NR 507 Week 2 Quiz – Questions and Answers with Explanation
Document Content and Description Below
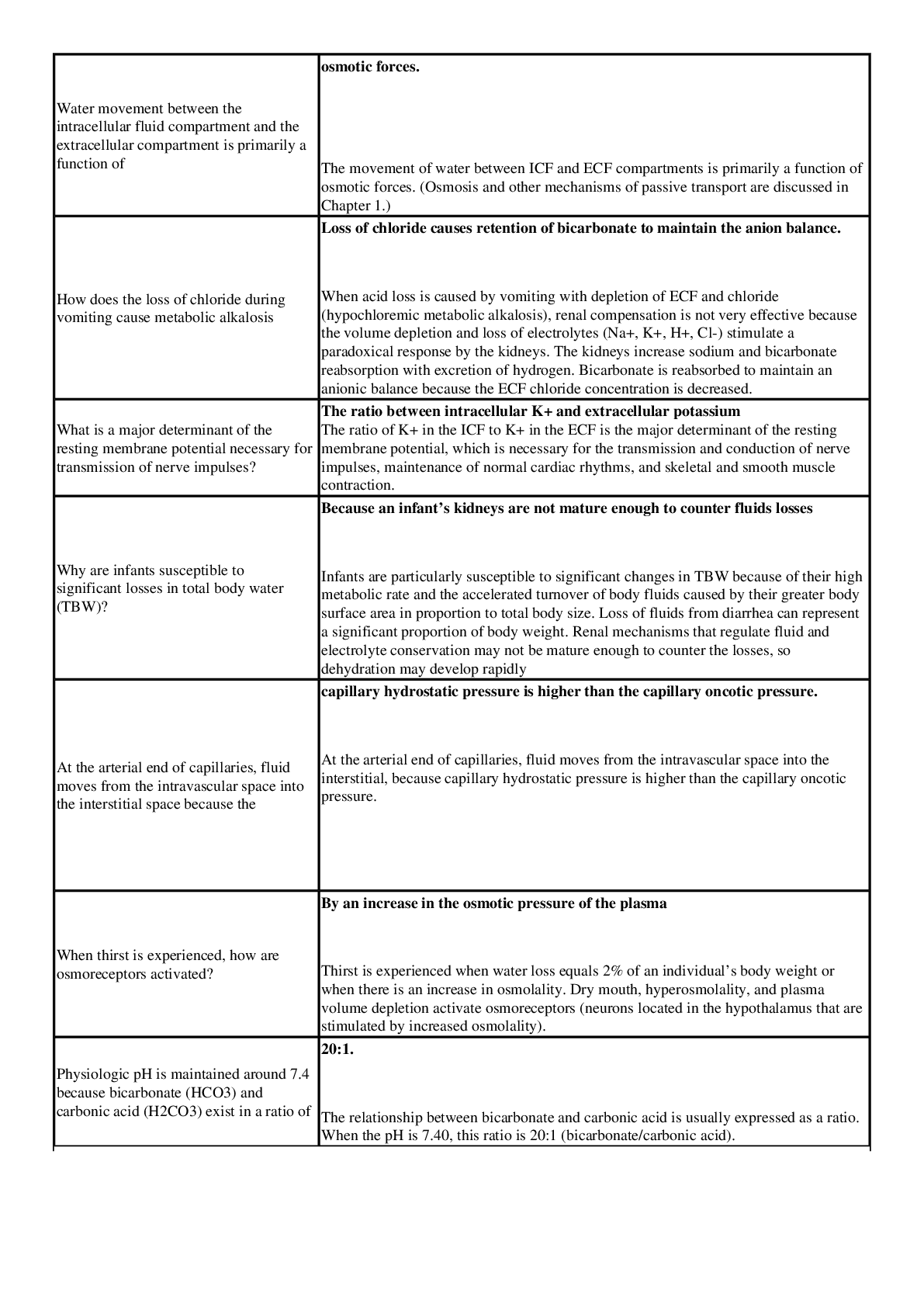
NR 507 Week 2 Quiz – Questions and Answers with Explanation Water movement between the intracellular fluid compartment and the extracellular compartment is primarily a function of osmotic forces. ... The movement of water between ICF and ECF compartments is primarily a function of osmotic forces. (Osmosis and other mechanisms of passive transport are discussed in Chapter 1.) How does the loss of chloride during vomiting cause metabolic alkalosis Loss of chloride causes retention of bicarbonate to maintain the anion balance. When acid loss is caused by vomiting with depletion of ECF and chloride (hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis), renal compensation is not very effective because the volume depletion and loss of electrolytes (Na+, K+, H+, Cl-) stimulate a paradoxical response by the kidneys. The kidneys increase sodium and bicarbonate reabsorption with excretion of hydrogen. Bicarbonate is reabsorbed to maintain an anionic balance because the ECF chloride concentration is decreased. What is a major determinant of the resting membrane potential necessary for transmission of nerve impulses? The ratio between intracellular K+ and extracellular potassium The ratio of K+ in the ICF to K+ in the ECF is the major determinant of the resting membrane potential, which is necessary for the transmission and conduction of nerve impulses, maintenance of normal cardiac rhythms, and skeletal and smooth muscle contraction. Why are infants susceptible to significant losses in total body water (TBW)? Because an infant’s kidneys are not mature enough to counter fluids losses Infants are particularly susceptible to significant changes in TBW because of their high metabolic rate and the accelerated turnover of body fluids caused by their greater body surface area in proportion to total body size. Loss of fluids from diarrhea can represent a significant proportion of body weight. Renal mechanisms that regulate fluid and electrolyte conservation may not be mature enough to counter the losses, so dehydration may develop rapidly At the arterial end of capillaries, fluid moves from the intravascular space into the interstitial space because the capillary hydrostatic pressure is higher than the capillary oncotic pressure. At the arterial end of capillaries, fluid moves from the intravascular space into the interstitial, because capillary hydrostatic pressure is higher than the capillary oncotic pressure. .....continued... [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages
Instant download
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Also available in bundle (1)

NR 507 Week 1-Week 7 Quizzes and Answers
NR 507 Week 1-Week 7 Quizzes and Answers
By YourTutor 3 years ago
$45.5
11
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 13, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
56