*NURSING > HESI > NURS 3550 HESI OB/ MATERNIT V1 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers, Download to Score A (All)
NURS 3550 HESI OB/ MATERNIT V1 (GRADED A) Questions and Answers, Download to Score A
Document Content and Description Below
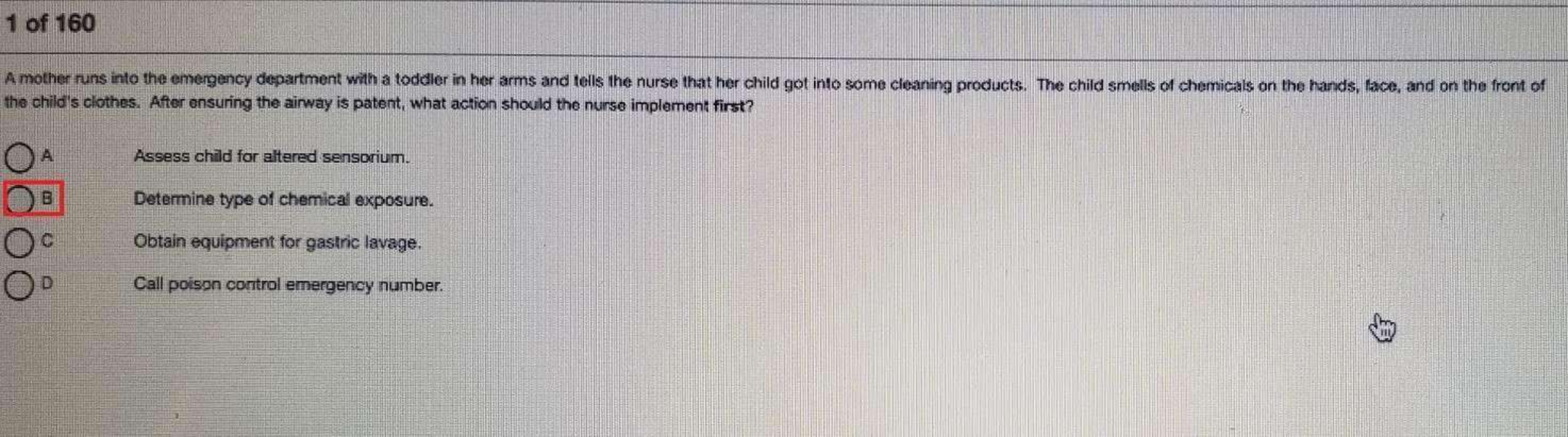
HESI OB/MATERNITY V 1 1. A 3-day postpartum client, who is not immune to rubella, is to receive the vaccine at discharge. Which of the following must the nurse include in her discharge teaching regar... ding the vaccine? 1. The woman should not become pregnant for at least 4 weeks. 2. The woman should pump and dump her breast milk for 1 week. 3. The mother must wear a surgical mask when she cares for the baby. 4. Passive antibodies transported across the placenta will protect the baby. 208 MATERNAL AND NEWBORN SUCCESS 2. A 3-day-postpartum client questions why she is to receive the rubella vaccine before leaving the hospital. Which of the following rationales should guide the nurse’s response? 1. The client’s obstetric status is optimal for receiving the vaccine. 2. The client’s immune system is highly responsive during the postpartum period. 3. The client’s baby will be high risk for acquiring rubella if the woman does not receive the vaccine. 4. The client’s insurance company will pay for the shot if it is given during the immediate postpartum period. 3. A patient, G2P1102, who delivered her baby 8 hours ago, now has a temperature of 100.2ºF. Which of the following is the appropriate nursing intervention at this time? 1. Notify the doctor to get an order for acetaminophen. 2. Request an infectious disease consult from the doctor. 3. Provide the woman with cool compresses. 4. Encourage intake of water and other fluids. 4. To prevent infection, the nurse teaches the postpartum client to perform which of the following tasks? 1. Apply antibiotic ointment to the perineum daily. 2. Change the peripad at each voiding. 3. Void at least every two hours. 4. Spray the perineum with a povidone-iodine solution after toileting. 5. A 3-day-postpartum breastfeeding woman is being assessed. Her breasts are firm and warm to the touch. When asked when she last fed the baby her reply is, “I fed the baby last evening. I let the nurses feed him in the nursery last night. I needed to rest.” Which of the following actions should the nurse take at this time? 1. Encourage the woman exclusively to breastfeed her baby. 2. Have the woman massage her breasts hourly. 3. Obtain an order to culture her expressed breast milk. 4. Take the temperature and pulse rate of the woman. 6. A breastfeeding woman has been counseled on how to prevent engorgement. Which of the following actions by the mother shows that the teaching was effective? 1. She pumps her breasts after each feeding. 2. She feeds her baby every 2 to 3 hours. 3. She feeds her baby 10 minutes on each side. 4. She supplements each feeding with formula. 7. A 2-day-postpartum breastfeeding woman states, “I am sick of being fat. When can I go on a diet?” Which of the following responses is appropriate? 1. “It is fine for you to start dieting right now as long as you drink plenty of milk.” 2. “Your breast milk will be low in vitamins if you start to diet while breastfeeding.” 3. “You must eat at least 3000 calories per day in order to produce enough milk for your baby.” 4. “Many mothers lose weight when they breastfeed because the baby consumes about 600 calories a day.” 8. A G2P2002, who is postpartum 6 hours from a spontaneous vaginal delivery, is assessed. The nurse notes that the fundus is firm at the umbilicus, there is heavy lochia, and perineal sutures are intact. Which of the following actions should the nurse take at this time? 1. Do nothing. This is a normal finding. 2. Massage the woman’s fundus. 3. Take the woman to the bathroom to void. 4. Notify the woman’s primary health care provider. 9. A client informs the nurse that she intends to bottlefeed her baby. Which of the following actions should the nurse encourage the client to perform? 1. Increase her fluid intake for a few days. 2. Massage her breasts every 4 hours. 3. Apply heat packs to her axillae. 4. Wear a supportive bra 24 hours a day. 10. The nurse in the obstetric clinic received a telephone call from a bottlefeeding mother of a 3-day-old. The client states that her breasts are firm, red, and warm to the touch. Which of the following is the best action for the nurse to advise the client to perform? 1. Intermittently apply ice packs to her axillae and breasts. 2. Apply lanolin to her breasts and nipples every 3 hours. 3. Express milk from the breasts every 3 hours. 4. Ask the primary health care provider to order a milk suppressant. 11. A multigravid, postpartum woman reports severe abdominal cramping whenever she nurses her infant. Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate? 1. Suggest that the woman bottlefeed for a few days. 2. Instruct the patient on how to massage her fundus. 3. Instruct the patient to feed using an alternate position. 4. Discuss the action of breastfeeding hormones. 12. The nurse is caring for a breastfeeding mother who asks advice on foods that will provide both vitamin A and iron. Which of the following should the nurse recommend? 1. 1⁄2 cup raw celery dipped in 1 ounce cream cheese. 2. 8 ounce yogurt mixed with 1 medium banana. 3. 12 ounce strawberry milk shake. 4. 11⁄2 cup raw broccoli. 13. A breastfeeding mother states that she has sore nipples. In response to the complaint, the nurse assists with “latch on” and recommends that the mother do which of the following? 1. Use a nipple shield at each breastfeeding. 2. Cleanse the nipples with soap 3 times a day. 3. Rotate infant positions at each feed. 4. Bottle feed for 2 days then resume breastfeeding. 14. Which of the following statements is true about breastfeeding mothers as compared to bottlefeeding mothers? 1. Breastfeeding mothers usually involute completely by 3 weeks postpartum. 2. Breastfeeding mothers have decreased incidence of diabetes mellitus later in life. 3. Breastfeeding mothers show higher levels of bone density after menopause. 4. Breastfeeding mothers are prone to fewer bouts of infection immediately postpartum. 15. A breastfeeding woman, 11⁄2 months postdelivery, calls the nurse in the obstetrician’s office and states, “I am very embarrassed but I need help. Last night I had an orgasm when my husband and I were making love. You should have seen the milk. We were both soaking wet. What is wrong with me?” The nurse should base the response to the client on which of the following? 1. The woman is exhibiting signs of pathological galactorrhea. 2. The same hormone stimulates orgasms and the milk ejection reflex. 3. The woman should have a serum galactosemia assessment done. 4. The baby is stimulating the woman to produce too much milk. 16. A client who is 3 days postpartum asks the nurse, “When may my husband and I begin having sexual relations again?” The nurse should encourage the couple to wait until after which of the following has occurred? 1. The client has had her six-week postpartum check-up. 2. The episiotomy has healed and the lochia has stopped. 3. The lochia has turned to pink and the vagina is no longer tender. 4. The client has had her first postpartum menstrual period. 17. A breastfeeding client, 7 weeks postpartum, complains to an obstetrician’s triage nurse that when she and her husband had intercourse for the first time after the delivery, “I couldn’t stand it. It was so painful. The doctor must have done something terrible to my vagina.” Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate? 1. “After a delivery the vagina is always very tender. It should feel better the next time you have intercourse.” 2. “Does your baby have thrush? If so, I bet you have a yeast infection in your vagina.” 3. “Women who breastfeed often have vaginal dryness. A vaginal lubricant may remedy your discomfort.” 4. “Sometimes the stitches of episiotomies heal too tight. Why don’t you come in for an assessment?” 18. The nurse monitors his or her postpartum clients carefully because which of the following physiological changes occurs during the early postpartum period? 1. Decreased urinary output. 2. Increased blood pressure. 3. Decreased blood volume. 4. Increased estrogen level. 19. A woman, 24 hours postpartum, is complaining of profuse diaphoresis. She has no other complaints. Which of the following actions by the nurse is appropriate? 1. Take the woman’s temperature. 2. Advise the woman to decrease her fluid intake. 3. Reassure the woman that this is normal. 4. Inform the neonate’s pediatrician. 20. Which of the following laboratory values would the nurse expect to see in a normal postpartum woman? 1. Hematocrit 39%. 2. White blood cell count 16,000 cells/mm3. 3. Red blood cell count 5 million cells/mm3. 4. Hemoglobin 15 grams/dL. 21. Which of the following client statements indicates a need for additional teaching about selfcare during pregnancy? ■ 1. “I should use nonskid pads when I take a shower or bath.” ■ 2. “I should avoid using soap on my nipples to prevent drying.” ■ 3. “I should sit in a hot tub for 20 minutes to relax after working.” ■ 4. “I should avoid douching even if my vaginal secretions increase.” 22. The nurse is discussing the importance of doing Kegel exercises during the postpartum period. Which of the following should be included in the teaching plan? 1. She should repeatedly contract and relax her rectal and thigh muscles. 2. She should practice by stopping the urine flow midstream every time she voids. 3. She should get on her hands and knees whenever performing the exercises. 4. She should be taught that toned pubococcygeal muscles decrease blood loss. 23. The nurse is evaluating the involution of a woman who is 3 days postpartum. Which of the following findings would the nurse evaluate as normal? 1. Fundus 1 cm above the umbilicus, lochia rosa. 2. Fundus 2 cm above the umbilicus, lochia alba. 3. Fundus 2 cm below the umbilicus, lochia rubra. 4. Fundus 3 cm below the umbilicus, lochia serosa. 24. During a home visit, the nurse assesses a client 2 weeks after delivery. Which of the following signs/symptoms should the nurse expect to see? 1. Diaphoresis. 2. Lochia alba. 3. Cracked nipples. 4. Hypertension. 25. The day after delivery a woman, whose fundus is firm at 1 cm below the umbilicus and who has moderate lochia, tells the nurse that something must be wrong, “All I do is go to the bathroom.” Which of the following is an appropriate nursing response? 1. Catheterize the client per doctor’s orders. 2. Measure the client’s next voiding. 3. Inform the client that polyuria is normal. 4. Check the specific gravity of the next voiding. 26. A breastfeeding client, G10P6408, delivered 10 minutes ago. Which of the following assessments is most important for the nurse to perform at this time? 1. Pulse. 2. Fundus. 3. Bladder. 4. Breast. 27. The nurse is caring for a client who had a cesarean section under spinal anesthesia less than 2 hours ago. Which of the following nursing actions is appropriate at this time? 1. Elevate the head of the bed 60 degrees. 2. Report absence of bowel sounds to the physician. 3. Have her turn and deep breathe every 2 hours. 4. Assess for patellar hyperreflexia bilaterally. 28. The nurse is caring for a postpartum client who experienced a second-degree perineal laceration at delivery 2 hours ago. Which of the following interventions should the nurse perform at this time? 1. Apply an ice pack to the perineum. 2. Advise the woman to use a sitz bath after every voiding. 3. Advise the woman to sit on a pillow. 4. Teach the woman to insert nothing into her rectum. 29. A woman had a cesarean section yesterday. She states that she needs to cough but that she is afraid to. Which of the following is the nurse’s best response? 1. “I know that it hurts but it is very important for you to cough.” 2. “Let me check your lung fields to see if coughing is really necessary.” 3. “If you take a few deep breaths in, that should be as good as coughing.” 4. “If you support your incision with a pillow, coughing should hurt less.” 30. A woman is receiving patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) post–cesarean section. Which of the following must be included in the patient teaching? 1. The client should monitor how often she presses the button. 2. The client should report any feelings of nausea or itching to the nurse. 3. The family should press the button whenever they feel the woman is in pain. 4. The family should inform the nurse if the client becomes sleepy. 31. An 18-week gestation client telephones the obstetrician’s office stating, “I’m really scared. I think I have breast cancer. My breasts are filled with tumors.” The nurse should base the response on which of the following? 1. Breast cancer is often triggered by pregnancy. 2. Nodular breast tissue is normal during pregnancy. 3. The woman is exhibiting signs of a psychotic break. 4. Anxiety attacks are especially common in the second trimester. 32. A woman states that she frequently awakens with “painful leg cramps” during the night. Which of the following assessments should the nurse make? 1. Dietary evaluation. 2. Goodell’s sign. 3. Hegar’s sign. 4. Posture evaluation. 33. Which of the following exercises should be taught to a pregnant woman who complains of backaches? 1. Kegeling. 2. Pelvic tilting. 3. Leg lifting. 4. Crunching. 34. A woman in her third trimester advises the nurse that she wishes to breastfeed her baby, “but I don’t think my nipples are right.” Upon examination, the nurse notes that the client has inverted nipples. Which of the following actions should the nurse take at this time? 1. Advise the client that it is unlikely that she will be able to breastfeed. 2. Refer the client to a lactation consultant for advice. 3. Call the labor room and notify them that a client with inverted nipples will be admitted. 4. Teach the woman exercises in order to evert her nipples. 35. Which of the following vital sign changes should the nurse highlight for a pregnant woman’s obstetrician? 1. Prepregnancy blood pressure (BP) 100/60 and third trimester BP 140/90. 2. Prepregnancy respiratory rate (RR) 16 rpm and third trimester RR 22 rpm. 3. Prepregnancy heart rate (HR) 76 bpm and third trimester HR 88 bpm. 4. Prepregnancy temperature (T) 98.6ºF and third trimester T 99.2ºF. 36. A nurse midwife has advised a 39-week gestation gravid to take evening primrose oil 2500 mg daily as a complementary therapy. This suggestion was made because evening primrose has been shown to perform which of the following actions? 1. Relieve back strain. 2. Improve development of colostrum. 3. Ripen the cervix. 4. Reduce the incidence of hemorrhoids. 37. A 38-week gestation client, Bishop score 1, is advised by her nurse midwife to take evening primrose daily. The office nurse advises the client to report which of the following side effects that has been attributed to the oil? 1. Skin rash. 2. Pedal edema. 3. Blurred vision. 4. Tinnitus. 38. A 37-week gravid client states that she noticed a “white liquid” leaking from her breasts during a recent shower. Which of the following nursing responses is appropriate at this time? 1. Advise the woman that she may have a galactocele. 2. Encourage the woman to pump her breasts to stimulate an adequate milk supply. 3. Assess the liquid because a breast discharge is diagnostic of a mammary infection. 4. Reassure the mother that this is normal in the third trimester. 39. A 36-week gestation gravid client is complaining of dyspnea when lying flat. Which of the following is the likely clinical reason for this complaint? 1. Maternal hypertension. 2. Fundal height. 3. Hydramnios. 4. Congestive heart failure. 40. The nurse is providing anticipatory guidance to a woman in her second trimester regarding signs/symptoms that she might experience in the coming weeks. Which of the following comments by the client indicates that further teaching is needed? 1. “During the third trimester I may experience frequent urination.” 2. “During the third trimester I may experience heartburn.” 3. “During the third trimester I may experience back pain.” 4. “During the third trimester I may experience persistent headache.” 41. The nurse is analyzing the three-generation pedigree below. In which generation is the proband? 1. I. 2. II. 3. III. 4. There is not enough information to answer this question. 42. A woman is seeking genetic counseling during her pregnancy. She has a strong family history of diabetes mellitus. She wishes to have an amniocentesis to determine whether or not she is carrying a baby who will “develop diabetes.” Which of the following replies by the nurse would be most appropriate for the nurse to make? 1. “Doctors don’t do amniocenteses to detect diabetes.” 2. “Diabetes cannot be diagnosed by looking at the genes.” 3. “Although diabetes does have a genetic component, diet and exercise also determine whether or not someone is diabetic.” 4. “Even if the baby doesn’t carry the genes for diabetes, the baby could still develop the disease.” 43. A 25-year-old woman, G0 P0000, enters the infertility clinic stating that she has just learned she is positive for the BRCA1 and the BRCA2 genes. She asks the nurse what her options are for getting pregnant and breastfeeding her baby. The nurse should base her reply on which of the following? 1. Fertility of women who carry the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes is similar to that of unaffected women. 2. Women with these genes should be advised not to have children because the children could inherit the defective genes. 3. Women with these genes should have their ovaries removed as soon as possible to prevent ovarian cancer. 4. Lactation is contraindicated for women who carry the BRCA1 and BRCA 2 genes. 44. A woman asks a nurse about presymptomatic genetic testing for Huntington’s disease. The nurse should base her response on which of the following? 1. There is no genetic marker for Huntington’s disease. 2. Presymptomatic testing cannot predict whether or not the gene will be expressed. 3. If the woman is positive for the gene for Huntington’s, she will develop the disease later in life. 4. If the woman is negative for the gene, her children should be tested to see whether or not they are carriers. 45. A woman, who has undergone amniocentesis, has been notified that her baby is XX with a 14/21 Robertsonian chromosomal translocation. The nurse helps the woman to understand which of the following? 1. The baby will have a number of serious genetic defects. 2. It is likely that the baby will be unable to have children when she grows up. 3. Chromosomal translocations are common and rarely problematic. 4. An abortion will probably be the best decision under the circumstances. 46. A woman who has had multiple miscarriages is advised to go through genetic testing. The client asks the nurse the rationale for this recommendation. The nurse should base his or her response on which of the following? 1. The woman’s pedigree may exhibit a mitochondrial inheritance pattern. 2. The majority of miscarriages are caused by genetic defects. 3. A woman’s chromosomal pattern determines her fertility. 4. There is a genetic marker that detects the presence of an incompetent cervix. 47. A nurse has just taken a family history on a 10-week gravid client and created the family pedigree shown below. Which of the following actions should the nurse take at this time? 1. Advise the woman that she should have an amniocentesis. 2. Encourage the doctor to send her for genetic counseling. 3. Ask the woman if she knew any of the relatives who died. 4. Inform the woman that her pedigree appears normal. 48. A woman is informed that she is a carrier for Tay Sachs disease, an autosomal recessive illness. What is her phenotype? 1. She has one recessive gene and one normal gene. 2. She has two recessive genes. 3. She exhibits all symptoms of the disease. 4. She exhibits no symptoms of the disease. 49. During a genetic evaluation, it is discovered that the woman is carrying one autosomal dominant gene for a serious late adult-onset disease while her partner’s history is unremarkable. Based on this information, which of the following family members should be considered high risk and in need of genetic counseling? Select all that apply. 1. The woman’s fetus. 2. The woman’s sisters. 3. The woman’s brothers. 4. The woman’s parents. 5. The woman’s partner. 50. Which statement by a gravid client who is a carrier for muscular dystrophy, an X-linked recessive disease, indicates that she understands the implications of her status? 1. “If I have a girl, she will be healthy.” 2. “None of my children will be at risk of the disease.” 3. “If I have a boy, he will be a carrier.” 4. “I am going to abort my fetus because it will be affected.” 51. A woman, G1 P0000, 40 weeks’ gestation, entered the labor suite stating that she is in labor. Upon examination it is noted that the woman is 2 cm dilated, 30% effaced, contracting every 12 min 30 sec. Fetal heart rate is in the 140s with good variability and spontaneous accelerations. What should the nurse conclude when reporting the findings to the primary health care practitioner? 1. The woman is high risk and should be placed on tocolytics. 2. The woman is in early labor and could be sent home. 3. The woman is high risk and could be induced. 4. The woman is in active labor and should be admitted to the unit. 52. A nurse concludes that a woman is in the latent phase of labor. Which of the following signs/symptoms would lead a nurse to that conclusion? 1. The woman talks and laughs during contractions. 2. The woman complains about severe back labor. 3. The woman performs effleurage during a contraction. 4. The woman asks to go to the bathroom to defecate. 53. A G1P0, 8 cm dilated, is to receive pain medication. The health care practitioner has decided to order an opiate analgesic with an analgesic-potentiating medication. Which of the following medications would the nurse expect to be ordered as the analgesic-potentiating medication? 1. Seconal (secobarbital). 2. Phenergan (promethazine). 3. Benadryl (diphenhydramine). 4. Tylenol (acetaminophen). 54. On vaginal examination, it is noted that a woman with a well-functioning epidural is in the second stage of labor. The station is 2 and the baseline fetal heart rate is 130 with no decelerations. Which of the following nursing actions is appropriate at this time? 1. Coach the woman to hold her breath while pushing 3 to 4 times with each contraction. 2. Administer oxygen via face mask at 8 to 10 liters per minute. 3. Delay pushing until the baby descends further and the mother has a strong urge to push. 4. Place the woman on her side and assess her oxygen saturation. 55. A nurse is assisting an anesthesiologist who is inserting an epidural catheter. Which of the following positions should the nurse assist the woman into? 1. Fetal position. 2. Lithotomy position. 3. Trendelenburg position. 4. Lateral recumbent position. 56. Which of the following actions would the nurse expect to perform immediately before a woman is to have regional anesthesia? Select all that apply. 1. Assess fetal heart rate. 2. Infuse 1000 cc of Ringer’s lactate. 3. Place woman in Trendelenburg position. 4. Monitor blood pressure every 5 minutes for 15 minutes. 5. Have woman empty her bladder. 57. Immediately following administration of an epidural anesthesia, the nurse must monitor the mother for which of the following? 1. Paresthesias in her feet and legs. 2. Drop in blood pressure. 3. Increase in central venous pressure. 4. Fetal heart accelerations. 58. A client, G2P1001, 5 cm dilated and 40% effaced, has just received an epidural. Which of the following actions is important for the nurse to make at this time? 1. Assess the woman’s temperature. 2. Place a wedge under the woman’s side. 3. Place a blanket roll under the woman’s feet. 4. Assess the woman’s pedal pulses. 59. The practitioner is performing a fetal scalp stimulation test. Which of the following fetal responses would the nurse expect to see? 1. Spontaneous fetal movement. 2. Fetal heart acceleration. 3. Increase in fetal heart variability. 4. Resolution of late decelerations. 60. The nurse is interpreting the results of a fetal blood sampling test. Which of the following reports would the nurse expect to see? 1. Oxygen saturation of 99%. 2. Hgb of 11 gm/dL. 3. Serum glucose of 140 mg/dL. 4. pH of 7.30. 61. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to perform when caring for a Chinese-speaking woman in active labor? 1. Apply heat to the woman’s back. 2. Inquire regarding the woman’s pain level. 3. Make sure that the woman’s head is covered. 4. Accept the woman’s loud verbalizations. 62. A nurse is caring for women from four different countries. Which of the women is most likely to request that her head be kept covered throughout her hospitalization? 1. Arabic woman. 2. Chinese woman. 3. Russian woman. 4. Greek woman. 63. The nurse is caring for an Orthodox Jewish woman in labor. It would be appropriate for the nurse to include which of the following in the plan of care? 1. Encourage the father to hold his partner’s hand during labor. 2. Ask the woman if she would like to speak with her priest. 3. Provide the woman with a long-sleeved hospital gown. 4. Place an order for the woman’s postpartum vegetarian diet. 64. Which of the following nonpharmacological interventions recommended by nurse midwives may help a client at full term to go into labor? Select all that apply. 1. Engage in sexual intercourse. 2. Ingest evening primrose oil. 3. Perform yoga exercises. 4. Eat raw spinach. 5. Massage the breast and nipples. 65. The nurse is providing acupressure to provide pain relief to a woman in labor. Where is the best location for the acupressure to be applied? 1. On the malleolus of the wrist. 2. Above the patella of the knee. 3. On the medial aspect of the lower leg. 4. Below the medial epicondyle of the elbow. 66. The nurse is assessing fetal position for a 32-year-old client in her eighth month of pregnancy. As shown below, the fetal position can be described as which of the following? ■ 1. Left occipital transverse. ■ 2. Left occipital anterior. ■ 3. Right occipital transverse. ■ 4. Right occipital anterior. 67. Which of the following statements by the nurse would be most appropriate when responding to a primigravid client who asks, “What should I do about this brown discoloration across my nose and cheeks?” ■ 1. “This usually disappears after delivery.” ■ 2. “It is a sign of skin melanoma.” ■ 3. “The discoloration is due to dilated capillaries.” ■ 4. “It will fade if you use a prescribed cream.” 68. A 36-year-old primigravid client at 22 weeks’ gestation without any complications to date is being seen in the clinic for a routine visit. The nurse should assess the client’s fundal height to: ■ 1. Determine the level of uterine activity. ■ 2. Identify the need for increased weight gain. ■ 3. Assess the location of the placenta. ■ 4. Estimate the fetal gestational age. 69. After the nurse reviews the physician’s explanation of amniocentesis with a multigravid client, which of the following indicates that the client understands a serious risk of the procedure.? ■ 1. Premature rupture of the membranes. ■ 2. Possible premature labor. ■ 3. Fetal limb malformations. ■ 4. Fetal organ malformations. 70. A primigravid client at 28 weeks’ gestation tells the nurse that she and her husband wish to drive to visit relatives who live several hundred miles away. Which of the following recommendations by the nurse would be best? ■ 1. “Try to avoid traveling anywhere in the car during your third trimester.” ■ 2. “Limit the time you spend in the car to a maximum of 4 to 5 hours.” ■ 3. “Taking the trip is okay if you stop every 1 to 2 hours and walk.” ■ 4. “Avoid wearing your seat belt in the car to prevent injury to the fetus.” 71. Which of the following recommendations would be most helpful to suggest to a primigravid client at 37 weeks’ gestation who is complaining of leg cramps? ■ 1. Change positions frequently throughout the day. ■ 2. Alternately flex and extend the legs. ■ 3. Straighten the knee and flex the toes toward the chin. ■ 4. Lie prone in bed with the legs elevated. 72. Which of the following recommendations would be the most appropriate preventive measure to suggest to a primigravid client at 30 weeks’ gestation who is experiencing occasional heartburn? ■ 1. Eat smaller and more frequent meals during the day. ■ 2. Take a pinch of baking soda with water before meals. ■ 3. Decrease fluid intake to four glasses daily. ■ 4. Drink several cups of regular tea throughout the day. 73. When performing Leopold’s maneuvers on a primigravid client at 22 weeks’ gestation, the nurse performs the first maneuver to do which of the following? ■ 1. Locate the fetal back and spine. ■ 2. Determine what is in the fundus. ■ 3. Determine whether the fetal head is at the pelvic inlet. ■ 4. Identify the degree of fetal descent and flexion. 74. A primigravid adolescent client at approximately 15 weeks’ gestation who is visiting the prenatal clinic with her mother is to undergo alphafetoprotein (AFP) screening. When developing the teaching plan for this client, the nurse should include which of the following? ■ 1. Ultrasonography usually accompanies AFP testing. ■ 2. Results are usually very accurate until 20 weeks’ gestation. ■ 3. A clean-catch midstream urine specimen is needed. ■ 4. Increased levels of AFP are associated with neural tube defects. 75. Which of the following statements best identifies the rationale for why the nurse reinforces the need for continued prenatal care throughout the pregnancy with an adolescent primigravid client? ■ 1. Pregnant adolescents are at high risk for pregnancy-induced hypertension. ■ 2. Gestational diabetes during pregnancy commonly develops in adolescents. ■ 3. Adolescents need additional instruction related to common discomforts. ■ 4. The father of the baby is rarely involved in the pregnancy. Antepartal Care 39 76. Which of the following would be included in the teaching plan about pregnancy-related breast changes for a primigravid client? ■ 1. Growth of the milk ducts is greatest during the first 8 weeks of gestation. ■ 2. Enlargement of the breasts indicates adequate levels of progesterone. ■ 3. Colostrum is usually secreted by about the 16th week of gestation. ■ 4. Darkening of the areola occurs during the last month of pregnancy. 77. A primigravid client at 32 weeks’ gestation is enrolled in a breast-feeding class. Which of the following statements indicate that the client understands the breast-feeding education? Select all that apply. ■ 1. “My milk supply will be adequate since I have increased a whole bra size during pregnancy.” ■ 2. “I can hold my baby several different ways during feedings.” ■ 3. “If my infant latches on properly, I won’t develop mastitis.” ■ 4. “If I breast-feed, my uterus will return to prepregnancy size more quickly.” ■ 5. “Breast milk can be expressed and stored at room temperature since it is natural.” ■ 6. “I need to feed my baby when I see feeding cues and not wait until she is crying.” 78. When planning a class for primigravid clients about the common discomforts of pregnancy, which of the following physiologic changes of pregnancy should the nurse include in the teaching plan? ■ 1. The temperature decreases slightly early in pregnancy. ■ 2. Cardiac output increases by 25% to 50% during pregnancy. ■ 3. The circulating fibrinogen level decreases as much as 50% during pregnancy. ■ 4. The anterior pituitary gland secretes oxytocin late in pregnancy. 79. When teaching a primigravid client at 24 weeks’ gestation about the diagnostic tests to determine fetal well- being, which of the following should the nurse include? ■ 1. A fetal biophysical profile involves assessments of breathing movements, body movements, tone, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal heart rate reactivity. ■ 2. A reactive nonstress test is an ominous sign and requires further evaluation with fetal echocardiography. ■ 3. Contraction stress testing, performed on most pregnant women, can be initiated as early as 16 weeks’ gestation. ■ 4. Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling uses a needle inserted through the vagina to obtain a sample. 80. When teaching a primigravid client how to do Kegel exercises, the nurse explains that the expected outcome of these exercises is to: ■ 1. Prevent vulvar edema. ■ 2. Alleviate lower back discomfort. ■ 3. Strengthen the perineal muscles. ■ 4. Strengthen the abdominal muscles. 81. During a routine clinic visit, a 25-year-old multigravid client who initiated prenatal care at 10 weeks’ gestation and is now in her third trimester states, “I’ve been having strange dreams about the baby. Last week I dreamed he was covered with hair.” The nurse should tell the mother: ■ 1. “Dreams like the ones that you describe are very unusual. Please tell me more about them.” ■ 2. “Commonly when a mother has these dreams, she is trying to cope with becoming a parent.” ■ 3. “Dreams about the baby late in pregnancy usually mean that labor is about to begin soon.” ■ 4. “It’s not uncommon to have dreams about the baby, particularly in the third trimester.” 82. A primigravid client at 36 weeks’ gestation tells the nurse that she has been experiencing insomnia for the past 2 weeks. Which of the following suggestions would be most helpful? ■ 1. Practice relaxation techniques before bedtime. ■ 2. Drink a cup of hot chocolate before bedtime. ■ 3. Drink a small glass of wine with dinner. ■ 4. Exercise for 30 minutes just before bedtime. 83. A woman with postpartum depression has been prescribed Zoloft (sertraline) 50 mg daily. Which of the following should the client be taught about the medication? 1. Chamomile tea can potentiate the effect of the drug. 2. Therapeutic effect may be delayed a week or more. 3. The medication should only be taken whole. 4. A weight gain of up to ten pounds is commonly seen. 84. A breastfeeding woman has been diagnosed with retained placental fragments 4 days postdelivery. Which of the following breastfeeding complications would the nurse expect to see? 1. Engorgement. 2. Mastitis. 3. Blocked milk duct. 4. Low milk supply. 85. The nurse assesses a 2-day postpartum, breastfeeding client. The nurse notes blood on the mother’s breast pad and a crack on the mother’s nipple. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform at this time? 1. Advise the woman to wash the area with soap to prevent mastitis. 2. Provide the woman with a tube of topical lanolin. 3. Remind the woman that the baby can become sick if he drinks the blood. 4. Get the woman an order for a topical anesthetic. 86. A client just delivered the placenta pictured below. The nurse will document that the woman delivered which of following placentas? 1. Circumvallate placenta. 2. Succenturiate placenta. 3. Placenta with velamentous insertion. 4. Battledore placenta. 87. The nurse administers RhoGAM to a postpartum client. Which of the following is the goal of the medication? 1. Inhibit the mother’s active immune response. 2. Aggressively destroy the Rh antibodies produced by the mother. 3. Prevent fetal cells from migrating throughout the mother’s circulation. 4. Change the maternal blood type to Rh positive. 88. Which of the following comments suggest that a client, whose baby was born with a congenital defect, is in the bargaining phase of grief? 1. “I hate myself. I caused my baby to be sick.” 2. “I’ll take him to a specialist. Then he will get better.” 3. “I can’t seem to stop crying.” 4. “This can’t be happening.” 89. A client is 1-day post–cesarean section with spinal anesthesia. Even though the nurse advised against it, the client has had the head of her bed in high Fowler’s position since delivery. Which of the following complications would the nurse expect to see in relation to the client’s action? 1. Postpartum hemorrhage. 2. Severe postural headache. 3. Pruritic skin rash. 4. Paralytic ileus. 90. A client is receiving IV heparin for deep vein thrombosis. Which of the following medications should the nurse obtain from the pharmacy to have on hand in case of heparin overdose? 1. Vitamin K. 2. Protamine. 3. Vitamin E. 4. Mannitol. 91. A client, who had no prenatal care, delivers a 10 lb 10 oz–baby boy whose serum glucose result 1 hour after delivery was 20 mg/dL. Based on these data, which of the following tests should the mother have at her 6-week postpartum checkup? 1. Glucose tolerance test. 2. Indirect Coombs’ test. 3. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN). 4. Complete blood count (CBC). 92. A client is to receive a blood transfusion after significant blood loss following a placenta previa delivery. Which of the following actions by the nurse is critical prior to starting the infusion? Select all that apply. 1. Look up the client’s blood type in the chart. 2. Check the client’s arm bracelet. 3. Check the blood type on the infusion bag. 4. Obtain an infusion bag of dextrose and water. 5. Document the time the infusion begins. 93. A nurse is caring for the following four laboring patients. Which client should the nurse be prepared to monitor closely for signs of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH)? 1. G1P0000, delivery at 29 weeks’ gestation. 2. G2P1001, prolonged first stage of labor. 3. G2P0010, delivery by cesarean section. 4. G3P0200, delivery of 2200-gram neonate. 94. A client is 3-days post–cesarean delivery for eclampsia. The client is receiving hydralazine (Apresoline) 10 mg 4 times a day by mouth. Which of the following findings would indicate that the medication is effective? 1. The client has had no seizures since delivery. 2. The client’s blood pressure has dropped from 160/120 to 130/90. 3. The client’s postoperative weight has dropped from 154 to 144 lb. 4. The client states that her headache is gone. 95. A home care nurse is visiting a breastfeeding client who is 2 weeks postdelivery of a 7-lb baby girl over a midline episiotomy. Which of the following findings should take priority? 1. Lochia is serosa. 2. Client cries throughout the visit. 3. Nipples are cracked. 4. Client yells at the baby for crying. 96. A client who is post–cesarean section for severe preeclampsia is receiving magnesium sulfate via IV pump and morphine sulfate via patient-controlled anesthesia (PCA) pump. The nurse enters the room on rounds and notes that the client is not breathing. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform first? 1. Give two breaths. 2. Discontinue medications. 3. Call a code. 4. Check carotid pulse. 97. A breastfeeding client is being seen in the emergency department with a hard, red, warm nodule in the upper outer quadrant of her left breast. Her vital signs are: T 104.6ºF, P 100, R 20, and BP 110/60. She has a recent history of mastitis and is crying in pain. Which of the following nursing diagnoses is highest priority? 1. Ineffective breastfeeding. 2. Infection. 3. Ineffective individual coping. 4. Pain. 98. A client is receiving an IV heparin drip at 16 mL/hr via an infusion pump for a diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. The label on the liter bag of D5W indicates 50,000 units of heparin have been added. How many units of heparin is the client receiving per hour? 800 units per hour. 99. A nurse massages the atonic uterus of a woman who delivered 1 hour earlier. The nurse identifies the nursing diagnosis: Risk for injury related to uterine atony. Which of the following outcomes indicates that the client’s condition has improved? 1. Moderate lochia flow. 2. Decreased pain level. 3. Stable blood pressure. 4. Fundus above the umbilicus. 100. Intermittent positive pressure boots have been ordered for a client who had an emergency cesarean section. Which of the following is the rationale for that order? 1. Postpartum clients are high risk for thrombus formation. 2. Post–cesarean clients are high risk for fluid volume deficit. 3. Postpartum clients are high risk for varicose vein development. 4. Post–cesarean clients are high risk for poor milk ejection reflex. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 17, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 17, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
39



.png)



.png)




.png)




, Latest Questions and Answers with Explanations, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)
 - Over 500 Questions (Latest 2021) Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)


 Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A.png)