*NURSING > SHADOW HEALTH > NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment | Chamberlain College of Nur (All)
NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment | Chamberlain College of Nursing | Latest 2020/2021
Document Content and Description Below
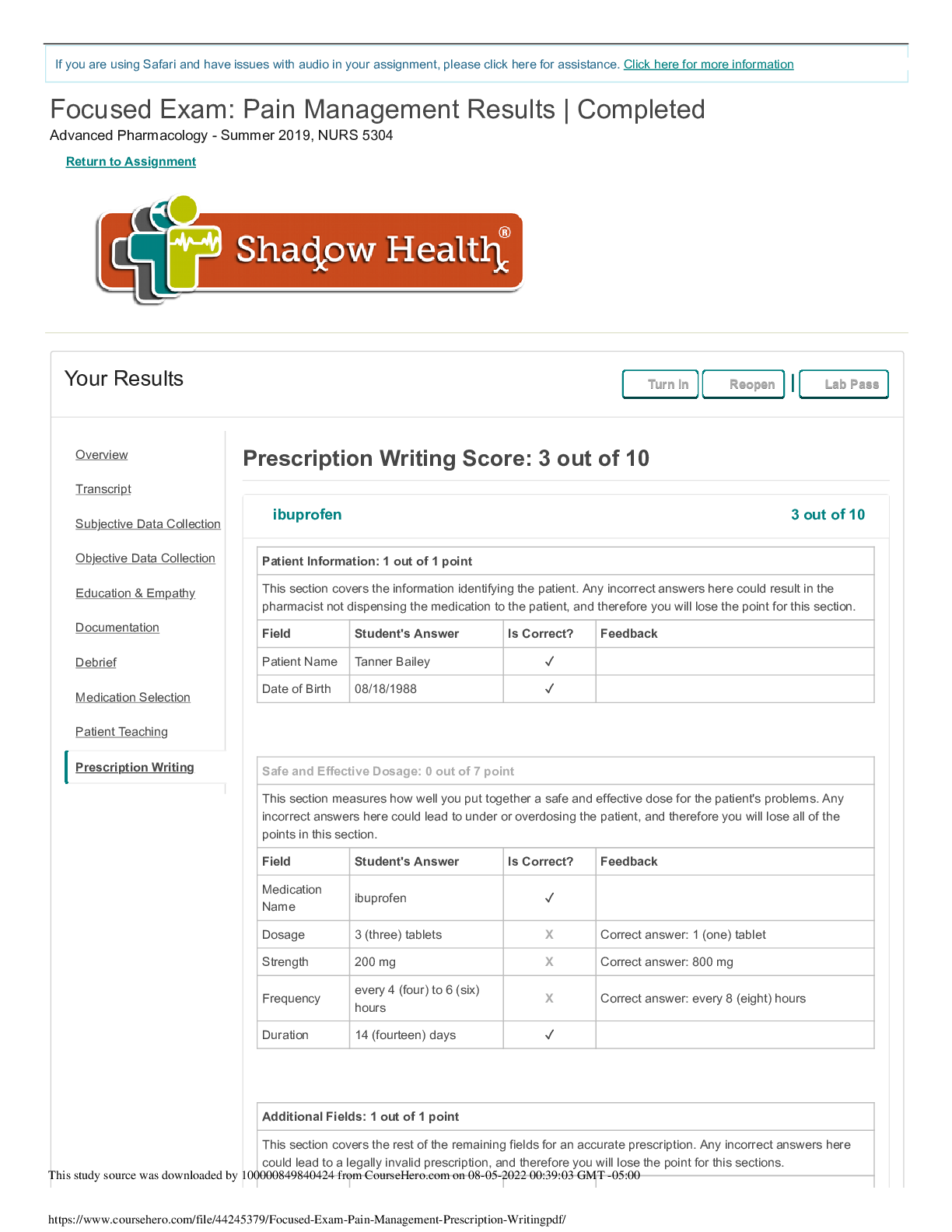
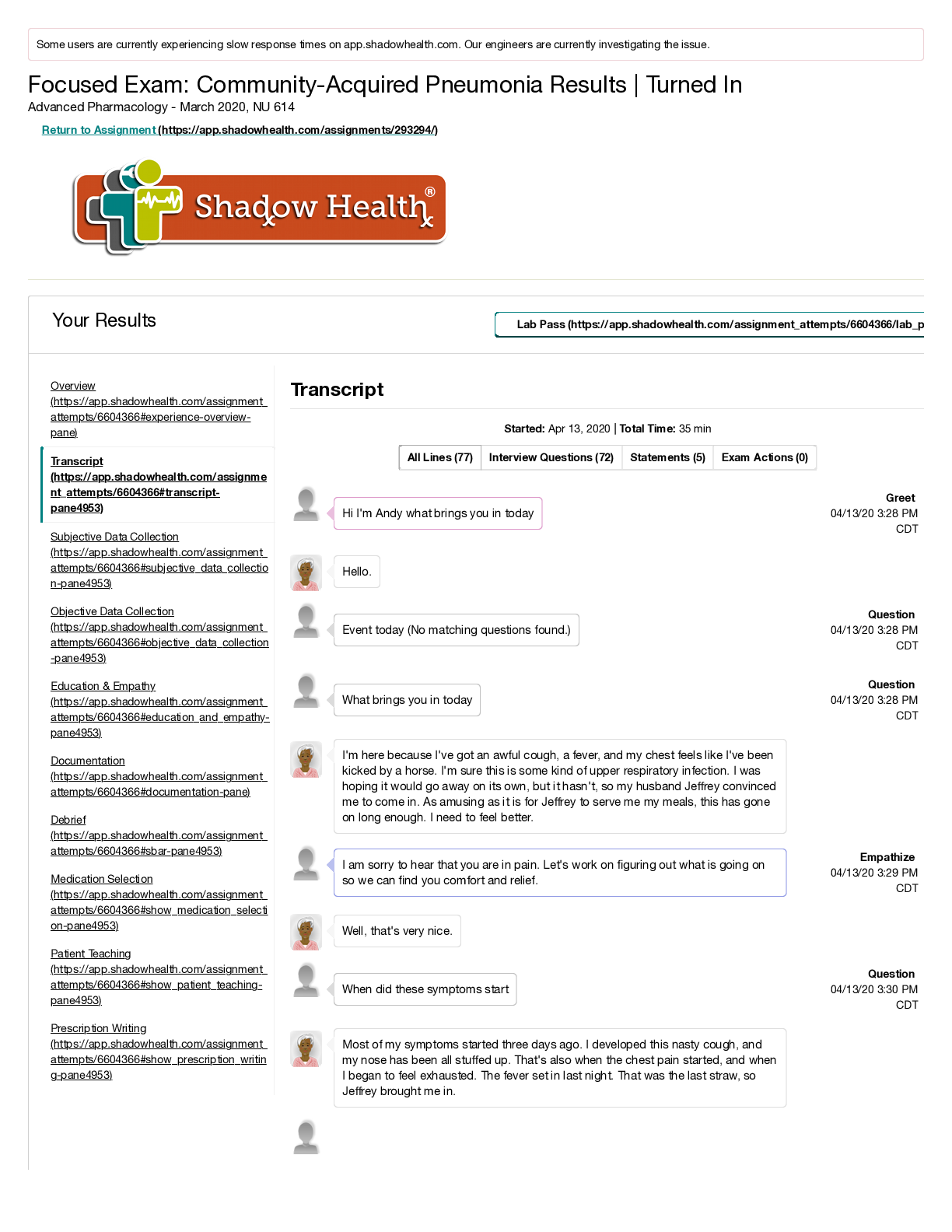
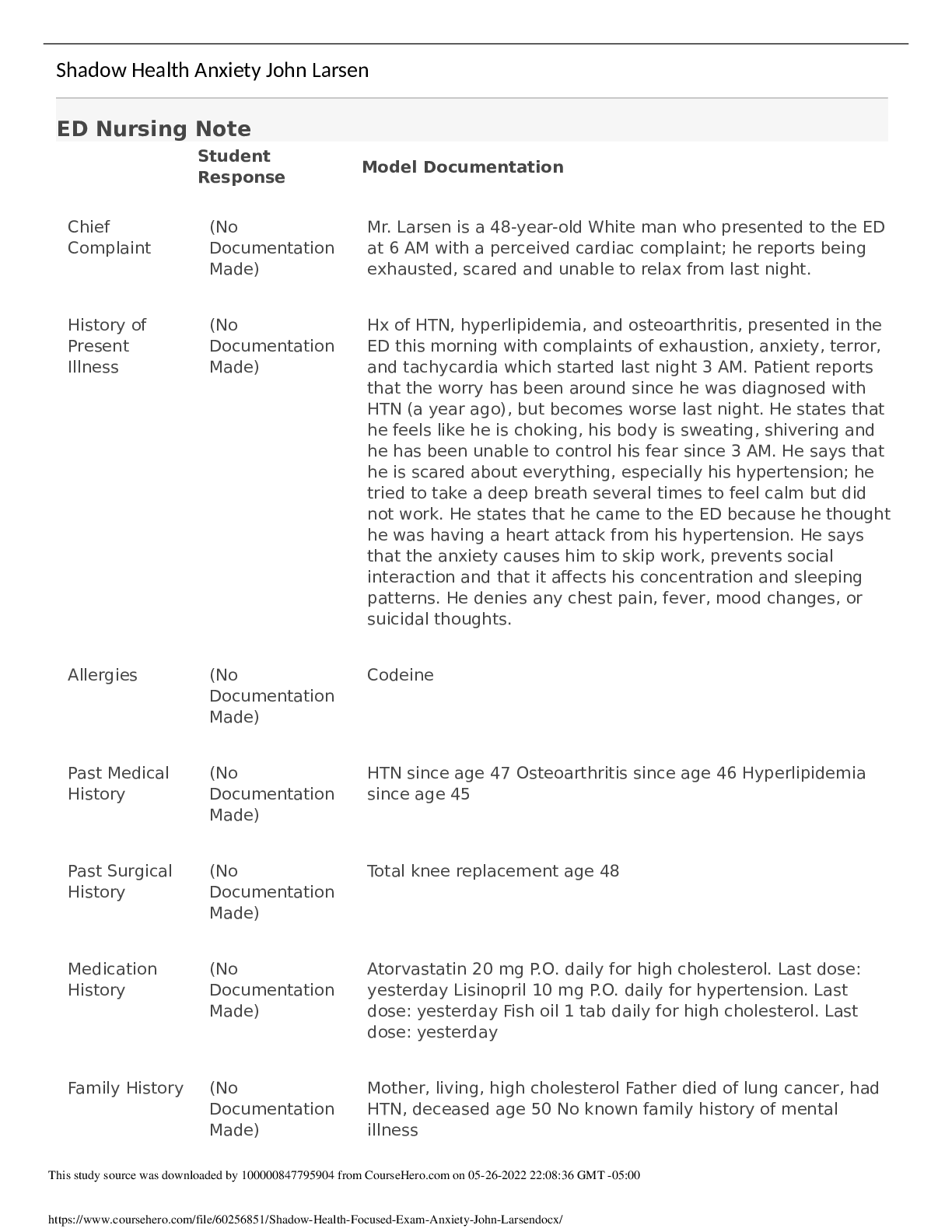
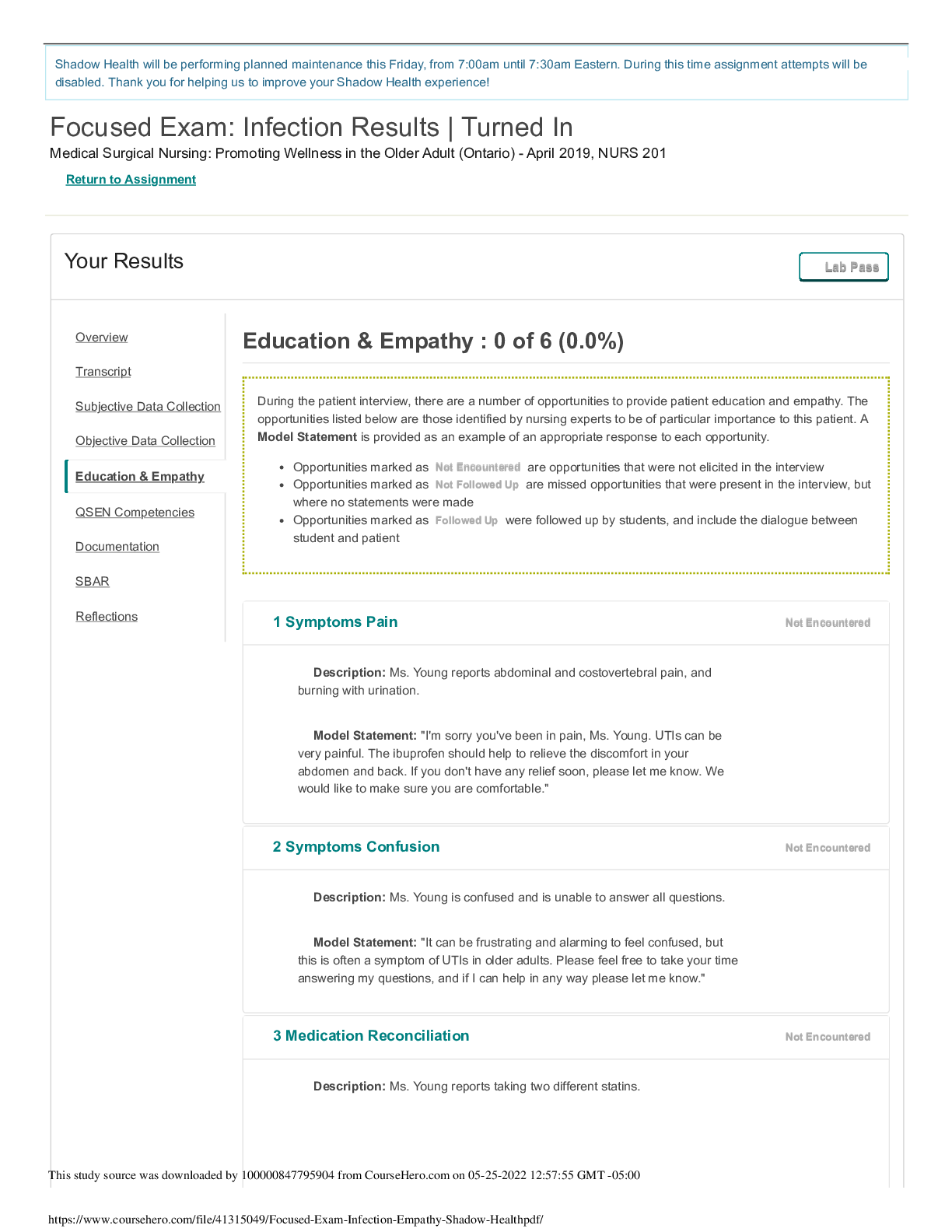
NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment Pre Brief Two days after a minor, low-speed car acc... ident in which Tina was a passenger, she noticed daily bilateral headaches along with neck stiffness. She reports that it hurts to move her neck, and she believes her neck might be swollen. She did not lose consciousness in the accident and denies changes in level of consciousness since that time. She states that she gets a headache every day that lasts approximately 1-2 hours. She occasionally takes 650 mg of over the counter Tylenol with relief of the pain. This case study will allow you the opportunity to examine the patient’s optic nerve via use of the ophthalmoscope as well as assess her visual acuity. You will need to document your findings using appropriate medical terminology. Be sure to assess for foot neuropathy using the monofilament test. Reason for visit: Patient presents complaining of headache. NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment. . • Results: Transcript • Results: Subjective Data Collection • Results: Objective Data Collection • Results: Education & Empathy • Results: Documentation / Electronic Health Record • Results: Pre – Survey Lifespan • Results: Review Questions • Results: Self-Reflection • NR 509 Week 3 Shadow Health Neurological Physical Assessment Assignment Objective Data Collection: 36.75 of 37 (99.32%) • Correct • Partially correct • Incorrect • Missed Confirmed orientation 1 of 1 point To Person (1/3 point) • Oriented to person • Not oriented to person To Place (1/3 point) • Oriented to place • Not oriented to place To Time (1/3 point) • Oriented to time • Not oriented to time Evaluated abstract thinking 1 of 1 point Abstractness (1/2 point) • Abstract • Concrete Relevance (1/2 point) • Relevant • Not relevant Evaluated attention span 1 of 1 point Serial 7s Test (1/1 point) • Accurate • Not accurate Evaluated comprehension 1 of 1 point Observations (1/1 point) • Able to follow instructions • Unable to follow instructions Evaluated general knowledge 1 of 1 point Accuracy (1/1 point) • Accurate • Not accurate Evaluated judgment 1 of 1 point Observations (1/1 point) • Intact • Not intact Evaluated memory 1 of 1 point Remote Memory (1/3 point) • Intact • Not intact Immediate Memory (1/3 point) • Intact • Not intact New Learning Ability (1/3 point) • Accurate • Not accurate Observed vocabulary 1 of 1 point Complexity (1/1 point) • Expected complex for patient’s age, education level, and general ability • Not expected complexity Observed articulation 1 of 1 point Observations (1/1 point) • No observed problems with pronunciation or expression • Imprecise pronunciation of consonants • Slurring • Hesitation • Stutter Tested olfactory nerve 1 of 1 point Sense Of Smell (1/2 point) • Able to discriminate • Not able to discriminate Symmetric (1/2 point) • Symmetric bilaterally • Asymmetric Tested visual acuity (optic nerve) 1 of 1 point Right (1/2 point) • 20/100 • 20/70 • 20/50 • 20/40 • 20/30 • 20/25 • 20/20 • 20/15 • 20/13 • 20/10 Left (1/2 point) • 20/100 • 20/70 • 20/50 • 20/40 • 20/30 • 20/25 • 20/20 • 20/15 • 20/13 • 20/10 Examined retina with ophthalmoscope (optic nerve) 0.75 of 1 point Right: Fundus (No point) • No visible abnormal findings • Myelinated nerve fibers • Papilledema Subjective Data Collection: 20 of 20 (100.0%) Hover To Reveal… Hover over the Patient Data items below to reveal important information, including Pro Tips and Example Questions. • Found: Indicates an item that you found. • Available: Indicates an item that is available to be found. Category Scored Items Experts selected these topics as essential components of a strong, thorough interview with this patient. Patient Data Not Scored A combination of open and closed questions will yield better patient data. The following details are facts of the patient’s case. Chief Complaint Finding: Established chief complaint Finding: Reports recent “fender bender” (Found) Pro Tip: Patients choose to seek treatment for a variety of reasons. Asking why Tina chose to seek treatment today might indicate primary concerns, the severity of her symptoms, or failure to manage symptoms herself. Example Question: Why are you seeking treatment today? Finding: Reports headaches (Found) Pro Tip: Symptoms often vary from patient to patient. Asking Tina if she’s had headaches specifies the way her individual symptoms and pain manifest. Example Question: Have you had any headaches? Finding: Reports neck symptoms (Found) Pro Tip: Symptoms often vary from patient to patient. Asking Tina if she’s had neck stiffness specifies the way her individual symptoms and pain manifest. Example Question: Have you had any neck stiffness? History of Present Illness Finding: Asked about onset of symptoms Finding: Reports accident occurred 1 week ago (Available) Pro Tip: Soliciting a relevant history of Tina’s car accident will allow you to understand the context in which she was injured and the injuries she sustained. Example Question: When did the accident happen? Finding: Reports symptoms began 2 days after accident (Found) Pro Tip: Symptoms often vary from patient to patient. Asking Tina when the headaches begin specifies the way her individual symptoms and pain manifest. Example Question: When did the headaches begin? Finding: Followed up on details of car accident Finding: Denies loss of consciousness (Found) Pro Tip: Soliciting a relevant history of Tina’s car accident will allow you to understand the context in which she was injured and the injuries she sustained. Example Question: Did you lose consciousness during the car accident? Finding: Reports low vehicle speed (Found) Pro Tip: Soliciting a relevant history of Tina’s car accident will allow you to understand the context in which she was injured and the injuries she sustained. Example Question: How fast was the car going? Finding: Reports wearing seatbelt Transcript Started: Mar 18, 2020 | Total Time: 219 min All Lines (155)Interview Questions (94)Statements (3)Exam Actions (58) Hello Tina. Welcome to our clinic. Am Pam, i will be interviewing you today, and later do a physical examination on you Hey. Greet What brings you to the clinic today? Question Well, I got into a little fender bender a week ago and I’ve been getting these headaches ever since. And my neck is sore too. Am sorry to hear that you are having headaches Empathize Thanks for saying that. Have you had any neck stiffness? Question Yeah. When did the neck stiffness begin? Question My neck started hurting about two days after the accident. Am sorry that you got an accident (No matching questions found.) Question Am sorry that you got an accident Empathize Thanks. And when did the headaches begin? (Clarified to When did the headache begin?.) Question Review QuestionsActivity Time: 6 min To assess spinal levels L2, L3 and L4 in Tina, which deep tendon reflexes would have to be tested? Correct: The patellar deep tendon reflex involves the sensory and motor nerve fibers associated with spinal segments L2, L3, and L4. Location of abnormal reflexes may be helpful in identifying neurological pathologies of the spine. • Achilles • Biceps • Patellar (Correct Response) • Triceps Imagine that you were preparing to irrigate a Foley catheter of a patient with a spinal cord injury at T4 in a urology clinic. Upon moving the leg bag, the patient became suddenly flushed and diaphoretic above the nipple line. What would you suspect was happening? Correct: Autonomic dysreflexia is the sudden increase in blood pressure caused by dysregulation of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems reacting to a noxious stimulus below the site of spinal injury. Other symptoms include bradycardia, anxiety, blurred vision, headache, flushing, and sweating. The noxious stimulus (pulling of the Foley catheter) should be alleviated to resolve the condition. • Odynophagia • Febrile reaction • Idiopathic spinal reaction • Autonomic dysreflexia (Correct Response) Which of the following is not a common symptom of Parkinson’s disease? Correct: Parkinson’s disease is characterized by tremors at rest, bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity, postural instability, festination, lack of facial expression, reduced arm swing, autonomic and neuroendocrine dysfunctions, and a variety of psychological issues such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. • Lack of facial expression • Festination • Cogwheel rigidity • Intention tremors (Correct Response) Name at least three ways to assess cerebellar function during a physical exam. Student Response: Test cerebellar function by assessing gait and instructing the patient to perform the finger-to-finger, finger-to-nose, heel-to-shin, rapid alternating movements Model Note: The cerebellum is responsible for smooth and accurate coordination of voluntary movements. You can test cerebellar function by assessing gait and by instructing the patient to perform the finger-to-finger, finger-to-nose, heel-to-shin, rapid alternating movements, and Romberg tests. If Tina had a fever and photophobia, you would have had to test for meningitis. Describe how you would have tested for the Kernig’s sign. Lifespan Activity Time: 10 min Tina’s three-year-old neighbor presents to the clinic with fever, neck pain, headache, and confusion. He has no symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. The parents mention that they do not believe in immunizations. Based on the information given, what diagnosis is of the greatest concern? What is your next action? Student Response: Rule out bacterial meningitis, there was no immunizations to increase meningitis risk. Model Note: Bacterial Meningitis needs to be ruled out immediately. He has not had immunizations which puts him at increased risk for meningitis from Haemophilus influenzae type B. Seizure disorder does not cause fever. Children with immunodeficiency syndrome are at increased risk for meningitis but this child has no previous history of chronic infections. Although children with strep throat can present with fever and neck pain, they are not confused. He needs an immediate spinal tap to determine the nature of the meningitis, and broad spectrum antibiotics should be started as soon as possible. He should be sent to the emergency room. Tina’s 83-year-old great uncle forgets where he is during his yearly check-up. He doesn’t remember if he’s had memory problems before and no family members came to your office with him. List your dif erential diagnosis. What assessments would you perform? Student Response: Differential diagnosis include stroke… [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 11 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2021
Number of pages
11
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
120