*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NUR 2092 Health Assessment Final Study Guide, A+ Help. (All)
NUR 2092 Health Assessment Final Study Guide, A+ Help.
Document Content and Description Below
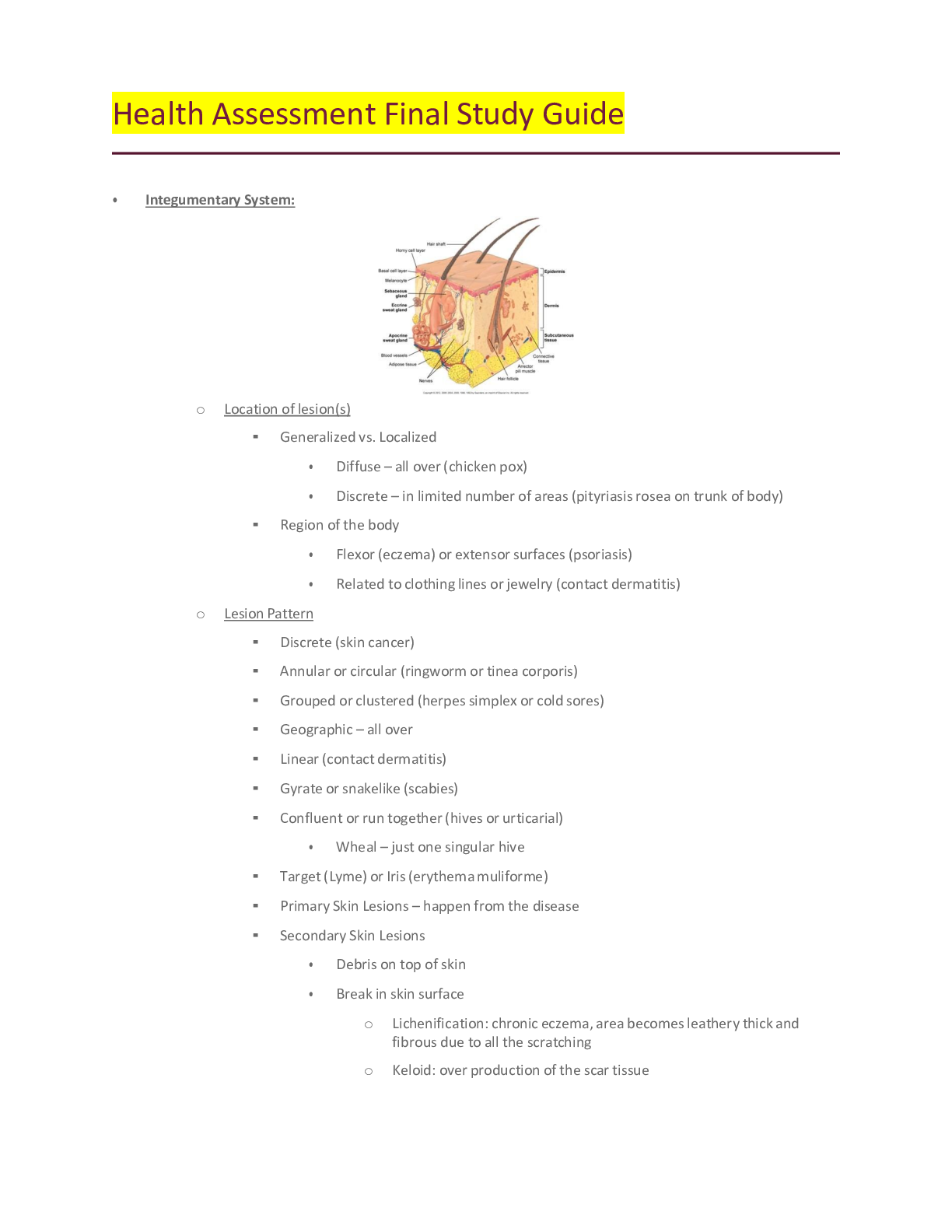
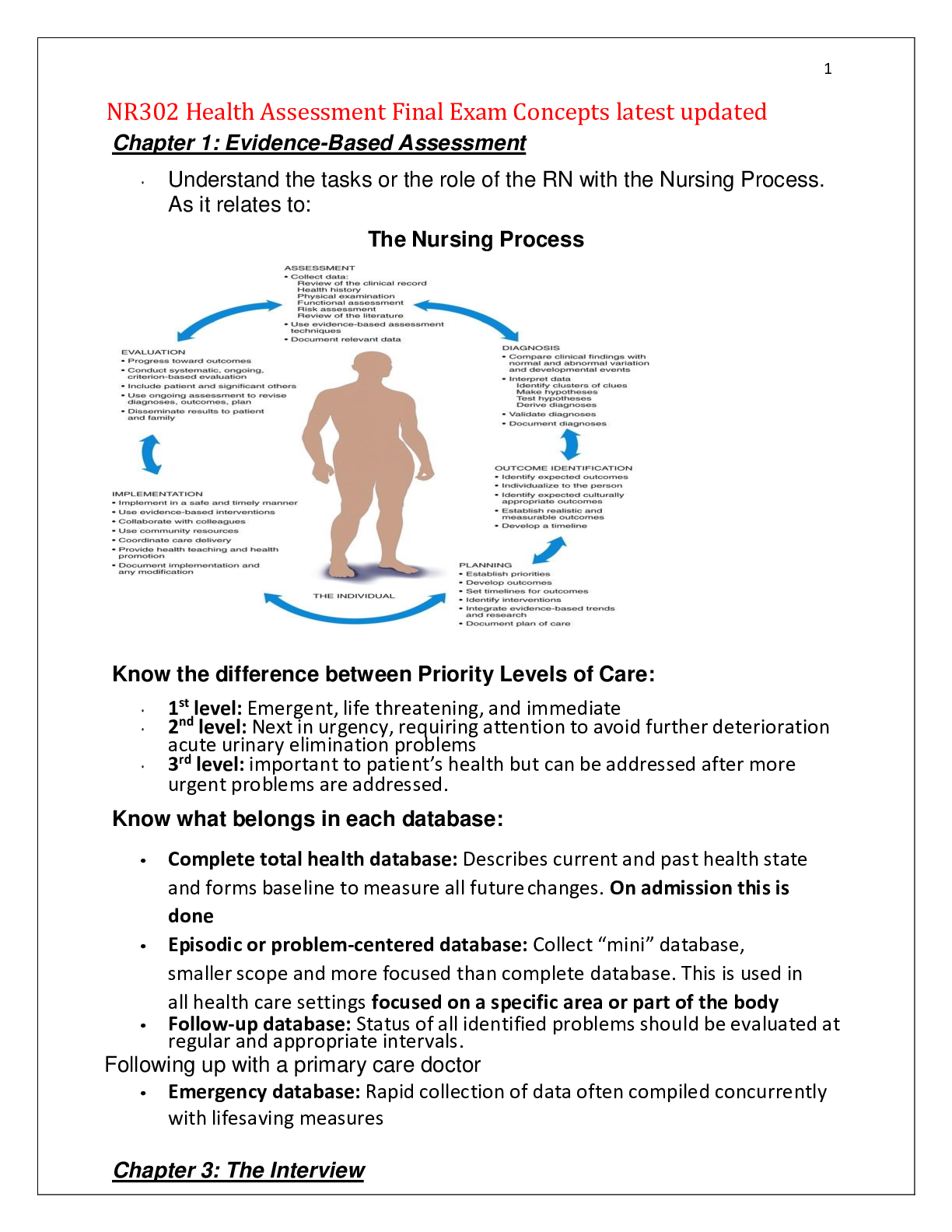
Final Exams Concepts 1. Know the difference between subjective and objective data. 2. Barriers to communication. What are they? 3. Traps of interviewing-Chapter 3 4.Open ended questions vs close... d ended questions. Know the difference and when to use them during the interview process. 5. Components of a Health History -Chapter 4. Know this Chapter!! 6. General survey and what it consists of. 7. Skills requisite of physical exam. Chapter 8. Know the correct order for assessment. (Inspection, palpation etc). Know the different order for abdominal exam. 8. Know the normal range of respirations. Above and below that range, what's it called? 9. Lung sounds- Know difference between normal vs abnormal and where they are heard. 10. Characteristics of pulse and how to document it. 11. Blood pressure cuff sizes and impact on blood pressure readings. 12. Changes in blood pressure in the elderly caused by what? 13. Assessment of ALL pulses and their locations. (Apical, radial, popliteal, etc) 14. Carotid pulse- location and abnormality is called? 15. How does the physical assessment differ of newborn , toddler, adolescent and elderly. What is important to consider with each stage? What to do differently when performing exam with each age group? 16. Diastolic vs Systolic. Know the differences. 17. What is PERRLA? 18. Psoriasis- what is it? Location on body commonly found? 19. Musculoskeletal -know different muscle movements. (Flexion, extension, etc) 20. Skin lesions- Malignant vs Non Malignant and their characteristics. 21. Know differences of Lordosis, Kyphosis, Scoliosis and Spondylosis. 22. Functional ability- what is it in the elderly population? What does it mean? How is it addressed? 23. Skin lesions-Chapter 12- know vesicles, papules, macules, cysts, wheals, pustules and know psoriasis as above. How do you document these? Using what to document them? Also, know common shapes and configurations of lesions. 24. Headaches-Migraine vs cluster- signs and symptoms of each 25. Tonsillitis-what is it? Know grading scale used to document them. 26. Edema and grading scale used to document the findings. 27. Cardiac sounds and location of each. 28. What is the Glascow coma scale? 29. Cerebellar function tests. 30. Cranial nerves and their functions and how to test them. 31. Testing reflexes and ALL superficial reflexes. • • Superficial reflex: any withdrawal reflex elicited by noxious or tactile stimulation of the skin, cornea, or mucous membrane, including the corneal, pharyngeal, and cremasteric reflexes. 32. Abdominal exam- What organs are found in each quadrant. 33. Bowel sounds-normal vs abnormal. 34. Pain level assessments and differences in the elderly. 35. Range of motion- active vs passive. 36. Know difference between- Tinnitus, vertigo and otitis media 37. Cataract vs glaucoma vs conjunctivitis. 38. Tests used for visual acuity and the difference tests used for toddlers, adolescents, elderly etc. 39. Instrumental Activities of Daily Living in the older adult. What activities are considered these? 40. Arterial vs venous insufficiency and changes found in regards to skin. 41. Assessing the differences between adult and child's ear canals. 42. Care giver burn out-signs of this? 43. Stroke prevention and common symptoms. Part 2 1. Breast cancer risk factors. 2. Location and names of lymph nodes on head and neck. 3. Carpal tunnel and tests used to determine this. 4. Know Eating disorders- Anorexia, Bulimia, Binge eating and Nervosa eating. 5. Assessing urinary elimination status-what comes first, next, last. 6. Assessment of liver disorders- jaundice in fair skinned, Asian and Dark skinned individuals. 7. Physical exam finding on patients who suffer from chronic hypoxia from pulmonary disease. 8. Gout- what is it? Risk factors in patients? 9. Testicular cancer- age most commonly found? 10. Know different breathing disorders- Orthopnea, Acute emphysema, Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, and acute shortness of breath episode. 11. Tonsillitis- physical exam findings and signs and symptoms found with this disorder. 12. Know how to test a client's hearing ability. 13. Wrist and hand abnormalities ONLY, Table 22-4, page 620. Be familiar with these. Think about most common ones! Focus on those! 14. Table 18-3, Configurations of thorax, page 441- focus on these: Pectus Carinatum, Barrel chest, Pectus excavatum and Kyphosis. 15. Costovertebral angle tenderness, page 552. Review this, we went over this in class. 16. Gynecomastia 17. Eye disorders- Ptosis, Nystagmus, Presbyopia and Exophthalmos. 18. Osteoporosis- Know what it is and Risk factors- see this link below for a good overview of risk factors NURSING NUR2092 - Final Exam Study Guide 1. Geriatrics: functional assessment-what is being tested, best approach to testing; caregiver concerns; IADLs, ADLs; disability concerns; tools to assess What is being tested Best approach to testing Caregiver concerns IADLs ADLs Disability concerns Tools to assess 2. Cultural assessment: culturally competent care; definition of ethnicity; spirituality; concepts such as assimilation, acculturation, etc. Culturally competent care Ethnicity Spirituality Ethnocentrism Acculturation Assimilation Biculturalism 3. Therapeutic communication: examples of effective and ineffective techniques e.g. clarification, reflection, blaming, etc. Therapeutic communications Examples of Therapeutic communications Barriers to communication 10 Traps of Interviewing 4. General survey – what is included? General Survey Temperature Heart rate Respiratory rate Blood pressure 5. Nutrition: Dietary assessment; abnormal eating patterns Dietary assessment Abnormal eating patterns 6. Skin: staging of decubitus ulcers, primary skin lesions like nodules, pustules, etc.; common skin lesions, for ex. Psoriasis, contact dermatitis; signs of malignant skin lesions; color differences seen in dark skinned individuals; lesion configurations 7. Musculoskeletal – range of motion techniques; points for comparison; osteoporosis risk factors; spinal assessment findings; testing various joints including jaw Range of motion techniques Points of comparison Osteoporosis risk factors Spinal assessment findings Testing various joints including jaw 8. Thorax/Respiratory assessment – auscultation, palpation; normal and abnormal sounds; proper method of auscultation; methods- e.g. voice sounds, thoracic expansion, vocal fremitus, etc.; chest shapes Auscultation Palpation Normal and abnormal sounds Methods Chest shapes 9. Heart: cardiac cycle; auscultation sites Cardiac cycle Auscultation sites 10. HEENT: eye examination techniques; hearing tests Eye examination techniques Hearing tests 11. Pulses- where are they, how do you document information about them; peripheral vascular assessment, edema – appearance, scale Pulses Document pulses Peripheral vascular assessment Edema Edema scale 12. Neuro – Glasgow coma scale; reflexes; cranial nerves – how do you test each one; testing for cerebellar function; tests such as graphestheisa, position sense, two point discrimination, stereognosis, etc. Glasgow coma scale Reflexes Cranial nerves Testing for cerebellar function Tests 13. Vital signs: BP – proper method, findings if not done properly; normal ranges Blood pressure Proper method Findings if not done properly 14. Abdomen – methods of assessment Methods of assessment 15. Pain assessment techniques Techniques Tools 16. Domestic abuse – when to assess When to assess ALL THE TIME! 17. Substance abuse Alcohol use Quick assessment 18. History taking/symptom analysis – components of a health history (what is in each component); subjective vs objective data; examples of open and closed ended questions; history first Components of a health history Subjective vs objective data Open ended questions Closed ended questions - What is included in a health history? Biographic data [Name, address, DOB, occupation, gender, martital status, primary language, ethnicity] Reason for seeking care: Subjective from pt Present health status Medications, Immunizations, What improves it, What makes it worse, Past medical history Surgical history, OB /GYN Nutritional Hx Family history First generation Personal and psychosocial history Support, living environment, Substances, Safety Review of body systems: PQRSTU Define subjective and objective. Subjective: What pt says about themself Objective: what is observed during assessment Give an example of an open ended question. Tell me about , how are you doing today Now a closed question Do you have pain? What is redirecting, silence, restating? Communication that client has time to think; silence can be uncomfortable; provides you w/ chance to observe client and note nonverbal cues What should be included in social history? where do they live, are they safe, do they have clean water, head, air conditioning, do you work, do you feel safe, smoke, alcohol, recreational drugs, safety devices, do you exercise, safety equipment, sun screen Why is this information necessary? When do you screen for intimate partner violence? Always What questions do you need to ask each time you enter a patient’s room? (2 of them) -Name and DOB Pain assessment: what scale do you use? 0-10 How often do you do a pain assessment? Every Assessment Non pharmacological and pharmacological pain management. Describe 2 methods. Deep or patterned breathing Relaxation techniques Warm or cool compresses Compression/elevation Quiet dark room Position change Pillows/clean linens Bathing Music distraction What questions do you ask regarding pain? What kind of pain? When did it start? Where? Worse or better? PQRST Proactive/Palliation:Quality:Region:Severity:Timing Barriers to communication: Name 3 -Lack of interest or attention/lack of respect -Physical barriers: a curtain, a door, a computer, a monitor, pain, room temperature -The patient’s inability to hear you, hearing deficit, or language barrier -Language/ use of jargon, or speaking above someone’s educational level -Safety: fear -Psychological barriers: embarrassment, disbelief, shock, anger, fear, grief, fatigue, hostility What is clarification, ordering? Useful when person's word choice is ambiguous or confusing Summarize person's words, simplify the statement, and ensure that you are on the right track What is assessed during a general survey? What is bulimia? What is anorexia? What is a fast way to assess nutritional intake? 1. HEALTH HISTORY 2. TYPES OF ASSESSMENT 3. VITALS 4. COMMUNICATION 5. INTEGUMENT/SKIN 6. HEENT 7. CARDIAC AND PERIPHERAL VASCULAR 8. RESPIRATOY/THORACIC 9. ABDOMEN 10. GENITOURINARY [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 29 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 04, 2020
Number of pages
29
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 04, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
32


















.png)

.png)