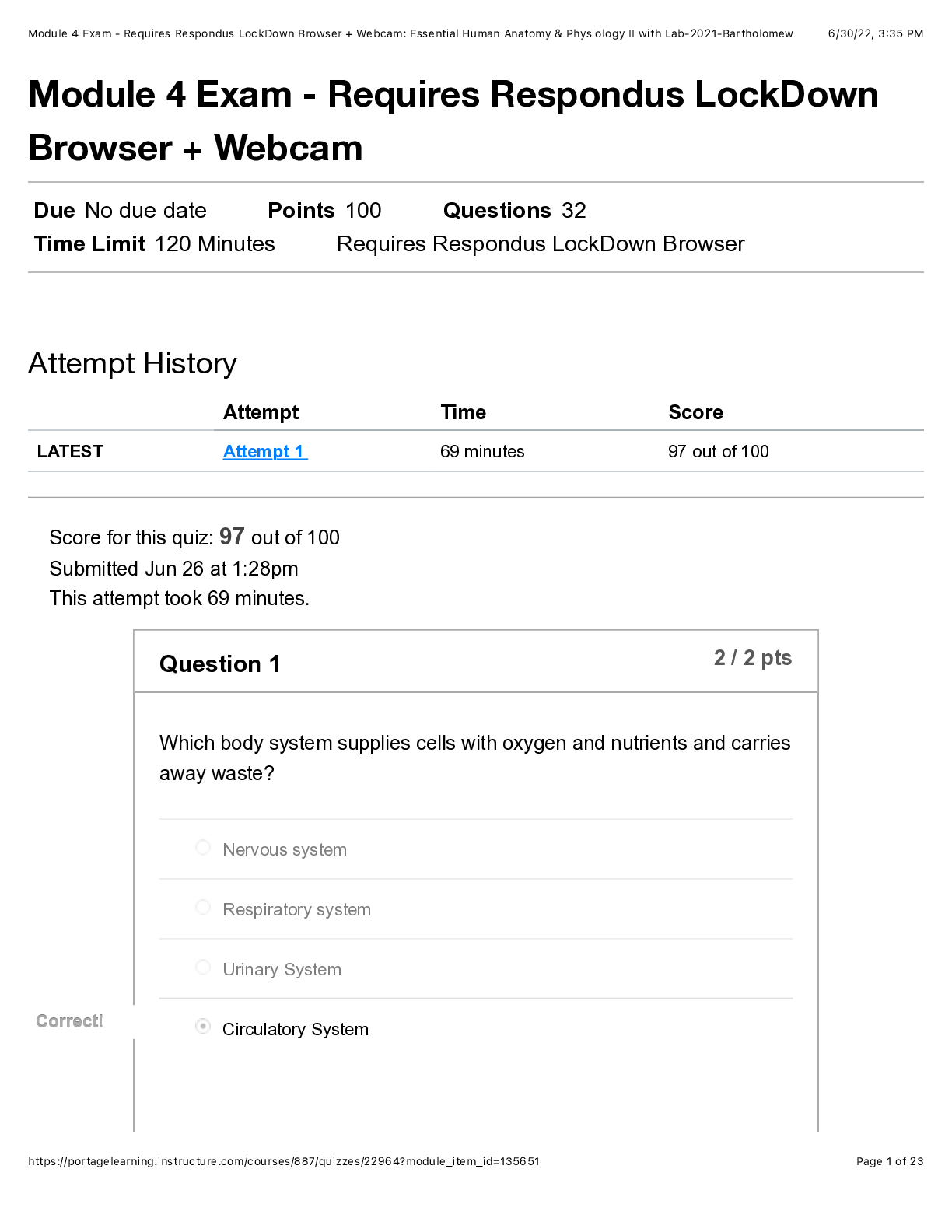
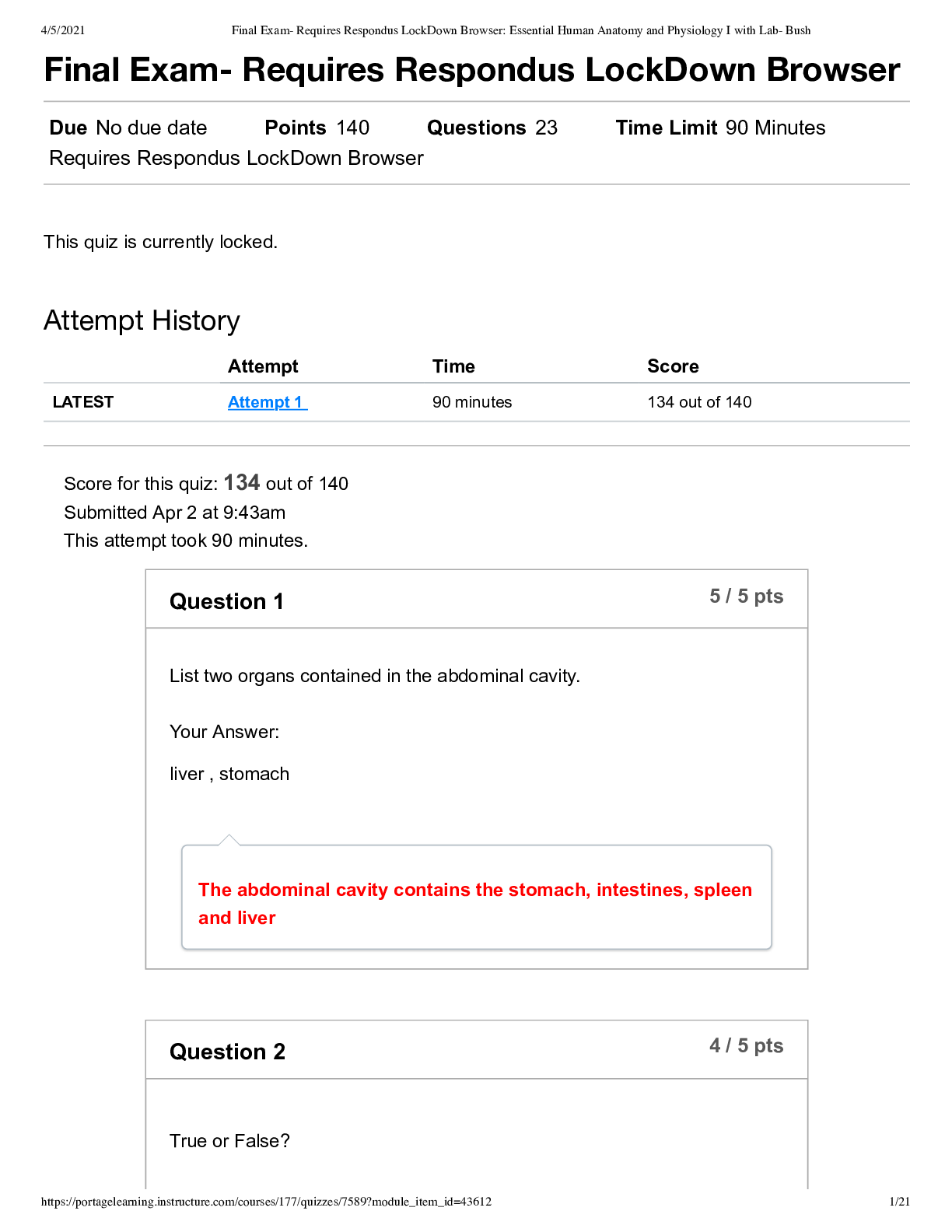
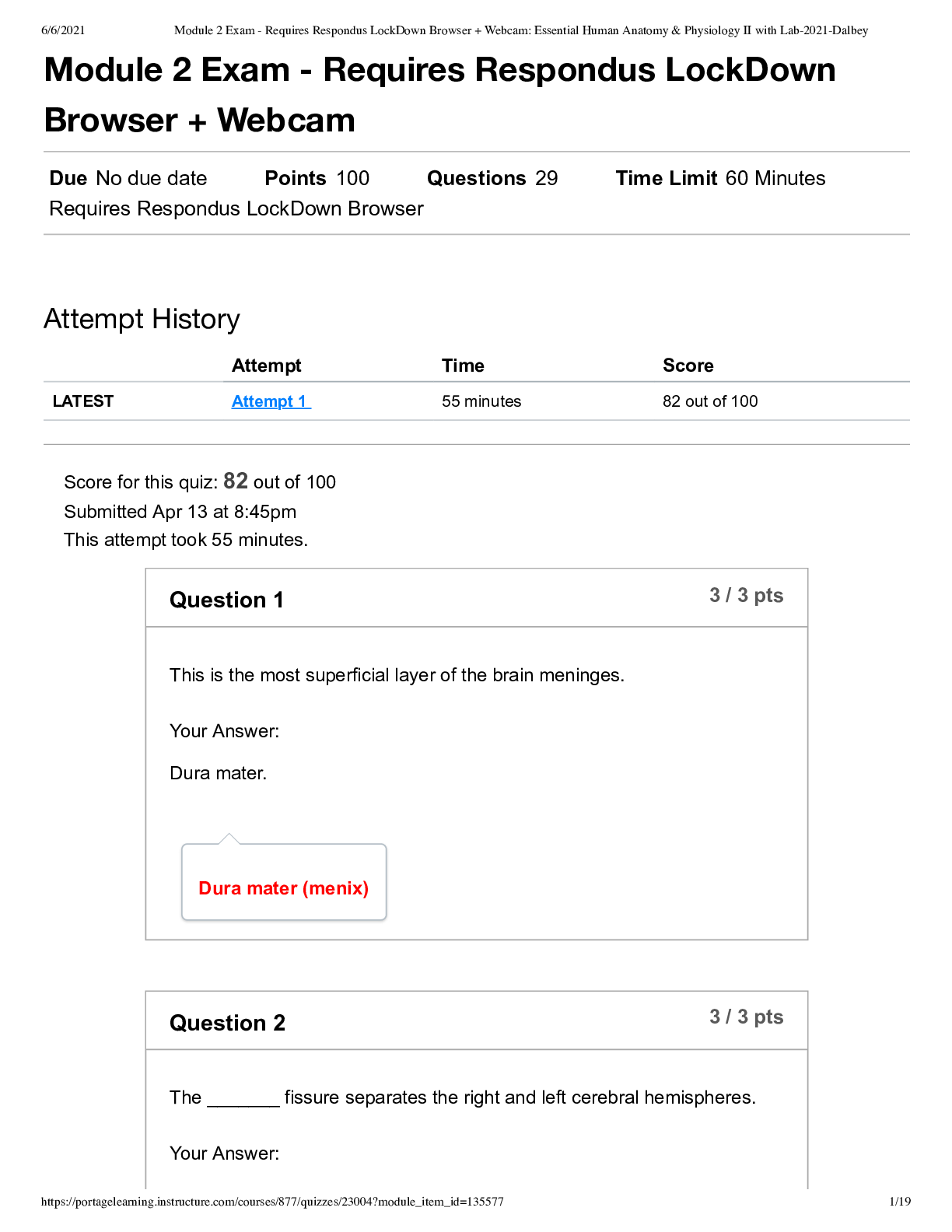
PN1 Test 2 Review 1. The most accurate information concerning a client’s pain comesfrom the nurse’s assessment or the client? Information from the client Is objective orsubjective data more imp... ortant? Subjective When objective and subjective data about a client’s pain are in conflict, which report should the nurse consider as the primary source? Pain is always subjective “subject says”. 2. When administering pain medication, is it the most appropriate to administer the minimum dose and reevaluate the client’s pain after 30 minutes or administer the highest pain medication dosage to ensure the client’s pain is relieved? If BP is slow,start low. If patient comes out ofsurgery and pain is an 8 pushing the max dose is at the nurses discretion. 3. What physiological changes can occur when a client is in acute pain? - BP, Resp Rate, Pulse - Dilated Pupils - Perspiration (Diaphoresis/sweating) - Pallor (pale skin) How can a nurse assess a non-verbal client for pain? Wong Baker Face Scale, or non-verbal cues (grimacing, rolling on bed, fetal position). What isthe difference between pain quality and intensity? Quality = Type (sharp, dull, stabbing, numb) Intensity = How bad it hurts (scale of 1-10) 4. What are the signs of a client in chronic pain? - Lasts over 6 months - Persistent - Constant/recurrent - Produces negative changesin life (withdrawn, frail) - Body adapts (moves slowly to avoid movement of painful areas) - Needs reg assessment & diff approach to treatment 5. What is the gate control theory? Things other than medications can help relief pain (communication ie. Saying someone will be okay and rubbing their backs, therapy, acupuncture) 6. Review hypertension stepped-care approach, food with elevated sodium levels, know which ethnic group tends to develop hypertension earlier in life. African Americans are higher risk, change in lifestyle & diet first, then diuretics (which eliminate water from the body by passing urine more frequently). 7. Review the difference between primary (essential) hypertension and secondary hypertension. PN1 Test 2 Review (Cont.) 2 - Primary Hypertension: More common, is the in BP due to unknown causes - Secondary Hypertension: Rarer, renal or endocrine disease process that results in BP Which type is rarer? Secondary 8. What mm/hg is normal for blood pressure? 120/80 What are palpitations? Heart is racing, pounding, fluttering, skipping a beat often, bothersome but rarely a sign of heart attack. What is the “fifth” vitalsign? - Body temperature - Pulse - Respirations - Blood Pressure - Pain 9. Review the Joint Commissionsstandards related to pain management. Each client’s pain must be treated individually due to different interpretations of pain and different goals of pain relief. Do previous experiences, cultures, age, poverty level, or educational level affect a client’s pain experience? (Which ones do not?) Education level & poverty level do not. 10. Do older clients fear being labeled as “complainers” and avoid requesting medications? They often live with the pain in fear of being labeled as a complainer or a bother, nurse should encourage to request pain relief when needed. 11. Know about the normal vital signs and morphine dosage range. Normal= 12 RR Below 8-10 they will get Narcan (reverses) Be able to decide if a pain medication can be given based upon the client’s vital signs and physicians order. Always by Physicians order Would breathing changes,such as Cheyne-Stokes pattern prevent you from administering the client’s pain medication if their vital signs are normal? Cheyne-Stokes-> increase, decrease, then temporary stop in breathing (ie. Sleep apnea) Probably not but monitor closely. 12. Are clients who are able to gain pain relief able to function normally and comfortably? Yes, don’t chase the pain. 13. When using the SBAR technique for telephone communication, information in the S (situation) should include the nurse’s name, the client name, the circumstances leading up to the call. PN1 Test 2 Review (Cont.) 3 What does the BAR include? -S: Situation (Nurses name, PT name, circumstances leading to event) -B: Background -A: Assessment -R: Recommendation Scenario 1: An RN on the Medical Floor has an order for a patient to receive an exam that requiresIV contrast. The patient’s creatinine level is 2.9. The ordering physician needs to be called to clarify this order. 1. Situation: “Dr. Smith, this is Darlene on Med/Surg at OMH. I have an orderfor a PE study for Mr. Marino. His creatinine is elevated and I wanted to clarify the order with you.” 2. Background: “Isee that Mr. Marino came into the ED with right-sided chest pain and difficulty breathing. The CT for rule-out PE was ordered.” 3. Assessment: “Mr. Marino’s creatinine level is 2.9, far above the allowable level for a rule-out PE study.” 4. Recommendation: “I think that the ordershould be changed from a CT for rule-out PE to an order for a VQ scan.” 14. What are the definitions of inflammation and/or infection? Inflammation- Body attempting to rally (blood rushesto inflamed area). Infection- Invader is stronger than the host. The infection overpowers the body such as a “war”. How do inflammation and infection differ? What are the signs of each? Inflammation- Nonspecific, in CRP (c-reactive protein), cellular response to tissue injury, redness, pain, swelling and pus, heat, loss of function NOT sensation. Infection- WBC (white blood count) 15. What is RICE? How is this utilized within the first 72 hours of an injury, especially when pain and edema are present? (Soft tissue injuries mostly) -R: Rest -I: Ice (24-72 hours, controls Edema) -C: Compression -E: Elevation 16. Be able to name some common infections. MRSA, UTI, Syphilis PN1 Test 2 Review (Cont.) 4 - Bacterial (can be cured with antibiotics): Diarrhea, pneumonia,sinusitis, UTI, cellulitis, meningitis, gonorrhea, otitis media, & impetigo. - Viral (cannot be cured, but maintained): Influenza, Measles, common cold, Chicken Pox, Hep B, Genital Herpes, & HIV. 17. What is disinfection? Elimination of pathogens aka. germs (not sores) from inanimate objects with disinfectants & germicides. 18. What issterilization? Total elimination of microorganisms from instruments and other supplies used. Ie. Surgery, sterile, kills the spores. 19. What is antiseptic technique? Disinfection Which one is used to eliminate pathogens, except spores, from inanimate objects? Disinfection Which one is used to prevent the transmission of pathogens? Sterilization 20. What are some types of barrier protection? Gloves, gown, masks, face shields, shoe covers… What isstandard, contact, droplet, airborne, and neutropenic precautions? - Contact: Used for infections, diseases, or germs that are spread by touching the patient or items in the room (MRSA, VRE, open wounds, RSV, diarrheal illnesses). - Droplet: Used for diseases or germs that are spread in tiny droplets caused by coughing and sneezing (Pneumonia, Influenza, Whooping Cough, Bacterial Meningitis). - Airborne: Used for diseases or very small germs that are spread through the air from one person to another (Tuberculosis, Measles, Chickenpox). - Neutropenic: Wash hands often, bathe daily, brush teeth 2 times a day, do not share personal items with anyone. It is a condition that causes you to have low neutrophils (a type of WBC that helps your body fight infection and bacteria) in your blood. What protective equipment is required for each? - Standard: Hand hygiene & gloves. - Contact: Hand hygiene, gown (used for contact patients), & gloves. - Droplet: Hand hygiene, gown (used for contact patients), gloves,surgical mask within 3ft of patient. - Airborne: Hand hygiene, gown, gloves, particulate respirator, & possibly a negative pressure room N-95. 21. Should clients always be taught to take all of their antibiotics as prescribed? Why is this important? PN1 Test 2 Review (Cont.) 5 Yes, to make sure all of the bacteria is killed, and the infection doesn’t return. 22. What is a superinfection? A previously infected cell gets co-infected with a diff strain of the virus (or another virus) later in time. Ie. Fungal infection or CDiff What causes a superinfection? Not cleaning the environment thoroughly or properly (germs willsit, collect, & mutate over time). What isthe most effective way to decrease the spread of infection? Disinfecting properly and often, & HAND HYGIENE. 23. What factors related to aging places older clients at risk for infections? Slower immune systems, skin integrity (get older, work slower) 24. Can nurses orderspecific pain medications for a client, or is ordering [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 09, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 09, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
176

.png)