*NURSING > EXAM > NSG6005 Quiz 2 QuizBank With Latest Questions And VERIFIED UPDATED SOLUTIONS GRADE A (All)
NSG6005 Quiz 2 QuizBank With Latest Questions And VERIFIED UPDATED SOLUTIONS GRADE A
Document Content and Description Below
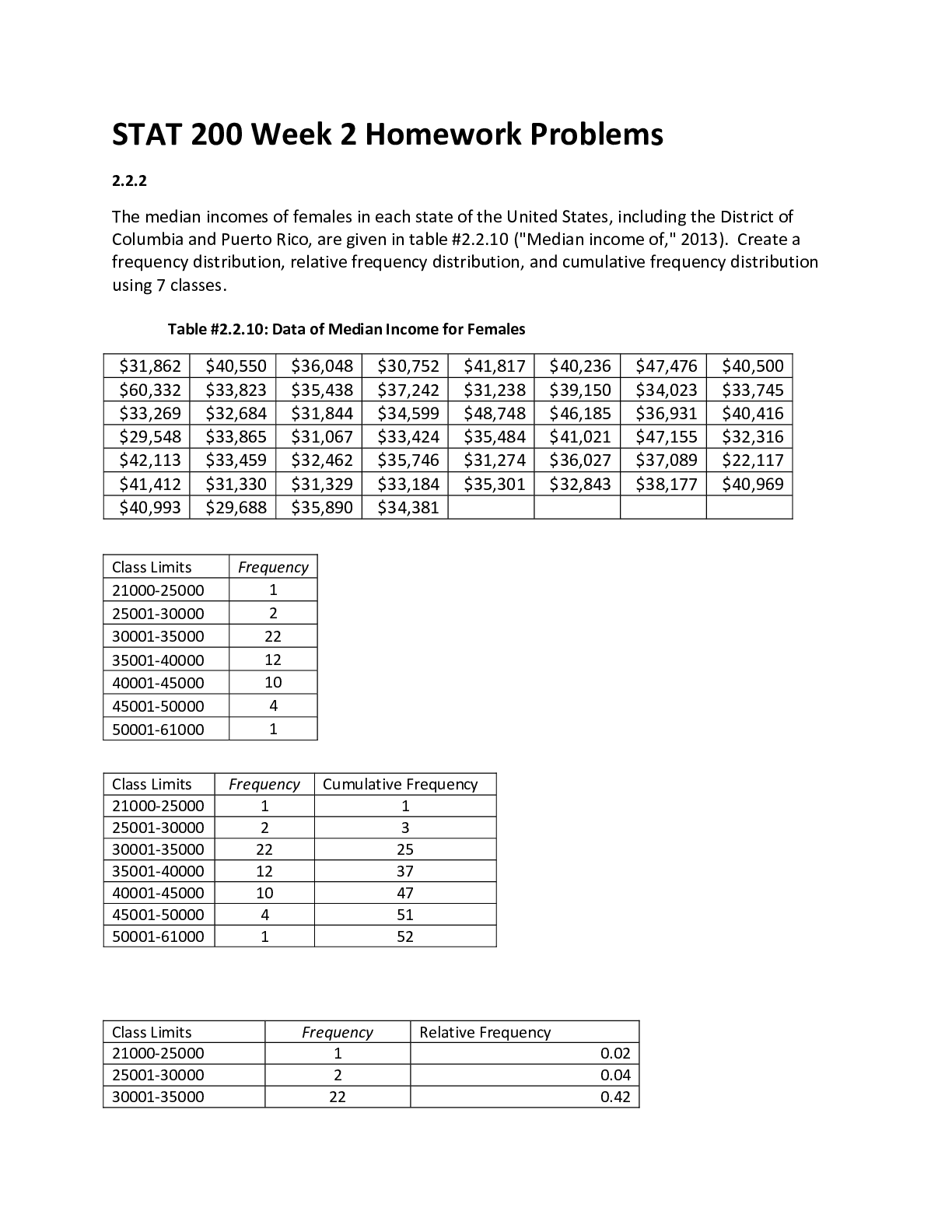
NSG6005 Quiz 2 Q Bank ____ 1. A patient’s nutritional intake and lab work reflects hypoalbuminemia. This is critical to prescribing because: ____ 2. Drugs that have a significant first-pass effect: ... ____ 3. The route of excretion of a volatile drug will likely be: ____ 4. Medroxyprogesterone (Depo Provera) is prescribed IM to create a storage reservoir of the drug. Storage reservoirs: ____ 5. The NP chooses to give cephalexin every 8 hours based on knowledge of the drug’s: ____ 6. Azithromycin dosing requires the first day’s dose be twice those of the other 4 days of the prescription. This is considered a loading dose. A loading dose: ____ 7. The point in time on the drug concentration curve that indicates the first sign of a therapeutic effect is the: ____ 8. Phenytoin requires a trough level be drawn. Peak and trough levels are done: ____ 9. A laboratory result indicates the peak level for a drug is above the minimum toxic concentration. This means that the: ____ 10. Drugs that are receptor agonists may demonstrate what property? ____ 11. Drugs that are receptor antagonists, such as beta blockers, may cause: ____ 12. Factors that affect gastric drug absorption include: ____ 13. Drugs administered via intravenous (IV) route: ____ 14. When a medication is added to a regimen for a synergistic effect, the combined effect of the drugs is: ____ 15. Which of the following statements about bioavailability is true? ____ 16. Which of the following statements about the major distribution barriers (blood-brain or fetal placental) is true? ____ 17. Drugs are metabolized mainly by the liver via Phase I or Phase II reactions. The purpose of both of these types of reactions is to: ____ 18. Once they have been metabolized by the liver, the metabolites may be: A. More active than the parent drug B. Less active than the parent drug C. Totally “deactivated” so that they are excreted without any effect ____ 19. All drugs continue to act in the body until they are changed or excreted. The ability of the body to excrete drugs via the renal system would be increased by: ____ 20. Steady state is: ____ 21. Two different pain meds are given together for pain relief. The drug-drug interaction is: ____ 22. Actions taken to reduce drug-drug interaction problems include all of the following EXCEPT: ____ 23. Phase I oxidative-reductive processes of drug metabolism require certain nutritional elements. Which of the following would reduce or inhibit this process? A. Protein malnutrition B. Iron deficiency anemia C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B ____ 24. The time required for the amount of drug in the body to decrease by 50% is called: ____ 25. An agonist activates a receptor and stimulates a response. When given frequently over time the body may: ____ 26. Drug antagonism is best defined as an effect of a drug that: ____ 27. Instructions to a client regarding self-administration of oral enteric-coated tablets should include which of the following statements? ____ 28. The major reason for not crushing a sustained release capsule is that, if crushed, the coated beads of the drugs could possibly result in: ____ 29. Which of the following substances is the most likely to be absorbed in the intestines rather than in the stomach? ____ 30. Which of the following variables is a factor in drug absorption? ____ 31. An advantage of prescribing a sublingual medication is that the medication is: ____ 32. Drugs that use CYP 3A4 isoenzymes for metabolism may: ____ 33. Therapeutic drug levels are drawn when a drug reaches steady state. Drugs reach steady state: ____ 34. Up-regulation or hypersensitization may lead to: Chapter 5: Adverse Drug Reactions ____ 1. Which of the following patients would be at higher risk of experiencing adverse drug reactions (ADRs): ____ 2. Infants and young children are at higher risk of ADRs due to: ____ 3. The elderly are at high risk of ADRs due to: ____ 4. The type of adverse drug reaction that is the result of an unwanted but otherwise normal pharmacological action of a drug given in the usual therapeutic doses is ____ 5. Digoxin may cause a Type A adverse drug reaction due to: ____ 6. Changes in the individual pharmacokinetic parameters of adsorption, distribution, or elimination may result in high concentrations of the drug in the body, leading to which type of adverse drug reaction? ____ 7. According to the World Health Organization Classification, Type B adverse reactions are: D. An allergic or idiosyncratic response ____ 8. Sarah developed a rash after using a topical medication. This is a Type __ allergic drug reaction. D. IV ____ 9. A patient may develop neutropenia from using topical Silvadene for burns. Neutropenia is a(n): A. Cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction ____ 10. Anaphylactic shock is a: ____ 11. James has hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression from chronic prednisone (a corticosteroid) use. He is at risk for what type of adverse drug reaction? ____ 12. The treatment for a patient who experiences hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression while taking the corticosteroid prednisone, a Type C adverse drug reaction, is to: ____ 13. The ACE inhibitor lisinopril is a known teratogen. Teratogens cause Type ____ adverse drug reaction. ____ 14. Cardiac defects are a known Type D adverse drug reaction to lithium. Lithium causes a Type D adverse drug reaction because it is: ____ 15. Immunomodulators such as azathioprine may cause a delayed adverse drug reaction known as a Type D reaction because they are known: ____ 16. A 24-year-old male received multiple fractures in a motor vehicle accident that required significant amounts of opioid medication to treat his pain. He is at risk for Type __ adverse drug reaction when he no longer requires the opioids. ____ 17. Drugs that may cause a Type E adverse drug reaction include: ____ 18. Unexpected failure of drug therapy is a Type __ adverse drug reaction, commonly caused by____. ____ 19. Clopidogrel treatment failure may occur when it is co-administered with omeprazole, known as a Type __ adverse drug reaction. Chapter 6: Factors that Foster Positive Outcomes ____ 1. A comprehensive assessment of a patient should be holistic when trying to determine competence in drug administration. Which of the following factors would the NP omit from this type of assessment? 2. Elena Vasquez’ primary language is Spanish and she speaks very limited English. Which technique would be appropriate to use in teaching her about a new drug you have just prescribed? ____ 3. Rod, age 68, has hearing difficulty. Which of the following would NOT be helpful in assuring that he understands teaching about his drug? ____ 4. Which of the following factors may adversely affect a patient’s adherence to a therapeutic drug regimen? ____ 5. The health-care delivery system itself can create barriers to adherence to a treatment regimen. Which of the following system variables creates such a barrier? ____ 6. Adverse drug reactions and patients’ perceptions of them are likely to produce non-adherence. Which of the following ADRs are least likely to produce non-adherence? ____ 7. Ralph’s blood pressure remains elevated despite increased doses of his drug. The NP is concerned that he might not be adhering to his treatment regimen. Which of the following events would suggest that he might not be adherent? ____ 8. Non-adherence is especially common in drugs that treat asymptomatic conditions, such as hypertension. One way to reduce the likelihood of non-adherence to these drugs is to prescribe a drug that: ____ 9. Factors in chronic conditions that contribute to non-adherence include: ____ 10. While patient education about their drugs is important, information alone does not necessarily lead to adherence to a drug regimen. Patients report greater adherence when: ____ 11. Patients with psychiatric illnesses have adherence rates to their drug regimen between 35% and 60%. To improve adherence in this population, prescribe drugs: ____ 12. Many disorders require multiple drugs to treat them. The more complex the drug regimen, the less likely the patient will adhere to it. Which of the following interventions will NOT improve adherence? D. Give the patient a clear drug schedule that the provider devises to fit the characteristic of the drug. ____ 13. Pharmacologic interventions are costly. Patients for whom the cost/benefit variable is especially important include: ____ 14. Providers have a responsibility for determining the best plan of care, but patients also have responsibilities. Patients the provider can be assured will carry through on these responsibilities include those who: ____ 15. Monitoring adherence can take several forms, including: ____ 1. A good history of herb and supplement use is critical before prescribing because approximately ____ of patients in the United States are using herbal products. ____ 2. A potential harmful effect to patients who take some herbal medication is: ____ 3. A thorough understanding of herbs is critical to patient safety. An example is the use of cinnamon to treat Type II diabetes. It is important the patient uses Ceylon cinnamon, as the commercially available cassia cinnamon contains: ____ 4. Traditional Chinese medicine utilizes yin (cooling) versus yang (warming) in assessing and treating disease. Menopause is considered a time of imbalance, therefore the Chinese herbalist would prescribe: ____ 5. According to Traditional Chinese Medicine, if a person who has a fever is given a herb that is yang in nature, such as golden seal, the patient’s illness will: ____ 6. In Ayurvedic medicine treatment is based on the patient’s dominant dosha, which is referred to as the person’s: ____ 7. Herbs and supplements are regulated by the Food and Drug Administration. ____ 8. When melatonin is used to induce sleep, the recommendation is the patient: C. Not take melatonin more than three nights a week ____ 9. Valerian tea causes relaxation and can be used to help a patient fall asleep. Overdosage of valerian (more than 2.5 gm/dose) may lead to: ____ 10. The standard dosage of St John’s Wort for the treatment of mild depression is: ____ 11. Patients need to be instructed regarding the drug interactions with St John’s Wort, including: ____ 12. Ginseng, which is taken to assist with memory, may potentiate: ____ 13. Licorice root is a common treatment for dyspepsia. Drug interactions with licorice include: A. Antihypertensives, diuretics, and digoxin ____ 14. Patients should be warned about the overuse of topical wintergreen oil to treat muscle strains, as overapplication can lead to: C. Salicylates poisoning ____ 15. The role of the NP in the use of herbal medication is to: C. Educate patients and guide them to appropriate sources of care Chapter 13: Over-the-Counter Medications ____ 1. Michael asks you about why some drugs are over-the-counter and some are prescription. You explain that in order for a drug to be approved for over-the-counter use the drug must: A. Be safe and labeled for appropriate use ____ 2. In the United States, over-the-counter drugs are regulated by: B. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research ____ 3. As drugs near the end of their patent, pharmaceutical companies may apply for the drug to change to over-the-counter status in order to: ____ 4. New over-the-counter drug ingredients must undergo the U.S. Food and Drug Administration New Drug Application process, just as prescription drugs do. ____ 5. The ailment that generates the greatest over-the-counter annual drug sales is: ____ 6. Common over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen: ____ 7. When obtaining a drug history from Harold, he gives you a complete list of his prescription medications. He denies taking any other drugs, but you find that he occasionally takes aspirin for his arthritis flare ups. This is an example of: ____ 8. The Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act, which is part of the 2006 U.S. Patriot Act: ____ 9. When prescribing a tetracycline or quinolone antibiotic it is critical to instruct the patient: ____ 10. The OTC antidiarrheal bismuth subsalicylate (PeptoBismol) is recommended: ____ 11. Sadie’s adult daughter reports that when Sadie (age 84 years) takes Tylenol PM (acetaminophen and diphenhydramine) to help her sleep she has “strange dreams” including wandering and thinking she is at her childhood home. You understand: ____ 12. Vanessa is a 19-year-old female who calls the advice nurse worried that a condom broke yesterday when she was having intercourse. She reports a normal menses 10 days ago. One recommendation for care is: [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 06, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 06, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
44





.png)







.png)