Health Care > STUDY GUIDE > RBT Exam Study Guide: latest Updated A + Score Guide (All)
RBT Exam Study Guide: latest Updated A + Score Guide
Document Content and Description Below
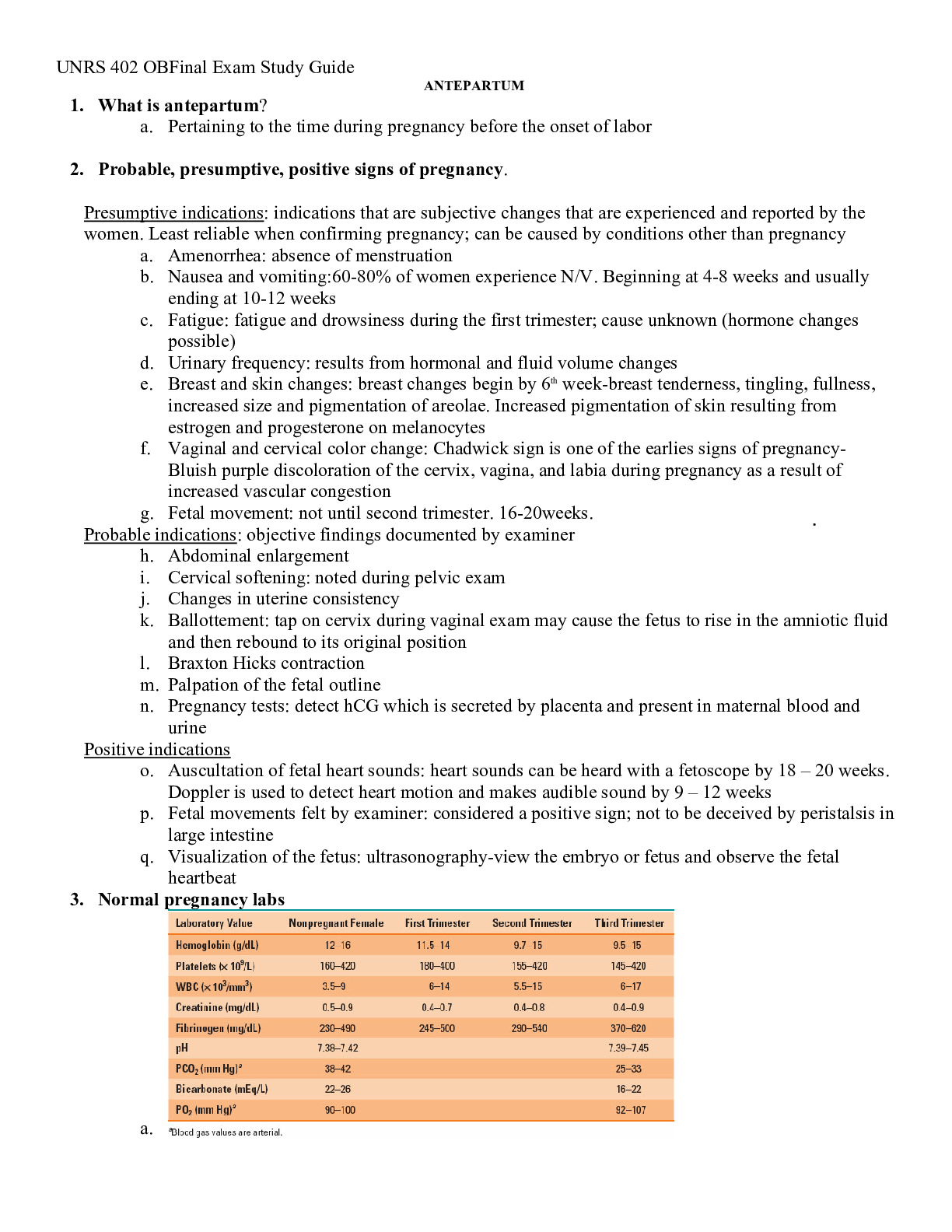
Continuous Measurement Procedures (Ans- records every possible behavioral occurrence Frequency- recording each instance of behavior Duration- number of seconds each instance of behavior occurs... Latency- elapsed time from onset of stimulus to initiation of response. Inter-Response Time (IRT)- elapsed time between two successive responses. Discontinuous Measurement Procedures (Ans- Recording a sample of instances of the target behavior according to predetermined schedule (e.g., momentary time sampling, partial interval, and whole interval) Partial Interval (Ans- behavior is recorded as occurring, if it occurs at least once during the predetermined interval Whole Interval (Ans- behavior is recorded as occurring if it is observed throughout an ENTIRE INTERVAL -> all or nothing Momentary time sample (Ans- at the end of a predetermined interval, a recording is made if the target behavior is occurring AT THAT MOMENT Permanent Product Recording (Ans- Recording tangible items or environmental effects that result from a behavior, for example, written academic work (also called outcome recording). line graph (Ans- x- axis : TIME y- axis : MEASUREMENT Phase Change Line (line graph) (Ans- allows for separation of data from before treatment (baseline) and during/after treatment to compare changes in bx cumulative records (Ans- record of behaviors that have occurred over time Assessment category (Ans- Describe the behavior and environment in observable & measurable terms. Reinforcement and punishment are part of which category? (Ans- assessment Reinforcement vs. Punishment (Ans- reinforcement increases behavior, punishment decreases behavior positive punishment (Ans- the administration of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring negative punishment (Ans- the removal of a stimulus to decrease the probability of a behavior's recurring positive reinforcement (Ans- Increasing behaviors by presenting positive stimuli, such as food. A positive reinforcer is any stimulus that, when presented after a response, strengthens the response. negative reinforcement (Ans- Increasing behaviors by stopping or reducing negative stimuli, such as shock. A negative reinforcer is any stimulus that, when removed after a response, strengthens the response. (Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment.) Conduct preference assessments (Ans- Determining what items are the most preferred by a client in order to increase the clients motivation to complete tasks and instructions. ex: Single stimuli, Multiple stimuli with replacement, Multiple stimuli without replacement Single Stimulus (Ans- present one at a time in random order and the person's reaction to each is recorded Multiple stimuli with replacement (Ans- Item chosen by the learner remains in the array and all other items that were not selected are replaced with new ones Multiple stimuli without replacement (Ans- Chosen item is removed from the array, the order or replacement of the remaining items is rearranged, and the next trial begins with a reduced number of items in the array. free operant (Ans- A response that is emitted without any constraints or prompts, thereby leaving the individual in a position freely to emit the next identical or similar response curriculum based (Ans- academic skills developmental based (Ans- adaptive living skills Social skills (Ans- communication skills 4 functions of behavior (Ans- EATS (1) escape/avoidance (2) attention (3) access tangible/activity (4) sensory (automatic reinforcement) skill acquisition (Ans- Offenders introduced to range of techniques and skills to help deal with anger-provoking situation more rationally, techniques cognitive, behavioral or physiological Unconditioned Reinforcement (Ans- A stimulus change that increases the future frequency of a behavior without prior pairing with any other reinforcement. Ex: food, water, sleep, comfort. conditioned reinforcement (Ans- Conditioned reinforcement is learned, as opposed to unconditioned reinforcers that require no learning history. Money is a conditioned reinforcer because it is paired with what it can get a person. Unconditioned reinforcement and Conditioned reinforcement PRIMARY/SECONDARY OR UNLEARNED AND LEARNED (Ans- Unconditioned reinforcement : Primary and unlearned Conditioned reinforcement : Secondary and learned Intermittent schedules (Ans- (1) Fixed ratio: "fixed" number of behaviors must occur before you provide reinforcement (2) Fixed interval: first behavior is reinforced after a specific or "fixed" amount of time has passed [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 24 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 21, 2023
Number of pages
24
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 21, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
45
.png)














 Study Guide.png)
 Exam Study Guide.png)


















.png)


