*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 599 INFORMATICS MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE COMPLETED (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 599 INFORMATICS MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE COMPLETED
Document Content and Description Below
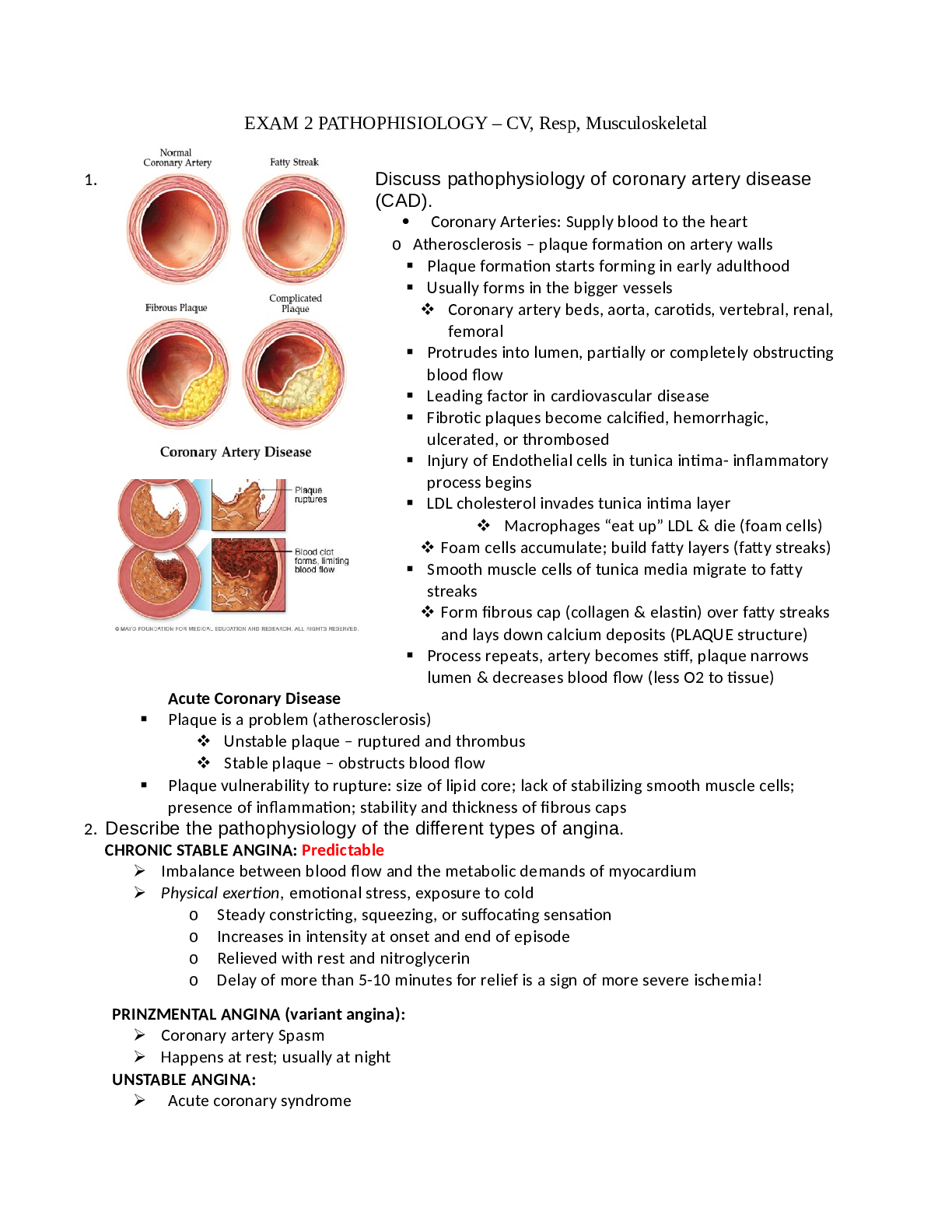
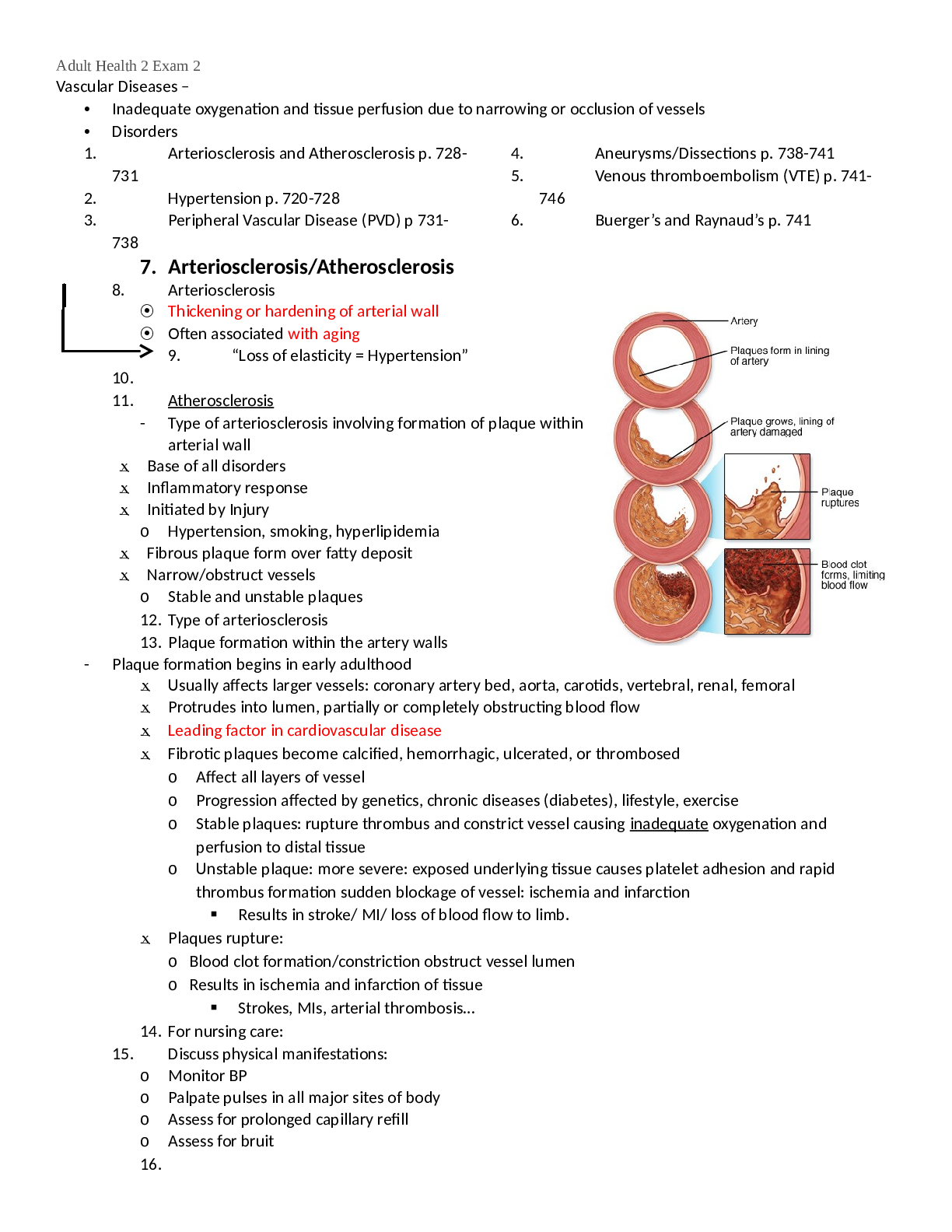
Midterm Study guide NR 599 Informatics General principles of Nursing Informatics Nursing informatics is the specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information management and analyt... ical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice. One of the most frequently quoted and widely accepted definitions of nursing informatics is that it is a combination of nursing science, information science and computer science · Knowledge •All nurses have the opportunity to be involved in the formal dissemination of knowledge via their participation in professional conferences either as presenters or attendees. •All nurses, regardless of the practice arena, must use informatics and technology to inform and support that practice. · Wisdom •Wisdom is the application of knowledge to an appropriate situation. •In the practice of nursing science, we expect action and/or actions directed by wisdom. •Wisdom uses knowledge and experience to heighten common sense and insight to exercise sound judgment in practical matters. It is developed through knowledge, experience, insight and reflection. · Scientific Underpinning The scientific underpinnings of practice provide the basis of knowledge for advanced nursing practice. These scientific underpinnings include sciences such as biology, physiology, psychology, ethics, and nursing. · The Foundation of Knowledge Model According to Mastrain and McGonigle (2009), one of the most prominent models associated with nursing informatics is the Foundation of Knowledge model. This theory involves integrating four main kinds of knowledge, which are: knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination, knowledge generation and knowledge processing. Knowledge acquisition: application of knowledge acquired through education, research, and practice to provide services and interventions to patients to maintain, enhance, or restore their health, and to acquire,process, generate, and dis- seminate nursing knowledge to advance the nursing profession. Knowledge Dissemination: Disturbing and sharing of knowledge learned Knowledge Generation: Creating new knowledge by changing and evolving knowledge based on your experience, education and input from others Knowledge Processing: The activity or process of gathering, collecting or perceiving, analyzing, saving and transmitting knowledge The Foundation of Knowledge model specifically prompts nurses to extend their theoretical and metaphorical knowledge into practical, holistic determinations based on a variety of factors and contexts. Because competencies in informatics include but are not limited to information literacy, computer literacy, and the ability to use strategies and system applications to manage data, knowledge, and information, the ability of nursing students to use computer-mediated communication skills is essential to their success in the nursing field and as a means to improve patient safety. •Organizing conceptual framework for text •Helps to explain the ties between nursing science and informatics and knowledge •Informatics is viewed as a tool for founding knowledge · Computer science · Computer science is introduced through a focus on computers and the hardware and software that make up these evolving systems; computer science is one of the building blocks of nursing informatics. Computer science offers extremely valuable tools that, if used skillfully, can facilitate the acquisition and manipulation of data and information by nurses, who can then synthesize these into an evolving knowledge and wisdom base. Data storage, management, retrieval, and processing. · Cognitive science Interdisciplinary field that studies the mind, intelligence, and behavior from an information processing perspective. A field that involves both cognitive informatics and artificial intelligence. The science of understanding what information is housed in and processed by the brain (Cognitive informatics) · Information science the science of information studying the application and usage of information and knowledge in organizations and the interfacing or interaction between people,organizations and information systems. Integrates features from cognitive science, communication science, computer science, library science and social sciences · Informatics Competencies Have been developed to encompass all levels of practice and ensure that entrylevel nurses are ready to enter the more technologically advanced field of nursing. And establish advanced competencies for specialty practice. These competencies may be used to determine the educational needs of current staff members · Information literacy Ability to recognize when info is needed as well as the skills to evaluate and use needed info effectively. this nurse can recognize significant, relevant research and know how to apply it to practice. ability to recognize when information is needed as well as the skills to find, evaluate, and use needed information effectively · Health literacy degree to which individuals can obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions · Meaningful Use use of health information technology to collect specific data with the intent to improve care, engage patients, improve population health, and ensure the privacy and security · Patient-centered Information Systems supports the use and documentation of nursing activities -provides tools for managing and delivery of nursing care -two goals: nursing functions and nursing practice Clinical Decision support systems A computer-based program designed to assist clinicians in making clinical decisions by filtering or integrating vast amounts of information and providing suggestions for clinical intervention. · Electronic Medical Records legal record created in hospitals and ambulatory environments that is the source of data for the EHR -long referred to as single episode treatment-comprised of structured and unstructured data · Human-Technology Interface The hardware and software through which the user interacts with any technology (e.g., computers, patient monitors, telephone, etc.). · Health Information Technology Management and processing of information with the assistance of computers. Computers and IT provide tools that aid data collection and the analysis associated with research to support the overall work of nurses. · Alarm fatigue You get so many alerts that you get numb to them and begin ignoring them · Digital natives Not computer smart, unable to navigate through computers easily. Lack of computer skills. · Information Literacy Competency Standards for Nursing Developed by the TIGER initiative. Three components identified: (1) information literacy, (2) computer literacy, and (3) clinical information management 1. Information literacy a. Ability to identify when information is needed as well as the skills to find, evaluate, and effectively use the same b. Evaluation of online resources for quality c. Able to search literature databases effectively 2. Computer literacy a. Basic familiarity with computer uses and common applications b. Ability to navigate hyperlinks c. Able to set up and use a database 3. Clinical information management a. Uses clinical decision making (CDS) and system safeguards to protect patients and protected health information (PHI) b. Able to request and evaluate reports for the purpose of informed decision making c. Participate in the selection, design, and evaluation of clinical information systems and patient-care technologies d. Uses available technologies to appropriately and effectively communicate · HITECH Actpush for more technology to be used especially for education · TIGER-based Nursing Informatics Competencies Model The work of the Technology Informatics Guiding Education Reform team. This team of nursing leaders developed a vision for utilizing information technology to transform nursing practice. Pillars of the TIGER vision include: management and leadership, education, communication and collaboration, informatics design, information technology, policy, and culture. WEEK ONE READING/KEY POINTS McGonigle, D. & Mastrian, K. (2018). ● Chapter 1 ○ Nursing informatics: specialty that integrates nursing science, computer science, cognitive science, and information science ○ For information to be valuable & quality it must be: ■ Accessible & Utility: right user obtain right information at the right time in the right format ■ Accurate: ■ Timely: available when needed for the right purpose at the right time ■ Complete: contains all necessary essential data ■ Cost-effective ■ Flexible: information may be used for a variety or purposes ■ Reliable: authoritative or credible source ■ Relevant: subjective descriptor that has relevant information that is useful ■ Simple ■ Verifiable ■ Transparency: allows user to apply their intellect to accomplish tasks while tools housing the information disappears into the background ■ Secure ■ Reproducibility: ability to produce the same information again ● Chapter 2 ○ Data: raw facts ○ Information: processed data that has meaning ○ Data integrity: whole, complete, correct, and consistent data ○ Dirty data: database that contains errors such as duplicate, incomplete, or outdated records○ Information science: study of information science-- concerned with input, processing, output, and feedback of data and information through technology integration with a focus on comprehending the perspective of the stakeholders involved and then applying IT as needed. ■ Systemically based-- deals with big picture, opposed to individual pieces of technology ■ Integrates communication science, computer science, cognitive science, library science, and social science ■ Links people and technology ■ Machines (inorganic ISs) Humans (organic ISs) ■ Focuses on why and how technology can be put to best use to serve the information flow within an organization ○ Information systems: handle the needs of the entire organization (communication, tracking, and research) ○ Input: collecting and acquiring raw data ■ Keyboards, touch screen, mice, light pens, automatic scanners ○ Processing: retrieval, analysis, synthesis of data-- transforms data into useful information and outputs ■ Storing for future use, making calculations, comparing data ○ Output: dissemination-- produces helpful information ■ Reports, documents, summaries, alerts, outcomes ● Chapter 3 ○ Motherboard: central nervous system of the computer-- facilitates communication among all components of the computer ○ Hard disk: permanent data storage area that holds gigabytes of data, information, documents even when the computer is turned off. Backing up important files are important because disk drives are not infallible ○ Random-access memory: temporary storage that allows the processor to access program codes and data while working on a task--the contents of RAM are lost once the system is rebooted or shuts off ○ Software: application programs ■ OS software ● Most important software on any computer ● Very first program to load on computer start-up and is fundamental for the operation of all other software and the computer hardware ● Allows user to multitask with ease ● Described in 6 basic processes: Memory, device, processor, and storage management, application and user interface ■ Productivity software● Provide all the basic programs that a user needs to do their work (word, spreadsheet, email, etc) ■ Creativity software ● Allows user to draw, paint, render, record music and sound, and incorporate multimedia in professional aesthetic ways to share and convey information and knowledge ■ Communication software ● Allows user to share, dialogue, and network with other users via exchange of email or instant message ○ Cloud computing: web-browser based login-accessible data, software, and hardware that you can access and use ■ Public cloud: owned and operated by companies offering public access to computing resources ■ Private cloud: operated for a single organization with the infrastructure being managed internally or outsourced to a third party [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 06, 2021
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 06, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
32