*NURSING > NCLEX > Mark Klimek Audio Lectures Lecture 11 Fetal Heart Monitoring Fetal Monitoring Patterns During Labor (All)
Mark Klimek Audio Lectures Lecture 11 Fetal Heart Monitoring Fetal Monitoring Patterns During Labor and Delivery.
Document Content and Description Below
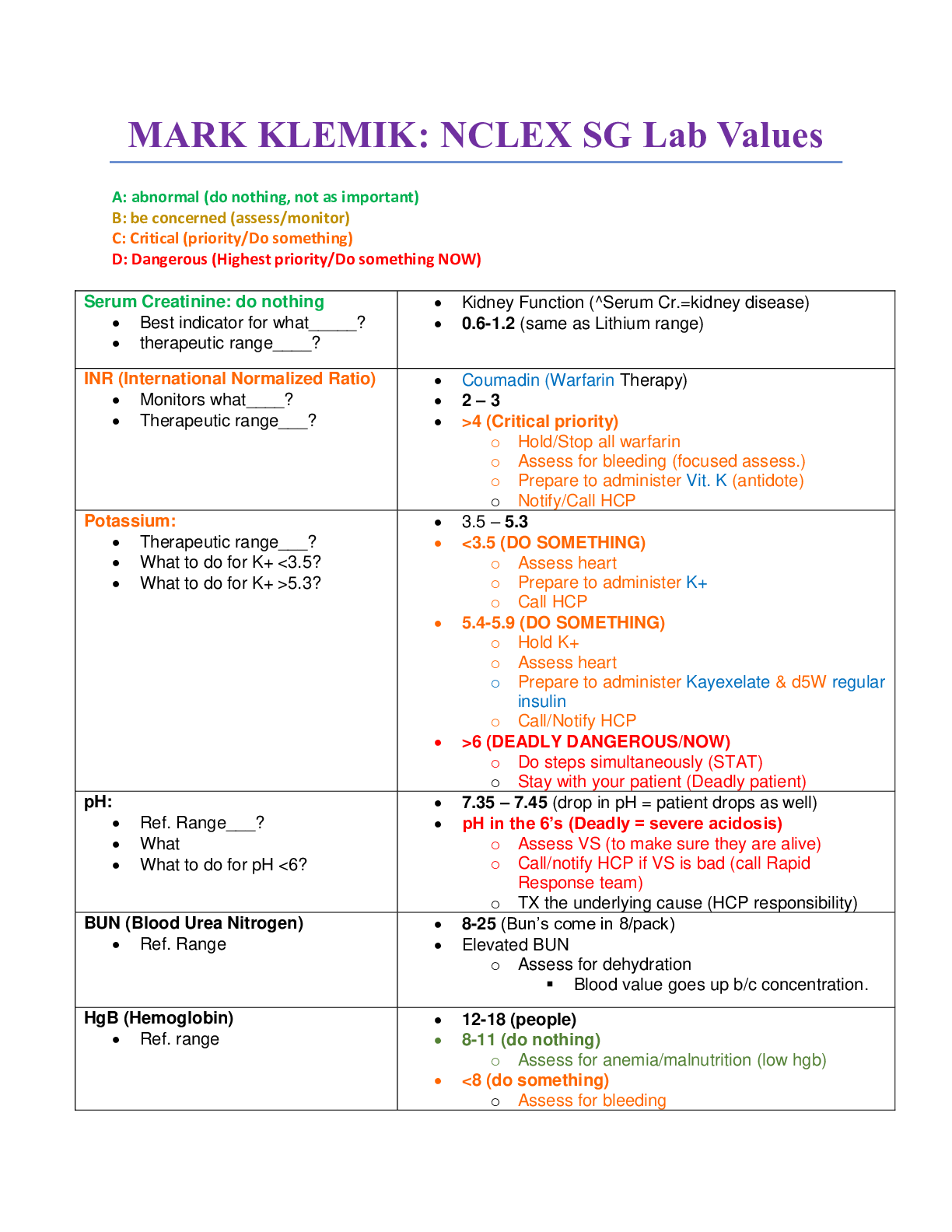
Mark Klimek Audio Lectures Lecture 11 Fetal Heart Monitoring Fetal Monitoring Patterns During Labor and Delivery Mark Klimek Audio Lectures Lecture 11 Fetal Heart Monitoring Fetal Monitoring Pat... terns During Labor and Delivery - It takes 3 things to pass the NCLEX exam - Knowledge - Confidence - Exam Proficiency - You can’t apply what you don't know, but you have to be able to apply what you do know. - Go with majority: if something is 75% fatal, consider it fatal. - If you try to learn everything you will master nothing. Lecture 11 Fetal Heart Monitoring Fetal Monitoring Patterns During Labor and Delivery - There are 7 fetal monitoring patterns you should know. 1. Low Fetal Heart Rate (a fetal heart rate under 110) - A fetal heart rate under 110 is BAD - When the fetal monitor registers a fetal heart rate below 110 do LION - L: Lay the mother on her Left side - I: Increase IV fluids - O: Apply oxygen - N: Notify physician - If Pitocin is running stop it immediately, then perform LION 2. High Fetal Heart Rate (a fetal heart rate over 160) - A fetal heart rate over 160 is no big deal, document. - Take moms temperature. (Most likely has a fever) 3. Low Baseline Variability (the baby’s heart rate remains relatively constant) - A fetal heart rate that does not change frequently is BAD - When the fetal heart rate does not vary do LION. - L: Lay the mother on her Left side - I: Increase IV fluids - O: Apply oxygen - N: Notify physician 4. High Baseline Variability (the baby’s heart rate is constantly changing) - When the babies heart rate is constantly changing that's good, document 5. Late Decelerations: - Late deceleration refers to the baby’s heart rate decelerating (slowing down) near or at the end of a contraction. This is BAD. - If a fetal heart rate is showing late decelerations do LION. - L: Lay the mother on her Left side - I: Increase IV fluids - O: Apply oxygen - N: Notify physician 6. Early Decelerations: - Early deceleration refers to the baby’s heart rate decelerating (slowing down) before or at the beginning of a contraction. - This is normal, document. 7. Variable Decelerations: - Variable deceleration is when the baby’s heart rate decelerates (slows down) and varies in duration, intensity, and uterine contractions. - This is VERY BAD, this means prolapsed cord. - Stick hand in mother’s vagina and push the baby’s head up. - Position her in keen chest (hands and knees), with hand still on baby’s head - Rush to the operating room in this position for an emergency cesarean section - The fetal monitor heart rate patterns that start with “L” are bad and you do “LION” - The fetal monitor heart rate patterns that don't start with “L” are normal occurrences, document and continue monitoring. - A fetal monitor heart rate that shows Variable deceleration is VERY BAD, this means prolapsed cord. - VEEL CHOP table for fetal heart rate monitoring. C H O P V (variable) Chord compression E (early deceleration) Head compression A (Acceleration) Okay (normal) L (late deceleration) Placental insufficiency Delivery of the Baby - First you deliver the head. - Suction the mouth and then nose. (While the body is still in the birth canal) - Check for a Nuchal cord (when the umbilical cord is wrapped around the neck. - Main goal is to prevent cord compression. - Then you deliver the body. - The baby must have an ID band on before it leaves the delivery area. Delivery of the Placenta - First, make sure the placenta is all there. - Second, check for a 3-vessel cord. - 2 Arteries - 1 vein Recovery - The first 2 hours after the delivery of the placenta. - There are 4 things you do, 4 times and hour (every 15 minutes), in the 4th stage. 1. Monitor vital signs for shock: - Low blood pressures - Increased heart rate - Pale, cold, and clammy 2. Check the fundus: - If the fundus is boggy (soft) you massage it. - If the fundus is displaced (not midline) you catheterize. 3. Check the perineal pads: - If she is bleeding excessively she will 100 % saturate a pad in less than 15 minutes. - Give her a new pad. 4. Roll her over: - Check for bleeding underneath of her. - It’s possible for a pad to be half saturated but leaking underneath her. Post-partum [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 02, 2021
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 02, 2021
Downloads
1
Views
801