Statistics > SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Milestone 3_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Mile (All)
MATH 1280 Milestone 3_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Milestone 3_Introduction to Statistics (2020)
Document Content and Description Below
1 MATH 1280 Milestone 3_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People Tracie spins the four-colored spinner shown below. She records the total number of times the spinne... r lands on the color red and constructs a graph to visualize her results. Which of the following statements is TRUE? • If Tracie spins the spinner 1,000 times, it would land on red close to 250 times. • If Tracie spins the spinner 1,000 times, the relative frequency of it landing on red will remain constant. • If Tracie spins the spinner 4 times, it will land on red at least once. • The theoretical probability of the spinner landing on red will change with every spin completed. RATIONALE If we make the assumption that the area of the colors represents the true proportion, then each color is equally weighted. Since there are four colors we would expect them to come up roughly 1/4 of the time. So on 1000 rolls the expected value = n*p = 1000*0.25 = 250. CONCEPT Law of Large Numbers/Law of Averages 2 Two sets A and B are shown in the Venn diagram below. Which statement is TRUE? • There are a total of 17 elements shown in the Venn diagram. • Set A has 12 elements. • Set B has 5 elements. • Sets A and B have 15 common elements. RATIONALE The number of elements of Set A is everything in Circle A, or 10+2 = 12 elements. The number of elements of Set B is everything in Circle B, or 5+2 = 7 elements, not 5 elements. The intersection, or middle section, would show the common elements, which is 2 elements, not 15 elements. To get the total number of items in the Venn diagram, we add up what is in A and B and outside, which is 10+2+5+3 = 20 elements, not 17 elements. CONCEPT Venn Diagrams 3 Using the Venn Diagram below, what is the conditional probability of event B occurring, assuming event A has happened [P(B|A)]? • 0.41 • 0.63 • 0.24 • 0.77 RATIONALE To get the probability of B given A has occurred, we can use the following conditional formula: The probability of A and B is the intersection, or overlap, of the Venn diagram, which is 0.41. The probability of A is all of Circle A, or 0.24 + 0.41 = 0.65. CONCEPT Conditional Probability 4 The gender and age of Acme Painting Company's employees are shown below. Age Gender 23 Female 23 Male 24 Female 26 Female 27 Male 28 Male 30 Male 31 Female 33 Male 33 Female 33 Female 34 Male 36 Male 37 Male 38 Female 40 Female 42 Male 44 Female If the CEO is selecting one employee at random, what is the chance he will select a male OR someone in their 40s? • 1/3 • 1/2 • 11/18 • 1/18 RATIONALE Since it is possible for an employee to be a male and a person in their 40s, these two events are overlapping. We can use the following formula: Of the 18 employees, there are 9 females and 9 males, so . There are a total of 3 people in their 40s, so . Of the people in their 40s, only one is male so . CONCEPT "Either/Or" Probability for Overlapping Events 5 Which of the following is a condition of binomial probability distributions? • All observations are mutually exclusive. • All observations are made randomly. • All observations made are dependent on each other. • All observations made are independent of each other. RATIONALE In the binomial distribution we always assume independence of trials. This is why we simply multiply the probability of successes and failures directly to find the overall probability. CONCEPT Binomial Distribution 6 La'Vonn rolled a die 100 times. His results are below. Number Times Rolled 1 18 2 20 3 15 4 17 5 14 6 16 What is the relative frequency for La'Vonn rolling a 3? Answer choices are rounded to the hundredths place. • 0.01 • 0.15 • 0.07 • 0.38 RATIONALE The relative frequency of a 3 is: CONCEPT Relative Frequency Probability/Empirical Method 7 For a math assignment, Jane has to roll a set of six standard dice and record the results of each trial. She wonders how many different outcomes are possible after rolling all six dice. What is the total number of possible outcomes for each trial? • 216 • 46,656 • 7,776 • 36 RATIONALE We can use the general counting principle and note that for each step, we simply multiply all the possibilities at each step to get the total number of outcomes. Each die has 6 possible outcomes, so the overall number of outcomes for rolling 6 die with 6 possible outcomes each is: CONCEPT Fundamental Counting Principle 8 Zhi and her friends moved on to the card tables at the casino. Zhi wanted to figure out the probability of drawing a face card or an Ace. Choose the correct probability of drawing a face card or an Ace. Answer choices are in the form of a percentage, rounded to the nearest whole number. • 31% • 8% • 25% • 4% RATIONALE Since the two events, drawing a face card and drawing an ace card, are non-overlapping, we can use the following formula: CONCEPT "Either/Or" Probability for Non-Overlapping Events 9 Colleen has 6 eggs, one of which is hard-boiled while the rest are raw. Colleen can't remember which of the eggs are raw. Which of the following statements is true? • The probability of Colleen selecting the hard-boiled egg on her first try is 1/5. • If Colleen selected one egg, cracked it open and found out it was raw, the probability of selecting the hard-boiled egg on her second pick is 1/5. • If Colleen selected one egg, cracked it open and found out it was raw, the probability of selecting the hard-boiled egg on her second pick is 1/6. • The probability of Colleen selecting a raw egg on her first try is 1/6. RATIONALE The probability of choosing the hard-boiled egg is 1/6. If she cracks an egg and it is not the hard-boiled egg, then it becomes 1/5 on the next try because there are now only 5 eggs remaining and one has to be the hard-boiled egg as she did not pick it on the first try. CONCEPT Independent vs. Dependent Events 10 Eric is randomly drawing cards from a deck of 52. He first draws a red card, places it back in the deck, shuffles the deck, and then draws another card. What is the probability of drawing a red card, placing it back in the deck, and drawing another red card? Answer choices are in the form of a percentage, rounded to the nearest whole number. • 4% • 22% • 25% • 13% RATIONALE Since Eric puts the card back and re-shuffles, the two events (first draw and second draw) are independent of each other. To find the probability of red on the first draw and second draw, we can use the following formula: Note that the probability of drawing a red card is or for each event. CONCEPT "And" Probability for Independent Events 11 A basketball player makes 60% of his free throws. We set him on the free throw line and asked him to shoot free throws until he misses. Let the random variable X be the number of free throws taken by the player until he misses. Assuming that his shots are independent, find the probability that he will miss the shot on his 6th throw. • 0.03110 • 0.00614 • 0.04666 • 0.01866 RATIONALE Since we are looking for the probability until the first success, we will use the following Geometric distribution formula: The variable k is the number of trials until the first success, which in this case, is 6 throws. The variable p is the probability of success, which in this case, a success is considered missing a free throw. If the basketball player has a 60% of making it, he has a 40%, or 0.40, chance of missing. CONCEPT Geometric Distribution 12 Three hundred students in a school were asked to select their favorite fruit from a choice of apples, oranges, and mangoes. This table lists the results. Boys Girls Apple 66 46 Orange 52 41 Mango 40 55 If a survey is selected at random, what is the probability that the student is a girl who chose apple as her favorite fruit? Answer choices are rounded to the hundredths place. • 0.37 • 0.41 • 0.15 • 0.59 RATIONALE If we want the probability that the survey is from a girl and also chose apple as her favorite, we just need to look at the box that is associated with both categories, or 46. To calculate the probability, we can use the following formula: CONCEPT Two-Way Tables/Contingency Tables 13 Which of the following situations describes a continuous distribution? • A probability distribution showing the amount of births in a hospital in a month • A probability distribution showing the average number of days mothers spent in the hospital • A probability distribution showing the weights of newborns • A probability distribution showing the number of vaccines given to babies during their first year of life RATIONALE Since the weight of newborns can be an infinite number of values, such as 8 pounds, 9 ounces, etc, this would be an example of a continuous distribution. CONCEPT Probability Distribution 14 A credit card company surveys 125 of its customers to ask about satisfaction with customer service. The results of the survey, divided by gender, are shown below. Males Females Extremely Satisfied 25 7 Satisfied 21 13 Neutral 13 16 Dissatisfied 9 14 Extremely Dissatisfied 2 5 If you were to choose a female from the group, what is the probability that she is satisfied with the company's customer service? Answer choices are rounded to the hundredths place. • 0.13 • 0.62 • 0.38 • 0.24 RATIONALE The probability of a person being "satisfied" given she is a female is a conditional probability. We can use the following formula: Remember, to find the total number of females, we need to add all values in this column: 7 + 13 + 16 + 14 + 5 = 55. CONCEPT Conditional Probability and Contingency Tables 15 Annika was having fun playing poker. She needed the next two cards dealt to be diamonds so she could make a flush (five cards of the same suit). There are 15 cards left in the deck, and five are diamonds. What is the probability that the two cards dealt to Annika (without replacement) will both be diamonds? Answer choices are in percentage format, rounded to the nearest whole number. • 13% • 10% • 33% • 29% RATIONALE If there are 15 cards left in the deck with 5 diamonds, the probability of being dealt 2 diamonds if they are dealt without replacement means that we have dependent events because the outcome of the first card will affect the probability of the second card. We can use the following formula: The probability that the first card is a diamond would be 5 out of 15, or . The probability that the second card is a diamond, given that the first card was also a diamond, would be because we now have only 14 cards remaining and only 4 of those cards are diamond (since the first card was a diamond). So we can use these probabilities to find the probability that the two cards will both be diamonds: CONCEPT "And" Probability for Dependent Events 16 David is playing a game where he flips two coins and counts the total number of heads. The possible outcomes and probabilities are shown in the probability distribution below. What is the expected value for the number of heads from flipping two coins? • 1 • 3 • 1.5 • 2 RATIONALE The expected value, also called the mean of a probability distribution, is found by adding the products of each individual outcome and its probability. We can use the following formula to calculate the expected value, E(X): CONCEPT Expected Value 17 Luke went to a blackjack table at the casino. At the table, the dealer has just shuffled a standard deck of 52 cards. Luke has had good luck at blackjack in the past, and he actually got three blackjacks with Queens in a row the last time he played. Because of this lucky run, Luke thinks that Queens are the luckiest card. The dealer deals the first card to him. In a split second, he can see that it is a face card, but he is unsure if it is a Queen. What is the probability of the card being a Queen, given that it is a face card? Answer choices are in a percentage format, rounded to the nearest whole number. • 4% • 77% • 33% • 8% RATIONALE The probability of it being a Queen given it is a Face card uses the conditional formula: Note that there are 12 out of 52 that are face cards. Of those 12 cards, only 4 of them are also Queens. CONCEPT Conditional Probability 18 Select the following statement that describes non-overlapping events. • Jon needs to roll an even number to win. When it’s his turn, he rolls a two. • To win, Jon needs a red card. He receives a Queen of Diamonds. • Jon wants a face card so he can have a winning hand, and he receives the eight of clubs. • Receiving the King of Hearts fulfills Jon's need of getting both a face card and a heart. RATIONALE Events are non-overlapping if the two events cannot both occur in a single trial of a chance experiment. Since he wants a face card {Jack, Queen or King} and he got an eight {8}, there is no overlap. CONCEPT Overlapping Events 19 Tim rolls two six-sided dice and flips a coin. All of the following are possible outcomes, EXCEPT: • 1, Tails, 6 • Heads, 3, 4 • 2, 8, Heads • 5, 2, Tails RATIONALE Recall that a standard coin has two values, {Heads or Tails}, while a standard die has six values {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6}. So, obtaining a 2 is possible, however the 8 is not. CONCEPT Outcomes and Events 20 The average number of babies born at a private hospital's maternity wing is 6 per hour. What is the probability that three babies are born during a particular 1-hour period in this maternity wing? • 0.16 • 0.13 • 0.09 • 0.20 RATIONALE Since we are finding the probability of a given number of events happening in a fixed interval when the events occur independently and the average rate of occurrence is known, we can use the following Poisson distribution formula: The variable k is the given number of occurrences, which in this case, is 3 babies. The variable λ is the average rate of event occurrences, which in this case, is 6 babies. CONCEPT Poisson Distribution 21 Mark looked at the statistics for his favorite baseball player, Jose Bautista. Mark looked at seasons when Bautista played 100 or more games and found that Bautista's probability of hitting a home run in a game is 0.173. If Mark uses the normal approximation of the binomial distribution, what will be the variance of the number of home runs Bautista is projected to hit in 100 games? Answer choices are rounded to the tenths place. • 14.3 • 17.3 • 3.8 • 0.8 RATIONALE In this situation, we know: n = sample size = 100 p = success probability = 0.173 We can also say that q, or the complement of p, equals: q = 1 - p = 1 - 0.173 = 0.827 The variance is equivalent to n*p*q: CONCEPT Normal Distribution Approximation of the Binomial Distribution 22 Using this Venn diagram, what is the probability that event A or event B occurs? • 0.60 • 0.78 • 0.42 • 0.22 RATIONALE To find the probability that event A or event B occurs, we can use the following formula for overlapping events: The probability of event A is ALL of circle A, or 0.39 + 0.18 = 0.57. The probability of event B is ALL of circle B, or 0.21 + 0.18 = 0.39. The probability of event A and B is the intersection of the Venn diagram, or 0.18. We can also simply add up all the parts = 0.39 + 0.18 + 0.21 = 0.78. CONCEPT "Either/Or" Probability for Overlapping Events 23 Peter randomly draws a card from a deck of 24. The odds in favor of his drawing a spade from the cards are 1:3. What is the probability ratio for Peter to draw a spade? • • • • RATIONALE Recall that we can go from "" odds to a probability by rewriting it as the fraction "". So odds of 1:3 is equivalent to the following probability: CONCEPT Odds 24 What is the probability of NOT rolling a four when rolling a six sided die? • • • RATIONALE Recall that the probability of a complement, or the probability of something NOT happening, can be calculated by finding the probability of that event happening, and then subtracting from 1. Note that the probability of rolling a four would be 1/6. So the probability of NOT rolling a four is equivalent to: CONCEPT Complement of an Event 25 A magician asks an audience member to pick any number from 6 to 15. What is the theoretical probability that an individual chooses the number the magician has in mind? • • • • RATIONALE If we suppose that the card chosen by the magician is fixed, then there are 10 possible values, {6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, or 15}, that are all equally likely. So, the probability that a specific value is chosen is: CONCEPT Theoretical Probability/A Priori Method 26 Which of the following is an example of a false negative? • Test results confirm that a woman is not pregnant. • Test results indicate that a woman is not pregnant when she is. • Test results confirm that a woman is pregnant. • Test results indicate that a woman is pregnant when she is not. RATIONALE Since the test results indicate negatively, showing that the woman is not pregnant when in fact she is pregnant, this is a false negative. CONCEPT False Positives/False Negatives 27 Kendra was trying to decide which type of frozen yogurt to restock based on popularity: flavors with chocolate or flavors without chocolate. After studying the data, she noticed that chocolate flavors sold best on the weekdays and on the weekends, but not best overall. Which paradox has Kendra encountered? • False Negative • Simpson's Paradox • Benford's Law • False Positive RATIONALE This is an example of Simpson's paradox, which is when the trend overall is not the same that is examined in smaller groups. Since the sale of chocolate flavors is larger on the weekends, but this trend changes when looking at sales overall, this is a reversal of the trend. CONCEPT Paradoxes [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages
 – University of the People.png)
Reviews( 0 )
Recommended For You
Statistics> SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Practice Milestone UNIT 1 Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Practice Milestone UNIT 1 Introduction to Statistics (2020) (All)
 – University of the People.png)
MATH 1280 Practice Milestone UNIT 1 Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Practice Milestone UNIT 1 Introduction to Statistics (2020)
1 MATH 1280 Practice Milestone UNIT 1 Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People Which of the following data types will be continuous? • Number of cars produced by a car c...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2020
$16.5
Statistics> SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Milestone 2_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH 1280 Milestone 2_Introduction to Statistics (2020) (All)
 – University of the People.png)
MATH 1280 Milestone 2_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH 1280 Milestone 2_Introduction to Statistics (2020)
1 MATH 1280 Milestone 2_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People Hannah noted the height of each student in her class and found that the mean height of the students is 56 i...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2020
$16.5
Statistics> SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Milestone 4_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Milestone 4_Introduction to Statistics (2020) (All)
 – University of the People.png)
MATH 1280 Milestone 4_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Milestone 4_Introduction to Statistics (2020)
1 MATH 1280 Milestone 4_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People Which statement about correlation is FALSE? • The correlation of a data set can be positive, negativ...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2020
$16.5
Statistics> SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Milestone 1_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Milestone 1_Introduction to Statistics (2020) (All)
 – University of the People.png)
MATH 1280 Milestone 1_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People | MATH1280 Milestone 1_Introduction to Statistics (2020)
1 MATH 1280 Milestone 1_Introduction to Statistics (2020) – University of the People The administrator of a hospital conducted a survey among patients in the cardiology wing to determine servi...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2020
$16.5
Statistics> SOPHIA PATHWAY > MATH 1280 Graded Exam Unit 8 Practice questions only (2020) – University of the people | MATH1280 Graded Exam Unit 8 Practice questions only (2020) (All)
 – University of the people.png)
MATH 1280 Graded Exam Unit 8 Practice questions only (2020) – University of the people | MATH1280 Graded Exam Unit 8 Practice questions only (2020)
MATH 1280 Graded Exam Unit 8 test questions only (2020) – University of the people Information Flag question Information text Recall that the population average of the heights in the file "po...
By Martin Freeman , Uploaded: Sep 14, 2020
$6
Environmental Science> SOPHIA PATHWAY > Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 4 Milestone 4,100% CORRECT (All)

Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 4 Milestone 4,100% CORRECT
Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 4 Milestone 4
By securegrades , Uploaded: Jan 01, 2022
$14
Biology> SOPHIA PATHWAY > SOPHIA PATHWAY_Human Biology_Unit 5 Milestone 5. Concepts indicated and ALL CORRECT ANSWERS HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW. (All)
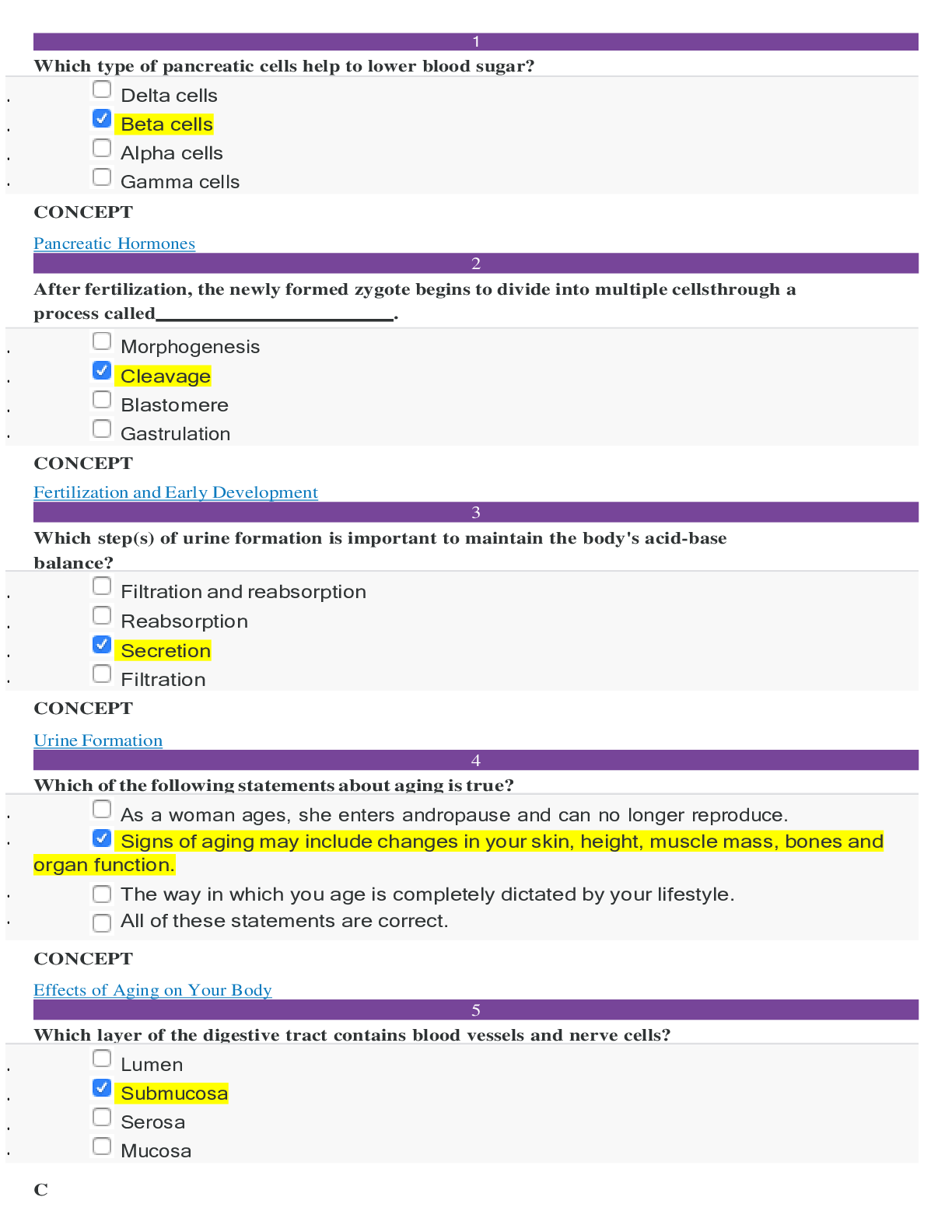
SOPHIA PATHWAY_Human Biology_Unit 5 Milestone 5. Concepts indicated and ALL CORRECT ANSWERS HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW.
Sophia - Human Biology - Unit 5 Milestone 51 Correct Answers Highlighted in Yellow Which type of pancreatic cells help to lower blood sugar? • Delta cells • Beta cells • Alpha cells • Ga...
By QuizMaster , Uploaded: Oct 10, 2020
$8
*NURSING> SOPHIA PATHWAY > PALS - Team Response Final Scenario: Sophia Giamanti COMPLETE SOLUTION 2022 (All)
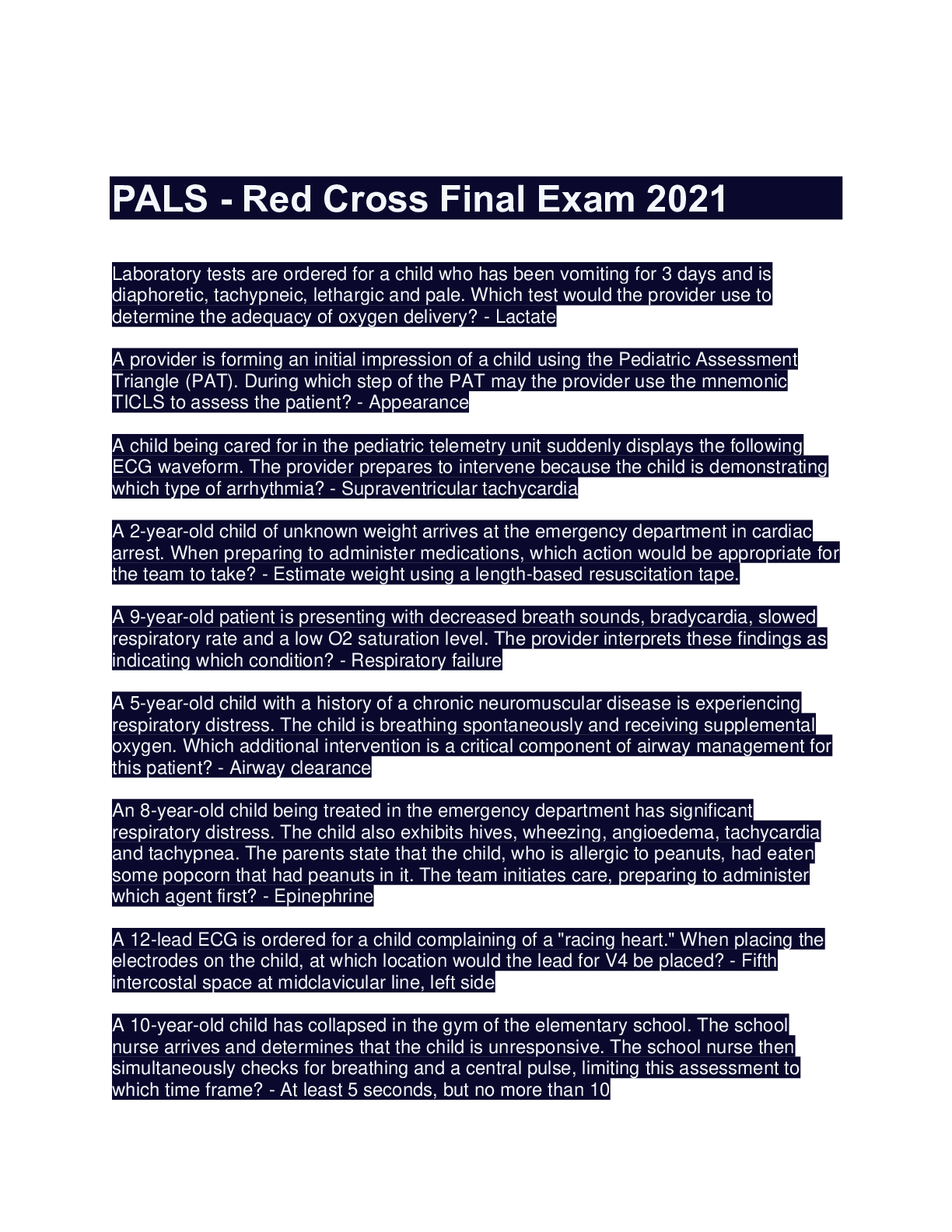
PALS - Team Response Final Scenario: Sophia Giamanti COMPLETE SOLUTION 2022
PALS - Team Response Final Scenario: Sophia Giamanti COMPLETE SOLUTION 2022 Which of the following should Jeremy do immediately after checking for responsiveness using the shouttap-shout sequence? -...
By Prof.Pierro , Uploaded: Jul 11, 2022
$6
Environmental Science> SOPHIA PATHWAY > Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1 (All)
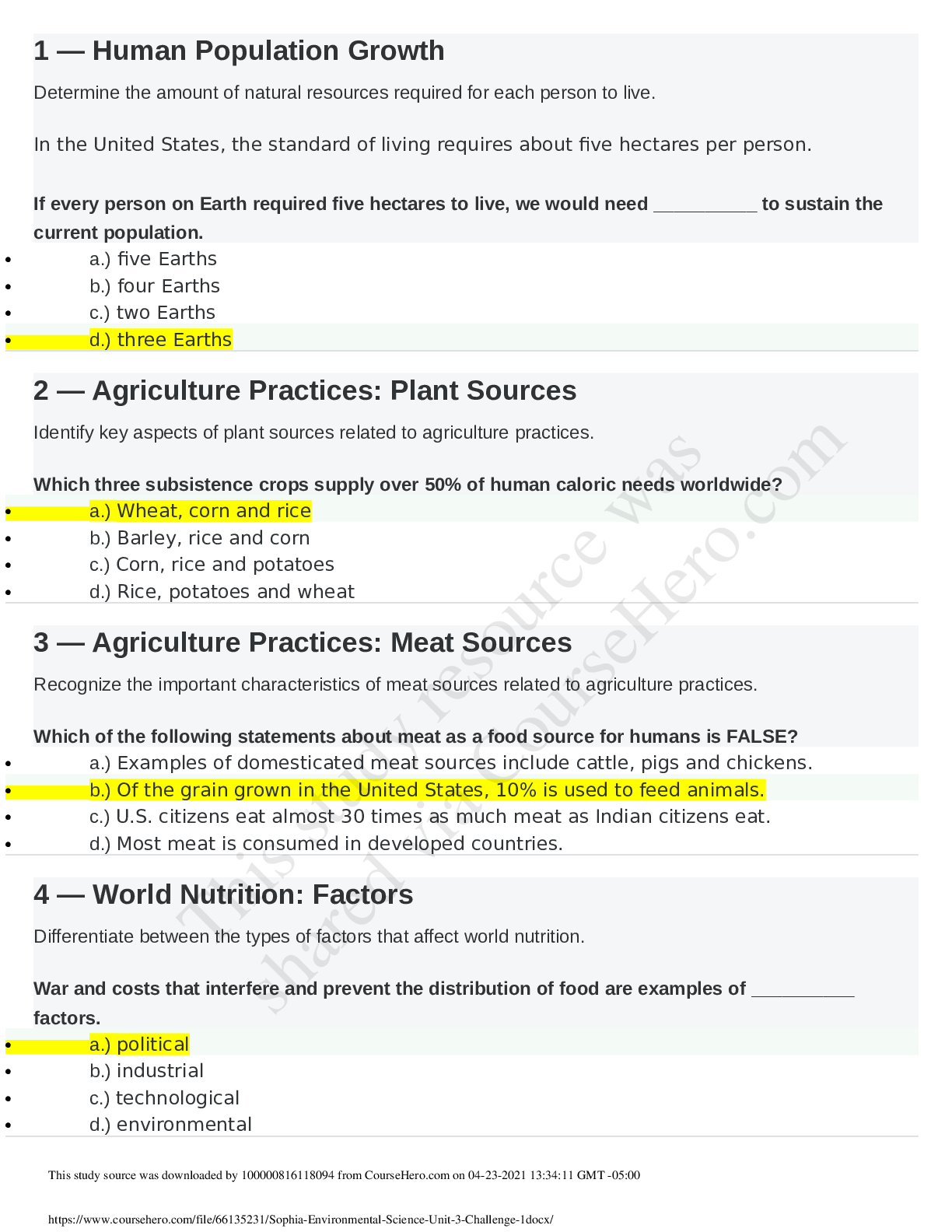
Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1
Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1/Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1/Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1/Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Chal...
By PROF , Uploaded: Apr 23, 2021
$10
*NURSING> SOPHIA PATHWAY > Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1 (All)

Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1
Sophia - Environmental Science - Unit 3 Challenge 1
By PROF , Uploaded: Feb 08, 2021
$13.5
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 14, 2020
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 14, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
228






