*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 327 Study Guide Exam 1 (All)
NR 327 Study Guide Exam 1
Document Content and Description Below
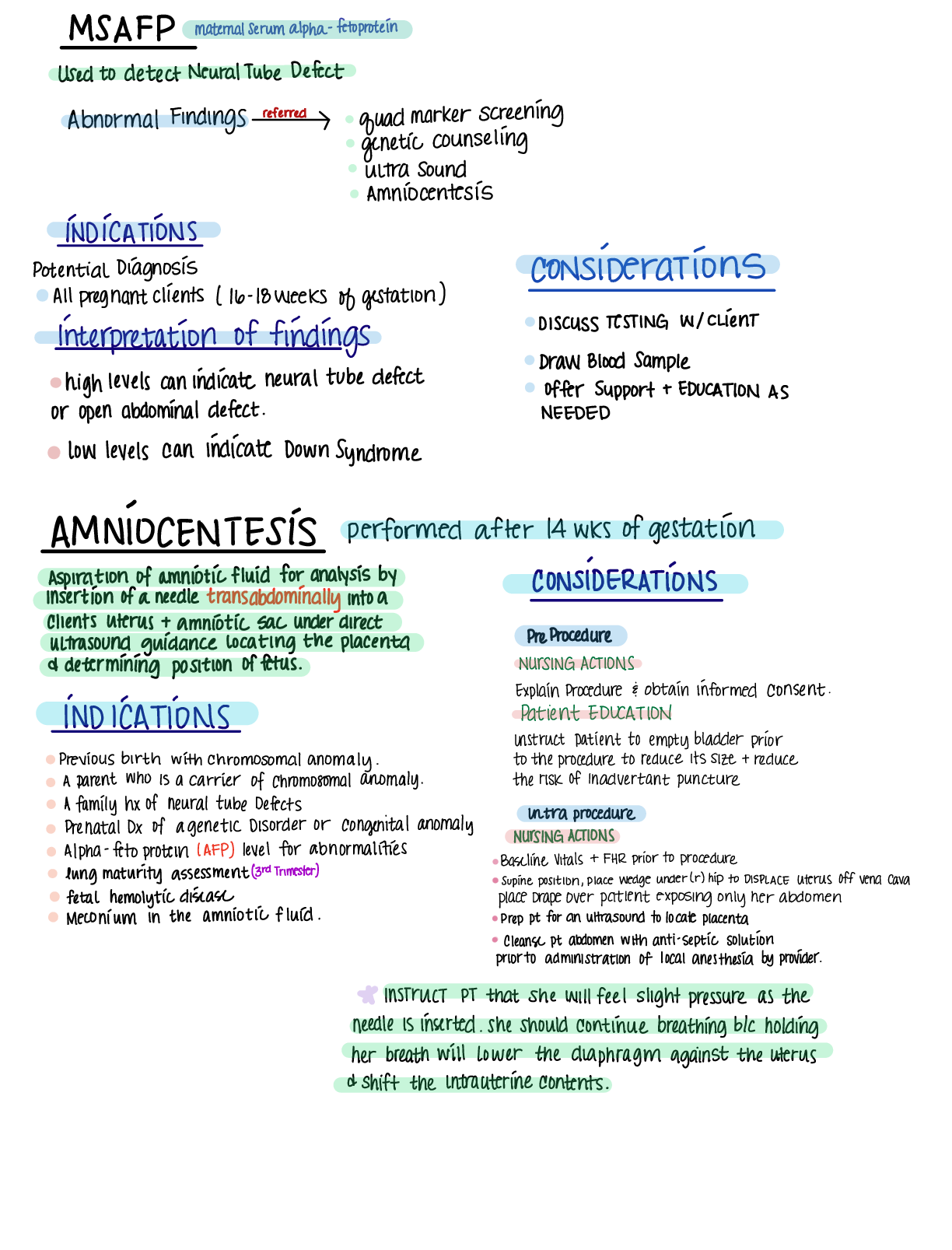
NR 327 Study Guide Exam 1 1. Describe the Chadwick’s sign, Goodell’s sign, and Hegar’s sign a. Hegar’s sign: softening and compressibility of lower uterus. b. Goodell’s sign: softening of... cervical tip. c. Chadwick’s sign: deepened violet-bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa. 2. Differentiating between presumptive, probable, and positive signs of pregnancy a. PRESUMPTIVE SIGNS Presumptive signs are changes that the woman experiences that make her think that she might be pregnant. These changes might be subjective symptoms or objective signs. Signs also might be a result of physiological factors other than pregnancy (peristalsis, infections, stress). Amenorrhea Fatigue Nausea and vomiting Urinary frequency Breast changes: darkened areolae, enlarged Montgomery’s glands Quickening: slight fluttering movements of the fetus felt by a woman, usually between 16 to 20 weeks of gestation Uterine enlargement b. PRO BABLE SIGNS Probable signs are changes that make the examiner suspect a woman is pregnant (primarily related to physical changes of the uterus). Signs can be caused by physiological factors other than pregnancy (pelvic congestion, tumors). Abdominal enlargement related to changes in uterine size, shape, and position Hegar’s sign: softening and compressibility of lower uterus Chadwick’s sign: deepened violet-bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa Goodell’s sign: softening of cervical tip Ballottement: rebound of unengaged fetus Braxton Hicks contractions: false contractions that are painless, irregular, and usually relieved by walking Positive pregnancy test Fetal outline felt by examiner c. POSITIVE SIGNSPositive signs are those that can be explained only by pregnancy. Fetal heart sounds Visualization of fetus by ultrasound Fetal movement palpated by an experienced examiner 3. Identify the physiologic changes of the pregnant women to the various systems. Cardiovascular Cardiac output increases (30% to 50%) and blood volume increases (30% to 45% at term) to meet the greater metabolic needs. Heart rate increases during pregnancy beginning around week 5 and reaches a peak (10 to 15/min above pre-pregnancy rate) around 32 weeks of pregnancy. GI Nausea and vomiting might occur due to hormonal changes and/or an increase of pressure within the abdominal cavity as the pregnant client’s stomach and intestines are displaced within the abdomen. Constipation might occur due to increased transit time of food through the gastrointestinal tract and, thus, increased water absorption. Respiratory Maternal oxygen needs increase. During the last trimester, the size of the chest might enlarge, allowing for lung expansion, as the uterus pushes upward. Respiratory rate increases and total lung capacity decreases. Skin Chloasma: an increase of pigmentation on the face Linea nigra: dark line of pigmentation from the umbilicus extending to the pubic area Striae gravidarum: stretch marks most notably found on the abdomen and thighs Urinary frequency Musculoskeletal Body alterations and weight increase necessitate an adjustment in posture. Pelvic joints relax. Posture changes due to the weight of the growing uterus (Lordosis) Relaxation of the bones of the pelvis occur Round ligament pain occurs as the uterus becomes more gavid. Uterus grows up & out of the pelvic floor to accommodate the fetal growth Palpated at 12 weeks week of pregnancy 16 weeks can be found midway between the symphysis pubis & the umbilicus 20 weeks can be found at the umbilicus 36 weeks reaches the highest near the xyphoid process pushing up on the diaphragm (this makes it difficult to breath especially lying down). 38 weeks the fetal head descends into the birth canal & drops the fundal height. Braxton hicks contractions throughout pregnancy as uterus grows 10-13% of maternal cardiac output goes to the uterus RenalUterine position causes urinary frequency. Progesterone causes hypertrophy & hyperplasia (smooth muscle) Bladder capacity doubles by the last trimester & tone is decreased leading to stress incontinence. Nocturia is common Kegel exercises after childbirth reduce urinary incontinence by strengthening the pelvic floor. 5. Identify the essential reasons for balanced nutrition and increase in caloric needs of the pregnant woman, appropriate weight gain per trimester. Exercise in pregnancy. a. Normal BMI: 25-35 lbs b. Above lbs: 15-25 lbs c. Obese lbs: 11-20 lbs d. Below: 28-40 lbs e. 2/3 weight gained in the second and third trimester. f. Too little weight gain is associated with low birth weight and SGA infants. (SGA is small for gestational age, below the 10th percentile) g. Too much weight gain: gestational diabetes, macrosomia (Large for Gestational age), prolonged labor, birth trauma, and preeclampsia. h. Nutrition: Increase caloric 340 calories per day, should get a minimum of 2200 calories per day. i. Adequate rest ii. Exercise, do not overdo it, exercise 30 minutes a day for gestational diabetes. The safest and productive exercises is swimming, brisk walking, indoor stationary cycling, and low-impact aerobics. iii. Avoid caffeine iv. Increase intake 8-10 cups/day v. Vitamin supplements include iron & folic acid for oxygenation and neuro development, (Too much Vitamin A is toxic to the fetus). sources include fatty fish, egg yolks, butter, cream, and dark yellow/orange fruits and vegetables (carrots, yams, apricots, squash, cantaloupe) vi. Avoid sodium rich canned foods, large fish due to mercury content and contain bacteria and parasites. No soft cheese unless pasteurized. No unpasteurized products. (raw meat, raw eggs, wine, raw fish, processed meats.) 6. Identify the most common discomforts experienced by many women in all three of the trimesters of pregnancy and interventions for each. a. Nausea & vomiting: small more frequent meals b. Heartburn: sitting up after eating, smaller meals c. Backache: support devicesd. Round ligament pain: slowly change positions from sitting and standing, support devices e. Urinary Frequency/UTI’s: void q 2 hours, void before and after sex, wipe front and back. f. Varicosities: support hose g. Constipation: increase water intake, exercise, fiber h. Leg cramps i. Candida Albicans: (thick creamy white discharge that can cause vulvar redness, white patches on vaginal wall.) 7. Patient teaching as it relates to each trimester a. First Trimester: i. Visits 4 weeks apart ii. Fundal height and fetal heart tones, V.S. bleeding, fetal growth; 11 to 14 weeks: optional genetic testing performed b. Second Trimester: same as bullet point i. and ii from first trimester i. 15 to 20 weeks: Quad screening (HcG, MSAFP) which screens for genetic & Spinal cord abnormalities) ii. 18 and 20 weeks: Ultrasound iii. 27 to 28 weeks: glucose screening & hemoglobin check c. Third Trimester: same as bullet point i. and ii. From first trimester i. 28-36 weeks: visits are about 2-3 weeks apart. ii. 28 week: Rhogam if needed iii. 36 weeks: GBS & STI screening performed, pelvic exam for dilation, assessment of the fetal position. iv. 36 to 40 weeks: visits typically 1-2 weeks pelvic exam for dilation. 8. Education on smoking and the effects it can have in the developing fetus. a. Smoking can cause many risk factors such as i. Low birth weight ii. Prematurity iii. Still births, fetal death, infant death iv. Respiratory complications v. Congenital heart defects vi. CNS effects vii. Placental insufficiency; hypoxia (late decelerations) viii. Congenital anomalies (cleft lip, palate) 9. True vs false labor. Danger signs to report a. True Labor i. Lightening: the drop of the fetus allowing the mother to take a deeper breath. ii. Contractions1. Regular, rhythmic, consistent, stronger and come closer together. iii. Bloody show: normal bleeding that occurs with cervical dilation. iv. Loss of mucous plug: white/clear mucous v. Rupture of membranes: gush or consistent leak of amniotic fluid vi. Cervix Dilated!!! b. False Labor i. Contractions 1. Not consistent, often go away with activity, can have brownish show ii. No Dilation!!! c. Dangers to Report i. Bradycardia ii. Late decelerations iii. Tetanic contractions iv. Hard ridged uterus v. Bright red bleeding vi. Blood pressure (varies) vii. Fever viii. Dizziness 10. Compare the differences between ultrasonography and trans-vaginal ultrasonography and the nursing care associated with preparation for the procedure. a. Two-dimensional and three dimensional b. Use of soundwaves to create images i. Does not cause discomfort-very safe ii. MUST HAVE BLADDER FULL FOR PROCEDURE! iii. External Ultrasound (US) and transvaginal (internal) 1. BEST WAY TO DETERMINE APPROXIMATE GESTATIONAL AGE!!! 2. More accurate estimation in the early gestational period 3. Determines a. Fetal position b. Multiple babies c. Location of pregnancy d. Placenta e. Sex f. Viability g. Abnormalities (congenital or otherwise) iv. Clean patient after procedure, care, and explain the procedure, ALWAYS to the patient.11. Fetal Testing: MSAFP why is it done, when is it done? a. A screening tool (only) that is used in the Quad marker screening, Maternal serum Alpha-fetoprotein; High: neural tube defects (spina bifida and anencephaly); Low: Down Syndrome i. High: >2.5 MoM ii. Low: <0.4 MoM b. HCG; High: Down Syndrome; Low: miscarriage; helps determine chromosomal abnormalities c. Unconjugated estriol: helps determine chromosomal abnormalities d. Placental hormone inhibin A: helps figure out trisomy 18 in women <35 y/o age; serum is drawn 16-18 weeks gestation. 12. Pre and post nursing care for a patient undergoing an amniocentesis. a. Needle aspiration of amniotic fluid from the amniotic sac performed under ultrasound guidance for examination. b. Usually performed 15-20 weeks, determine also in the third trimester for fetal lung maturity. c. Need to have an empty bladder d. Strenuous activity should be avoided for 24 hours. e. Woman may feel cramping during or after the procedure. f. Search for i. Trisomy 21 ii. Intrauterine infections iii. Rh positive fetus to Rh negative mother iv. Fetal hemolytic disease v. Fetal lung maturity g. Pre-care: explain procedure, prep the patient, assist the MD, baseline strip h. Post-care: Since it is invasive you must assess for labor and bleeding following. 13. Describe how to calculate an EDC/EDD/EDB Nageles Rule? a. In order to use this rule you will need LMP date b. (-3) months (+7) days 1 year from LMP. 14. Describe Gravida and Para and its significance to the nurse with the health assessment of the woman. a. Gravida: a woman who is or was pregnant (number of pregnancies) i. Nulligravida: never been pregnant ii. Primigravida: 1st pregnancy iii. Multigravida: more than 1 pregnancy b. Parity: the number of pregnancies that reached 20 weeks of gestation regardless of live birth.i. Nullipara: never been pregnant or has not reached completed 20 weeks of gestation. ii. Primipara: has 1 pregnancy and has reached 20 weeks of gestation. iii. Multipara: has had 2 or more pregnancies of at least 20 weeks of gestation. 15. GTPAL classification a. It is a system used to clarify pregnancy history b. GRAVIDA: a woman who is pregnant or was pregnant. c. TERM: term pregnancies delivered 37 weeks or more. d. PRETERM: pregnancies that reached 20 weeks of gestation regardless if the infant was born alive but delivered before 39 weeks. e. ABORTIONS: spontaneous or elective f. LIVING CHILDREN 16. Describe the major milestones in each of the trimester with the growth and development of the fetus. a. First Trimester: (1-12) i. By week 12 the fetus has developed all of these: 1. Eyes (9th week eyes closed) & ears. 2. Mouth, lips, tooth buds 3. Arms, hands, fingers, legs, toes 4. Kidneys, gall bladder, stomach 5. Heart (can hear heart beat by 10-12th week) 6. Sex 7. Placenta fully functioning 8. CRL is determined in ultrasound imagery from head to trunk @ 45 grams by the end of the trimester. b. Second Trimester (13-27) i. Quickening manifested; face is more human-like at 16 week ii. Fingerprints @ 20 week iii. Viable & can hear 24 weeks iv. CRL 820 g by the end of the trimester c. Third Trimester (28-40) i. Surfactant is formed, eyelids are open, greatest fetal weight gain, testes descend @ 28 weeks ii. Brown fat deposited, begin storing Fe, Ca, Phosphorus @ 32 weeks iii. Maternal antibodies transferred @ 36 weeks iv. Lightening: backaches increase; Braxton hicks (+) @ 36-40 weeks 17. Evaluation of fetal heart tones with Doppler. a. Not continuous this allows for the clinician to hear FHR for a few seconds to a few minutes.b. Used in the MD offices. c. Used when having difficulty locating fetus. 18. When completing a NST, CST or the interpretation the results of a BPP, be able to explain and teach to patient why, and how these tests are completed. a. NST: mother is placed on a fetal monitor. i. Increased FHR w/ movement= fetal w/ adequate oxygenation; ability of the fetus to respond to stimuli. (NEGATIVE/REACTIVE IS GOOD) (15 RATE INCREASE X 15 SECONDS) ii. If the fetus does not elevate FHR or w/o movement= hypoxia, further test is ordered. (POSITIVE/NONREACTIVE IS BAD) (NO 15 RATE INCREASE X 15 SECONDS.) b. CST: used to determine fetal well being during contraction i. A healthy placenta & fetus will be able to tolerate temporary disruption of low oxygen levels during a uterine contraction ii. Fetal Heart rate should remain same or accelerate immediately following contraction-known as “variability” reactive. iii. NEED 3 CTX’s ON A FETAL STRIP iv. Contractions are produced by nipple stimulation or oxytocin challenge which is a dilute amount of oxytocin IVPB (Intravenous Piggy-Back) v. Explain the procedure to the mom vi. NEGATIVE IS A GOOD TEST BECAUSE THERE IS NO DROP IN FHR PRESENT. vii. POSITIVE IS BAD AND REQUIRES FURTHER TESTING BECAUSE THERE IS A DROP OF FHR AT LEAST 50% OF THE CONTRACTIONS. c. BPP: Biophysical Profile: test used to determine the overall condition of the fetus. i. It is a combination of a NST, an ultrasound, and a parameter which is given 1. 10 is perfect 2. 8-10 is normal 3. <6 repeat or >36 weeks deliver baby 4. 0-2 Certain asphaxia; test for 120 min-persistent score, <4 deliver regardless of gestational age. ii. Explain that the BPP is an US procedure and has an NST component to it. iii. The 5 parameters of fetal wellbeing are: 1. FHR 2. fetal breathing movements 3. gross fetal movements4. fetal muscle tone 5. amniotic fluid volume (fetus swallows 1L/day) 19. NST procedure what to do when you are monitoring and there is no fetal movement what is your next steps (primary step)? a. Feed the patient and give some fluids to accelerate the metabolism and wake up the baby to establish fetal movement. b. If doesn’t work, then reposition mom (left lateral side) c. Reposition monitors d. Vibroacoustic stimulators (not in use anymore because it is not healthy to startle the fetus with this tool.) 20. Describe each of the stages of labor & and the nursing care associated with each of the four stages. a. First Stage: (Dilation & Effacement) i. Begins with dilation of the cervix ii. Ends with 10cm dilated and 100% effaced iii. Assist with the comfort of the patient, supportive measures, education, and hygiene. b. Second Stage: (Delivery of Infant) i. Begins with the patient being 10cm dilation and 100% effacement ii. Ends with delivery of infant. iii. Contractions may diminish or slow down but are still powerful. iv. “The baby is coming” “I have to push.” v. Nulliparous: @ 50-60 min (w/o epidural), @ 80 min (w/epidural) vi. Mutliparas: @ 15-20 min (w/o epidural), @ 45 min (w/epidural) vii. Assist with delivery, assessment of potential complications, assist with infant bonding, breastfeeding, and hygiene. c. Third Stage: (Delivery of the Placenta) i. Begins with the delivery of the infant ii. Ends with the expulsion of the placenta iii. Is the shortest age: lasts 6 min, can go up to 30 min iv. Normal separation there will be a “gush of blood” rise of uterus in the abdomen, firmer uterus, lengthening and descent of the uterus. v. There is no difference in time between nulliparous and multiparous. vi. Pain with assist with breastfeeding and bonding, complications, and hygiene. d. Fourth Stage: (Recovery) i. Recovery of the delivery ii. Begins after delivery of the placenta iii. Ends @ 4 hours placental delivery iv. RN assesses fundal height/firmness, complicationsv. Vaginal bleeding (boggy fundus) vi. VS & pain vii. Bladder distention (deviated fundus) viii. LOC 21. Be able to understand what and where various stations are located. The role of cervical dilation and how it progresses (1-10) a. Dilation: opening of the cervix from 0-10 centimeters. b. Effacement: is the thinning of the cervix from 0-100% c. Station: baby descending above, on, or below the ischial spines of the pelvis, this tells us where the baby is sitting at. i. Negative inside pelvis ii. 0 is at ischial spines iii. Positive is outside pelvis 22. Complete a drug card for each of the following medications: nursing implications & side effects. Pitocin, Terbutaline, Folic Acid 23. Describe the nursing care of the patient receiving an epidural; possible side effects, and nursing management. a. Placed by an anesthesiologist or CRNA b. Lasts longer than a spinal c. (Duramorph, Ropivacaine) is injected into the epidural space and then the patient can control the amount of pain medication when injecting. d. S/S: HYPOTENSION!!!, bladder distention, prolonged delivery of baby, catheter mitigation, C-section, fever, headache, pruritus, N&V, heaviness in the legs e. Explanation of the procedure, VS, bladder distention, assist with positioning & repositioning, instruct the feeling of numbness may last several hours after post-delivery. 24. Describe nonpharmacological pain management- effleurage, guided imagery, hypnosis, distraction, counter pressure, a. Effleurage: form of massage that uses the palm of the hand in a circular motion. b. Guided imagery: the use of words and music to evoke imaginary scenarios in a subject with a view to bringing about a beneficial effect. c. Hypnosis: induction to a state of consciousness highly responsive to suggestion d. Distraction: aromatherapy, breathing, mediation, prayer e. Counter pressure: pressure in the location of pain. 25. What are vaginal assisted deliveries? (Forceps vs Vacuum) what are the contraindications? a. Vaccum: assisted-device via a suction mechanismb. Performed by an MD or CNM for both maternal and fetal indications: i. Maternal exhaustion or inability to push any longer ii. Fetal strip failure to rotate or descend placental separation c. Contraindications: Fetal distress, high fetal station, disproportions d. Risk factors: hematomas, trauma e. Nursing Considerations: responsible for the on and off suction f. Mom: bright red bleeding, edema, other tears g. Baby: hematoma, cuts, swelling h. Apply ICE PACKS, MONITOR i. Forceps: like salad tongs i. Fetal: placental separation, respiratory and cardiac issues, inability of the mother to push, and strip failure. ii. Contraindications: fetal distress, high fetal station, disproportion, no face presentations, head down preferred iii. Risks: trauma, laceration hematomas iv. Nursing Considerations: Post delivery assess for trauma 1. Mom: bright red bleeding, edema, other tears 2. Baby: hematomas, cuts, swelling 3. APPLY ICE PACKS, MONITOR 26. Criteria for a labor to be induced? Bishop Score? Gestational Age? a. 39 weeks of gestation required b. Medical Indication: i. Infection ii. Growth restriction iii. Diabetes iv. PIH v. Fetal death vi. Placental insufficiency vii. <5 not favorable viii. 6> favorable ix. 27. What is the nursing care associated with augmentation of labor with Pitocin? a. Explain the procedure b. IV Pitocin 10 units in 1000 mL of LR starts at 1 mu/mL then progress until contraction pattern is established c. Monitor fetal heart rate & contractions q 15 minutes i. UC: frequency, duration, strength ii. HR: monitor for signs of distressd. Discuss plan for pain control e. I & O f. Keep MD updated on progress g. Prepare for delivery h. Support measures 28. What is the pre and post nursing care with an Amniotomy, what is the primary focus post amniotomy? a. Amniotomy: artificial rupture of the membranes b. Typically performed during inductions, augmentations, and internal monitoring. c. Nursing Considerations: Assess color of fluid (clear vs. meconium; green), amount of fluid (polyhydramnios & oligohydramnios) d. ALWAYS assess Fetal heart tones before, during, and after the procedure to ensure there is no prolapse cord. e. Patient at risk for infection post rupture f. Pre-procedure i. Obtain baseline fetal heart tones ii. Place multiple pads under the patient iii. Assist MD with sterilization (sterile gloves, amnihook, or fingercot, lubricant) g. Post-procedure i. Identify complications by monitoring fetal heart tones ii. Clean patient up post procedure 29. Describe non-stress test (NST) vs. Contraction stress test (CST) on the pregnant patient? a. NST is a noninvasive just utilized fetal monitors to evaluate the fetus that is not under any stress (no contractions) b. CST is invasive if there is a need to start IV Pitocin this also utilizes the fetal monitor to evaluate the fetus but it places the fetus under stress because there are contractions associated with this type of test. 30. Describe the assessment of the fetus during labor and delivery? a. Fetal assessment is performed through fetal monitoring b. Looking for baseline fetal heart rate and fluctuations in that heart rate that will tell the provider potential issues that may be going on. c. Accelerations d. Variability yes or no? How much? e. Declarations what type? 31. Describe the various patterns of uterine contractions and fetal heart rate in relationship to the fetal monitor. Be able to identify appropriate interventions for each (if needed) of the types of decelerations.a. Baseline i. Fetal Heart rate typically is around 110-160 b. Variables i. Fluctuations in the baseline of the FHR within a 10-minute window ii. Significant part of the FHR assessment because it shows adequate oxygenation & evaluates the nervous system of the fetus. iii. Causes: may be decreased like fetal sleep (narcotics), alcohol, drugs, fetal sepsis, fetal tachycardia, prematurity, fetal anomalies, hypoxia, maternal hypoxia iv. Classified as: 1. Absent: undetectable 2. Minimal: Undetectable to <5bpm 3. Moderate: 6-25 bpm 4. Marked: >25bpm c. Accelerations i. An abrupt temporary increase in the FHR that should peak 15 beats per minute x 15 seconds after 32 weeks, prior to 32 weeks is 10 beats per minute x 10 seconds. d. Decelerations i. A decrease in the FHR below the normal range or the established baseline ii. Types 1. Early: occurs during a contraction, is okay, have a gradual decrease, MIRROR contractions, not associated with fetal compromise 2. Late: nonreassuring pattern caused by uteroplacental insufficiency a. Gradual but uniformed with a decrease in FHR that begins mid contraction with a baseline return after the contraction is over. b. Can be intermittent, persistent, subtle, or prolonged 32. Describe the difference between external vs. internal (ISE/IUPC) monitoring. When is an ISE/IUPC contraindicated? a. External: monitors are applied on the outside of the mother via the US and the TOCO. b. Internal: monitors applied on the inside of the mother via the Internal (Fetal) scalp electrode (ISE) and Intrauterine pressure catheter (IUPC), the fluid is broken and has access to the baby’s head where the electrode is applied. c. Contraindications: i. Hepatitisii. Infection iii. Herpes iv. HIV v. Structural abnormalities vi. Prolapse cord 33. Identify what issues may occur that lead a patient to receiving a cesarean birth. a. It is a safe surgical procedure. i. Risks 1. Infection 2. Hemorrhage 3. Urinary tract trauma 4. Ileus 5. Deep vein thrombosis 6. Aesthesia complications 7. Fetal risks injury (lacerations, bruising, fractures) transient tachypnea b. Types of incisions i. Classical (quick to perform easier visualization of the uterus; easier for obese women) ii. Low Transverse/Pfannenstiel (unlikely to rupture with other pregnancies, less blood loss, easy to repair, less adhesion formation c. Reason for a C-section i. Fetal distress ii. Prolapsed cord iii. Fetal presentation iv. ROM (Rupture of Membranes) over 24 hours v. Failed VBAC attempt (Previous uterine incision must be low transverse (need medical record of previous surgery.) vi. Classical C/S (Caesarean section) incision history vii. Active Herpes, HPV, Acute HIV + viii. Placenta Previa or Placenta abruption d. Nursing Considerations i. Emotional Support ii. Education pre and post procedure iii. Promotion of safety (food intake, ambulation) iv. Post-operative care v. Monitor for complications 34. Responsibilities of nurse to prepare a patient for surgery. a. Emotional support b. Education pre and post-surgeryc. Promotion of safety (food intake, ambulation) d. Post-operative care e. SCD’s f. Foley 35. Pt teaching regarding gestational diabetes- treatment, blood sugar monitoring, diet, fetal monitoring a. It is a carbohydrate intolerance of any variable severity that develops or recognized during pregnancy. b. Places patient at higher risk to develop type 2 diabetes onwards. c. Risk Factors i. Overweight ii. Over the age of 25 iii. Previous birth outcome: neonatal macrosomia, maternal HTN, unexplained congenital anomalies, previous fetal death iv. GDM in previous Pregnancy v. Family history d. Perform Screenings i. Glucose Challenge test 1. Done in 24 to 28th week of gestation 2. Low or high risk moms 3. No prep, not NPO 4. An oral glucose is ingested & blood work is taken 1 hour later 5. Blood serum glucose greater than 140 is considered positive & a 3-hour glucose intolerance test is required. ii. GDM is diagnosed when: 1. Fasting >95mg/dL 2. 1 hour >180mg/dL 3. 2 hours >155mg/dL 4. 3 hours >140mg/dL iii. Management 1. Goal is to maintain normal glucose levels through exercise, diet, and may need insulin for glucose control. 2. May have increased episodes of hyper/hypo-glycemia due to change of metabolic needs during pregnancy. 3. Diet: 30 kcal/kg/day is recommended generally, or 25 kcal/kg/day is for an obese person, with a smaller % of carbohydrate intake 4. Exercise: a graduated exercise plan5. Blood glucose monitoring: if there are repeated results reflecting fasting (>95%) & postprandial (2 hours after food) (>120)- insulin may be required 6. Fetal surveillance a. Kick counts b. NST c. BPP d. US e. Fetal growth 36. Missed Quiz Concepts a. What is a fundus? i. The top of the uterus b. What is Linea nigra? i. A dark pigmented line from the fundus of the uterus to the pubic symphysis. c. What weeks is the glucose intolerance test performed? i. 24 to 28 weeks ii. Diagnosis hyperglycemia >140 mg/dL d. Name Three Breech positions? i. Frank, Complete, Footling e. What are the four stages of labor? i. 1st: Cervical dilation ii. 2nd: Delivery of the baby iii. 3rd: Delivery of the placenta iv. 4th: Recovery Stage f. Amniocentesis is performed? i. 15-20 weeks g. Quad Screening is performed? i. 16-18 weeks of gestation h. What is a version? i. Ultrasound guided procedure performed ion 36 to 37 weeks of gestation to externally manipulate the fetus into a cephalic lie. ii. A fetus in a breech or transverse position >36 wk [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 29, 2021
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 29, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
38













.png)

.png)








