*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 226_ Fundamentals - Patient Care Week 5 Concepts . Managing Fluid and Electrolyte Alterations Cha (All)
NR 226_ Fundamentals - Patient Care Week 5 Concepts . Managing Fluid and Electrolyte Alterations Chamberlain University College of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
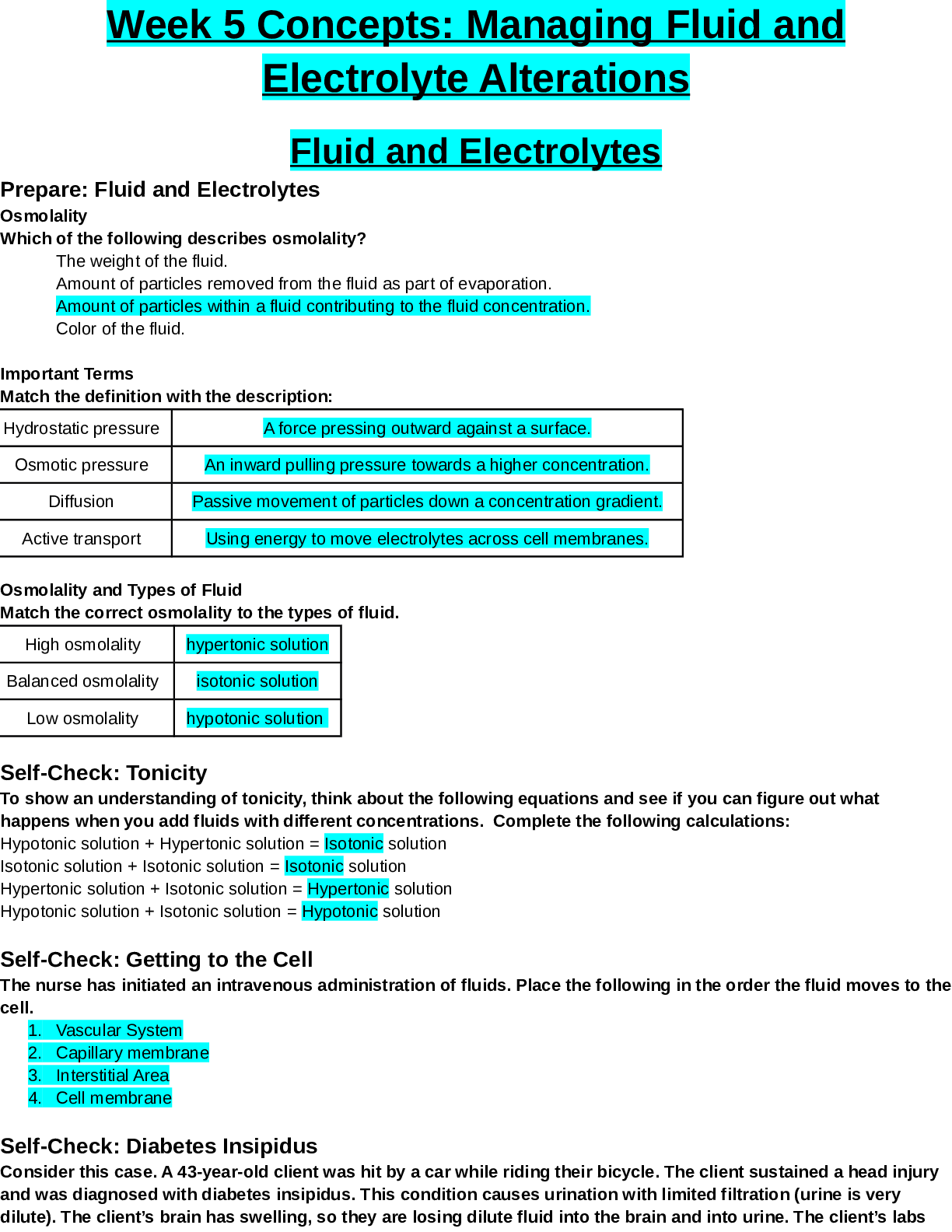
NR 226_ Fundamentals - Patient Care Week 5 Concepts . Managing Fluid and Electrolyte Alterations Chamberlain University College of Nursing Week 5 Concepts: Managing Fluid and Electrolyte Alterations ... Fluid and Electrolytes Prepare: Fluid and Electrolytes Osmolality Which of the following describes osmolality? The weight of the fluid. Amount of particles removed from the fluid as part of evaporation. Amount of particles within a fluid contributing to the fluid concentration. Color of the fluid. Important Terms Match the definition with the description: Hydrostatic pressure A force pressing outward against a surface. Osmotic pressure An inward pulling pressure towards a higher concentration. Diffusion Passive movement of particles down a concentration gradient. Active transport Using energy to move electrolytes across cell membranes. Osmolality and Types of Fluid Match the correct osmolality to the types of fluid. High osmolality hypertonic solution Balanced osmolality isotonic solution Low osmolality hypotonic solution Self-Check: Tonicity To show an understanding of tonicity, think about the following equations and see if you can figure out what happens when you add fluids with different concentrations. Complete the following calculations: Hypotonic solution + Hypertonic solution = Isotonic solution Isotonic solution + Isotonic solution = Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution + Isotonic solution = Hypertonic solution Hypotonic solution + Isotonic solution = Hypotonic solution Self-Check: Getting to the Cell The nurse has initiated an intravenous administration of fluids. Place the following in the order the fluid moves to the cell. 1. Vascular System 2. Capillary membrane 3. Interstitial Area 4. Cell membrane Self-Check: Diabetes Insipidus Consider this case. A 43-year-old client was hit by a car while riding their bicycle. The client sustained a head injury and was diagnosed with diabetes insipidus. This condition causes urination with limited filtration (urine is very dilute). The client’s brain has swelling, so they are losing dilute fluid into the brain and into urine. The client’s labs show the following: ● Serum osmolality of 318mmol/kg (normal 280-300) ● Urine specific gravity of 1.001 (normal 1.002 to 1.030) ● Serum sodium is 155 mEq/L (normal 135 to 145) Which of the following would be most appropriate to help the client get better? A hypertonic solution given IV No need for fluids at this time A hypotonic solution given IV A isotonic solution given IV Self-Check: Osmotic and Hydrostatic 2 Select the correct choices to complete the following statement. If particles are pushed from one compartment to the next regardless of the concentration of the different compartments, hydrostatic pressure is used. When particles are pulled to an area that has less of a concentration of those particles, it is called osmotic pressure. Self-Check: Electrolyte Imbalance Which of the following will cause an electrolyte imbalance? Select all that apply. Furosemide injection Renal insufficiency Taking a daily multivitamin Clostridium difficile infection Ingesting an oral electrolyte replacement fluid Reflect: Fluid and Electrolytes Patient Scenario – Heart Failure Sally, a 75-year-old female is admitted with heart failure. She has pitting edema to both lower extremities. Her labs show the following: ● Serum osmolality of 275 mmol/kg (normal 280-300) ● Serum sodium is 130 mEq/L (normal 135 to 145) Which of the following would be most appropriate to help her get better? A isotonic solution given IV A hypertonic solution given IV A hypotonic solution given IV No need for fluids at this time. Electrolyte Abnormalities The healthcare provider orders a diuretic (furosemide 80mg IV) for Sally, who is in heart failure. Which of the following electrolyte abnormalities would you be most concerned about in the next two to four hours as the medication works? Hypokalemia Hyponatremia Hyperkalemia Hypernatremia [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 28, 2023
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 28, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
89



























