HESI A2 latest complete Biology Study Guide 2021
Document Content and Description Below
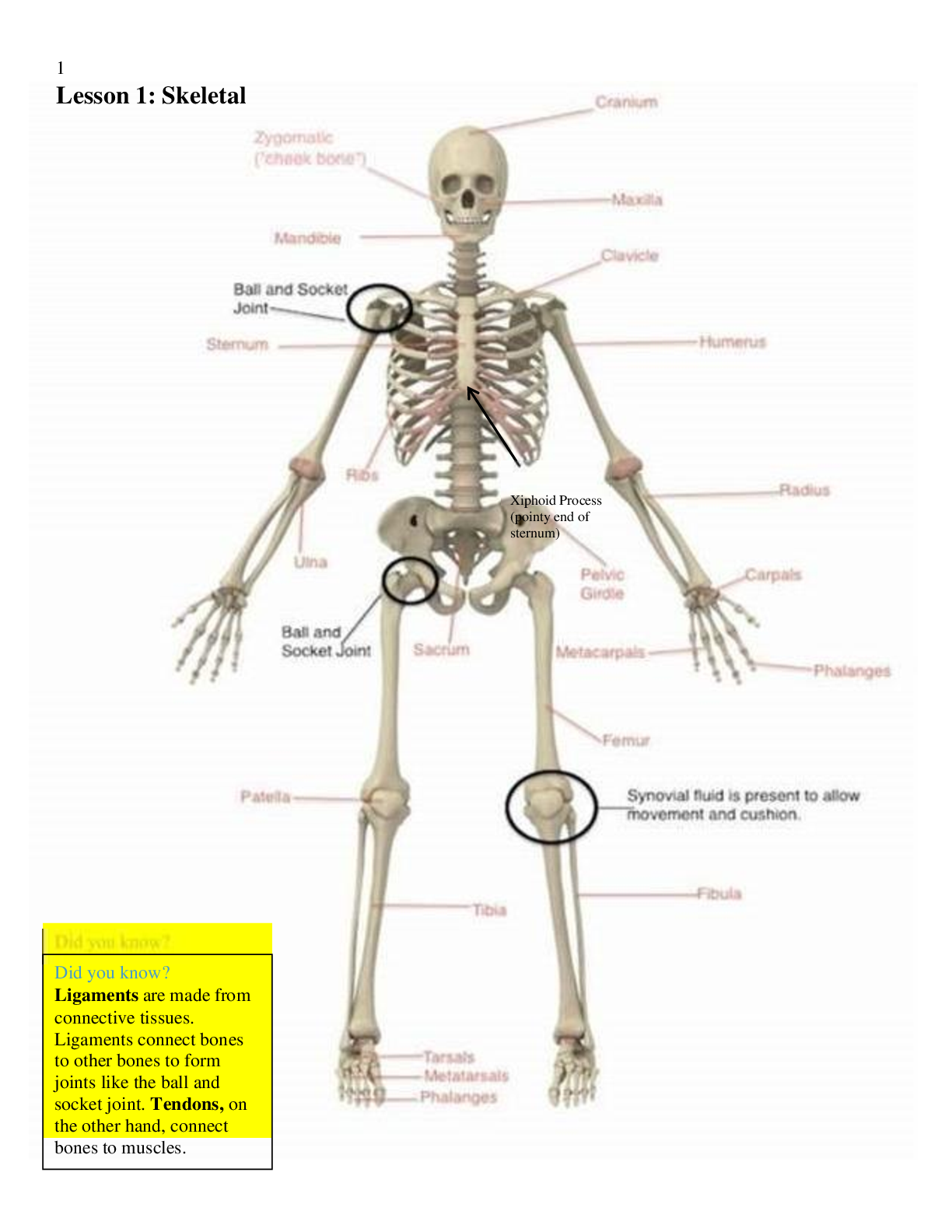
Ready For The HESI A2 Biology Study Guide • Chapter summaries • Biology vocabulary • HESI-style Biology Practice Questions • Diagrams and explanations HESI A2 Biology Study Guid... e Cellular respiration Cellular respiration is the process inside of cells that converts nutrients (such as sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids) into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is used throughout the organism for energy. Large molecules are broken into smaller molecules, which releases both energy and waste. Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of Oxygen and has four main stages: • Glycolysis: Larger sugar molecule is broken down into 2 smaller sugar molecules in the cytoplasm. Net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH • Formation of Acetyl CoA: Pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to form Acetyl coenzyme A. 1 CO2 is released as waste. Net gain of 2 NADH. • Citric acid cycle: also known as Krebs cycle. The 2 small sugar molecules produced during glycolysis are oxidized forming new products. Gain of 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2. • Electron transport chain: redox reaction involving the electrons removed during glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Protons are pumped across the mitochondrial membrane to form a gradient, which drives the synthesis of 34 ATP. Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration which occurs when oxygen is not present. This process is most commonly performed by bacteria and Achaea. These organisms use this process to obtain energy because they live in environments with low oxygen levels. Example: Achaea called methanogens use carbon dioxide to accept electrons. Methanogens can be found in soil and the digestive systems of animals called ruminants, which includes cows and sheep. Anaerobic respiration, similar to aerobic cellular respiration, uses electrons from the fuel molecules to pass through the electron transport chain, which drives ATP synthesis. The electron transport chain moves electrons to create a proton gradient that allows for the synthesis of ATP. Electron transport chains are used for extracting energy. This can happen in plants, where the energy from the sunlight is used to create glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis in the chloroplast. Eukaryotes perform this process in the mitochondria. Fermentation is another type of cellular respiration which occurs in the absence of Oxygen. Organisms capable of fermentation include prokaryotes, yeast, and multicellular organisms such as humans. Feature Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic Respiration Oxygen requirement Yes, always No, never Waste products Carbon dioxide and water Carbon dioxide and ethanol Efficiency in releasing energy from glucose Very efficient (most of the energy is released from glucose) Less efficient (some energy locked in ethanol is not released) Some energy released as heat Yes Yes, but less than that for aerobic respiration Antibiotics Antibiotics are a kind of medicine used to treat bacterial infections. Not all bacteria are bad or unhealthy. Humans and other animals actually have a healthy ecosystem of bacteria, called normal flora. These are the good kind of bacteria. Pathogenic bacteria are the type which can cause infection. Some bacteria will cause infection no matter where they are, but others are safe in some areas of the body, but become infectious when they wander to a new location in the body. An example of this is if the bacteria in the gut, or intestines, were to try and live in the bladder or another organ. This is what happens in case of a urinary tract infection. The body’s immune system must try to fight and destroy the invading bacteria. Antibiotics are chemicals that enter and stick to certain parts of the bacterial cell. The parts where the antibiotics can attach can be the proteins/sugars in the bacterial cell wall or the important enzymes that make new bacterial DNA or proteins. This act of blocking these parts interferes with the bacteria’s ability to survive and multiply. If the correct antibiotic is used, the bacteria will stop growing or die. Without antibiotics, bacteria can grow and multiply, especially if the immune system cannot battle the bacteria. If enough antibiotic is present, the bacterial cell is crippled and stops growing, known as bacteriostatic, or it simply dies, known as the bactericidal effect. Antibiotics do not affect viruses, fungi or parasites as they bind only to bacterial cell targets. Some bacteria have the ability to become antibiotic resistant. This happens when bacteria have overexposure to antibiotics. The bacteria no longer are affected by the antibiotic because it undergoes mutations. Cells and tissues The basic building block of the body is the cell. Cells can perform a wide variety of functions, depending on the specialized type of cell that it is. Every type of cell plays a vital role in growth, development, and maintenance of the body. Cells from all organisms, ranging from humans to plants to bacteria, share certain characteristics. There are two categories that cells fall into: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms from the domains Bacteria and Archaea. “Pro-” means before and “kary-” means nucleus, hence prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes are made of two or more cells. “Eu-” means true, which means that eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. All types of cells share four key components: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA and ribosomes. Prokaryotic cells have DNA, but it is not housed in a nucleus. The majority of the DNA in prokaryotic cells is found in a central region of the cell called the nucleoid. Bacteria are a specific type of prokaryotic cell. Most bacteria are surrounded by a rigid cell wall, which provides an extra layer of protection, helps the cell maintain its shape and prevent dehydration. Many bacteria have an outermost capsule that is sticky and helps the cell attach to its surroundings. Some bacteria also have a flagellum. It is a whip-like structure that acts like a motor to help the bacteria to move. Fimbriae are hair-like structures that are used to attach to other surfaces or host cells. Sometimes bacteria have pili, which allows the cell to transfer DNA to other bacteria or helps with locomotion (movement). Eukaryotic cells are significantly more complex compared to prokaryotic cells. They contain a variety of different compartments that have specialized functions, and are separated by layers of membrane. This organization allows each compartment to maintain its respective conditions and do what it needs to carry out its job. These compartments are called organelles. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and multiple linear chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells have an array of organelles that are important for energy balance, metabolism, and gene expression. .....................................................................CONTINUED................................................................................ [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 05, 2021
Number of pages
5
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 05, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
114


























 (1).png)




