NCLEX RN REVIEW NOTES
Document Content and Description Below
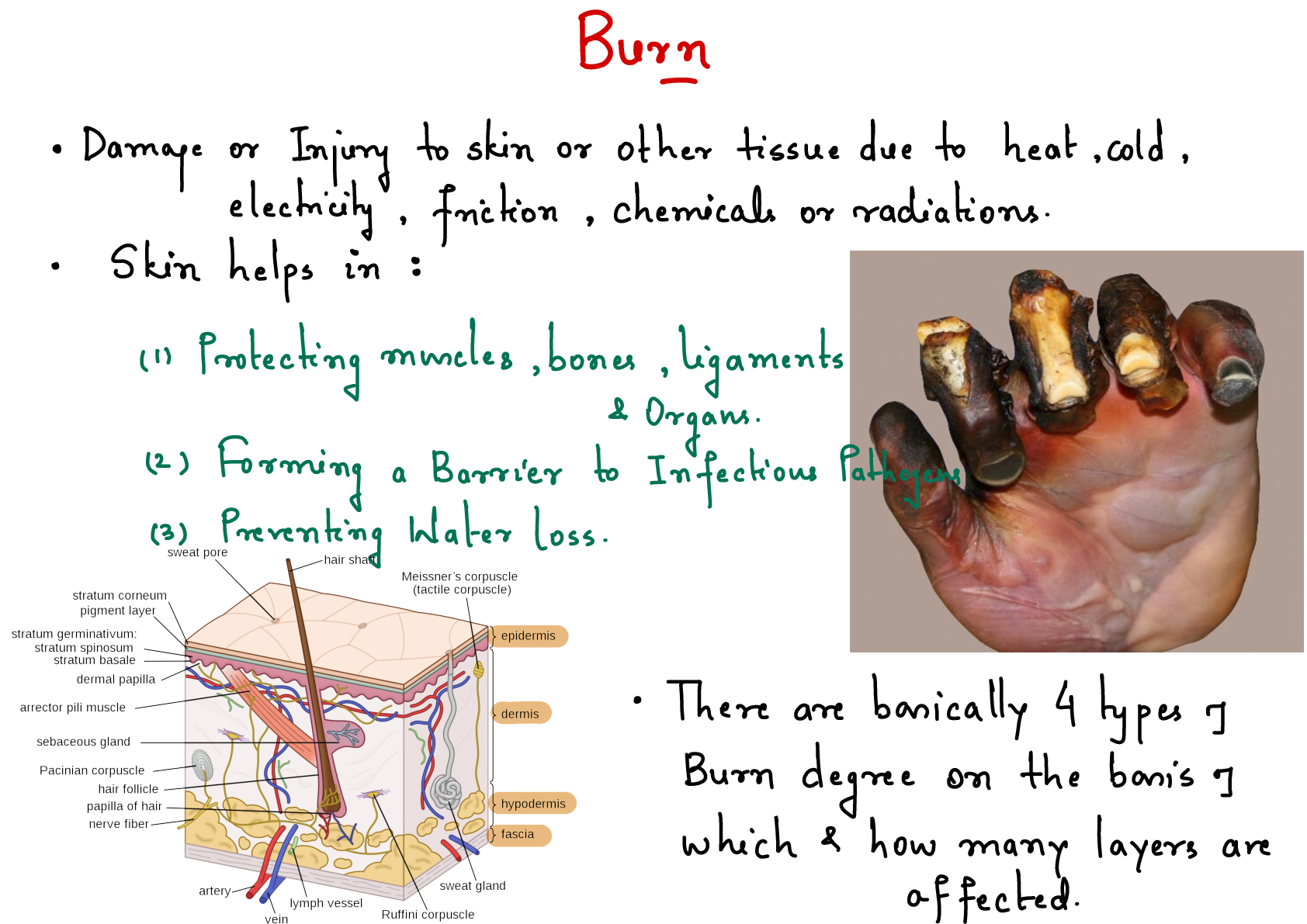
Delusion of grandeur (superior) - Delusion of persecution Mgt. ✓ Anti-psychosis = Haloperidol (ok-pregnant) WOF: EPS - ✓ Dystonia – loss of muscle tone, poor posture ✓ Tardive dyskinesia... (irreversible) – jaw swinging, involuntary repetitive facial movements, tongue protrusion, lip smacking, ✓ Akathisia – feeling of restlessness ✓ Pseudoparkinsonism – Mx bradykinesia, rigidity and tremors–tx Benztropine (Cogentin) ✓ - Acetylcholine ✓ Memory loss/dementia ✓ Mgt. Cognex (Tacrine), Aricept (Donepezil), Namenda (Memantine HCL) ✓ Chorea – involuntary dance like jerky movement ✓ Mgt. Tetrabenazine (Xenazine) CRANIAL NERVES DISORDERS 1. Trigeminal Neuralgia – tic douloureux Cranial nerve #5 ✓ Impulse of CNS ✓ Triggers ✓ Hot/cold food ✓ Hard food ✓ Facial stimulation Sensory Mx Motor Mx -excruciating pain - facial twitching, grimacing Mgt.DOC: Carbamazepine (Tegretol) – N- 5-12 mcg/ml Surgery: Facial Rhizotomy – electrode inserted face to the skull (base) via foramen ovale, heat current applied to CN5 to partially destroy it & to resolve Mx Health teaching: Avoid triggers 2. Bell’s Palsy Cranial nerve #7 ✓ Compress or inflammation due to autoimmune response or infection Herpes simplex/virus Sensory ✓Unilateral facial paralysis Motor ✓facial drooping ✓inability to close the eyelids complete Mgt. ✓ Corticosteroids ✓ Artificial tears- prevent corneal abrasions Health teaching – encourage facial massage/exercise CNS DISORDERS 1. SEIZURE - sudden surge of electrical impulse of the brain activity - it’s just a manifestation not a dse Seizure disorders a. Epilepsy – a repetitive seizure b. Status epilepticus – seizure episode that last for more than 5 min. - recurrent seizure without going back to the baseline (awake-seizure-unconscious-then seizure again) Causes of seizure ✓ High grade fever, brain trauma, tumor, infection, substance abuse or toxicity, severe hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalance - Na+, idiopathic (unknown) Seizure category a. Generalized – sudden impulse is initiated on the entire brain Type: • Tonic-clonic - Grand mal seizure • Absence seizure – Petit-mal ✓ Sudden behavioral arrest commonly 10-15 sec b. Partial – initiated on the specific part of the brain and it may spread Type: • Simplex – patient conscious • Complex – patient unconscious Diagnostic pro.: a. EEG – use H2O soluble adhesive gel prep: -avoid anticonvulsant ✓ hair shampoo- to attach electrodes easily ✓ avoid stimulants (caffeine) ✓ no sleep the night prior to a sleep EEG (test with/without a stressor) ✓ Not painful – inform pt, dec anxiety Phases of seizure a. Aura • flashes of lights • smell of a burning wire JITL BRiT KEEP OUR FRIENDLY LITTLE SECRET • metallic taste b. Unconscious - secretions c. Tonic- stiffening – shape of arch common d. Clonic – jerking e. Postictal – sleep phase ✓ Secretions Interventions 1. Stay calm 2. Mark the start time – assess seizure duration 3. If the patient is standing, lay the patient on the ground (rush to apply pillows) 4. If lying on the side - to prevent aspiration suction the secretions as needed, then provide O2. If sidelying is contraindicated just turn the head to the side, PRIO - Airway 5. Loosen the tight clothing and remove unnecessary materials near the patient 6. Observe for the duration ✓ Do not put anything in the patient’s mouth ✓ Do not promote abrupt temperature change, just TSB ✓ Side rails up 7. Monitor V/S and level of LOC DOC: Diazepam (Valium) – emergency drug ✓ (+) disorder of status epilepticus Maintenance drug Barbiturates – (CNS depressants) A/E – bone marrow depression ✓ CBC monitoring Dilantin (Phenytoin) – S/E- gingival hyperplasia ✓ 10-20 mcg/ml- therapeutic level Valproic acid (Depakene)- 50-100 mcg/ml therapeutic level Lamictal or Phenobarbital 2. MENINGITIS ✓ Meninges – covering of the brain ✓ Causes: ✓ Bacteria (streptococcus pneumonia or Neisseria meningitidis), deadly even an hour < 20 y.o. ✓ Virus- entero/coxsackie virus- common <5 y.o. ✓ Fungal – cryptococcal meningitis Mx: ✓ Fever ✓ Rigidity/nuchal rigid ✓ Brudzinski’s sign (back of neck)– patient lie flat, flex the neck (outcome hips and neck flexion) ✓ Kernig’s sign (Hamst [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 153 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 30, 2021
Number of pages
153
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 30, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
44