NSG 6420 Midterm Exam 2 – Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
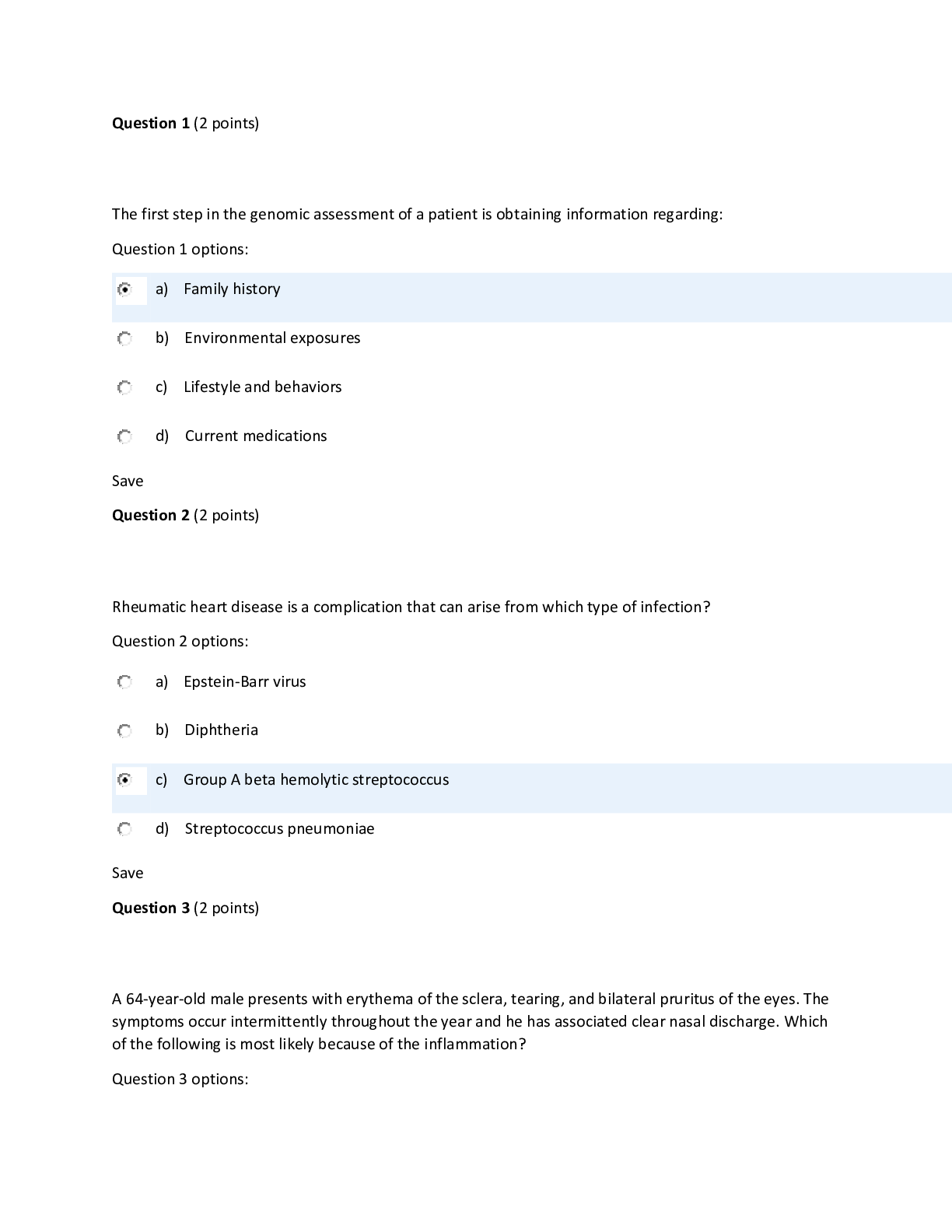
NSG 6420 Midterm Exam 2 – Questions and Answers Question 1 (2 points) The first step in the genomic assessment of a patient is obtaining information regarding: Question 1 options: a) Fam... ily history b) Environmental exposures c) Lifestyle and behaviors d) Current medications Save Question 2 (2 points) Rheumatic heart disease is a complication that can arise from which type of infection? Question 2 options: a) Epstein-Barr virus b) Diphtheria c) Group A beta hemolytic streptococcus d) Streptococcus pneumoniae Save Question 3 (2 points) A 64-year-old male presents with erythema of the sclera, tearing, and bilateral pruritus of the eyes. The symptoms occur intermittently throughout the year and he has associated clear nasal discharge. Which of the following is most likely because of the inflammation? Question 3 options: a) Bacterium b) Allergen c) Virus d) Fungi Save Question 4 (2 points) Dan G., a 65-year-old man, presents to your primary care office for the evaluation of chest pain and left-sided shoulder pain. Pain begins after strenuous activity, including walking. Pain is characterized as dull, aching; 8/10 during activity, otherwise 0/10. Began a few months ago, intermittent, aggravated by exercise, and relieved by rest. Has occasional nausea. Pain is retrosternal, radiating to left shoulder, definitely affects quality of life by limiting activity. Pain is worse today; did not go away after he stopped walking. BP 120/80. Pulse 72 and regular. Normal heart sounds, S1 and S2, no murmurs. Which of the following differential diagnoses would be most likely? Question 4 options: a) Musculoskeletal chest wall syndrome with radiation b) Esophageal motor disorder with radiation c) Acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis d) Coronary artery disease with angina pectoris Save Question 5 (2 points) Which disease process typically causes episodic right upper quadrant pain, epigastric pain or chest pain that can last 4-6 hours or less, often radiates to the back (classically under the right shoulder blade) and is often accompanied by nausea or vomiting and often follows a heavy, fatty meal. Question 5 options: a) Acute pancreatitis b) Duodenal ulcer c) Biliary colic d) Cholecystitis Save Question 6 (2 points) Helicobacter pylori is implicated as a causative agent in the development of duodenal or gastric ulcers. What teaching should the nurse practitioner plan for a patient who has a positive Helicobacter pylori test? Question 6 options: a) It is highly contagious and a mask should be worn at home. b) Treatment regimen is multiple lifetime medications. c) Treatment regimen is multiple medications taken daily for a few weeks. d) Treatment regimen is complicated and is not indicated unless the patient is symptomatic. Save Question 7 (2 points) An obese middle-aged client presents with a month of nonproductive irritating cough without fever. He also reports occasional morning hoarseness. What should the differential include? Question 7 options: a) Atypical pneumonia b) Peptic ulcer disease c) Gastroesophageal reflux d) Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr) Save Question 8 (2 points) Jenny is a 24 year old graduate student that presents to the clinic today with complaints of fever, midsternal chest pain and generalized fatigue for the past two days. She denies any cough or sputum production. She states that when she takes Ibuprofen and rest that the chest pain does seem to ease off. Upon examination the patient presents looking very ill. She is leaning forward and states that this is the most comfortable position for her. Temp is 102. BP= 100/70. Heart rate is 120/min and regular. Upon auscultation a friction rub is audible. Her lung sounds are clear. With these presenting symptoms your initial diagnosis would be: Question 8 options: a) Mitral Valve Prolapse b) Referred Pain from Cholecystitis c) Pericarditis d) Pulmonary Embolus Save Question 9 (2 points) The pathophysiological hallmark of ACD is: Question 9 options: a) Depleted iron stores b) Impaired ability to use iron stores c) Chronic uncorrectable bleeding d) Reduced intestinal absorption of iron Save Question 10 (2 points) A key symptom of ischemic heart disease is chest pain. However, angina equivalents may include exertional dyspnea. Angina equivalents are important because: Question 10 options: a) Women with ischemic heart disease many times do not present with chest pain b) Some patients may have no symptoms or atypical symptoms; diagnosis may only be made at the time of an actual myocardial infarction c) Elderly patients have the most severe symptoms d) A & B only Save Question 11 (2 points) The cytochrome p system involves enzymes that are generally: Question 11 options: a) Inhibited by drugs b) Induced by drugs c) Inhibited or induced by drugs d) Associated with decreased liver perfusion Save Question 12 (2 points) Which of the following details are NOT considered while staging asthma? Question 12 options: a) Nighttime awakenings b) Long-acting beta agonist usage c) Frequency of symptoms d) Spirometry findings Save Question 13 (2 points) Jeff, 48 years old, presents to the clinic complaining of fleeting chest pain, fatigue, palpitations, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath. The pain comes and goes and is not associated with activity or exertion. Food does not exacerbate or relieve the pain. The pain is usually located under the left nipple. Jeff is concerned because his father has cardiac disease and underwent a CABG at age 65. The ANP examines Jeff and hears a mid-systolic click at the 4th ICS mid-clavicular area. The ANP knows that this is a hallmark sign of: Question 13 options: a) Angina b) Pericarditis c) Mitral valve prolapse d) Congestive heart failure Save Question 14 (2 points) Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA) is classified as a microcytic, hypochromic anemia. This classification refers to which of the following laboratory data? Question 14 options: a) Hemoglobin and Hematocrit b) Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH) c) Serum ferritin and Serum iron d) Total iron binding capacity and transferrin saturation Save Question 15 (2 points) What is the most common valvular heart disease in the older adult? Question 15 options: a) Aortic regurgitation b) Aortic stenosis c) Mitral regurgitation d) Mitral stenosis Save Question 16 (2 points) Your patient has been using chewing tobacco for 10 years. On physical examination, you observe a white ulceration surrounded by erythematous base on the side of his tongue. The clinician should recognize that very often this is: Question 16 options: a) Malignant melanoma b) Squamous cell carcinoma c) Aphthous ulceration d) Behcet’s syndrome Save Question 17 (2 points) A 59-year-old patient with history of alcohol abuse comes to your office because of ‘throwing up blood”. On physical examination, you note ascites and caput medusa. A likely cause for the hematemesis is: Question 17 options: a) Peptic ulcer disease b) Barrett’s esophagus c) Esophageal varices d) Pancreatitis Save Question 18 (2 points) Your 35-year-old female patient complains of feeling palpitations on occasion. The clinician should recognize that palpitations are often a sign of: Question 18 options: a) Anemia b) Anxiety c) Hyperthyroidism d) All of the above Save Question 19 (2 points) In AR disorders, carriers have: Question 19 options: a) Two mutated genes; one from each parent that cause disease b) A mutation on a sex chromosome that causes a disease c) A single gene mutation that causes the disease d) One copy of a gene mutation but not the disease Save Question 20 (2 points) Functional abilities are best assessed by: Question 20 options: a) Self-report of function b) Observed assessment of function c) A comprehensive head-to-toe examination d) Family report of function Save Question 21 (2 points) During auscultation of the chest, your exam reveals a loud grating sound at the lower anterolateral lung fields, at full inspiration and early expiration. This finding is consistent with: Question 21 options: a) Pneumonia b) Pleuritis c) Pneumothorax d) A and B Save Question 22 (2 points) During physical examination of a patient, you note resonance on percussion in the upper lung fields. This is consistent with: Question 22 options: a) COPD b) Pneumothorax c) A normal finding d) Pleural effusion Save Question 23 (2 points) A 26-year-old, non-smoker, male presented to your clinic with SOB with exertion. This could be due to: Question 23 options: a) Exercise-induced cough b) Bronchiectasis c) Alpha-1 deficiency d) Pericarditis Save Question 24 (2 points) A 24-year-old patient presents to the emergency department after sustaining multiple traumatic injuries after a motorcycle accident. Upon examination, you note tachypnea, use of intercostal muscles to breathe, asymmetric chest expansion, and no breath sounds over the left lower lobe. It is most important to suspect: Question 24 options: a) Pulmonary embolism b) Pleural effusion c) Pneumothorax d) Fracture of ribs Save Question 25 (2 points) If it has been determined a patient has esophageal reflux, you should tell them: Question 25 options: a) They probably have a hiatal hernia causing reflux b) They probably need surgery c) They should avoid all fruit juices d) Smoking, alcohol, and caffeine can aggravate their problem Save Question 26 (2 points) The following criterion is considered a positive finding when determining whether a patient with asthma can be safely monitored and treated at home: Question 26 options: a) Age over 40 b) Fever greater than 101 c) Tachypnea greater than 30 breaths/minute d) Productive cough Save Question 27 (2 points) In examination of the nose, the clinician observes gray, pale mucous membranes with clear, serous discharge. This is most likely indicative of: Question 27 options: a) Bacterial sinusitis b) Allergic rhinitis c) Drug abuse d) Skull fracture Save Question 28 (2 points) Symptoms in the initial human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection include all of the following except: Question 28 options: a) Sore throat b) Fever c) Weight loss d) Headache Save Question 29 (2 points) Essential parts of a health history include all of the following except: Question 29 options: a) Chief complaint b) History of the present illness c) Current vital signs d) All of the above are essential history components Save Question 30 (2 points) When palpating the posterior chest, the clinician notes increased tactile fremitus over the left lower lobe. This can be indicative of pneumonia. Areas of increased fremitus should raise the suspicion of conditions resulting in increased solidity or consolidation in the underlying lung tissue, such as in pneumonia, tumor, or pulmonary fibrosis. In the instance of an extensive bronchial obstruction: Question 30 options: a) No palpable vibration is felt b) Decreased fremitus is felt c) Increased fremitus is felt d) Vibration is referred to the non-obstructed lobe Save Question 31 (2 points) A nurse practitioner reports that your patient’s abdominal X-ray demonstrates multiple air-fluid levels in the bowel. This is a diagnostic finding found in: Question 31 options: a) Appendicitis b) Cholecystitis c) Bowel Obstruction d) Diverticulitis Save Question 32 (2 points) Which of the following findings should trigger an urgent referral to a cardiologist or neurologist? Question 32 options: a) History of bright flash of light followed by significantly blurred vision b) History of transient and painless monocular loss of vision c) History of monocular severe eye pain, blurred vision, and ciliary flush d) All of the above Save Question 33 (2 points) (*There are multiple questions on this exam related to this scenario. Be sure to read the whole way through to the question.) Mr. Keenan is a 42-year-old man with a mild history of GERD and a remote history of an appendectomy, presenting with an acute onset of significant right upper-quadrant abdominal pain and vomiting. His pain began after a large meal, was unrelieved by a proton-pump inhibitor, was unlike his previous episodes of heartburn, but upon questioning, reports milder, prodromal episodes of similar post-prandial pain. His pain seems to radiate to his back. Despite a family history of cardiac disease, he reports no classic anginal signs or chest pain. He furthermore denies respiratory or pleuritic signs and denies fever, night sweats, and unintended weight loss. Finally, there are no dermatologic signs, nor genitourinary symptoms. Of the following lab studies, which would provide little help in determining your differential diagnosis? Question 33 options: a) Abdominal plain films b) Liver function tests c) Amylase/lipase d) Urinalysis Save Question 34 (2 points) Which of the following is considered a “red flag” when diagnosing a patient with pneumonia? Question 34 options: a) Fever of 102 b) Infiltrates on chest X-ray c) Pleural effusion on chest X-ray d) Elevated white blood cell count Save Question 35 (2 points) A specific exam used to evaluate the gall bladder is: Question 35 options: a) Psoas sign b) Obturator sign c) Cullens sign d) Murphy’s sign .......continued....... [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 41 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)

NSG 6420 Midterm and Final
NSG 6420 Midterm and Final
By YourTutor 3 years ago
$45.5
4
Reviews( 0 )
$20.50
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 18, 2021
Number of pages
41
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 18, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
49