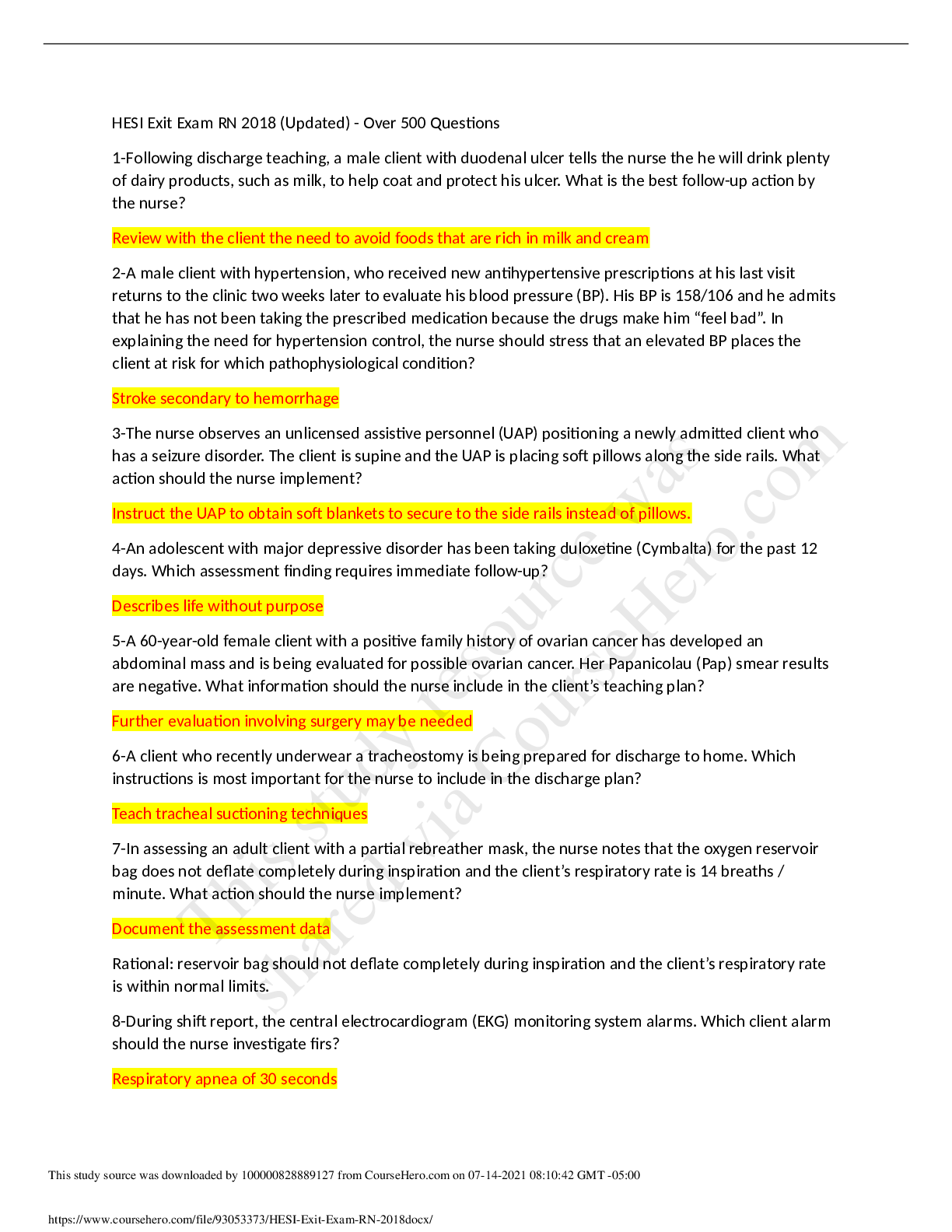PN Comprehensive Predictor 2017 (Rated A+).
Document Content and Description Below
protect their clients’ rights. Managing client care: requesting reassignment of a client - Assigning is performed in a downward or lateral manner with regard to members of the health care team. ... - The five major management functions are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. - The 5 rights of delegation: right task, circumstance, person, direction and communication. Protecting the rights of a dying client - Nurses are accountable for protecting the rights of clients. Situations that require particular attention include informed consent, refusal of treatment, advance directives, confidentiality, and information security. - Nurses must ensure that clients understand their rights. Nurses also must protect clients’ rights during nursing care. - Regardless of the client’s age, nursing needs, or the setting in which care is provided, the basic tenants are the same. Bulimia Nervosa - Pt demonstrates high interest in preparing food, but not eating. - Binge eating and inappropriate compensatory behaviors both occur on average of once per week for 3 months. - Most pts who have bulimia nervosa maintain a weight within the normal range or slightly higher. Reporting client care issues to an interprofessional team - Nurse‑provider collaboration should be fostered to create a climate of mutual respect and collaborative practice. - Collaboration occurs among different levels of nurses and nurses with different areas of expertise. - Collaboration should also occur between the interprofessional team, the client, and the client’s family/significant others when an interprofessional plan of care is being developed. Managing client care: initial assessment - Give priority to clients who have a reasonable chance of survival with prompt intervention. Clients who have a limited likelihood of survival even with intense intervention are assigned the lowest priority. - Use this framework for situations in which health resources are extremely limited (mass casualty, disaster triage). - Look first for a safety risk. For example, is there a finding that suggests a risk for airway obstruction, hypoxia, bleeding, infection, or injury? Recommendations for time management - Nurses must continuously set and reset priorities in order to meet the needs of multiple clients and to maintain client safety. - Priority setting requires that decisions be made regarding the order in which; - Clients are seen. - Assessments are completed. - Interventions are provided. - Steps in a client procedure are completed. - Components of client care are completed. - Establishing priorities in nursing practice requires that the nurse make these decisions based on evidence obtained: - During shift reports and other communications with members of the health care team. - Through careful review of documents. - By continuously and accurately collecting client data. Maintaining client safety - Augments core measures and promotes patient safety through patient identification, effective staff communication, safe medication use, infection prevention, safety risk identification, and preventing wrong‑site surgery. - Nurses are accountable for practicing nursing in accordance with the various sources of law affecting nursing practice. It is important that nurses know and comply with these laws. - Avoid disclosing any client health information online. Be sure no one can overhear conversations about a client when speaking on the telephone. Client safety vs breach of confidentiality - The nurse should share information about the client, either verbal or written, only with those who are responsible for implementing the client’s treatment plan. - Only if the client provides consent should the nurse share information with other persons not involved in the client's treatment plan. - When a breach of duty has occurred, it may be characterized as malpractice. The following basic elements of nursing malpractice lawsuit must be present. - A duty to the client existed based on the recognized standards of care. - A breach of duty occurred. - The client was injured. - The injury was directly caused by the breach of a standard of care. Electroconvulsive therapy - ECT uses electrical current to induce a brief seizure activity while the client is anesthetized. The exact mechanism of ECT is still unknown. - One theory suggests that the seizure activity produced by ECT enhances the effects of neurotransmitters (serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine) in the brain. - At the time of the procedure, an anesthesia provider administers a short‑acting anesthetic (methohexital, propofol) via IV bolus. Obtaining a telephone prescription from a provider - Have a second nurse listen to a telephone prescription. - Repeat it back, making sure to include the medication’s name (spell if necessary), dosage, time, and route. - Question any prescription that seems inappropriate for the client. - Make sure the provider signs the prescription in person within the time frame the facility specifies, typically 24 hr. Emergency management of an evisceration - Protrusion of the abdominal contents through the incisional wound of the abdominal cavity, caused by failure to splint when moving or coughing, delayed healing due to obesity or diabetes mellitus. - Call for help. - Cover the wound with sterile saline soaked dressings or towel. - Position the client in semi‑Fowler’s position with hips and knees bent. Supplies to have available at the client’s bedside during a seizure. - Have suction ready. - Administer AEDs such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, or gabapentin. - Get oxygen ready. Assisting with a tub bath - Bathe clients to cleanse the body, stimulate circulation, provide relaxation, and enhance healing. - Bathing clients is often delegated to assistive personnel. However, the nurse is responsible for data collection and client care. - Bathe clients whose health problems have exhausted them or limited their mobility. Discharging clients in a mass casualty event - These differ from the principles of triage typically followed during provision of day-to-day services in an emergency or urgent care setting. - During mass casualty events, casualties are separated related to their potential for survival, and treatment is allocated accordingly. This type of triage is based on doing the greatest good for the greatest number of people. - Nurses can find this situation very stressful because clients who are not expected to survive are cared for last. Interventions for a client who has herpes simplex - Pt will be on contact precautions. - Use an air mattress or bed cradle for pain prevention and control of affected areas. - Use lotions to help relieve itching and discomfort. Home inspection for a client - Inspect and remove sources of lead, such as paint chips, and provide parents with information about prevention of lead poisoning. - Place poisons, paint, and gasoline in locked cabinet. - Keep medications in child‑proof containers and locked up. Nursing care of newborns: home safety precautions - Never leave the newborn alone on a bed, couch, or table. Newborns move enough to reach the edge and fall off. - Never place the newborn on his stomach to sleep during the first few months of life. The back-lying position is the position of choice. The newborn can be placed on his abdomen when awake and being supervised. - Never provide a newborn with a soft surface to sleep on (pillows or water bed). The newborn’s mattress should be firm. Never put pillows, toys, bumper pads, or loose blankets in a crib. Crib linens should be tight-fitting. Applying restraints to a client - Time limits for seclusion or restraints are based upon the age of the client. - Age 18 years and older: 4 hr - Age 9 to 17 years: 2 hr - Age 8 years and younger: 1 hr - The nurse can use seclusion or restraints without first obtaining a written prescription if it is an emergency situation. If this emergency treatment is initiated, the nurse must obtain the written prescription within a specified period of time (usually 15 to 30 min). - Restraints are either physical or chemical, such as neuroleptic medication to calm the client. Tuberculosis - Persistent cough lasting longer than 3 weeks - Purulent sputum, possibly blood‑streaked - Fatigue and lethargy - Weight loss and anorexia - Night sweats and low‑grade fever in the afternoon Reinforcing teaching about cervical cap use - Can be inserted up to 6 hr before intercourse and needs to be left in place at least 6 hr after intercourse but for no more than 48 hrs at a time. - Replace every 2 years and refit after any gynecological surgery, birth, or major weight fluctuation. - Cervical cap should be washed with mild soap and warm water after each use. Contraindications for oral contraceptives - Women who have a history of thromboembolic disorders, stroke, heart attack, coronary artery disease, gallbladder disease, cirrhosis or liver tumor, headache with focal neurological manifestations, uncontrolled hypertension, diabetes mellitus with vascular involvement, breast or estrogen-related cancers, pregnancy, lactating, less than 6 weeks postpartum, or smoking (if older than 35 years) are advised not to take oral contraceptive medications. - Oral contraceptive effectiveness decreases when taking medications that affect liver enzymes, such as anticonvulsants and some antibiotics. - Contraindicated if a client is pregnant or has undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding. Understanding of panic attacks - Panic attacks typically last 15 to 30 min. - The client might experience behavior changes and persistent worries about when the next attack will occur. - Four or more of the following manifestations are present during a panic attack. - Palpitations - Shortness of breath - Choking or smothering sensation - Chest pain - Nausea - Feelings of depersonalization - Fear of dying or insanity - Chills or hot flashes Manifestations of alcohol withdrawal - Increased heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature - Diaphoresis - Tonic‑clonic seizures Treatment for adverse effects of hydromorphone - Withhold opioids for a respiratory rate less than 12/min, and notify the provider. - Have naloxone and resuscitation equipment available. - Discourage the use of opioids with other CNS depressants (barbiturates, benzodiazepines, alcohol). Expected findings with acetaminophen overdose - Results in liver damage with early manifestations of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sweating, and abdominal discomfort progressing to hepatic failure, coma, and death. - Monitor prothrombin time and INR levels, and report them to the provider for dosage adjustment of warfarin. - In the event of an overdose, clients receive acetylcysteine (the antidote for acetaminophen) IV or PO to prevent liver damage. PO administration through a nasogastric tube prevents emesis and subsequent aspiration. Psychotic Disorders: identifying negative symptoms of Schizophrenia - The client has psychotic thinking or behavior for at least 6 months. Areas of functioning, including school or work, self‑care, and interpersonal relationships, are significantly impaired. - Affect: Usually blunted (narrow range of expression) or flat (facial expression never changes). - Alogia: Poverty of thought or speech. The client might sit with a visitor but only mumble or respond vaguely to questions. Postoperative care following transurethral resection of the prostate - Postoperative treatment for a TURP usually includes placement of an indwelling three‑way catheter. - Monitor ability to control urine flow without incontinence or dribbling. - Monitor for bleeding (persistent bright‑red bleeding unresponsive to increase in CBI and traction on the catheter or reduced Hgb levels) and report to the provider. Monitoring correct application of Buck’s Traction - Buck’s traction is a temporary immobilization device applied to a client who has a femur or hip fracture to diminish muscle spasms and immobilize the affected extremity until surgery is performed. - Routinely monitor skin integrity and document. - Use heat/massage as prescribed to treat muscle spasms Interventions following knee arthroplasty - Older adult clients are at a higher risk for medical complications related to chronic conditions, including hypertension, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and obstructive pulmonary disease. - A continuous passive motion (CPM) machine is often prescribed to promote motion in the knee, promote circulation, and prevent scar tissue formation. CPM is usually placed and initiated immediately after surgery. CPM provides passive range of motion from full extension to the prescribed amount of flexion. Follow the prescribed duration of use, but turn it off during meals. - Positions of flexion of the knee are limited to avoid flexion contractures. - Avoid positioning the bed in a way that the knees are flexed or placing pillows behind the knee. - Place one pillow under the lower calf and foot to cause a slight extension of the knee joint and to prevent flexion contractures. The knee can also rest flat on the bed Action to take for a client who has diarrhea - Standard formulas that are enriched with fiber are recommended for clients who have constipation or diarrhea to normalize bowel movements. - Infusion pumps help ensure consistent flow rates. - This method is recommended for critically ill clients because of its association with smaller residual volumes, and a lower risk of aspiration and diarrhea. Assisting a stroke client with meals - Consult speech-language pathologist (SLP) to assess swallowing and gag reflexes before feeding. The SLP can request a swallowing study that can involve swallowing a barium substrate and radiography of the peristaltic activity of the esophagus. - Have the client eat in an upright position and swallow with the head and neck flexed slightly forward. - Place food in the back of the mouth on the unaffected side Caring for a client who is receiving progesterone medication - Instruct clients to take the medication at the same time each day, such as at bedtime. - Instruct clients to report menstrual changes (dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, breakthrough bleeding, breast changes). - Encourage clients to perform monthly breast self‑examinations and schedule annual gynecologic and breast examinations with the provider. Adverse effects of antidepressants - Sexual dysfunction - Weight changes - Orthostatic hypotension Administrations of medications for hemorrhage - Postpartum hemorrhage is considered to occur if the client loses more than 500 mL of blood after a vaginal birth or more than 1,000 mL of blood after a cesarean birth. Two complications that can occur following postpartum hemorrhage are hypovolemic shock and anemia. - Administer oxytocin - Administer Methylergonovine - Administer Misoprostol Nursing care of newborns: phytonadione injections - Administered to prevent hemorrhagic disorders. Vitamin K is not produced in the gastrointestinal tract of the newborn until around day 7. - Vitamin K is produced in the colon by bacteria that forms once formula or breast milk is introduced into the gut of the newborn. - Administer 0.5 to 1 mg intramuscularly into the vastus lateralis (where muscle development is adequate) within 1 hr after birth. Identifying client prior to medication - Check the patient’s arm band. administration - Identify the 5 rights of medication (right pt, drug, dose, route, and time.) - Identify the patient’s allergies Reinforcing teaching about Rifampin - Educate the pt to complete the full course of the prescribed medication. - Urine and other secretions will be orange. - Immediately report yellowing of the skin, pain or swelling of joints, loss of appetite, or malaise. Reinforcing teaching about insulin lispro and insulin glargine self-administration - Self‑administer a snack of 15 g carbohydrate (4 oz orange juice, 2 oz grape juice, 8 oz milk, glucose tablets per manufacturer’s suggestion to equal 15 g). - Notify the provider if there is a recurrent problem. - If severe hypoglycemia occurs, IV glucose might be needed. - Wear a medical alert bracelet Priority action when mixing insulin - Adjust the insulin dosage to meet insulin needs. - Ensure adequate glucose is available at the time of onset of insulin and during all peak times. - When mixing short‑acting insulin with longer‑acting insulin, draw the short‑acting insulin up into the syringe first. This prevents the possibility of accidentally injecting some of the longer‑acting insulin into the shorter‑acting insulin vial. (This can pose a risk for unexpected insulin effects with subsequent uses of the vial.) Creatinine clearance test - A 24‑hr collection for creatinine clearance measures the GFR for clients who have impaired kidney function. - Evaluates waste products from the kidney and detects urologic disorders. - To begin the test, have the client void. The test begins at the time of first void. This first void is discarded. However, all subsequent urine is collected for the next 24 hr. Evaluating treatment for anorexia nervosa - Rapid weight loss or weight loss of greater than 30% of body weight over 6 months. - Unsuccessful weight gain in outpatient treatment, failure to adhere to treatment contract. - Heart rate less than 40/min, systolic blood pressure less than 70 mm Hg, body temperature less than 36˚ C (96.8˚ F) ICP manifestations - Hearing loss or ringing in the ear - Difficulty swallowing - Nystagmus, crossed eyes, or decreased vision - Cranial nerve dysfunction (inability to discriminate sounds, loss of gag reflex, loss of blink response) Manifestations of dehydration - Dry mucous membranes - Decreased skin turgor - Decreased urine output DM reinforcing teaching about foot care - Inspect feet daily. Wash feet daily with mild soap and warm water. Test water temperature with hands before washing feet. - Pat feet dry gently, especially between the toes, and avoid lotions between toes to decrease excess moisture and prevent infection. - The best time to perform nail care is after a bath/ shower, when toenails are soft and easier to trim. Lupus Erythematosus, Gout, and Fibromyalgia: skin care - Use sunscreen when outside and exposed to sunlight. - Use mild protein shampoo and avoid harsh hair treatments. - Use steroid creams for skin rash. Chest pain - Anginal pain is often described as a tight, squeezing, heavy pressure, or constricting feeling in the chest. - The pain can radiate to the jaw, neck, shoulders, or arm. - Pain unrelieved by rest or nitroglycerin and lasting for more than 15 min differentiates MI from angina Care of a client receiving mechanical ventilation - Assess the patient’s airway - Perform hand hygiene and aseptic technique when performing care to the pt. - Ensure the pt’s bed of head is elevated (45-90 degrees_ Expected findings with varicella - Macules start in center of trunk, spreading to the face and proximal extremities. - Progresses from macules to papules, to vesicles, and crust formation follows. Lesions are present in multiple stages of progress at once. - Scabs appear in approximately 1 week. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$21.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 05, 2021
Number of pages
17
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 05, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
43