NR-304 Physical Assessment Study Guide – Exam 1/;RATED A
Document Content and Description Below
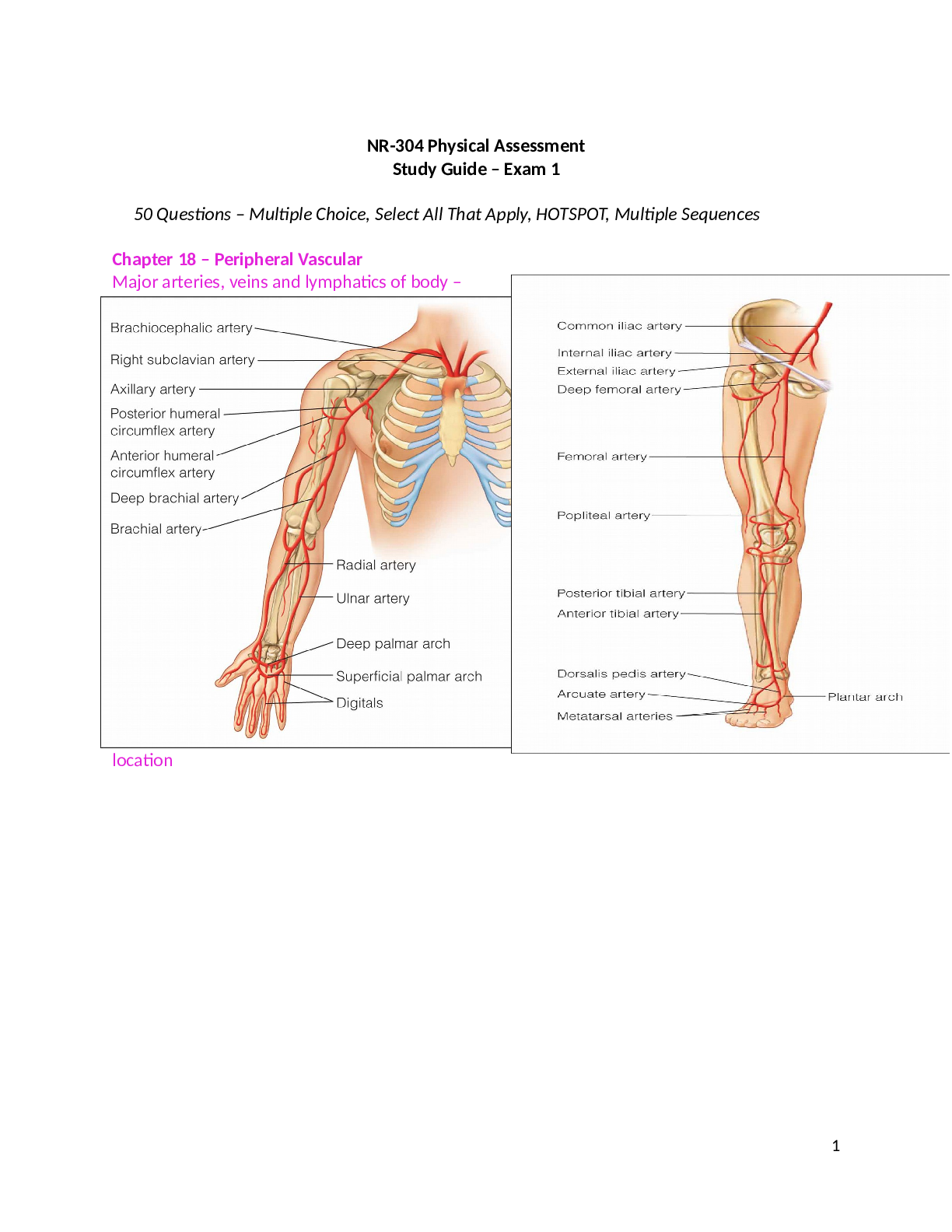
NR-304 Physical Assessment Study Guide – Exam 1 50 Questions – Multiple Choice, Select All That Apply, HOTSPOT, Multiple Sequences Chapter 18 – Peripheral Vascular Major arteries, veins a... nd lymphatics of body – location Pediatric (BP measurements; lymph nodes) Pregnant (BP changes throughout, varicosities) Geriatric (Systolic BP & pulse changes; enlargement of calf veins; lymph nodes) Subjective Leg pain or cramps – differences between acute and chronic arterial and venous pain (see handout) Claudication distance; 6 Ps; Leriche syndrome; risk factors/conditions Skin changes – color (redness, pallor, blueness, brown); varicose veins; ulcers (arterial versus venous) Swelling – bilaterally versus unilateral; aggravating and relieving factors; associated symptoms Lymphedema Medications (oral contraceptives, hormone replacement) Objective Techniques (inspection, palpation, auscultation, BP measurement) BP measurement – NIH guidelines normal for systolic and diastolic BP Inspection & Palpation of Arms (normal findings for color, temperature, texture, turgor, clubbing, capillary refill, pulses, and lymph nodes) Raynaud’s Disease (description, tricolor changes, associated symptoms, risk factors) Normal characteristics of peripheral pulses (Rate, rhythm, symmetry, amplitude) Normal and Abnormal Pulses (Normal, Absent, Bounding, Pulsus Alternans, Pulsus Bigeminus, Pulsus Paradoxus) – Know characteristics and contributing conditions Allen Test (Know technique and normal findings) Inspection & Palpation of Legs (normal findings for color, hair distribution, venous pattern, size, lymph nodes, pulses, pretibial edema) Stasis dermatitis; Ulcers (arterial versus venous) Pitting edema (grading system); Non-pitting edema (measurement) Venous tests (Manual compression test; Homan’s sign) Arterial test (Color change; Ankle-Brachial Index and normal/abnormal findings) Chapter 19 – Abdomen Abdominal landmarks; 4 versus 9 quadrants Pediatric – contour, respirations, peristalsis; hernias Pregnant – fundal height, GI symptoms, skin changes (linea nigra, straie) Geriatric considerations – contour, intestinal activity, teeth and dietary changes Subjective Appetite change, anorexia Anorexia nervosa versus anorexia bulimia Dysphagia Food intolerance (types of foods and reactions; pyrosis; eructation; GERD Abdominal pain (visceral versus parietal; colic); referred cutaneous pain areas; acute versus chronic Nausea/Vomiting (hematemesis; symptom analysis questions) Bowel Habits (symptom analysis questions; meaning of different colors of stool) Past Abdominal history (conditions) Medications/Habits/Conditions (NSAIDs, alcohol, smoking, H-pylori) Nutritional Assessment (Differences between toddlers, geriatric, and teenagers) Objective Techniques (Inspection, auscultation, percussion, palpation) – note order change Inspection (normal findings for contour, symmetry, umbilicus, skin, pulsation, hair distribution, demeanor); Know all different types of contours and conditions associated with each Auscultation (Why is this technique second? Which quadrant do you start? Which side of stethoscope? Normal bowel sounds are called? ) Characteristics of normal, hypoactive, and hyperactive bowel sounds. Know 3 types of vascular sounds, stethoscope use, auscultatory areas for vascular sounds, and causative factors for each sound. Percussion (General note over abdomen? Normal liver span @ RMCL and midsternal?) Percussive notes over liver, spleen? Technique and meaning of CVA tenderness? Percussive notes associated with ascites and techniques to detect extent of fluid? Palpation (General instructions; light versus deep palpation; bimanual technique; abnormal findings and characteristics of a mass if detected; normal findings for liver, spleen, kidneys and aorta; why should you not palpate enlarged spleen or abdominal aorta? Special Procedures Psoas muscle test (technique and meaning of positive test) Rebound tenderness (Blumberg sign) (technique and meaning of positive test) Inspiratory arrest (Murphy sign) (technique and meaning of positive test) Hernias (hiatal, ventral, umbilical) [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 2 pages
.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 30, 2021
Number of pages
2
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 30, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
40












 (1).png)
 (1).png)
 (1).png)