BioChemistry > Lab Report > Partial purification and characterization of yeast invertase using Enzyme Kinetics (using Fraction 4 (All)
Partial purification and characterization of yeast invertase using Enzyme Kinetics (using Fraction 4) and Acrylamide Electrophoresis University of the West Indies at St. Augustine - BIOC 2169PS LAB 4
Document Content and Description Below
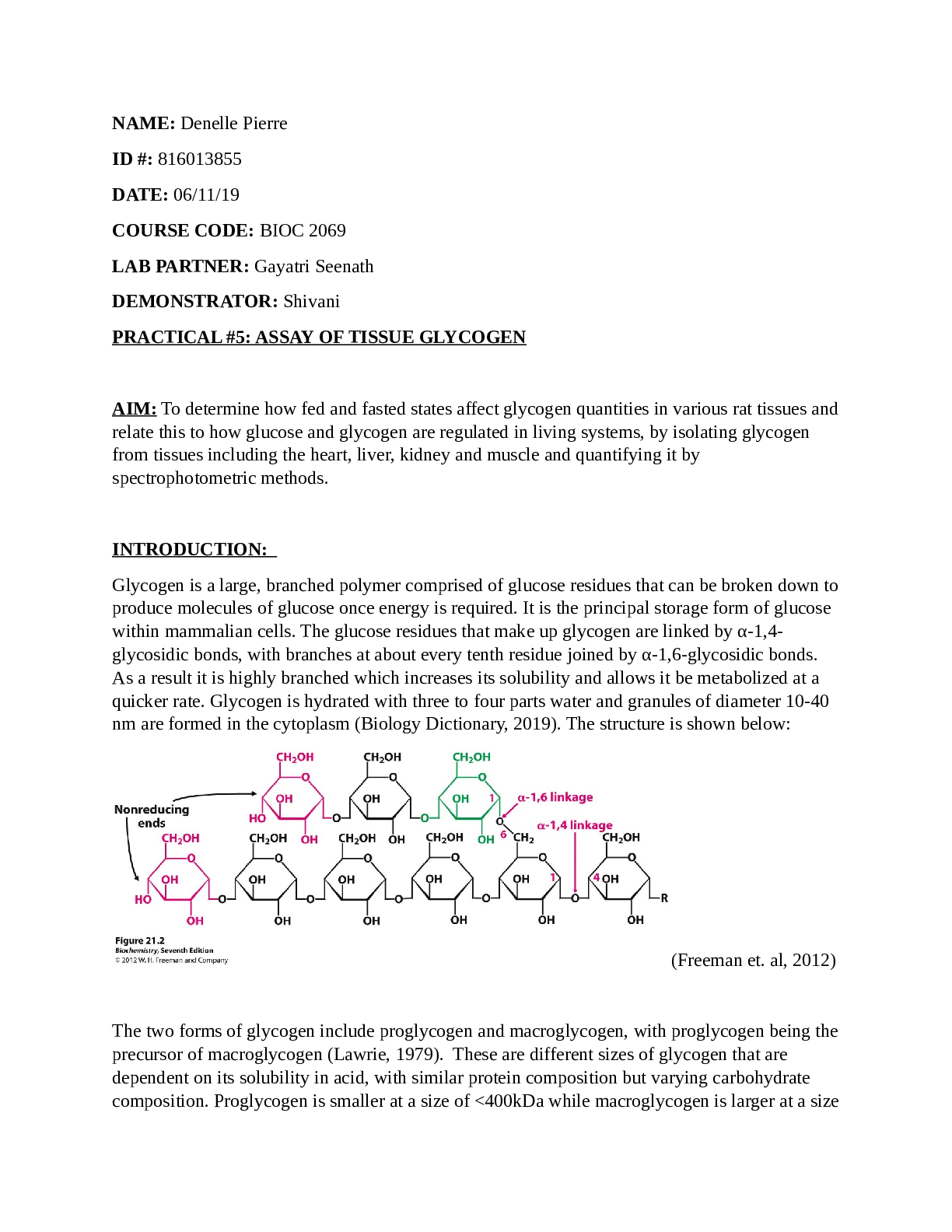
TITLE Partial purification and characterization of yeast invertase using Enzyme Kinetics (using Fraction 4) and Acrylamide Electrophoresis. AIM To obtain valid Michaelis-Menten Kinetic data for In... vertase Enzyme using Fraction 4 and Acrylamide Electrophoresis. INTRODUCTION Enzymes are catalyst that speeds up biochemical reactions, however they remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. Enzymes consist of an active site which is a space where other molecules can bind to it, this other molecule is known as the substrate. The two molecules combined are known as the enzyme-substrate complex, they are held in place by temporary bonds. Enzymes increases the rate of a reaction by lowering the activation energy of the substrate or by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur. Enzymes are made up of one or more amino acid chains which is known as polypeptide chains, the sequence of amino acids determines the folding patterns of the structure. This structure of the protein is vital to enzyme specificity. The specificity of an enzyme is the ability to select the right substrate from those that are similar. Enzymes bind to molecules with a specific conformation. “The four types of enzymes specificity are, absolute specificity where only one reaction will be catalysed, in Group specificity on molecules with a certain functional group will be acted upon by the enzyme. Linkage specificity, the enzyme will only act upon a specific type of chemical bond regardless of the rest of the structure. Lastly, in stereochemical specificity a particular steric or optical isomer will be acted on by the enzymes.” (Worthington Biochemical Corp,2015) Specificity constant is known as the measurement for enzyme specificity. Specificity constant= Kcat/KM Kcat = the number of reactants per catalytic site per second (1/s) KM = Michaelis- Menta constant (Substrate concentration at half the maximum velocity)FIGURE 1- GRAPH SHOWING THE EFFECT OF SUBSTRATE CONCENTRATION. (“Introduction to Enzymes.” Substrate Concentration (Introduction to Enzymes). Accessed April 27, 2020. http://www.worthingtonbiochem.com/introBiochem/substrateConc.html.) In the event that the substrate concentration is gradually increasing and the amount of enzyme is kept steady, the velocity of the reaction will increment until maximum is achieved. At the point when maximum is reached, the available enzymes are changed to the enzyme substrate complex. This is known as VMAX on the graph. Michaelis- Menten developed the equation based on this. FIGURE 2- MICHAELIS- MENTEN EQUATION. (“Introduction to Enzymes.” Substrate Concentration (Introduction to Enzymes). [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 25 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 13, 2021
Number of pages
25
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
91




.png)