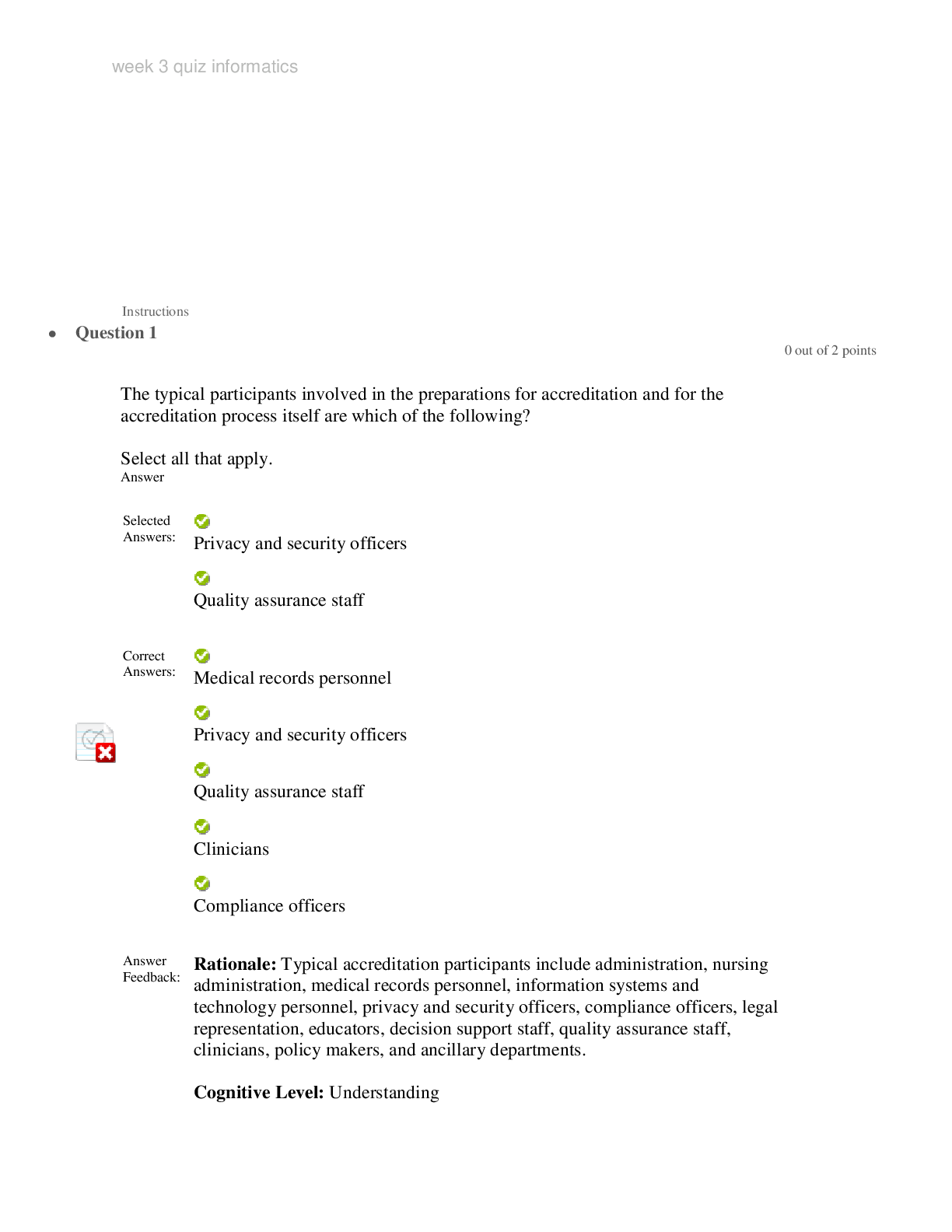
*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 603 Week 3 Quiz Study Guide: 34 Pages (All)
NR 603 Week 3 Quiz Study Guide: 34 Pages
Document Content and Description Below
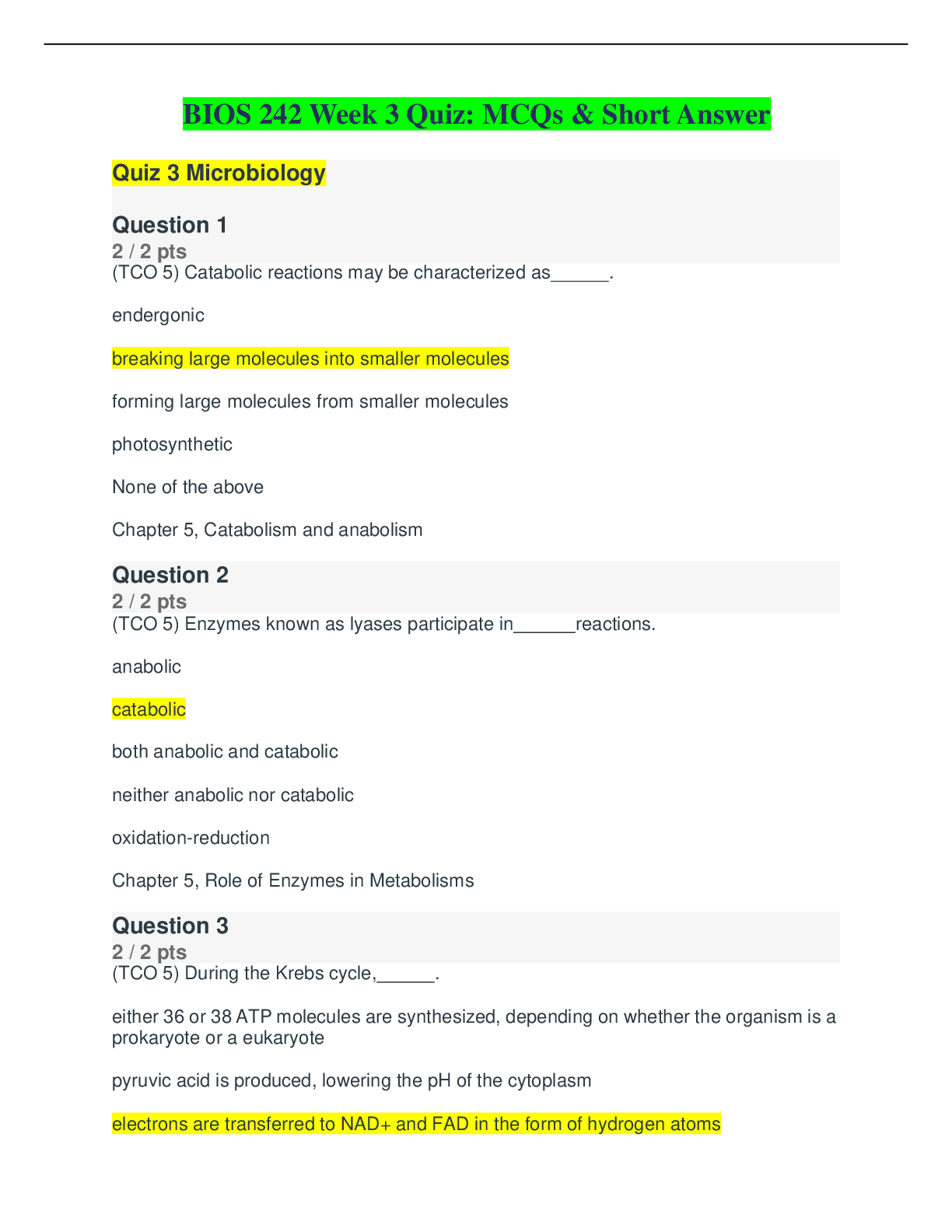
NR 603 Week 3 Quiz Study Guide: 34 Pages Preview of Starting Page….. Heart Failure Heart failure (HF) is a complex syndrome characterized by the inability of the heart to meet the body's... metabolic demands; it is a clinical diagnosis. It results from any structural or functional cardiac disorder that impairs the ventricle's ability to fill or to eject blood properly. Etiology The etiology of HF can be divided into the following three broad categories: 1. Anatomic or functional abnormalities of the coronary vessels, myocardium, or cardiac valves, of either sudden or gradual onset 2. Neurohormonal overexpression that causes activation of the adrenergic nervous system and renin-angiotensin system 3. Extracardiac factors that cause excessive demand on the cardiovascular system The most common diseases associated with HF are coronary artery disease, hypertension, and dilated cardiomyopathies Preview of Last Page….. Pathophysiology The pathogenesis of congenital cholesteatoma is the presence of embryonic squamous epithelial cells in an ear without a history of tympanic membrane (TM) perforation or ear infection. 1 Congenital cholesteatomas arise in fetal development, but the exact cause is unclear. Primary acquired cholesteatomas are also the result of an unknown pathology but are related to retraction of the TM, usually in the pars flaccida. 1 The cause may be related to abnormal function of the eustachian tube or a chronic inflammatory cascade of events initiated by a middle ear infection. 2 The result is an accumulation of squamous epithelium, progressive erosion of the associated structures, and destruction of the delicate bones of the ossicular chain. Secondary acquired cholesteatomas develop as squamous epithelial cells enter the middle ear either after a surgical procedure (e.g., tympanoplasty) or as a direct consequence of epithelial cell shifting from the TM. 1 Advanced cholesteatomas can become secondarily infected. Typical organisms causing infected cholesteatomas include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus species, Enterobacter, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and anaerobes. 1 Over time, cholesteatomas can spread into intratemporal structures, causing tinnitus, otorrhea, hearing loss, twitching of the facial nerve, or paralysis of the fac [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 34 pages

Also available in bundle (2)

NR 603 Week 1- Week 8 Course Bundle
NR 603 Week 1- Week 8 Course Bundle
By Amanda Rosales 3 years ago
$75
55

NR 603 Week 3 - Case Discussion Cardiovascular And Quizzes With Answers
NR 603 Week 3 - Case Discussion Cardiovascular And Quizzes With Answers/NR 603 Week 3 - Case Discussion Cardiovascular And Quizzes With Answers
By Amanda Rosales 3 years ago
$45
12
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 04, 2021
Number of pages
34
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 04, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
83






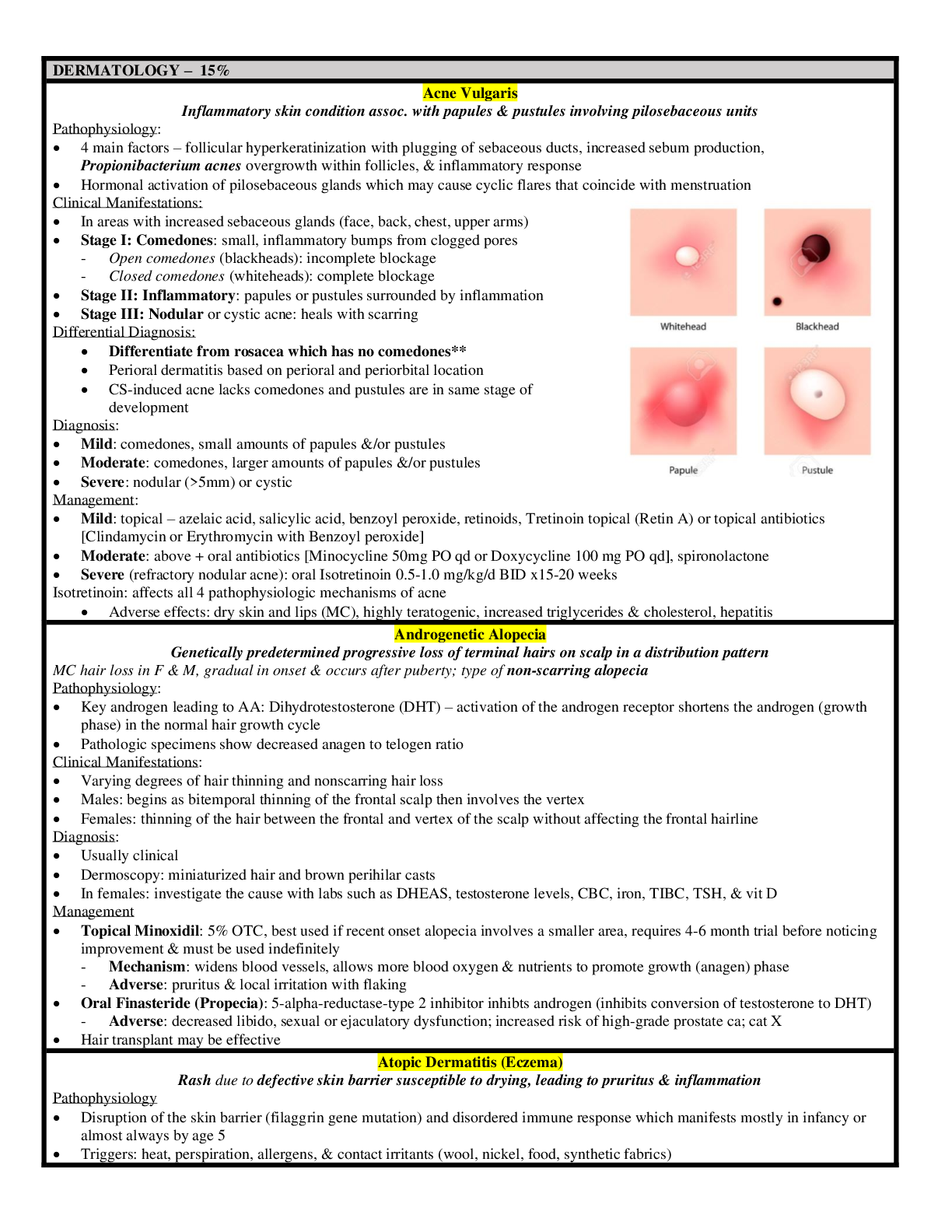






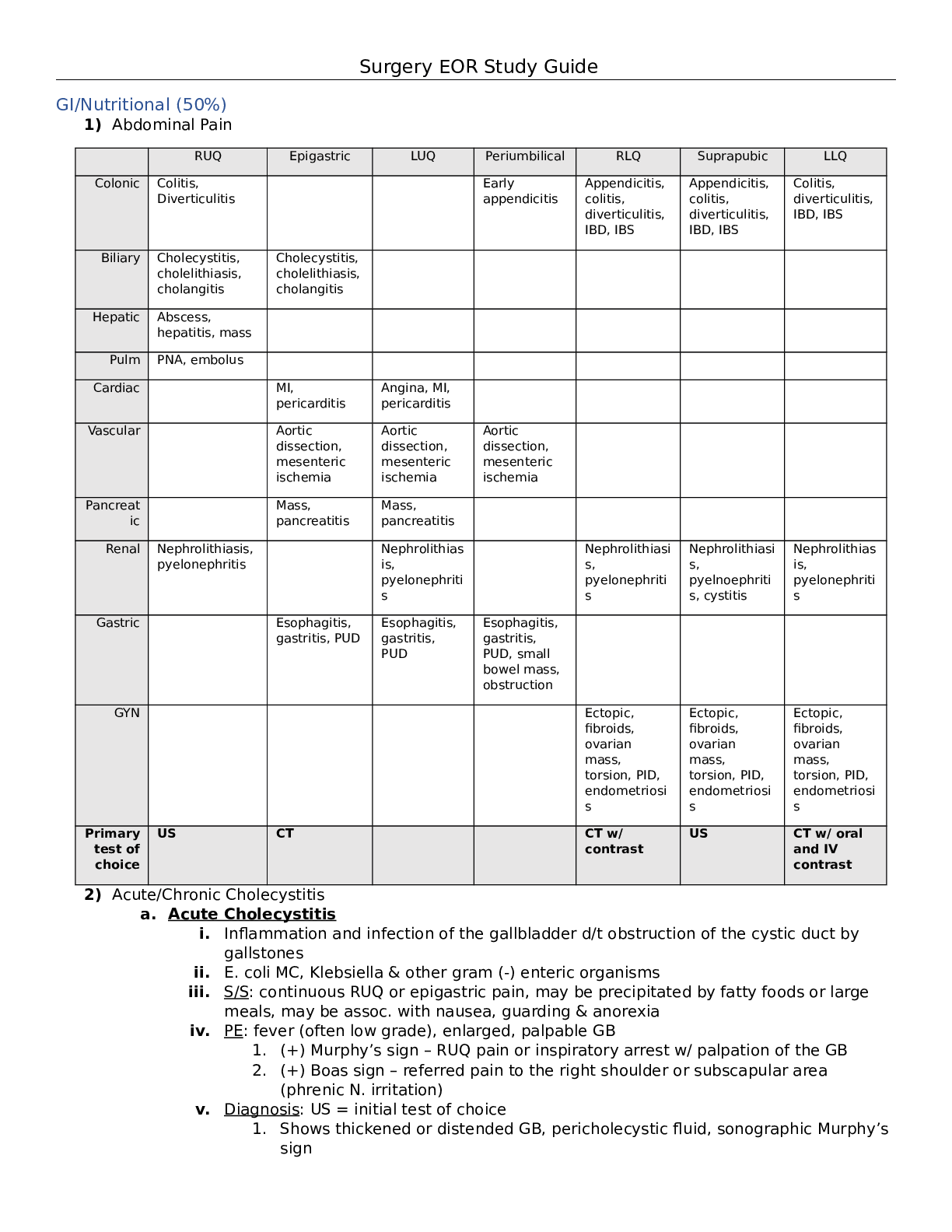


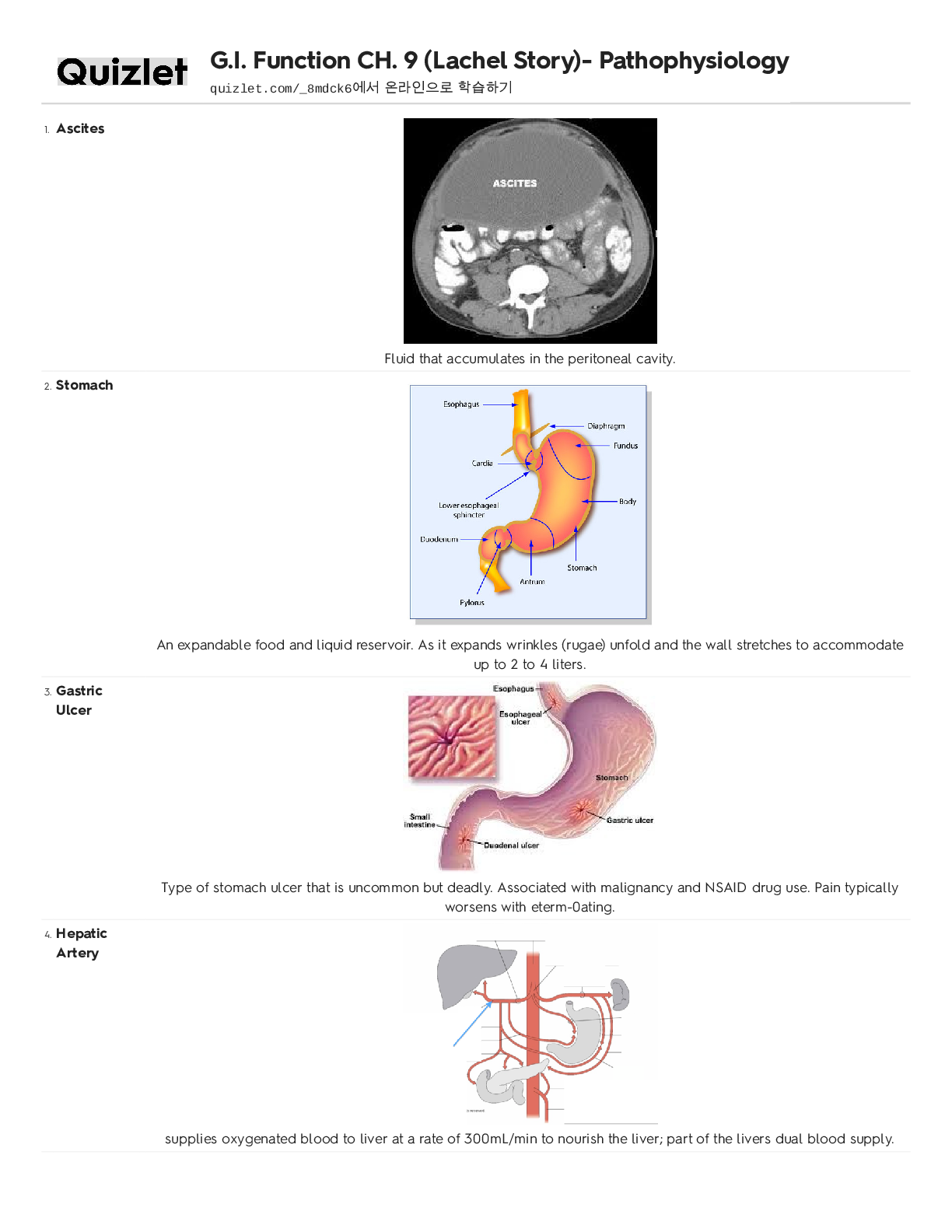









.png)




.png)