Mathematics > Solutions Guide > Linear Programming Solutions homework 2 (All)
Linear Programming Solutions homework 2
Document Content and Description Below
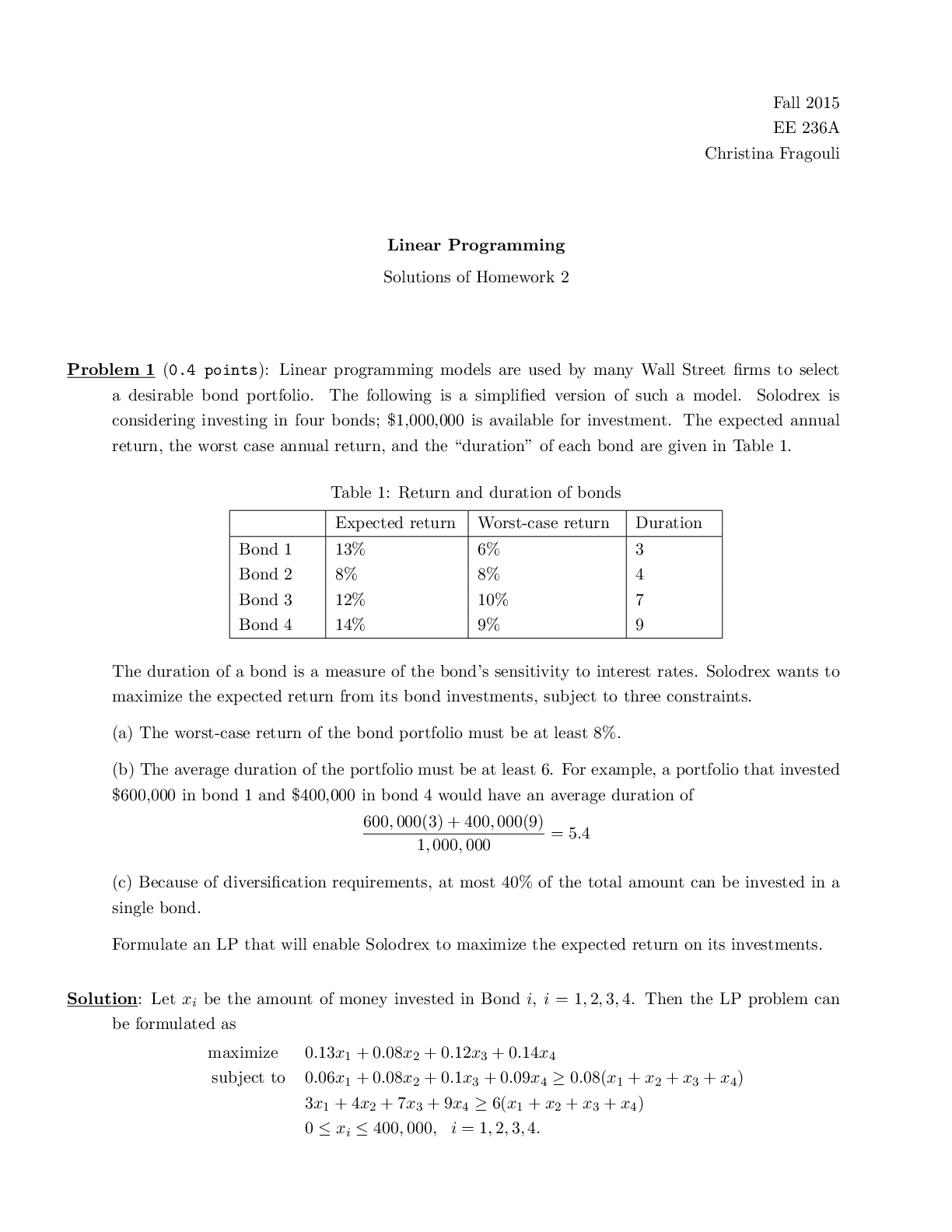
Linear Programming Solutions of Homework 2 Problem 1 (0.4 points): Linear programming models are used by many Wall Street firms to select a desirable bond portfolio. The following is a simplified v... ersion of such a model. Solodrex is considering investing in four bonds; $1,000,000 is available for investment. The expected annual return, the worst case annual return, and the \duration" of each bond are given in Table 1. Table 1: Return and duration of bonds Expected return Worst-case return Duration Bond 1 13% 6% 3 Bond 2 8% 8% 4 Bond 3 12% 10% 7 Bond 4 14% 9% 9 The duration of a bond is a measure of the bond’s sensitivity to interest rates. Solodrex wants to maximize the expected return from its bond investments, subject to three constraints. (a) The worst-case return of the bond portfolio must be at least 8%. (b) The average duration of the portfolio must be at least 6. For example, a portfolio that invested $600,000 in bond 1 and $400,000 in bond 4 would have an average duration of 600; 000(3) + 400; 000(9) 1; 000; 000 = 5:4 (c) Because of diversification requirements, at most 40% of the total amount can be invested in a single bond. Formulate an LP that will enable Solodrex to maximize the expected return on its investments. Solution: Let xi be the amount of money invested in Bond i, i = 1; 2; 3; 4. Then the LP problem can be formulated as maximize 0:13x1 + 0:08x2 + 0:12x3 + 0:14x4 subject to 0:06x1 + 0:08x2 + 0:1x3 + 0:09x4 ≥ 0:08(x1 + x2 + x3 + x4) 3x1 + 4x2 + 7x3 + 9x4 ≥ 6(x1 + x2 + x3 + x4) 0 ≤ xi ≤ 400; 000; i = 1; 2; 3; 4:Problem 2 (0.4 points, Exer. 14 (a) in Linear Programming Exercises): An illumination problem. We consider an illumination system of m lamps, at positions l1; · · · ; lm 2 R2, illuminating n flat patches. The patches are line segments; the i-th patch is given by [vi; vi+1], where v1; · · · ; vn+1 2 R2. The variables in the problem are the lamp powers p1; · · · ; pm, which can vary between 0 and 1. The illumination at (the midpoint of) patch i is denoted by Ii. We will use a simple model for the illumination: Ii = mXj =1 aijpj; aij = rij −2 maxfcos θij; 0g; where rij denotes the distance between lamp j and the midpoint of patch i, and θij denotes the the angle between the upward normal of patch i and the vector from the midpoint of patch i to lamp j, as shown in the figure. This model takes into account \self-shading" (i.e., the fact that a patch is illuminated only by lamps in the halfspace it faces) but not shading of one patch caused by another. Of course, we could use a more complex illumination model, including shading and even reflections. This just changes the matrix relating the lamp powers to the patch illumination levels. The problem is to determine lamp powers that make the illumination levels close to a given desired illumination level Ides, subject to the power limits 0 ≤ pi ≤ 1. Suppose we use the maximum deviation φ(p) = max k=1;··· ;n jIk − Idesj (1) as a measure for the deviation from the desired illumination level. Formulate the illumination problem using this criterion as a linear programming problem. Solution: We can formulate the problem as the following LP: minimize t subject to −t ≤ aT k p − Ides ≤ t; k = 1; · · · ; n 0 ≤ p ≤ 1: The variables are p 2 Rm and t 2 R.Problem 3 (0.4 points, Exer. 12 in Linear Programming Exercises): We are given p matrices Ai 2 Rn×n, and we would like to find a single matrix X 2 Rn×n that we can use as an approximate right-inverse for each matrix Ai, i.e., we would like to have AiX ≈ I; i = 1; · · · ; p We can do this by solving the following optimization problem with X as a variable: minimize max i=1;··· ;p kI − AiXk1: (2) Here kHk1 is the infinity-norm or max-row-sum norm of a matrix H, defined as kHk1 = max i=1;··· ;m nXj =1 jHijj if H 2 Rm×n. Express problem (2) as an LP. You don't have to reduce the LP to a canonical form, as long as you are clear about what the variables are, what the meaning is of any auxiliary variables that you introduce, and why the LP is equivalent to the problem (2). [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 07, 2022
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
55










.png)