Health Care > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ATI Care of the Patient with an Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or Pancreatic, Chapter 12: Perrin: Unde (All)
ATI Care of the Patient with an Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or Pancreatic, Chapter 12: Perrin: Understanding the Essentials of Critical Care Nursing: Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 341 (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solutions
Document Content and Description Below
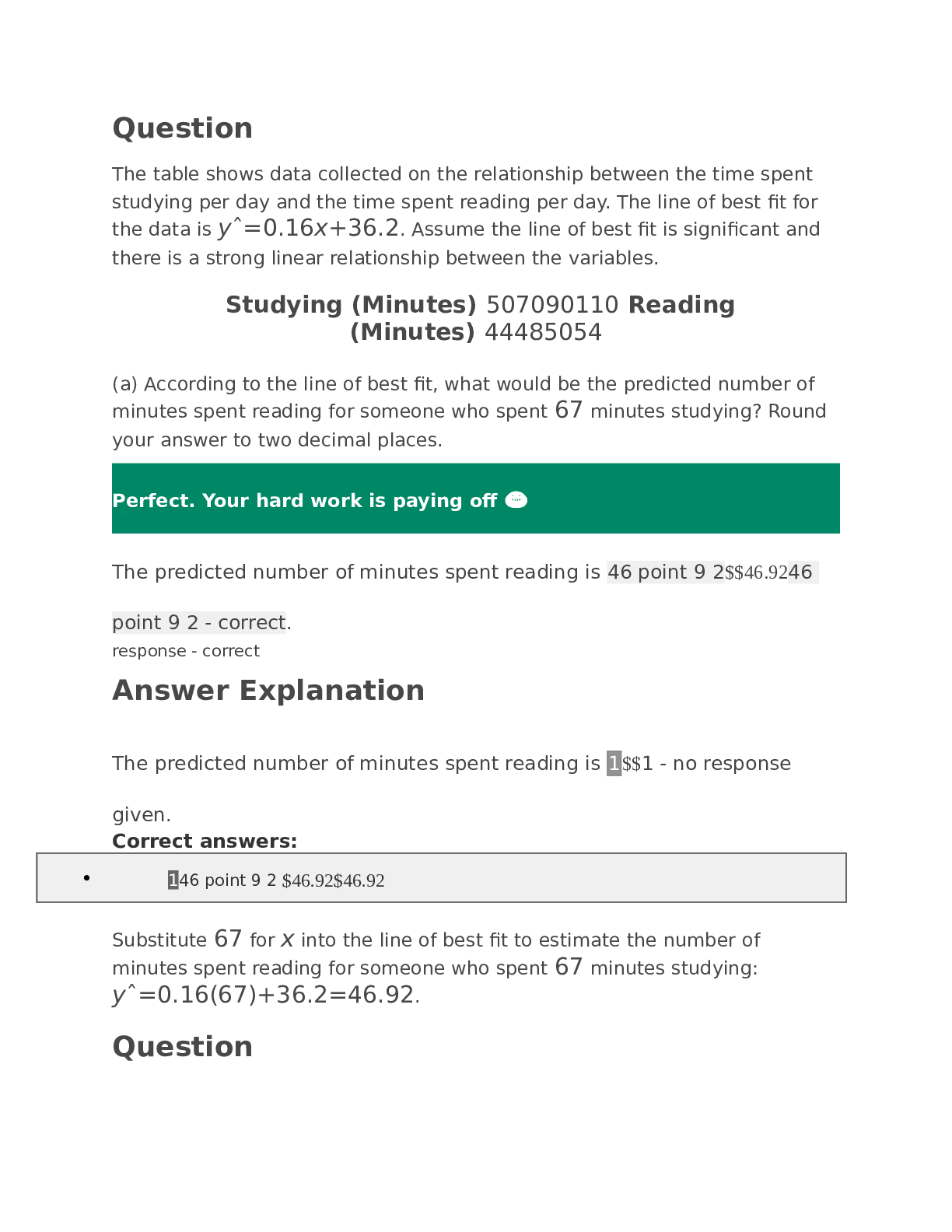
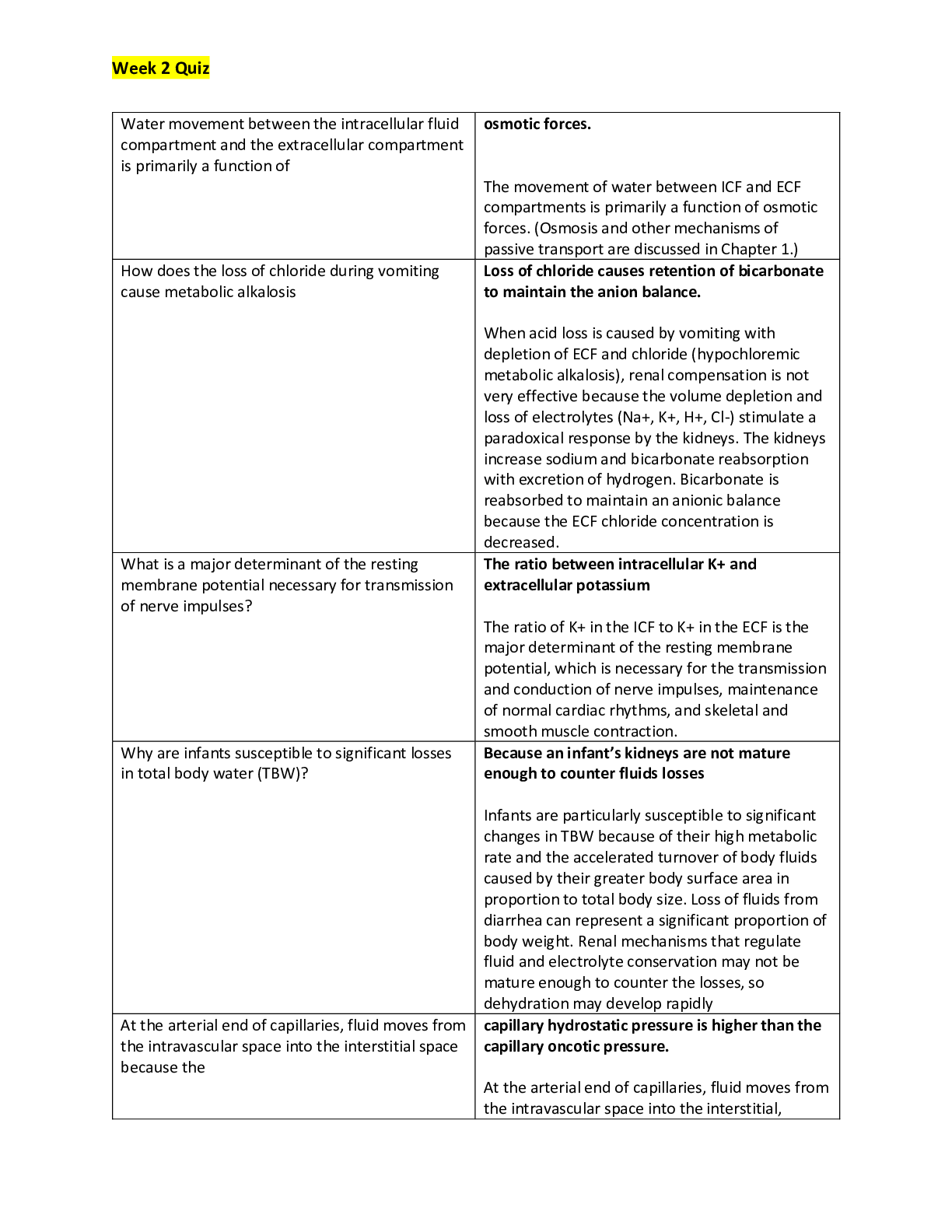
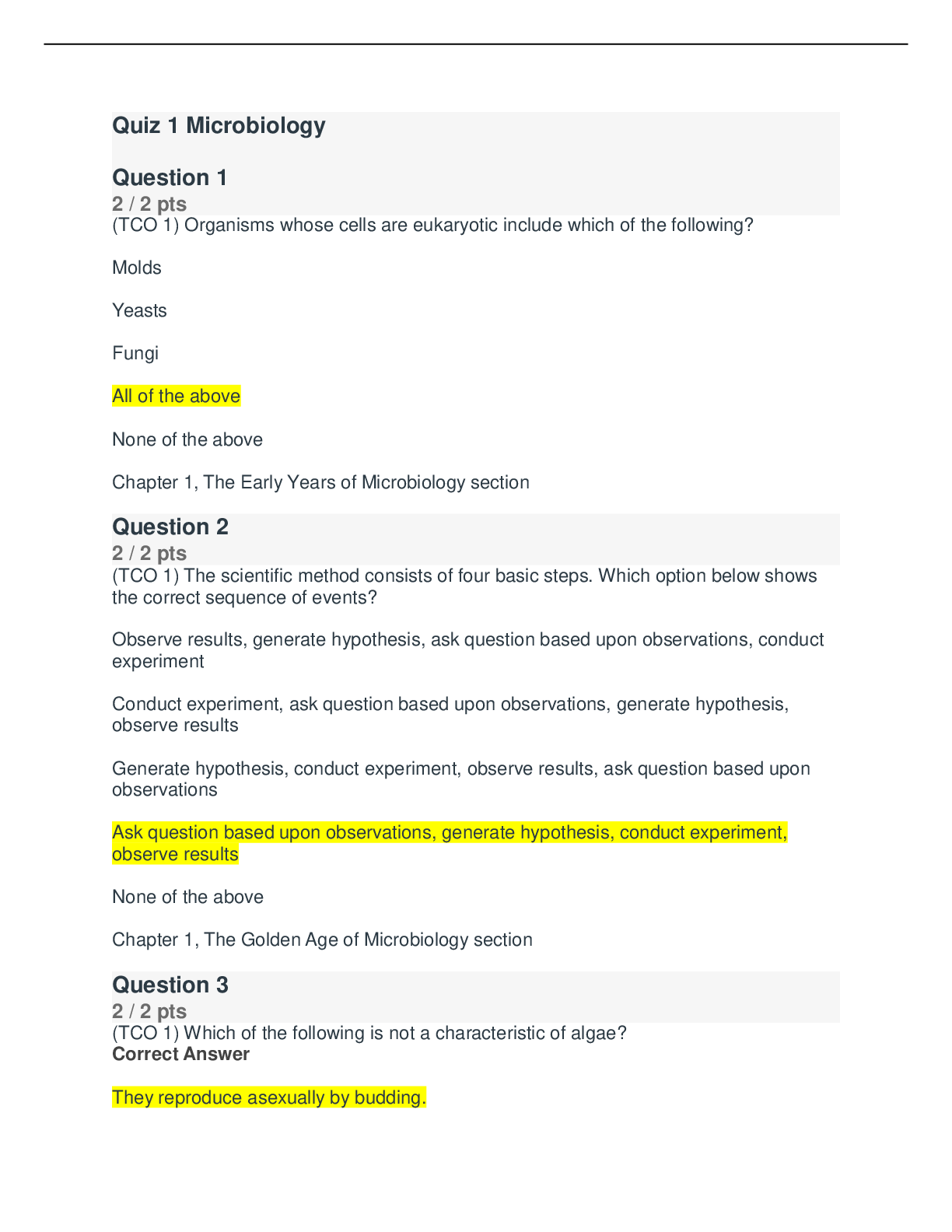
ATI Care of the Patient with an Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or Pancreatic, Chapter 12: Perrin: Understanding the Essentials of Critical Care Nursing: Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 341 (A Graded) ... Latest Questions and Complete Solutions Perrin: Understanding the Essentials of Critical Care Nursing Chapter 12: Care of the Patient with an Acute Gastrointestinal Bleed or Pancreatic MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the questions 1) A patient arrives in the emergency department with clinical manifestations consistent with a lower gastrointestinal bleed. Which of the following should the nurse assess to determine the patient's stability? The patient's: A) Hemoglobin. B) Hematocrit. C) Vital signs. D) Abdominal rigidity to determine the amount of blood being lost. Answer: C Explanation: A) The evaluation of vital signs is the best means to determine the patient's stability. Vital signs provide information concerning cardiac and vascular compensation. #1 and #2 are not correct. Initially the patient's hemoglobin and hematocrit will not illustrate the true blood loss. This is due to a- 162 hour delay in intravascular equilibrium related to blood loss. #4 is not correct. Abdominal rigidity will provide a key to the presence of blood in the abdomen but it does not distinguish the amount of bleeding or the patient's level of homeostasis nor does it pinpoint the location. Nursing Process: Assessment Cognitive Level: Analysis Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Physiological Adaptation B) The evaluation of vital signs is the best means to determine the patient's stability. Vital signs provide information concerning cardiac and vascular compensation. #1 and #2 are not correct. Initially the patient's hemoglobin and hematocrit will not illustrate the true blood loss. This is due to a- 162 hour delay in intravascular equilibrium related to blood loss. #4 is not correct. Abdominal rigidity will provide a key to the presence of blood in the abdomen but it does not distinguish the amount of bleeding or the patient's level of homeostasis nor does it pinpoint the location. Nursing Process: Assessment Cognitive Level: Analysis Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Physiological Adaptation C) The evaluation of vital signs is the best means to determine the patient's stability. Vital signs provide information concerning cardiac and vascular compensation. #1 and #2 are not correct. Initially the patient's hemoglobin and hematocrit will not illustrate the true blood loss. This is due to a- 162 hour delay in intravascular equilibrium related to blood loss. #4 is not correct. Abdominal rigidity will provide a key to the presence of blood in the abdomen but it does not distinguish the amount of bleeding or the patient's level of homeostasis nor does it pinpoint the location. Nursing Process: Assessment Cognitive Level: Analysis Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Physiological Adaptation D) The evaluation of vital signs is the best means to determine the patient's stability. Vital signs provide information concerning cardiac and vascular compensation. #1 and #2 are not correct. Initially the patient's hemoglobin and hematocrit will not illustrate the true blood loss. This is due to a- 162 hour delay in intravascular equilibrium related to blood loss. #4 is not correct. Abdominal rigidity will provide a key to the presence of blood in the abdomen but it does not distinguish the amount of bleeding or the patient's level of homeostasis nor does it pinpoint the location. Nursing Process: Assessment Cognitive Level: Analysis Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Physiological Adaptation 2) A nurse has completed a shift assessment on a patient who has been hospitalized for treatment of a lower gastrointestinal bleed. During the assessment the nurse notes that the patient has a capillary refill of 3 seconds, urinary output of 20 mL/hour, heart rate 88, and reports "feeling tired." Which of these findings should the nurse report to the physician? A) Capillary refill of 3 seconds B) Urinary output of 20 mL/hour C) Heart rate of 88 bpm D) Reports of fatigue Answer: B Explanation: A) The patient's urinary output is indicative of a worsening condition related to hypovolemia and reduced renal perfusion. Urinary output less than 30 cc/hour should be reported to the physician. A normal urine output is- 01.5mL/kg/hour. #2 and #3 are not correct. A capillary refill of 3 seconds and a heart rate of 88 bpm are normal findings #4 is not correct. The hospitalized patient with a lower gastrointestinal bleed will likely report feelings of fatigue related to the blood loss. Nursing Process: Implementation Cognitive Level: Evaluation Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Reduction of Risk Potential B) The patient's urinary output is indicative of a worsening condition related to hypovolemia and reduced renal perfusion. Urinary output less than 30 cc/hour should be reported to the physician. A normal urine output is- 01.5mL/kg/hour. #2 and #3 are not correct. A capillary refill of 3 seconds and a heart rate of 88 bpm are normal findings #4 is not correct. The hospitalized patient with a lower gastrointestinal bleed will likely report feelings of fatigue related to the blood loss. Nursing Process: Implementation Cognitive Level: Evaluation Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Reduction of Risk Potential C) The patient's urinary output is indicative of a worsening condition related to hypovolemia and reduced renal perfusion. Urinary output less than 30 cc/hour should be reported to the physician. A normal urine output is- 01.5mL/kg/hour. #2 and #3 are not correct. A capillary refill of 3 seconds and a heart rate of 88 bpm are normal findings #4 is not correct. The hospitalized patient with a lower gastrointestinal bleed will likely report feelings of fatigue related to the blood loss. Nursing Process: Implementation Cognitive Level: Evaluation Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Reduction of Risk Potential D) The patient's urinary output is indicative of a worsening condition related to hypovolemia and reduced renal perfusion. Urinary output less than 30 cc/hour should be reported to the physician. A normal urine output is- 01.5mL/kg/hour. #2 and #3 are not correct. A capillary refill of 3 seconds and a heart rate of 88 bpm are normal findings #4 is not correct. The hospitalized patient with a lower gastrointestinal bleed will likely report feelings of fatigue related to the blood loss. Nursing Process: Implementation Cognitive Level: Evaluation Category of Need: Physiological Integrity–Reduction of Risk Potential [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 60 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 24, 2021
Number of pages
60
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 24, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
46





, (A Grade), Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 (LATEST-2021) CORRECT ANSWERS, DOWNLOAD TO SCORE A.png)
, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 110 OUT OF THE 160 TOTAL QUESTIONS FOR EACH VERSION AUTHENTIC Questions and Answers (latest Update), Correct, Download to Score A.png)
, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 (Verified Answers, COMPLETE GUIDE FOR EXAM PREPARATION).png)
, Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 (LATEST-2021) CORRECT ANSWERS, DOWNLOAD TO SCORE A.png)
, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 All Correct Answers, Download to Score A.png)
, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)








.png)