Pharmacology > EXAM > Adv Pharm FINAL EXAM TxTBk Woo Answrs (All)
Adv Pharm FINAL EXAM TxTBk Woo Answrs
Document Content and Description Below
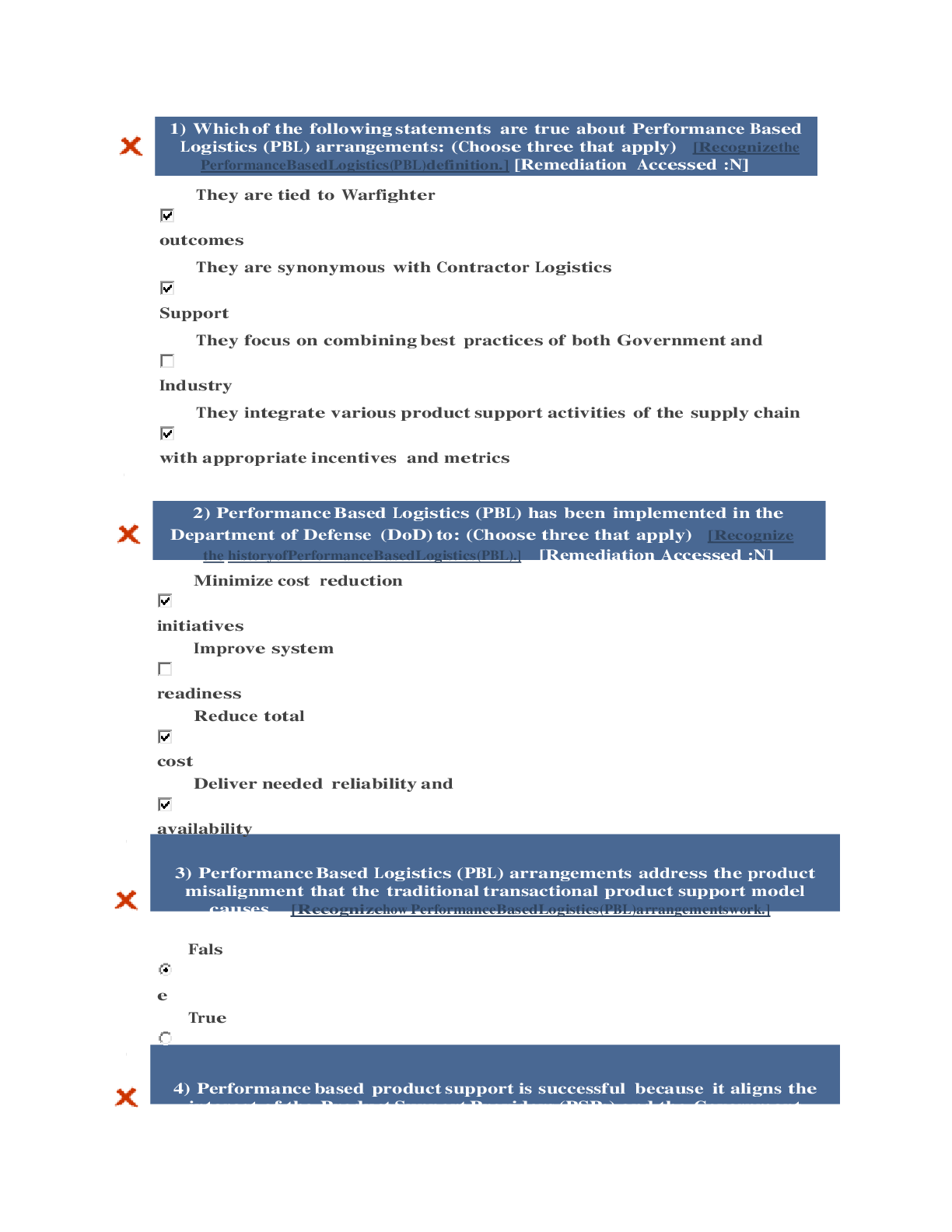
Adv Pharm FINAL EXAM TxTBk Woo Answrs Chapter 1. The Role of the Nurse Practitioner 1. Nurse practitioner prescriptive authority is regulated by: 2. The ... benefits to the patient of having an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) prescriber include: 3. Clinical judgment in prescribing includes: 4. Criteria for choosing an effective drug for a disorder include: 5. Nurse practitioner practice may thrive under health-care reform because of: Chapter 2. Review of Basic Principles of Pharmacology 1. A patient’s nutritional intake & laboratory results reflect hypoalbuminemia. This is critical to prescribing because: 2. Drugs that have a significant first-pass effect: 3. The route of excretion of a volatile drug will likely be the: 4. Medroxyprogesterone (Depo Provera) is prescribed intramuscularly (IM) to create a storage reservoir of the drug. Storage reservoirs: 5. The NP chooses to give cephalexin every 8 hours based on knowledge of the drug’s: 6. Azithromycin dosing requires that the first day’s dosage be twice those of the other 4 days of the prescription. This is considered a loading dose. A loading dose: 7. The point in time on the drug concentration curve that indicates the first sign of a therapeutic effect is the: 8. Phenytoin requires that a trough level be drawn. Peak & trough levels are done: 9. A laboratory result indicates that the peak level for a drug is above the minimum toxic concentration. This means that the: 10. Drugs that are receptor agonists may demonstrate what property? 11. Drugs that are receptor antagonists, such as beta blockers, may cause: 12. Factors that affect gastric drug absorption include: 13. Drugs administered via IV: 14. When a medication is added to a regimen for a synergistic effect, the combined effect of the drugs is: 15. Which of the following statements about bioavailability is true? 16. Which of the following statements about the major distribution barriers (blood-brain or fetal-placental) is true? 17. Drugs are metabolized mainly by the liver via phase I or phase II reactions. The purpose of both of these types of reactions is to: 18. Once they have been metabolized by the liver, the metabolites may be: 19. All drugs continue to act in the body until they are changed or excreted. The ability of the body to excrete drugs via the renal system would be increased by: 20. Steady state is: 21. Two different pain medications are given together for pain relief. The drug—drug interaction is: 22. Actions taken to reduce drug—drug interaction problems include all of the following EXCEPT: 23. Phase I oxidative-reductive processes of drug metabolism require certain nutritional elements. Which of the following would reduce or inhibit this process? 24. The time required for the amount of drug in the body to decrease by 50% is called: 25. An agonist activates a receptor & stimulates a response. When given frequently over time, the body may: 26. Drug antagonism is best defined as an effect of a drug that: 27. Instructions to a client regarding self-administration of oral enteric-coated tablets should include which of the following statements? 28. The major reason for not crushing a sustained-release capsule is that, if crushed, the coated beads of the drugs could possibly result in: 29. Which of the following substances is the most likely to be absorbed in the intestines rather than in the stomach? 30. Which of the following variables is a factor in drug absorption? 31. An advantage of prescribing a sublingual medication is that the medication is: 32. Drugs that use CYP 3A4 isoenzymes for metabolism may: 33. Therapeutic drug levels are drawn when a drug reaches steady state. Drugs reach steady state: 34. Upregulation or hypersensitization may lead to: Chapter 3. Rational Drug Selection 1. An NP would prescribe the liquid form of ibuprofen for a 6-year-old child because: 2. In deciding which of multiple drugs used to use to treat a condition, the NP chooses Drug A because it: 3. A client asks the NP about the differences in drug effects between men & women. What is known about the differences between the pharmacokinetics of men & women? 4. The first step in the prescribing process according to the World Health Organization is: 5. Treatment goals in prescribing should: 6. The therapeutic goals when prescribing include(s): 7. When determining drug treatment the NP prescriber should: 8. Patient education regarding prescribed medication includes: 9. Passive monitoring of drug effectiveness includes: 10. Pharmacokinetic factors that affect prescribing include: 11. Pharmaceutical promotion may affect prescribing. To address the impact of pharmaceutical promotion, the following recommendations have been made by the Institute of Medicine: 12. Under new U.S. Food & Drug Administration labeling, Pregnancy Categories will be: Chapter 4. Legal & Professional Issues in Prescribing 1. The U.S. Food & Drug Administration regulates: 2. The U.S. Food & Drug Administration approval is required for: 3. An Investigational New Drug is filed with the U.S. Food & Drug Administration: 4. Phase IV clinical trials in the United States are also known as: 5. Off-label prescribing is: 6. The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration: 7. Drugs that are designated Schedule II by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration: 8. Precautions that should be taken when prescribing controlled substances include: 9. Strategies prescribers can use to prevent misuse of controlled prescription drugs include: 10. Behaviors predictive of addiction to controlled substances include: 11. Medication agreements or “Pain Medication Contracts” are recommended to be used: 12. A prescription needs to be written for: Chapter 6. Factors That Foster Positive Outcomes 1. A comprehensive assessment of a patient should be holistic when trying to determine competence in drug administration. Which of the following factors would the NP omit from this type of assessment? 2. Elena Vasquez’s primary language is Spanish, & she speaks very limited English. Which technique would be appropriate to use in teaching her about a new drug you have just prescribed? 3. Rod, age 68, has hearing difficulty. Which of the following would NOT be helpful in assuring that he understands teaching about his drug? 4. Which of the following factors may adversely affect a patient’s adherence to a therapeutic drug regimen? 5. The health-care delivery system itself can create barriers to adherence to a treatment regimen. Which of the following system variables creates such a barrier? 6. Ralph’s blood pressure remains elevated despite increased doses of his drug. The NP is concerned that he might not be adhering to his treatment regimen. Which of the following events would suggest that he might not be adherent? 7. Nonadherence is especially common in drugs that treat asymptomatic conditions, such as hypertension. One way to reduce the likelihood of nonadherence to these drugs is to prescribe a drug that: 8. Factors in chronic conditions that contribute to nonadherence include: 9. While patient education about their drugs is important, information alone does not necessarily lead to adherence to a drug regimen. Patients report greater adherence when: 10. Patients with psychiatric illnesses have adherence rates to their drug regimen between 35% & 60%. To improve adherence in this population, prescribe drugs: 11. Many disorders require multiple drugs to treat them. The more complex the drug regimen, the less likely the patient will adhere to it. Which of the following interventions will NOT improve adherence? 12. Pharmacologic interventions are costly. Patients for whom the cost/benefit variable is especially important include: 13. Providers have a responsibility for determining the best plan of care, but patients also have responsibilities. Patients the provider can be assured will carry through on these responsibilities include those who: 14. Monitoring adherence can take several forms, including: 15. Factors that explain & predict medication adherence include: Chapter 7. Cultural & Ethnic Influences in Pharmacotherapeutics 1. Cultural factors that must be taken into account when prescribing include(s): 2. Ethnic differences have been found in drug: 3. The National Standards of Culturally & Linguistically Appropriate Services are required to be implemented in all: 4. According to the National Standards of Culturally & Linguistically Appropriate Services, an interpreter for health care: 5. According to the U.S. Office of Minority Health, poor health outcomes among African Americans are attributed to: 6. The racial difference in drug pharmacokinetics seen in American Indian or Alaskan Natives are: 7. Pharmacokinetics among Asians are universal to all the Asian ethnic groups. 8. Alterations in drug metabolism among Asians may lead to: 9. Asians from Eastern Asia are known to be fast acetylators. Fast acetylators: 10. Hispanic native healers (cur&eras): Chapter 8. An Introduction to Pharmacogenomics 1. Genetic polymorphisms account for differences in metabolism, including: 2. Up to 21% of Asians are ultra-rapid 2D6 metabolizers, leading to: 3. Rifampin is a nonspecific CYP450 inducer that may: 4. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein by a drug such as quinidine may lead to: 5. Warfarin resistance may be seen in patients with VCORC1 mutation, leading to: 6. Genetic testing for VCORC1 mutation to assess potential warfarin resistance is required prior to prescribing warfarin. 7. Pharmacogenetic testing is required by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration prior to prescribing: 8. Carbamazepine has a Black Box Warning recommending testing for the HLA-B*1502 allele in patients with Asian ancestry prior to starting therapy due to: 9. A genetic variation in how the metabolite of the cancer drug irinotecan SN-38 is inactivated by the body may lead to: 10. Patients who have a poor metabolism phenotype will have: 11. Ultra-rapid metabolizers of drugs may have: 12. A provider may consider testing for CYP2D6 variants prior to starting tamoxifen for breast cancer to: Chapter 10. Herbal Therapy & Nutritional Supplements 1. A good history of herb & supplement use is critical before prescribing because approximately % of patients in the United States are using herbal products. 2. A potential harmful effect on patients who take some herbal medication is: 3. A thorough understanding of herbs is critical to patient safety. An example is the use of cinnamon to treat type II diabetes. It is important the patient uses Ceylon cinnamon, as the commercially available cassia cinnamon contains: 4. Traditional Chinese medicine utilizes yin (cooling) versus yang (warming) in assessing & treating disease. Menopause is considered a time of imbalance, therefore the Chinese herbalist would prescribe: 5. According to traditional Chinese medicine, if a person who has a fever is given a herb that is yang in nature, such as golden seal, the patient’s illness will: 6. In Ayurvedic medicine, treatment is based on the patient’s dominant dosha, which is referred to as the person’s: 7. Herbs & supplements are regulated by the U.S. Food & Drug Administration. 8. When melatonin is used to induce sleep, the recommendation is that the patient: 9. Valerian tea causes relaxation & can be used to help a patient fall asleep. Overdosage of valerian (more than 2.5 gm/dose) may lead to: 10. The standard dosage of St John’s wort for the treatment of mild depression is: 11. Patients need to be instructed regarding the drug interactions with St John’s wort, including: 1. MAO inhibitors 12. Ginseng, which is taken to assist with memory, may potentiate: 13. Licorice root is a common treatment for dyspepsia. Drug interactions with licorice include: 14. Patients should be warned about the overuse of topical wintergreen oil to treat muscle strains, as overapplication can lead to: 15. The role of the NP in the use of herbal medication is to: …………………………….continued………………………….. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 92 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 14, 2021
Number of pages
92
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 14, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
46







.png)





