Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS FINAL QUESTIONS. The most commonly tested 450 Questions (MCQ). All the Ans (All)
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS FINAL QUESTIONS. The most commonly tested 450 Questions (MCQ). All the Answers Listed in a Key at the end of the 135 Pages.
Document Content and Description Below
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS 2017-2018 FALL FINAL QUESTIONS---- G.KAZAR MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure above shows ... Clara's demand for CDs. If the price for a CD is $15, then Clara 1) A) receives no consumer surplus on the 6th CD she buys. B) a total of $10 of consumer surplus. C) 40 of consumer surplus. D) will buy no CDs. 2) Jane is willing to pay $50 for a pair of shoes. The actual price of the shoes is $30. Her marginal benefit is 2) A) $50. B) $80. C) $30. D) $20. 3) Which of the following represents the marginal cost of a soda? I. The opportunity cost of producing another soda. II. The minimum price someone is willing to pay for another soda. 3) A) Neither I nor II B) I and II C) I only D) II only 4) Consumer surplus is the 4) A) value of a good minus the price paid for it summed over the quantity bought. B) plus the price paid for it summed over the quantity bought. C) price of a good expressed in dollars. D) value of a good expressed in dollars. 5) Moving down along the market demand curve for hot dogs, the 5) A) marginal social benefit of hot dogs decreases. B) consumer surplus of the last hot dog consumed increases. C) marginal social cost of hot dogs increases. D) ximum price that people are willing to pay for hot dogs increases. G.KAZAR6) The market demand curve also is 6) A) an opportunity cost curve. B) a consumer surplus curve. C) marginal social benefit curve. D) marginal social cost curve. 7) Which of the following statements about supply curves is correct? I. A supply curve also can be a marginal cost curve. II. A supply curve tells the quantity of other goods and services that sellers must give up to produce another unit of the good. 7) A) II only B) I only C) both I and II D) neither I nor II 8) The above figure shows Dana's marginal benefit curve for ice cream. If the price of ice cream is $2 per gallon, then the gallon that gives Dana exactly zero consumer surplus is 8) A) the 16th gallon. B) the 20th gallon. C) the 8th gallon. D) the 12th gallon. 9) A used car was recently priced at $20,000.00. Seeing the car, Bobby thought, "It's nice, but if I have to pay more than $19,500 for this car, then I would rather do without it." After negotiations, Bobby purchased the car for $19,250.00. His consumer surplus was equal to 9) A) $0.00. B) $250.00. C) $19,500.00. D) $1,750.00. G.KAZAR10) In the figure above, when the market is in equilibrium, total consumer surplus on all the CDs bought will be 10) A) less than at any other price. B) greater than $30 million. C) $20 million. D) $15 million. 11) Alice is willing to pay $3 for the second slice of pizza she eats. The price she pays is $2. Alice's consumer surplus for this slice of pizza equals 11) A) $1. B) $0. C) $2. D) $3. 12) When the Smiths were shopping for their present home, the asking price from the previous owner was $250,000.00. The Smiths had decided they would pay no more than $245,000.00 for the house. After negotiations, the Smiths actually purchased the house for $239,000.00. Therefore, the previous owner earned a producer surplus of 12) A) $11,000.00. B) $250,000.00. C) $5,000.00. D) an amount unknown given the information in the question. G.KAZAR13) The figure above shows Clara's demand for CDs. At a price of $20 for a CD, the value of Clara's total consumer surplus for all the CDs she buys is 13) A) $40. B) $20. C) $30. D) $4. The table below shows the supply schedules for Fred's Pizza and Johnny's Pizza, the only sellers of pizza in the market. Price (dollars per slice) Fred's quantity supplied (slices per month) Johnny's quantity supplied (slices per month) 1.50 0 0 2.00 100 150 2.50 200 300 3.00 300 450 3.50 400 600 4.00 500 750 14) Using the table, Johnny's marginal cost of the 600th slice of pizza is 14) A) $1.50. B) $3.50. C) $12.50. D) Zero. G.KAZAR15) In the above figure, when the price of pretzels is $3.00 per pound, the total producer surplus from all the pretzels will be 15) A) greater than at any other price. B) less than at any other price. C) the sum of the difference between $3.00 and the marginal cost of all the pounds produced. D) zero. 16) The figure illustrates the market for hot dogs on Big Foot Island. The producer surplus is ________. 16) A) $60 an hour B) $240 an hour C) $1.20 a hot dog D) $180 an hour G.KAZAR17) The supply curve for CDs shows the 17) A) maximum price that consumers are willing to pay if a given quantity of CDs is available. B) minimum price that producers must be offered to get them to produce a given quantity of CDs. C) minimum price that consumers are willing to pay if a given quantity of CDs is available. D) maximum price that producers must be offered to get them to produce a given quantity of CDs. 18) The figure above shows Clara's demand for CDs. The price for a CD is $15. Which statement is true? 18) A) When Clara buys 6 CDs, she receives a total of $30 of consumer surplus. B) $15 of consumer surplus on her 6th CD. C) a total of $15 of consumer surplus. D) 45 of consumer surplus. 19) Four people each have a different willingness to pay for one unit of a good: George will pay $15, Glen will pay $12, Tom will pay $10, and Peter will pay $8. If price is equal to $9 per unit then the quantity demanded in the market will be ________ and the consumer surplus for this unit will be ________. 19) A) 3; $10 B) 3; $37 C) 4; $8 D) 3; $36 20) The producer surplus on a unit of a good is the 20) A) number of dollars' worth of other goods and services forgone to produce this unit of the good. B) difference between the total cost of the good and the marginal cost. C) price of the good and the marginal cost of producing the good. D) marginal social benefit and the marginal social cost. G.KAZAR21) When the Smiths were shopping for their present home, the asking price from the previous owner was $250,000.00. The Smiths had decided they would pay no more than $245,000.00 for the house. After negotiations, the Smiths actually purchased the house for $239,000.00. They, therefore, enjoyed a consumer surplus of 21) A) $5,000.00. B) $11,000.00. C) $239,000.00. D) $6,000.00. 22) The above figure shows Dana's marginal benefit curve for ice cream. If the price of ice cream is $2 per gallon, then Dana's consumer surplus from the 4th gallon 22) A) is the same as her consumer surplus from the 8th gallon. B) greater than her consumer surplus from the 8th gallon. C) could be greater than, equal to, or less than the consumer surplus from the 8th gallon. D) is less than her consumer surplus from the 8th gallon. Quantity of tennis rackets demanded Price (dollars) Jill Jed 60 1 0 50 2 0 40 2 1 30 3 2 20 4 3 23) Jill and Jed have individual demand curves for tennis rackets given in the table above and are the only two demanders in the market. What is the market quantity demanded at the price of $30? 23) A) 2 B) 18 C) 11 D) 5 G.KAZAR24) Producer surplus is the difference between the 24) A) price and the willingness to pay for the good. B) willingness to pay for the good and the marginal cost of producing the good summed over the quantity sold. C) marginal benefit of consuming the good and the marginal cost of producing the good summed over the quantity sold. D) price and the marginal cost of producing the good summed over the quantity sold. The table below shows the supply schedules for Fred's Pizza and Johnny's Pizza, the only sellers of pizza in the market. Price (dollars per slice) Fred's quantity supplied (slices per month) Johnny's quantity supplied (slices per month) 1.50 0 0 2.00 100 150 2.50 200 300 3.00 300 450 3.50 400 600 4.00 500 750 25) Using the table, what is the marginal social cost when the market quantity supplied is 750 slices of pizza per month? 25) A) $9 B) $3 C) $3.50 D) $7 26) The marginal cost curve 26) A) shows the maximum price that a producer must receive to induce it to produce a unit of a good or service. B) shows what buyers are willing to give up to get one more unit of a good or service. C) the minimum price sellers must receive to produce a unit of a good or service. D) is the same as the demand curve. 27) Marginal benefit 27) A) is the difference between total benefit and total cost. B) increases as consumption increases. C) s the maximum amount a person is willing to pay for one more unit of a good. D) same as the total benefit received from consuming a good. 28) Charlene is willing to pay $5.00 for a sandwich. If Charlene must pay ________ for a sandwich, she ________. 28) A) $6.00; receives consumer surplus B) $6.00; receives a marginal cost C) 4.00; does not receive consumer surplus D) 4.00; receives consumer surplus G.KAZAR29) The figure above shows Clara's demand for CDs. At a price of $5 for a CD, the value of Clara's total consumer surplus for all the CDs she buys is 29) A) $5. B) $25. C) $10. D) $125. 30) The market demand curve 30) A) shows the value of a good that consumers must give up to get another unit of a different good. B) can also be the marginal social benefit curve. C) cost curve. D) by itself determines equilibrium prices. 31) Which of the following statements is true? 31) A) Marginal social benefit decreases as the quantity consumed decreases. B) At the efficient quantity, marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. C) If marginal social benefit exceeds marginal social cost by as much as possible, production is efficient. D) Marginal social cost increases as the quantity produced decreases. 32) Which of the following can prevent markets from reaching efficiency? I. decreasing marginal benefit II. taxes III. quantity regulations that limit the quantity that may be produced 32) A) I and II B) I, II and III C) I and III D) II and III G.KAZAR33) What area in the above figure is the consumer surplus at the efficient quantity? 33) A) A. B) F. C) D + E + F. D) A + B + C. G.KAZAR34) The figure above shows the market for coffee. If one firm owns all the coffee outlets and sells 10 million pounds of coffee a month, 34) A) the market is efficient because the total social benefit from coffee exceed the total social cost. B) the market is efficient because the marginal social benefit from coffee exceeds its marginal social cost. C) there is a deadweight loss because the marginal social cost of the last pound of coffee exceeds its marginal social benefit. D) there is a deadweight loss because the marginal social benefit from the last pound of coffee exceeds its marginal social cost. G.KAZAR35) What area in the above figure is the producer surplus at the efficient quantity? 35) A) A B) D + E + F C) A + B + C D) F 36) The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of doughnuts in the nation of Kaffenia. What is the marginal social cost to the economy of Kaffenia of producing the 100th dozen doughnuts each day? 36) A) $10.00 per dozen B) $8.00 per dozen C) 6.00 per dozen D) 4.00 per dozen G.KAZAR37) The figure above shows the market for umbrellas in Sunville. What is the marginal social benefit that Sunville consumers receive from the 200th umbrella bought? 37) A) $50.00 B) $26.67 C) $23.33 D) $30.00 38) Suppose a tax is imposed on a good. This will 38) A) increase the price paid by the buyer and decrease the price received by the seller. B) received by the seller and decrease the price paid by the buyer. C) decrease the price received by the seller but leave the price received by the buyer unchanged. D) increase the price paid by the buyer but leave the price received by the seller unchanged. G.KAZAR39) The figure above shows the market for milk. The ________ price that producers must be offered to get them to produce 100 gallons of milk per day is ________. 39) A) maximum; $4.00 B) maximum; $2.50 C) minimum; $2.50 D) minimum; $3.00 G.KAZAR40) The figure above shows the market for coffee. If the government pays the coffee producers a subsidy and production increases to 30 million pounds per day, the market is 40) A) inefficient because the marginal social cost of the last pound of coffee exceeds its marginal social benefit. B) inefficient because the marginal social benefit from the last pound of coffee exceeds its marginal social cost. C) efficient because the marginal social benefit from the last pound of coffee exceeds its marginal social cost. D) efficient because the total social benefit from coffee exceed the total social cost. Quantity (DVDs per week) Marginal social benefit (dollars per DVD) Marginal social cost (dollars per DVD) 1 24 16 2 22 18 3 20 20 4 18 22 5 16 24 41) The schedules in the table give the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost of a DVD. If the number of DVD produced is cut to 2 a week, then the ________. 41) A) opportunity cost of the second DVD is $22 B) value of the second DVD is $20 C) minimum supply-price of the second DVD is $18 D) price is $18 a DVD G.KAZAR42) In the above figure, a price of $1.25 and a quantity of 5 million gallons of milk per day maximizes the 42) A) amount of producer surplus. B) consumer surplus. C) sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus. D) All of the above answers are correct. 43) A public good can be consumed by 43) A) everyone simultaneously, as long as they pay for it. B) even if they do not pay for it. C) only one person who has to pay for it. D) does not have to pay for it. G.KAZAR44) In the above figure, if the market produces the efficient amount of purses then producer surplus equals 44) A) trapezoid adec. B) triangle adc. C) rectangle bcde. D) triangle bcd. 45) Suppose a country produces only bikes and clothing. The country achieves an efficient allocation of resources when 45) A) the prices charged for the goods are as low as possible. B) the marginal social benefit of producing a bike equals the marginal social cost of producing a bike. C) it produces equal amount of bikes and clothes. D) can't produce any more bikes unless it gives up clothing. G.KAZAR46) In the above figure, if output were restricted to 300 million pounds of turkey, then 46) A) the marginal social benefit would exceed the marginal social cost on the last pound of turkey traded by $0.80. B) there would be inefficient underproduction of turkey. C) a deadweight loss of $40 million. D) All of the above answers are correct. 47) The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of chocolate in the nation of Kaffenia. What is the efficient quantity of chocolate to produce each day? 47) A) 250 pounds B) zero C) 100 pounds D) 150 pounds G.KAZAR48) An external benefit is a benefit that ________. 48) A) experiences increasing marginal returns B) is enjoyed by someone other than the buyer of a good C) always equals external cost D) is greatest at the equilibrium point 49) The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of chocolate in the nation of Kaffenia. There is no external benefit nor external cost. The demand curve for chocolate is the same as the 49) A) marginal social cost curve of chocolate. B) benefit curve minus the marginal social cost curve of chocolate. C) of chocolate. D) opportunity cost curve of chocolate. 50) The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of chocolate in the nation of Kaffenia. What is the marginal social cost of producing the 250th pound of chocolate each day? 50) A) $1.00 per pound B) $2.50 per pound C) 0.50 per pound D) 625.00 per pound 51) A firm that is the only seller of a product and is in sole control of a market has a 51) A) quantity regulations. B) monopoly. C) subsidy. D) public good. G.KAZAR52) The figure above shows the market for coffee. If 30 pound of coffee a month are available, the ________ price that consumers are willing to pay for the last pound is ________. 52) A) minimum; $4.00 B) minimum; $2.50 C) maximum; $4.00 D) maximum; $2.50 G.KAZAR53) In the above figure, 300,000 purses per month is 53) A) an inefficient amount to produce because producing 500,000 purses sets the marginal social benefit equal to zero. B) the efficient amount to produce because at 300,000 purses marginal social benefit is greater than marginal social cost. C) an inefficient amount to produce because at 300,000 purses marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. D) the efficient amount to produce because at 300,000 purses marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. G.KAZAR54) In the above figure, if output is 30 units, then the total deadweight loss is 54) A) $60. B) $10. C) $20. D) $5. 55) The above figure shows the marginal social benefit and marginal social cost curves of chocolate in the nation of Kaffenia. When the marginal social benefit is equal to the marginal social cost of chocolate in Kaffenia, 55) A) either 100 pounds or 250 pounds can be produced each day. B) 150 pounds will be produced each day. C) no chocolate is produced. D) any quantity up to 150 pounds will be efficient. G.KAZAR56) In the above figure, when the efficient quantity of gloves is produced, the total consumer surplus is 56) A) $22,500. B) $15,000. C) $45,000. D) $3,000. 57) Using the above figure, which of the following quantities of CDs has the largest deadweight loss? 57) A) 4 million CDs B) 3 million CDs C) 7 million CDs D) The deadweight losses associated with the three quantities given above are all equal. G.KAZARThe figure shows the competitive market for milk. 58) In the figure above, when the market is in equilibrium, what is the total surplus? 58) A) $1,000 B) $200 C) $800 D) $1,600 59) In the figure above, when the quantity of milk produced is 600 gallons per day, what is the deadweight loss? 59) A) $50 B) $250 C) $125 D) $500 G.KAZAR60) The figure above shows the market for umbrellas in Sunville. When the market for umbrellas in Sunville is in equilibrium, what is the total surplus? 60) A) $0 B) $24,000 C) $12,000 D) $16,000 61) Which of the following is NOT a potential impact of a rent ceiling set below the equilibrium rent? 61) A) a deadweight loss B) n increase in search C) a surplus D) None of the above because they are all impacts of a rent ceiling set below the equilibrium rent. G.KAZAR62) The above figure shows the labor market in an undeveloped nation. If the minimum wage is set at $5.00 per hour, what effect will it have on the market for low-skilled labor? 62) A) The minimum wage will attract more labor to the low-skilled labor market and cause the wage rate to fall. B) The minimum wage will create a surplus of low-skilled labor. C) have no effect when set above the equilibrium wage rate. D) create a shortage of low-skilled labor. 63) An example of a price floor is a 63) A) quota. B) rent control. C) minimum wage. D) subsidy. G.KAZAR64) The market for unskilled labor is illustrated in the figure above. The market is in equilibrium and then a minimum wage of $5 per hour is imposed. Employment will fall by 64) A) 10 million hours per year. B) 20 million hours per year. C) 30 million hours per year. D) 0 hours. 65) In the above figure, if the government imposed a minimum wage of $8 per hour in this labor market, the increase in the hourly wage for those who are able to keep their jobs is 65) A) $6 per hour. B) $2 per hour. C) $4 per hour. D) $8 per hour. G.KAZAR66) The market for unskilled labor is illustrated in the figure above. The market is in equilibrium and then a minimum wage of $3 per hour is imposed. Unemployment will equal 66) A) 10 million hours per year. B) 30 million hours per year. C) 0 hours. D) 20 million hours per year. 67) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of labor of students in Smallville. If the minimum wage is set at $6 per hour, how many hours do students work? 67) A) 6,000 hours B) 9,000 hours C) 12,000 hours D) None of the above answers is correct. G.KAZAR68) In the above figure, a black market emerges with a 68) A) price floor of $4. B) a rationed quantity 30. C) ceiling of $4. D) 2. 69) If policy makers believe that the equilibrium wage rate is too low, policy makers can raise wages by legislating a minimum wage, that is, a wage 69) A) ceiling below the equilibrium wage. B) floor above the equilibrium wage. C) below the equilibrium wage. D) above the equilibrium wage. Wage rate (dollars per hour) Labor supplied (millions of workers) Labor demanded (millions of workers 11 6 4 10 5 5 9 4 6 8 3 7 7 2 8 70) In the table above, what is the equilibrium wage rate in an unregulated market? 70) A) $11.00 per hour B) $9.00 per hour C) $10.00 per hour D) $8.00 per hour 71) A price floor is a price 71) A) that creates a surplus of the good if it is set above the equilibrium price. B) above which a seller cannot legally sell. C) below which a seller cannot legally sell. D) Both answers A and C are correct. G.KAZAR72) The above figure illustrates the labor market for fast food restaurants in a small city in Peru. What would be the effects of a minimum wage imposed at $4 per hour? 72) A) a shortage of 100 hours B) urplus of 200 hours C) hortage of 200 hours D) nothing because the minimum wage has no effect on the equilibrium price and quantity 73) The government sets a price floor for corn which is above the equilibrium price of corn. As a result, ________. 73) A) the corn market will be efficient B) a shortage of corn will be created C) deadweight loss will be created D) None of the above answers is correct 74) A minimum wage is a government-imposed price ________ that is designed to be ________ the equilibrium wage rate. 74) A) floor; above B) ceiling; above C) floor; below D) ceiling; below G.KAZAR75) In the figure above, if the minimum wage is $4 per hour, then 75) A) the quantity of labor supplied is 4 million hours and the quantity of labor demanded is 2 million hours. B) the quantity of labor supplied is less than the quantity of labor demanded. C) unemployment is 1 million hours. D) the quantity of labor supplied is 3 million hours and the quantity of labor demanded is 3 million hours. 76) The figure above shows the market for low-skilled labor in Midland city. The government sets a minimum wage at $6 per hour. The minimum wage ________ the employers' surplus by ________ million per year. 76) A) increases; $100 B) decreases; $60 C) increases; $40 D) decreases; $120 G.KAZAR77) In the above figure, at what minimum wage is the unemployment level equal to 200 million hours? 77) A) $2 per hour B) $4 per hour C) $8 per hour D) $6 per hour 78) In the above figure, if there is no minimum wage, the equilibrium employment is ________; if the government imposed a minimum wage of $8 per hour, employment is ________. 78) A) 4,000 hours; 3,000 hours B) 3,000 hours; 2,000 hours C) 3,000 hours; 4,000 hours D) 4,000 hours; 2,000 hours G.KAZAR79) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of labor of students in Smallville. If the minimum wage is set at $4 per hour, how many hours do students work? 79) A) 6,000 hours B) 12,000 hours C) 9,000 hours D) None of the above answers is correct. 80) In the above figure, a price ceiling of $4 would 80) A) result in a surplus in the long run. B) have no effect. C) result in a shortage in the long run. D) urplus in the short run but have no effect in the long run. G.KAZAR81) In the above figure, a minimum wage of ________ would result in employment of ________. 81) A) W2; L1 B) W2; L2 C) W1; L2 D) W1; L1 82) The figure above shows the market for low-skilled labor in Midland city. The government sets a minimum wage at $6 per hour. With the minimum wage law enacted, at the quantity of labor employed, the value to the firm of last worker hired is ________ the wage rate for which that person is willing to work. 82) A) $3 per hour greater than B) the same as C) less than D) 1 per hour greater G.KAZAR83) A minimum wage set above the equilibrium wage rate for low-skilled workers ________. 83) A) creates unemployment among low-skilled workers B) more employment opportunities for low-skilled workers C) prosperity among younger people D) increases the number of good paying jobs available to young people 84) In the above figure, without a minimum wage, the equilibrium quantity of labor employed ________ million hours, and the equilibrium wage rate is ________ per hour. 84) A) 100; $2 B) 400; $8 C) 300; $6 D) 200; $4 G.KAZAR85) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of labor of students in Smallville. If the minimum wage is set at $6 per hour, how many hours of students' labor are unemployed? 85) A) 9,000 hours B) 12,000 hours C) 0 hours D) 6,000 hours 86) In the figure above, D0 is the demand for labor curve. Imposing a minimum wage of $3 per hour will 86) A) have no effect on the market. B) result in a labor shortage. C) unemployment. D) immediately shift the demand curve to D1. G.KAZAR87) If a minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage rate, employment 87) A) will decrease. B) will increase. C) will not change. D) may increase, decrease or not change depending on how the supply of labor is affected by the minimum wage. 88) A minimum wage ________. 88) A) is an effective way of increasing employment B) price ceiling in the labor market C) floor in the labor market D) changes the demand for labor. 89) The market for unskilled labor is illustrated in the figure above. The market is in equilibrium and then a minimum wage of $5 per hour is imposed. Unemployment will equal 89) A) 30 million hours per year. B) 20 million hours per year. C) 0 hours. D) 10 million hours per year. 90) When a minimum wage is set above the equilibrium wage rate, ________. 90) A) the supply of low-skilled workers decreases and the supply curve shifts rightward B) - increases and the supply curve shifts leftward C) search activity decreases D) unemployment increases 91) Suppose that the equilibrium wage in the low-skilled labor market is $9.25. Further, suppose the federal government raises the minimum wage to $9.00 an hour from its present level of $8.15. The government's action of increasing the minimum wage will result in 91) A) a decrease in unemployment. B) shortage of low-skilled labor. C) n increase in unemployment. D) neither a shortage nor a surplus of labor in the low-skilled labor market. G.KAZAR92) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of rental housing in Smallton. If a rent ceiling is set at $400, there is 92) A) a shortage of 4,000 units of rental housing. B) urplus of 3,000 units of rental housing. C) hortage of 2,000 units of rental housing. D) neither a shortage nor a surplus of rental housing. 93) A rent ceiling results in a shortage. As a result, which of the following do you expect? 93) A) Discrimination as tenants choose their landlords, possibly based on race, age, or gender. B) In the long-run, more and more people will want to become landlords. C) A black market for apartments whereby higher rents are obtained through various other charges. D) A shortage of applicants for the apartments available. 94) A price ceiling, such as a rent ceiling, 94) A) always results in a surplus. B) results in a shortage if the ceiling price is less than the equilibrium price. C) urplus if the ceiling price is less than the equilibrium price. D) always results in a shortage. G.KAZAR95) The above figure shows the demand and supply curves for housing. What would be the effects of a rent ceiling equal to $500 per month? 95) A) a shortage equal to 3,000 apartments B) 250 apartments C) urplus equal to 3,000 apartments D) nothing because the rent ceiling has no effect on the equilibrium price and quantity 96) Which of the following is an effect of a price ceiling set below the equilibrium price? 96) A) Less of the good is produced with the ceiling than would be produced without the ceiling. B) Consumers can buy more than they can at the equilibrium price because the ceiling price is lower. C) The price ceiling has no effect on the market equilibrium. D) None of the above answers is correct. 97) Which of the following is a result of a rent ceiling set below the equilibrium rent? I. equity in the housing market II. efficient allocation of resources III. a shortage of housing units. 97) A) III only B) II only C) I and III D) I and II G.KAZAR98) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of rental housing in Smallton. If a rent ceiling is set at $800, what is the rent? 98) A) $400 B) $800 C) $600 D) None of the above answers is correct. 99) The above figure shows the apartment rental market in Bigtown. If there is a shortage of 200,000 apartments in the Bigtown rental market, it might be because the Bigtown Housing Authority has imposed a rent 99) A) floor of $750.00 monthly. B) ceiling of $500.00 monthly. C) 500.00 monthly. D) 750.00 monthly. G.KAZAR100) Search activity ________. 100) A) is unnecessary when a black market exists B) ncreases when an effective price ceiling is set on a good C) occurs when there is a surplus of the good D) decreases when an effective price ceiling is set on a good 101) In the figure above, the initial demand curve is D0. There are no rent ceilings nor rent floors. The equilibrium monthly rent is 101) A) $400 per month. B) $100 per month. C) 300 per month. D) 200 per month. 102) When a rent ceiling is imposed in a housing market, the opportunity cost of housing equals the 102) A) market equilibrium rent that would prevail in the absence of a rent ceiling. B) value of the time and resources spent searching plus the rent. C) consumer surplus. D) rent. G.KAZAR103) The above figure shows the apartment market in Big City. What is the equilibrium rent in Big City? 103) A) $1250 B) $1125 C) $1500 D) $1350 104) In order to have an effect, a price ceiling must be set ________. 104) A) by suppliers B) below the equilibrium price C) above the equilibrium price D) equal to the equilibrium price 105) A price ceiling can result in which of the following? 105) A) inefficiency B) increased search activities C) black markets D) All of the above answers are correct. G.KAZAR106) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of rental housing in Smallton. If a rent ceiling is set at $400, how many apartment units are rented? 106) A) 4,000 B) 2,000 C) 3,000 D) None of the above answers is correct. 107) Price ceilings, such as rent ceilings, set below the equilibrium price 107) A) might increase or decrease producer surplus. B) decrease producer surplus. C) increase producer surplus. D) do not affect producer surplus. G.KAZAR108) In the figure above, originally the apartment rental market is in short-run and long-run equilibrium with a rent of $600 per month. Then the government imposes a rent ceiling of $500 per month. The loss of producer surplus as a result of the price ceiling is 108) A) $500,000 per month. B) $250,000 per month. C) ,000 per month. D) more than $500,000 per month. 109) A price ceiling set below the equilibrium price ________ search activity and ________ the use of black markets. 109) A) decreases; increases B) increases; decreases C) decreases; decreases D) increases; increases G.KAZAR110) The figure above shows the demand for and supply of rental housing in Smallton. If a rent ceiling is set at $800, how many apartment units are rented? 110) A) 4,000 B) 2,000 C) 3,000 D) None of the above answers is correct. 111) In the figure above, originally the apartment rental market is in short-run and long-run equilibrium with a rent of $600 per month. Then the government imposes a rent ceiling of $500 per month. If the law is strictly enforced, the maximum for which an apartment will rent on the black market is 111) A) $600 per month. B) more than $700 per month. C) 700 per month. D) less than $600 per month. G.KAZAR112) In the figure above, the demand curve shifts rightward from D0 to D1 so that D1 is the relevant demand curve. Suppose the government imposes a rent ceiling of $300 per month. In the short run there will be 112) A) a shortage of 400,000 apartments. B) a shortage of 500,000 apartments. C) 200,000 apartments. D) no shortage nor a surplus of apartments. 113) A rent ceiling set above the equilibrium rent 113) A) decreases the quantity supplied but not the quantity demanded. B) has no effect on the market outcome. C) decreases the quantity demanded but not the quantity supplied. D) both the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied. G.KAZAR114) The above figure shows the apartment market in Big City. What could the Big City Housing Authority do if it wants to reduce the rents paid by its citizens? 114) A) impose a rent ceiling below $1350 B) impose a rent floor above $1350 C) above $1350 D) below $1350 115) Sherry wants to rent an apartment. Although rents are below what she is willing to pay, she cannot find an apartment. Then after a month of searching, she finds an apartment but she has to pay an additional $1,000 to have the locks changed. Sherry has just experienced the effects of ________. 115) A) a market working efficiently B) inelastic demand C) rent ceiling D) rent floor with a black market 116) A price ceiling ________. 116) A) makes it illegal to charge a higher price than the specified price B) occurs in housing markets only C) is necessary to maintain market equilibrium D) more effective when it is higher 117) Assume that your state government has placed a price ceiling of $.20 per kilowatt hour on electricity. The equilibrium price per kilowatt hour for electricity is $.25. The government's action will result in 117) A) an increase in producer surplus. B) deadweight loss. C) surplus of electricity in the electricity market. D) n increase in the price of electricity to $.25 per kilowatt hour. G.KAZAR118) The price ceiling depicted in the above figure results in 118) A) producer surplus decreasing from $24 thousand to $6 thousand. B) consumer surplus increasing from $30 thousand to $34.5 thousand. C) a deadweight loss of $16 thousand. D) Both answers A and B are correct. 119) A rent ceiling results in a shortage of apartments. As a result, there is 119) A) a loss of both consumer and producer surplus. B) only a loss of producer surplus for landlords. C) consumer surplus for tenants. D) a gain of both consumer and producer surplus. G.KAZAR120) In the figure above, originally the apartment rental market is in short-run and long-run equilibrium with a rent of $600 per month. Then the government imposes a rent ceiling of $500 per month. The loss of producer surplus 120) A) is larger than the gain in consumer surplus. B) the same size as the gain in consumer surplus. C) smaller than the gain in consumer surplus. D) could be smaller than, larger than, or the same size as the gain in consumer surplus. G.KAZAR121) To help pay for the cost of sport related injuries, the government imposes a tax on sellers of all sports equipment. The deadweight loss created by this tax would be greater than shown in the figure above if 121) A) the supply were more elastic. B) the demand were more elastic. C) neither of the above D) both A and B above 122) In the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. If it is illegal to sell, but not illegal to buy, then the price per unit will be 122) A) $400. B) $300. C) $200. D) $500. G.KAZAR123) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and has imposed penalties on any person caught selling a beer. Buying a beer, however, remains legal. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, beer consumption is decreased by 123) A) 200 quarts. B) 300 quarts. C) 500 quarts. D) 400 quarts. 124) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and imposes a fine on any person caught selling a beer. Buying beer, however, remains legal. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, what is the equilibrium price and quantity with this new law in effect? 124) A) $3 per quart and 100 quarts of beer B) $1 per quart and 300 quarts of beer C) 500 quarts of beer D) 5 per quart and 300 quarts of beer 125) When a government fines and/or imprisons persons convicted of using illegal drugs, the government is attempting to decrease the illegal drug trade by shifting the ________ curve for illegal drugs ________. 125) A) supply; rightward B) supply; leftward C) demand; rightward D) demand; leftward 126) If penalties are imposed only on buyers (but not on sellers) of marijuana, the equilibrium price of marijuana ________, and the equilibrium quantity of marijuana sold ________. 126) A) rise; increase B) fall; increase C) fall; decrease D) rise; decrease 127) In general, a fine on smoking cigarettes shifts the ________ curve of cigarettes ________. 127) A) demand; leftward B) supply; leftward C) rightward D) rightward G.KAZAR128) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and imposes a fine on anyone caught buying a beer. Selling beer, however, remains legal. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, what is the equilibrium price and quantity with this new law in effect? 128) A) $3 per quart and 500 quarts of beer B) $3 per quart and 100 quarts of beer C) 1 per quart and 300 quarts of beer D) 5 per quart and 300 quarts of beer 129) Using the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. What is the equilibrium price and quantity if beer is legal? 129) A) $3 per quart and 500 quarts of beer B) $3 per quart and 100 quarts of beer C) 1 per quart and 300 quarts of beer D) 5 per quart and 300 quarts of beer G.KAZARPrice (dollars per firework) Quantity demanded (fireworks per week) Quantity supplied (fireworks per week) 4 220 40 5 200 80 6 180 120 7 160 160 8 140 200 9 120 240 10 100 280 11 80 320 12 60 360 13 40 400 14 20 440 130) The table gives the demand and supply schedules for fireworks on the Island of Big Bang. In the past, because many deaths have resulted from accidents involving fireworks, the government has banned fireworks and is enforcing the ban. A $5 a firework penalty on buyers of fireworks and a $4 a firework penalty on sellers will reduce the number of fireworks bought to ________ a week and the price paid by buyers will be ________ a firework. 130) A) 0; an unknown amount B) 40; $13 C) 160; $11 D) 80; $7 131) Making the buying and selling of a good illegal shifts the demand curve ________ and shifts the supply curve ________. 131) A) rightward; rightward B) leftward; rightward C) leftward D) leftward 132) If buyers of illegal goods are punished but sellers are not, then the price ________ and the equilibrium quantity ________. 132) A) falls; decreases B) rises; decreases C) falls; increases D) rises; increases 133) If sanctions are imposed on buyers but NOT on sellers of an illegal good, then the equilibrium price ________ and the equilibrium quantity ________. 133) A) falls; decreases B) falls; increases C) rises; increases D) rises; decreases 134) Rather than prohibiting a good or service, the government might tax it. Imposing such a tax on a good or service ________ the equilibrium price and ________ the equilibrium quantity. 134) A) raises; increases B) lowers; decreases C) raises; decreases D) lowers; increases G.KAZAR135) In the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. If it is illegal to buy, but not illegal to sell, then the price per unit will be 135) A) $200. B) $500. C) $400. D) $300. 136) When a government fines and/or imprisons convicted drug dealers, it is attempting to reduce the illegal drug trade by shifting the ________ curve for illegal drugs ________. 136) A) demand; rightward B) demand; leftward C) supply; leftward D) supply; rightward G.KAZARPrice (dollars per firework) Quantity demanded (fireworks per week) Quantity supplied (fireworks per week) 4 220 40 5 200 80 6 180 120 7 160 160 8 140 200 9 120 240 10 100 280 11 80 320 12 60 360 13 40 400 14 20 440 137) The table gives the demand and supply schedules for fireworks on the Island of Big Bang. In the past, because many deaths have resulted from accidents involving fireworks, the government has banned fireworks and is enforcing the ban. A $6 a firework penalty on sellers of fireworks and no penalty on buyers will reduce the number of fireworks bought to ________ a week and increase the price paid by buyers to ________ a firework. 137) A) 80; $11 B) 140; $8 C) 40; $13 D) 0; an unknown amount 138) If enforcement is aimed at buyers of an illegal good, the result will be 138) A) an increase in the short-run supply of the good. B) price of the good. C) decrease in the short-run supply of the good. D) demand for the good. G.KAZAR139) In the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. If it is illegal to buy and sell, then the quantity of the good bought and sold will be 139) A) 200. B) 300. C) 100. D) 400. 140) In the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. If it is illegal to buy and sell, then the price per unit will be 140) A) $500. B) $300. C) $200. D) $400. G.KAZAR141) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and has imposed equal penalties on any person caught buying a beer and on any person caught selling a beer. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, what is the equilibrium price and quantity with this new law in effect? 141) A) $1 per quart and 300 quarts of beer B) $5 per quart and 300 quarts of beer C) 3 per quart and 500 quarts of beer D) 3 per quart and 100 quarts of beer 142) If penalties are imposed on both the buyers and the sellers of illegal goods or services, then an effect in the market for the illegal good or service would definitely be 142) A) an increase in the equilibrium price. B) a decrease in the equilibrium quantity. C) price. D) quantity. 143) Suppose penalties are imposed on both buyers and sellers of marijuana, but the cost of breaking the law to sellers is greater than that to buyers. This measure will ________ the equilibrium price of marijuana and ________ the equilibrium quantity of marijuana sold. 143) A) lower; increase B) not change; will decrease C) raise; decrease D) raise; increase 144) Compared to the situation in which a good is legal, making the good illegal and imposing ________ results in less being sold. 144) A) a much higher fine on buyers than on sellers B) ny fine on either the buyer or the seller C) much higher fine on sellers than on buyers D) ll of the above 145) In general, a fine on buying a product leads to the 145) A) supply curve shifting leftward. B) demand curve shifting leftward. C) rightward. D) rightward. G.KAZAR146) In the above figure, CBL is the cost of breaking the law. If the good in the figure is made illegal and penalties are imposed on both buyers and sellers, then its price per unit 146) A) will be lower than if it was not illegal. B) cannot be compared with its price when it was legal. C) will be the same as when it was not illegal. D) higher than if it was not illegal. 147) If penalties for trading illegal drugs are instituted on both buyers and sellers, the 147) A) price might rise or fall, but the quantity will decrease. B) quantity might increase or decrease but the price will rise. C) price and the quantity will both decrease. D) increase. G.KAZAR148) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and has imposed equal penalties on any person caught buying a beer and on any person caught selling a beer. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, beer consumption is decreased by 148) A) 200 quarts. B) 500 quarts. C) 400 quarts. D) 300 quarts. 149) Suppose the government has declared beer to be an illegal substance and has imposed penalties on any person caught buying a beer. Selling a beer, however, remains legal. Using the above figure, in which CBL is the cost of breaking the law, beer consumption is decreased by 149) A) 400 quarts. B) 300 quarts. C) 500 quarts. D) 200 quarts. 150) If penalties are imposed on the sellers of illegal goods or services, then the equilibrium price ________ and the equilibrium quantity ________. 150) A) falls; increases B) falls; decreases C) rises; increases D) rises; decreases 151) If enforcement is aimed at sellers of an illegal good, its equilibrium price will ________ and its equilibrium quantity will ________. 151) A) rise; increase B) fall; increase C) rise; decrease D) fall; decrease 152) The demand and the supply for a good are each neither perfectly elastic nor perfectly inelastic. If a sales tax on sellers of the good is imposed, the tax is paid by 152) A) only sellers. B) only buyers. C) neither buyers nor sellers. D) both buyers and sellers. 153) Suppose a $1 tax is placed on a good. The more elastic the supply of the good, the 153) A) less of the tax will be paid by the buyers. B) larger the increase in the after-tax price. C) more of the tax will be paid by the sellers. D) smaller the decrease in the quantity sold. 154) How a sales tax is divided between buyers and sellers is determined by 154) A) the revenue needs of government. B) the government's choice of whom to tax. C) who the law says must pay the tax. D) elasticities of supply and demand. G.KAZAR155) Consider the market for heart transplants. The demand for a heart transplant is perfectly inelastic and the supply curve is upward sloping. If a $1,000 tax per transplant tax is imposed on buyers (the recipients), how will the tax be divided between the buyer and seller? 155) A) The buyers will pay the entire tax. B) tax will be evenly divided between the sellers and buyers. C) sellers will pay the entire tax. D) More information is needed to determine how the tax is split. 156) The above figure shows the market for anti-freeze. The government imposes the sales tax shown in the figure on sellers. Anti-freeze sellers would pay a larger part of this tax than what is shown in the figure if the 156) A) supply were more elastic. B) supply were more inelastic. C) demand were more inelastic. D) demand curve were steeper. Price elasticity of supply Price elasticity of demand Hamburgers 1.2 1.8 French fries 1.7 1.4 Pizza 2.0 1.2 Ice cream 1.5 1.6 157) You are in the business of producing and selling hamburgers, french fries, pizza, and ice cream. The mayor plans to impose a tax on one of these products. Based on the elasticities in the above table, as a profit-minded business person who seeks to avoid taxes whenever possible, which good would you most prefer to have taxed? 157) A) hamburgers B) pizza C) French fries D) ice cream G.KAZAR158) The government of Healthyland imposes a tax on sellers of salt. The tax is $0.10 per pound. With no tax, the price of salt is $0.40 per pound. The demand for salt is perfectly inelastic and the elasticity of supply is 1.5. With the tax, the price of salt paid by buyers in Healthyland is 158) A) $0.45 per pound. B) $0.50 per pound. C) D) 35 per pound. 159) The figure illustrates the market for posters. The tax on a poster is ________ and the government's tax revenue from the sale of posters is ________ a month. 159) A) $0.35; $200 B) $0.35; $140 C) $0.35; $105 D) $0.50; $150 160) If supply is perfectly elastic, a sales tax imposed on sellers is paid by 160) A) both the buyers and sellers. B) only the buyers. C) sellers. D) None of the above answers is correct. 161) Which of the following outcomes is NOT a result of a tax imposed on sellers of gasoline? 161) A) Supply decreases, a deadweight loss is created, and the price rises. B) Demand decreases, the market becomes more efficient, and the price rises. C) oes not change, the price rises, and consumer surplus decreases. D) The market becomes less efficient and the government collects the tax revenue. 162) Which of the following leads to the demanders paying all of a tax? 162) A) The supply is perfectly inelastic. B) The demand is perfectly inelastic. C) unit elastic. D) elastic. 163) A sales tax is divided so that buyers pay the full amount if 163) A) supply is perfectly inelastic. B) demand is perfectly inelastic. C) has unitary elasticity. D) has unitary elasticity. G.KAZAR164) Suppose the government imposes a $1 tax on frisbees, and the price of a frisbee paid by demanders rises by $1. 164) A) The price could never rise this much, so this situation cannot happen. B) rise is consistent with a perfectly elastic demand for frisbees. C) supply for frisbees. D) downward- loping supply curve for frisbees. 165) The government of Healthyland imposes a tax on sellers of salt. The tax is $0.10 per pound. With no tax, the market price of salt is $0.40 per pound. The demand for salt is perfectly inelastic, and the elasticity of supply is 1.5. With the tax, the price that sellers of salt in Healthyland receive and keep is 165) A) $0.45 per pound. B) $0.50 per pound. C) 35 per pound. D) 166) In the above figure, the tax incidence is 166) A) that most of it is paid by the sellers. B) neither the buyers nor the sellers pay it. C) split equally so that the buyers and sellers pay the same amount. D) that most of it is paid by the buyers. G.KAZAR167) To help pay for the cost of sport related injuries, the government imposes a tax on sellers of all sports equipment. Referring to the above figure, the area that equals the tax revenue the government raises from this tax on sports equipment is 167) A) P1P3ed. B) ecd. C) P1P2cb. D) P0P2ca. Two small California cities, Richmond and El Monte, are planning to impose a penny per ounce tax on sugary drinks. They are being opposed by the soda industry that is vehemently against this new legislation. (Source: Reuters, September 6, 2012) 168) One reason why soda companies are so fervently against this tax might be because they assume sellers will pay the entire tax. Sellers will pay the entire tax if 168) A) the price elasticity of demand is between zero and 1. B) demand is perfectly inelastic. C) elastic. D) unit elastic. G.KAZAR169) To help pay for the cost of sport related injuries, the government imposes a tax on sellers of all sports equipment. The sports equipment consumers' share of this tax would be greater than that shown in the above figure 169) A) only if the demand was more elastic. B) if either the demand was more inelastic or the supply more elastic. C) only if the demand was more inelastic. D) supply was more elastic. 170) As long as the supply curve for a good is upward sloping and the demand curve is downward sloping, a sales tax imposed on sellers shifts the supply curve 170) A) rightward and possibly increases the equilibrium quantity. B) leftward and possibly raises the equilibrium price. C) definitely raises the equilibrium price. D) rightward and definitely decreases the equilibrium quantity. 171) Which of the following statements is true about taxes? 171) A) Taxes always create more deadweight loss than do price ceilings and price floors. B) Government revenue from a tax is always greater than the loss of producer surplus and consumer surplus. C) Taxes decrease both consumer surplus and producer surplus while creating a deadweight loss. D) Both answers A and C are correct. G.KAZAR172) The figure shows the market for books before and after a sales tax is introduced. Each week, the tax creates a deadweight loss of ________, decreases consumer surplus by ________ , and decreases producer surplus by ________. 172) A) $3; $10; $5 B) $12; $8; $4 C) $15; $10; $5 D) $3; $2; $1 173) The more elastic the demand for a good, the 173) A) more a sales tax raises the price paid by buyers. B) less a sales tax lowers the price paid by buyers. C) more a sales tax lowers the price paid by buyers. D) less a sales tax raises the price paid by buyers. G.KAZAR174) The above figure shows the market for blouses. The government decides to impose the sales tax on sellers, as shown in the figure. What is the deadweight loss? 174) A) $10,000 B) $30,000 C) $40,000 D) $20,000 175) A sales tax is divided so that the 175) A) buyers pay the full amount if supply is perfectly inelastic. B) sellers pay the full amount if supply is perfectly elastic. C) buyers pay the full amount if demand is perfectly elastic. D) sellers pay the full amount if demand is perfectly elastic. G.KAZAR176) The above figure shows the market for blouses. The government decides to impose the sales tax on sellers, as shown in the figure. The amount of the tax paid by the buyers would be greater than shown in the figure 176) A) if either the demand was more inelastic or the supply more elastic. B) only if the demand was more elastic. C) inelastic. D) supply was more elastic. 177) In the above figure, a sales tax of $1 per unit imposed on sellers ________ the price buyers pay and ________ the price that suppliers keep for themselves. 177) A) does not affect; does not affect B) does not affect; affects C) affects; affects D) affects; does not affect G.KAZAR178) The less elastic the supply, the 178) A) less elastic the demand. B) less likely the government is to tax the product. C) impose a price ceiling. D) arger the fraction of any tax imposed on the product that is paid by the suppliers. 179) The above figure depicts the market for video games. If the government imposed a $3 per game tax on sellers, what would be the new equilibrium price paid by consumers after the tax? 179) A) $27 per game B) less than $27 per game C) more than $27 per game. D) More information is needed to determine if the price is more than, less than, or equal to $27 per game. G.KAZAR180) In the above figure, who pays the larger share of the tax? 180) A) buyers B) sellers C) Buyers and sellers each pay the same amount of the tax, but the amount each pays is different than $10 per compact disc. D) Buyers and sellers each pay the same amount of the tax and each pays $10 per compact disc. 181) The principle of diminishing marginal utility says that 181) A) total utility decreases as the quantity of the good consumed increases. B) marginal utility is negative as the quantity of the good consumed increases. C) total utility increases by larger and larger amounts as the quantity of the good consumed increases. D) total utility increases by smaller and smaller amounts as the quantity of the good consumed increases. G.KAZAR182) In the figure above, the curve that shows the diminishing marginal utility is 182) A) total utility curve A because it is higher than total utility curves B or C. B) C gets flatter as consumption of tomatoes increases. C) total utility curve A steeper as consumption of tomatoes increases. D) C is lower than total utility curves B and C. Quantity (boxes) Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 X 1 30 30 2 50 20 3 66 16 4 ? 12 183) The table above gives Andy's utility from popcorn. Andy's total utility from four boxes of popcorn is 183) A) 82. B) 78. C) 66. D) 70. G.KAZARQuantity of magazines Marginal utility from magazines Quantity of gummy bears Marginal utility from gummy bears 0 0 1 100 1 200 2 75 2 180 3 50 3 160 4 25 4 140 5 5 5 120 184) Kelly's marginal utilities for magazines and packages of gummy bears are listed in the table above. For Kelly, what is the total utility received from consuming 5 magazines? 184) A) 255 B) 25 C) 20 D) 5 185) In the figure above, the marginal utility of the third crate of tomatoes for the person with total utility curve C is 185) A) 32 units of utility. B) 13 units of utility. C) 6 units of utility. D) 45 units of utility. 186) A measure of all the satisfaction you receive from all the coffee that you consume is your 186) A) marginal utility per dollar spent on coffee when you are in your consumer equilibrium. B) total utility from coffee. C) marginal utility per dollar spent on coffee. D) of coffee. G.KAZARQuantity Total utility Marginal utility 0 0 1 250 2 180 3 580 4 700 5 100 187) The above table gives some of Tammy's total and marginal utilities from comedy videos. Which of the following statements is true? 187) A) Tammy's marginal utility from the first comedy video is less than her marginal utility from the third comedy video. B) Tammy's total utility from five comedy videos is 800. C) marginal utility from the third comedy video is equal to 580/3. D) None of the above answers are correct. 188) Economists using marginal utility theory assume that consumers' objectives are to 188) A) maximize their income. B) maximize their total utility. C) marginal utility. D) none of the above 189) As consumption increases, total utility increases 189) A) at a constant rate. B) and marginal utility increases. C) decreasing rate. D) n increasing rate. 190) As Sally increases her consumption of a good, she experiences diminishing marginal utility if her total utility 190) A) increases at an increasing rate. B) increases at a decreasing rate. C) decreases. D) constant rate. 191) A person's consumption possibilities is defined by the budget line because 191) A) all consumers must consume on their budget line. B) it marks the boundary between what is affordable and unaffordable. C) represents the individual's preference for different combinations of goods. D) it marks the boundary between what can be produced and what is unattainable given the current state of technology and resources. 192) The total utility you get from eating slices of pizza on a given night is the 192) A) sum of the marginal utilities of all slices eaten. B) marginal utility of the last slice times the total number of slices eaten. C) sum of the differences in marginal utility as you increase the number of slices eaten. D) marginal utilities per dollar spent on all slices eaten. 193) According to the principle of diminishing marginal utility, as the quantity of a good or service consumed increases, total utility 193) A) decreases. B) is unchanging. C) is zero. D) increases. G.KAZAR194) As Goldilocks consumes more gummy bears, her total utility ________ and her marginal utility from gummy bears ________. 194) A) increases; decreases B) decreases; increases C) increases; increases D) decreases; decreases 195) The measure of the benefit you get from consuming the next cup of coffee is your 195) A) total utility from coffee. B) when you are at your consumer equilibrium. C) marginal utility of coffee. D) total utility per dollar spent on coffee. Fritos Fruit drinks Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 0 0 0 0 1 40 1 50 2 75 2 95 3 105 3 135 4 130 4 170 5 150 5 200 6 165 6 225 196) The table above shows the total utility from the two goods Freddy likes to consume. If Freddy has consumed 4 fruit drinks and then decides to drink another, 196) A) his total utility will increase. B) the marginal utility from the 5th drink equals 30. C) s equals 50. D) Both answers A and B are correct. 197) The principle of diminishing marginal utility implies that the 197) A) rate of change of total utility is diminishing as more units are consumed. B) marginal utility of a product is negative. C) total utility from a product is also diminishing as more units are consumed. D) rate of change of marginal utility is very low as more units are consumed. Quarts of ice cream Total utility from ice cream 0 0 1 80 2 150 3 210 4 260 198) From the information in the above table, what is the marginal utility of the third quart of ice cream? 198) A) 60 B) 80 C) 230 D) 70 G.KAZAR199) Liz's marginal utility for two different goods is determined by 199) A) summing her total utility from consumption of each good and then dividing by two. B) her average utility for the two goods. C) ow much benefit she gets from another unit of each of those goods. D) All of the above answers are correct. 200) Suppose Jill's consumption bundle is made up of 2 goods, apples and bottles of juice. If the price of an apple increases, then Jill's budget line would 200) A) shift towards the origin on the apples axis only. B) not change. C) shift towards the origin on both the apples and bottles of juice axes. D) away from the origin on the bottles of juice axis only. 201) In the figure above, diminishing marginal utility is shown by 201) A) total utility curve A. B) total utility curve B. C) C D) all three curves. G.KAZARQuantity of magazines Total utility from magazines Quantity of CDs Total utility from CDs 0 0 0 0 1 240 1 500 2 400 2 950 3 520 3 1350 4 620 4 1650 5 680 5 1800 6 716 6 1850 7 736 7 1870 8 740 8 1875 202) The table above gives Jane's total utility from magazines and CDs. The price of a magazine is $4 and the price of a CD is $10. Which of the following correctly illustrates the principle of diminishing marginal utility? The fact that 202) A) the marginal utility per dollar from the sixth magazine is less than the total utility from six magazines. B) the marginal utility of the third CD is less than the marginal utility of second CD. C) sixth magazine has less marginal utility than the sixth CD. D) Jane's marginal utility per dollar from the second magazine is the same as her marginal utility per dollar from the third CD. Box of doughnuts Homer's total utility 1 30 2 55 3 75 4 90 5 100 6 103 203) The above table shows Homer's total utility from boxes of doughnuts. As Homer's consumption of doughnuts increases, 203) A) his total utility increases, but his marginal utility decreases. B) both his total utility and his marginal utility increase. C) arginal utility decrease. D) his total utility decreases, but his marginal utility increases. 204) "I really enjoy watching movies. The first one is best. After that I still enjoy movies but the last one is not as much fun to watch as the one before it." This statement reflects the 204) A) principle of increasing marginal utility. B) law of supply. C) diminishing total utility. D) diminishing marginal utility. 205) As an individual's consumption of a good increases, 205) A) the price of the good increases. B) his or her total utility increases. C) marginal utility increases. D) All of the above answers are correct. G.KAZARQuantity of magazines Marginal utility from magazines Quantity of gummy bears Marginal utility from gummy bears 0 0 1 100 1 200 2 75 2 180 3 50 3 160 4 25 4 140 5 5 5 120 206) Kelly's marginal utilities for magazines and packages of gummy bears are listed in the table above. What is the extra utility received by Kelly when she decides to consume 3 packages of gummy bears instead of 2 packages? 206) A) 20 B) 540 C) 180 D) 160 207) Jeannie's marginal utility from her 4th book in a month is 50. Her marginal utility from her 5th book 207) A) is less than 50. B) equals 50. C) is greater than 50. D) might be more than, less than, or equal to 50 but more information is needed. 208) Which of the following statements is true? 208) A) As more of a good is consumed, its total utility increases, even if the good is subject to diminishing marginal utility. B) As more of a good is consumed, its total utility increases, unless the good is subject to diminishing marginal utility. C) No two people have identical utility functions, just as no two people have identical fingerprints. D) Both A and C above. 209) Utility is best defined as 209) A) the practical usefulness of a good. B) ice of a good. C) amount one is willing to pay for a good. D) satisfaction from consuming a good. 210) The total utility from three skirts is 210) A) three times the price of a skirt. B) skirts divided by total income. C) the sum of the marginal utility of the first skirt plus the marginal utility of the second skirt plus the marginal utility of the third skirt. D) three times the marginal utility of the third skirt. G.KAZARQuantity of DVDs Marginal utility from DVDs Quantity of pizza Marginal utility from pizza 1 150 1 200 2 120 2 180 3 100 3 150 4 90 4 120 5 60 5 100 6 40 6 60 211) Lisa spends all her income on pizzas and DVDs. The above table shows Lisa's marginal utility for pizza and marginal utility for DVDs. Suppose the price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a DVD is $10 and Lisa initially has $40 to spend on the two goods. Lisa gets a raise at work and so she now has $60 to spend on DVDs and pizza. With her increase in income, her consumption of DVDs ________ and hence DVDs are ________ good for Lisa. 211) A) falls; an inferior B) rises; an inferior C) falls; a normal D) rises; a normal Quantity of bottled water Marginal utility from bottled water Quantity of hamburgers Marginal utility from hamburgers 1 35 1 20 2 25 2 18 3 16 3 17 4 10 4 10 5 5 5 8 6 4 6 7 212) Given the data in the above table, if income is $16, and the price is $1 for a bottle of water and $2 for a hamburger, what is the quantity of water and the quantity of hamburgers that will maximize the consumer's total utility? 212) A) 6 bottles of water and 6 hamburgers B) 4 bottles of water and 6 hamburgers C) 5 hamburgers D) 5 bottles of water and 5 hamburgers G.KAZARPizza CDs Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 1 95 1 170 2 180 2 320 3 255 3 450 4 320 4 560 5 375 5 650 213) Bobby spends $100 per month on pizza and CDs. His utility from these goods is shown in the table above. The price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a CD is $20. Bobby currently buys 6 pizzas and 2 CDs. To maximize his utility, he should 213) A) buy more of both goods. B) pizza and fewer CDs. C) CDs and fewer pizza. D) stay with the current combination of goods. 214) Joe consumes pizza and movies. He is currently spending his entire income and his marginal utility of pizza is 10 and his marginal utility of movies is 5. If the price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a movie is $5, then to maximize his utility Joe should 214) A) increase consumption of pizza and decrease consumption of movies. B) not change his current bundle of movies and pizza. C) increase consumption of movies and decrease consumption of pizza. D) both goods. Quantity of skiing Marginal utility from skiing Quantity of skating Marginal utility from skating 0 0 1 50 1 70 2 40 2 40 3 30 3 30 4 20 4 20 5 10 5 5 215) Steve has two goods he can spend his income on, skiing and skating, and his marginal utilities from each are in the table above. The price of each unit of skiing is $10 and the price of each unit of skating is $5. Steve has $40 to spend. What quantities of skiing and skating should Steve consume to maximize his utility? 215) A) 2 units of skiing and 4 units of skating B) 4 units of skiing and 4 units of skating C) 1 unit of skiing and 2 units of skating D) 5 units of skiing and 5 units of skating 216) Teddy buys only chocolate chip cookies and hot chocolate and spends all of his income on the two items. Suppose that Teddy's marginal utility per dollar from cookies exceeds that from hot chocolate. Teddy can make himself better off if he buys 216) A) an equal amount of cookies and hot chocolate. B) only hot chocolate. C) fewer cookies and more hot chocolate. D) more cookies and less hot chocolate. G.KAZARMagazines Chocolate bars Quantity Marginal utility Quantity Marginal utility 1 50 8 26 2 42 10 23 3 34 12 20 4 26 14 17 5 18 16 14 6 10 18 11 7 4 20 8 217) Sonya's budget for magazines and chocolate bars is $50. Her marginal utility from these goods is shown in the table above. The price of a magazine is $5 and the price of a chocolate bar is $2.50. Sonya currently buys 2 magazines and 16 chocolate bars. To maximize her utility, she should 217) A) buy more chocolate bars and fewer magazines. B) magazines and fewer chocolate bars. C) of both goods. D) stay with the current combination of goods. 218) Which of the following is NOT an assumption of marginal utility theory? 218) A) People derive utility from their consumption. B) Utility can be measured and the units of utility are precisely defined. C) More consumption yields more total utility. D) arginal utility diminishes with more consumption. Pizza Pepsi Quantity Marginal utility Quantity Marginal utility 0 0 0 0 1 20 1 30 2 16 2 8 3 10 3 7 219) The above table shows Priscilla's marginal utility from the two goods she consumes, pizza and Pepsi. The price of a slice of pizza is $2 and of a can of Pepsi is $1. Suppose Priscilla has $6 to spend. If Priscilla chooses to eat 3 slices of pizza, 219) A) she is maximizing her total utility. B) not at a consumer equilibrium. C) equating marginal utility per dollar for pizza and Pepsi. D) Both answers B and C are correct. G.KAZARMilkshakes Sodas Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 0 0 0 0 1 600 1 240 2 1000 2 360 3 1300 3 460 4 1540 4 520 5 1590 5 570 6 1636 6 590 7 1676 7 602 8 1708 8 610 9 1728 9 616 10 1738 10 620 220) The table above shows Tom's total utility from milkshakes and sodas. A milkshake costs $2.00. How much marginal utility per dollar would Tom get if he purchased the ninth milkshake? 220) A) 1728 units per dollar B) 10 units per dollar C) 20 units per dollar D) none of the above Quantity of magazines Total utility from magazines Quantity of CDs Total utility from CDs 0 0 0 0 1 240 1 500 2 400 2 950 3 520 3 1350 4 620 4 1650 5 680 5 1800 6 716 6 1850 7 736 7 1870 8 740 8 1875 221) The table above gives Jane's total utility from magazines and CDs. The price of a magazine is $4 and the price of a CD is $10. What is the marginal utility per dollar from magazines when the sixth magazine is purchased? 221) A) 9 units B) 5 units C) 36 units D) 15 units G.KAZARQuantity of pens Total utility from pens Quantity of pencils Total utility from pencils 0 0 0 0 1 90 1 70 2 155 2 120 3 200 3 150 4 225 4 165 5 240 5 174 6 246 6 176 222) The table above gives the utility from pens and pencils. If pens and pencils both cost $.25 each and the consumer has an income of $2.25, which of the following combinations maximizes the consumer's utility? 222) A) 5 pens and 4 pencils B) 3 pens and 6 pencils C) 4 pens and 5 pencils D) 6 pens and 3 pencils 223) Usharani consumes 35 apples a week and 14 loaves of bread. Apples cost $1 each and bread costs $2 per loaf. Usharani is maximizing his utility and finds that the marginal utility from his 35th apple 223) A) is such that his total utility from apples equals his total utility from bread. B) equals his marginal utility from his 14th loaf of bread. C) is twice his marginal utility from his 14th loaf of bread. D) half his marginal utility from his 14th loaf of bread. 224) George spends all his income on sandwiches and juice. George's utility is maximized when he is consuming sandwiches and juice so that the 224) A) total utility from sandwiches equals the total utility from juice. B) marginal utility per dollar spent on sandwiches equals the marginal utility per dollar spent on juice. C) marginal utility from sandwiches equals the marginal utility from juice. D) is at a maximum. G.KAZARMilkshakes Sodas Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 0 0 0 0 1 600 1 240 2 1000 2 360 3 1300 3 460 4 1540 4 520 5 1590 5 570 6 1636 6 590 7 1676 7 602 8 1708 8 610 9 1728 9 616 10 1738 10 620 225) The table above shows Tom's total utility from milkshakes and sodas. Tom's total budget for milkshakes and sodas is $20.00 per week. Milkshakes cost $2.00 each and sodas cost $.50 each. What quantity of milkshakes does Tom purchase at his consumer equilibrium? 225) A) eight B) six C) seven D) five Quantity of bottled water Marginal utility from bottled water Quantity of hamburgers Marginal utility from hamburgers 1 35 1 20 2 25 2 18 3 16 3 17 4 10 4 10 5 5 5 8 6 4 6 7 226) Given the data in the above table, income of $13, a price of $1 for a bottle of water and $2 for a hamburger, what is the marginal utility per dollar spent on water and on hamburgers when the consumer is in consumer equilibrium? 226) A) 10 units of utility per dollar spent B) 1 unit of utility per dollar spent C) 5 units of utility per dollar spent D) 20 units of utility per dollar spent 227) When Ramona is in consumer equilibrium, 227) A) any change in prices would make her worse off. B) her total utility per dollar spent is equal for all goods. C) ies of all goods are equal. D) she is maximizing her utility, given her income and the prices of goods and services. G.KAZAR228) Joe consumes pizza and movies. He is currently spending his entire income and his marginal utility of pizza is 15 and his marginal utility of movies is 10. If the price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a movie is $5, then to maximize his utility Joe should 228) A) increase consumption of movies and decrease consumption of pizza. B) both goods. C) pizza and decrease consumption of movies. D) not change his current bundle of movies and pizza. Pizza CDs Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 1 95 1 170 2 180 2 320 3 255 3 450 4 320 4 560 5 375 5 650 229) Bobby spends $100 per month on pizza and CDs. His utility from these goods is shown in the table above. The price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a CD is $20. Bobby currently buys 2 pizzas and 6 CDs. To maximize his utility in the next period, he should 229) A) buy more pizza and fewer CDs. B) stay with the current combination of goods. C) buy more CDs and fewer pizza. D) of both goods. Quantity of skiing Marginal utility from skiing Quantity of skating Marginal utility from skating 0 0 1 50 1 70 2 40 2 40 3 30 3 30 4 20 4 20 5 10 5 5 230) Steve has two goods he can spend his income on, skiing and skating, and his marginal utilities from each are in the table above. The price of each unit of skiing is $10 and the price of each unit of skating is $10. Steve has $40 to spend. What quantities of skiing and ice skating will Steve consume to maximize his utility? 230) A) 2 units of skiing and 2 units of skating B) 0 units of skiing and 4 units of skating C) 4 units of skiing and 0 units of skating D) 231) If Katie purchases two slices of pizza and six breadsticks to maximize her total utility, then 231) A) a breadstick costs three times as much as a slice of pizza. B) slice of pizza costs three times as much as a breadstick. C) her marginal utility from the second slice of pizza divided by the price of a slice of pizza is equal to her marginal utility from the sixth breadstick divided by the price of a breadstick. D) Both answers A and C are correct. G.KAZAR232) Brian consumes only pizza and soda. When the price of a soda is $2 and the price of a slice of pizza is $4, Brian maximizes his utility by buying 5 sodas and 10 slices of pizza. If the marginal utility of the 5th soda is 100, then the marginal utility from the 10th slice of pizza must be ________. 232) A) 200 B) 50 C) 100 D) More information is needed to determine the marginal utility of the 10th slice of pizza. Cookies Cake Quantity Marginal utility Quantity Marginal utility 1 32 1 40 2 28 2 32 3 24 3 24 4 20 4 16 5 16 5 8 6 12 6 0 233) The above table shows Homer's marginal utility from consuming various quantities of chocolate chip cookies and cake. The price of cookies is $1 per pound, the price of cake is $2 per slice and Homer has $9 to spend on cookies and cake. Homer will consume ________ pounds of cookies and ________ slices of cake. 233) A) 2; 5 B) 5; 2 C) 3; 3 D) None of the above answers is correct. 234) Let MUa and MUb stand for the marginal utilities of apples and bagels. Let Pa and Pb stand for their prices. The general necessary condition for consumer equilibrium is 234) A) MUa = MUb. B) MUa/MUb = Pb/Pa. C) MUa = MUb and Pa = Pb. D) MUa/Pa = MUb/Pb. Chips Sodas Quantity Total utility Quantity Total utility 0 0 0 0 1 60 1 200 2 100 2 300 3 120 3 390 4 135 4 470 5 145 5 530 6 150 6 580 7 153 7 620 8 155 8 650 235) The table above shows Mary's utility from chips and soda. The table shows that Mary has diminishing marginal utility for 235) A) both chips and soda. B) chips, but not soda. C) neither chips nor soda. D) soda, but not chips. G.KAZAR236) A consumer has maximized his or her utility by consuming 236) A) so that the ratio of marginal utility to price is the same for all goods consumed. B) at the midpoint of the demand curve. C) so that the total utility of all goods consumed is the same. D) at the midpoint of the budget constraint line. Milkshakes Sodas Quantity Total utility Quantity utility Total 0 0 0 0 1 600 1 240 2 1000 2 360 3 1300 3 460 4 1540 4 520 5 1590 5 570 6 1636 6 590 7 1676 7 602 8 1708 8 610 9 1728 9 616 10 1738 10 620 237) The table above shows Tom's total utility from milkshakes and sodas. A soda costs $1.00. What is the marginal utility per dollar spent when the eighth soda is purchased? 237) A) 32 units per dollar B) 10 units per dollar C) 20 units per dollar D) 8 units per dollar Quantity of DVDs Marginal utility from DVDs Quantity of pizza Marginal utility from pizza 1 150 1 200 2 120 2 180 3 100 3 150 4 90 4 120 5 60 5 100 6 40 6 60 238) Lisa spends all her income on pizzas and DVDs. The above table shows Lisa's marginal utility for pizza and marginal utility for DVDs. If the price of a pizza is $10 and the price of a DVD is $10 and Lisa has $60 to spend on the two goods, what combination of pizza and DVDs will maximize her utility? 238) A) 3 DVDs and 5 pizzas B) 4 DVDs and 2 pizzas C) 3 pizzas D) 2 DVDs and 4 pizzas 239) Total utility is maximized when a consumer has spent all of his or her income and 239) A) spent equal amounts on all goods. B) the total utility per dollar from all goods is equal. C) marginal utility per dollar from all goods is equal. D) marginal utility is maximized. G.KAZARQuantity of steak Marginal utility from steak Quantity of chicken Marginal utility from chicken 1 100 1 40 2 80 2 35 3 35 3 25 4 25 4 20 5 10 5 15 6 5 6 10 240) John either buys a steak or chicken when dining out. John's marginal utility for steak and chicken is given in the above table. If the price of a steak is $5 and the price of a chicken is $5 and John has $25 to spend on the two goods, what combination of steak and chicken will John consume to maximize his utility? 240) A) 5 steaks and 6 chickens B) 3 steaks and 2 chickens C) 1 steak and 4 chickens D) 4 steaks and 3 chickens Pizza Pepsi Quantity Marginal utility Quantity Marginal utility 0 0 0 0 1 20 1 30 2 16 2 8 3 10 3 7 241) The above table shows Priscilla's marginal utility from the two goods she consumes, pizza and Pepsi. A slice of pizza costs $4 and a can of Pepsi $2. Suppose Priscilla has $12 to spend. If the price of pizza decreases, Priscilla's preferences (her marginal utility schedule) for pizza 241) A) will decrease. B) will increase. C) will not change. D) may increase or decrease depending on what happens to the price of Pepsi. 242) Suppose the price of soda is $2 each and the price of a pizza slice is $4 each. David maximizes his utility by buying only sodas and pizza. He buys 5 sodas and 10 slices of pizza. If the price of a soda increases to $3 each, David will 242) A) decrease the number of sodas bought and the demand curve for sodas will shift leftward. B) buy less pizza and the demand curve for pizza will shift leftward. C) more pizza and move along the demand curve for pizza. D) decrease the number of sodas bought and move along the demand curve for soda. 243) We can explain the paradox of value as follows: The consumer surplus from water, which is cheap, is ________ than the consumer surplus from gold, which is expensive; the total utility from gold is ________ than the total utility from water; and the marginal utility per dollar spent on water ________ the marginal utility per dollar spent on gold. 243) A) smaller; less; equals B) greater; less; equals C) greater; greater than D) less; greater; greater than G.KAZAR244) Marginal utility theory concludes that a decrease in the price of a good increases the quantity demanded and 244) A) increases total utility. B) decreases the demand for complements. C) increases the demand for substitutes. D) increases the total expenditure on the good. 245) Steve is in a consumer equilibrium. Then, the price of steak increases from $6 a pound to $8 a pound. Steve decreases the number of pounds of steaks he buys each week ________. 245) A) and decreases his total utility B) so that both his total utility and his marginal utility from steak fall C) only if his income also decreases D) so that the marginal utility per dollar spent on steaks is the same as it was when the price was $6 a pound 246) The fact that rubies are more expensive than milk reflects the fact that for most consumers, 246) A) the marginal utility from rubies equals that from milk. B) more milk is consumed than rubies. C) a quart of rubies is considered to be prettier than a quart of milk. D) the total utility from rubies exceeds that from milk. 247) Marginal utility theory predicts that as the price of coffee rises, the ________ a substitute for coffee ________ and the ________ coffee ________. 247) A) demand for; decreases; demand for; increases B) supply of; increases; demand for; decreases C) demand for; increases; quantity demanded of; decreases D) supply of; decreases; supply of; increases 248) Gunther rents Nintendo games and videos. The marginal utility from his last Nintendo game is 10 and that from his last video is 5. Nintendo games rent for $2 each. Gunther's demand curve for games is shown in the figure above. How many videos a week does Gunther rent? 248) A) 3 B) 4 C) 2 D) 1 G.KAZAR249) Renee consumes pizza and rice. An increase in her income causes her to consume fewer pizzas and more rice. The change in pizzas consumed means that 249) A) her marginal utility from consuming pizzas had been negative. B) zero. C) pizza is an inferior good for Renee. D) her total utility from consuming pizzas had been negative. 250) Marginal utility theory predicts that when the price of one good rises, the demand for another good is a substitute increases. This change occurs because of 250) A) a decrease in the marginal utility per dollar from the good whose price has risen. B) n increase in the marginal utility of the substitute good. C) decrease in the marginal utility of the good whose price has risen. D) n increase in the marginal utility per dollar from the substitute good. 251) Sue consumes only sub sandwiches and Mountain Dew. Subs and Mountain Dew are complements. If the price of a Mountain Dew increases, 251) A) Sue will move downward along her demand curve for Mountain Dews. B) upward along her demand curve for Mountain Dews. C) 's demand curve for sub sandwiches will shift rightward. D) Both answers A and C are correct. 252) With respect to water and diamonds, water 252) A) has a lower marginal utility than diamonds. B) is cheaper than diamonds because it has a lower total utility. C) higher total utility. D) has a higher marginal utility than diamonds. 253) Marginal utility theory shows us that water, which is very common, has a ________ marginal utility and a ________ total utility. 253) A) small; large B) large; large C) large; small D) small; small 254) In consumer equilibrium, Harold consumes pizza, sodas, and other goods. Pizza and soda are complements for Harold. The price of a pizza rises while his income remains the same. Harold then consumes 254) A) less pizza and less soda. B) more pizza and more soda. C) less soda. D) more soda. 255) Teddy buys only chocolate chip cookies and hot chocolate and spends all of his income on the two items. Suppose the price of a cookie rises. According to marginal utility theory, Teddy will buy 255) A) more cookies and less hot chocolate, which increases his marginal utility from cookies and decrease his marginal utility from hot chocolate. B) fewer cookies and more hot chocolate, which decreases his marginal utility from cookies and increases his marginal utility from hot chocolate. C) more cookies and less hot chocolate, which decreases his marginal utility from cookies and increases his marginal utility from hot chocolate. D) fewer cookies and more hot chocolate, which increases his marginal utility from cookies and decreases his marginal utility from hot chocolate. G.KAZAR256) Using marginal utility theory, when the price of a gallon of milk falls, a consumer will buy 256) A) the same amount of milk as before and buy more of all other goods. B) more milk. C) more milk only if its marginal utility is constant. D) increasing. 257) Sue consumes only sub sandwiches and Mountain Dew. Subs and Mountain Dew are complements. If the price of a sub sandwiches increases, 257) A) Sue will move upward along her demand curve for subs. B) 's demand curve for subs will shift leftward. C) Sue will move downward along her demand curve for subs. D) 's demand curve for subs will shift rightward. 258) Which of the following statements is true? 258) A) Utility is gained whenever someone wants a good. B) Total utility is equal to marginal utility. C) Utility units are observable. D) Marginal utility theory assumes that marginal utility diminishes as more of any good is consumed. 259) The diamond-water paradox of value can be explained by 259) A) the fact that utility cannot be measured. B) water's high level of utility relative to diamonds. C) distinguishing between total utility and marginal utility. D) water's low price relative to diamonds. 260) According to marginal utility theory, a rise in income will 260) A) increase consumption of all goods. B) increase the marginal utility of all goods. C) a consumer's total utility. D) None of the above answers is correct. Pizza Pepsi Quantity Marginal utility Quantity Marginal utility 0 0 0 0 1 20 1 30 2 16 2 8 3 10 3 7 261) The above table shows Priscilla's marginal utility from the two goods she consumes, pizza and Pepsi. Initially, a slice of pizza costs $4 and a can of Pepsi $2. Suppose Priscilla has $12 to spend. If the price of pizza falls to $2, Priscilla will choose to 261) A) consume more pizza. B) consume more Pepsi. C) less pizza. D) Both answers A and B are correct. G.KAZAR262) Which of the following statements is true? 262) A) Marginal utility theory makes no prediction about a consumer's responses to hikes in the prices of the goods and services he or she consumes. B) Marginal utility theory predicts that an increase in a consumer's income increases consumption of all goods. C) It is possible to derive the law of demand – that a higher price decreases the quantity demanded – using marginal utility theory. D) Marginal utility theory predicts that all goods are normal goods and that all goods are substitutes for each other. 263) Kirk consumes normal goods. If Kirk's income decreases and the prices of all goods remain unchanged, in his new consumer equilibrium, his marginal utility from each good will ________ and his total utility will ________. 263) A) increase; decrease B) decrease; increase C) decrease; decrease D) increase; increase 264) Ricardo buys cola and popcorn. Cola sells for $0.50 a can and popcorn sells for $1 per bag. He is in consumer equilibrium. The price of a cola jumps to $1 per can. In his new consumer equilibrium, Ricardo's 264) A) marginal utility of cola will decrease. B) total utility will be higher. C) marginal utility of cola will be equal to his marginal utility of popcorn. D) per dollar spent will be 2. 265) Bianca consumes pizza. Marginal utility theory predicts that when the price of pizza increases, 265) A) will buy less pizza. B) 's demand curve for pizza will shift leftward. C) marginal utility from pizza will increase. D) total utility from pizza will increase. 266) The predictions of marginal utility theory 266) A) support the idea that the demand curve slopes downward. B) contradict the idea that the supply curve slopes upward. C) demand curve slopes downward. D) support the idea that the supply curve slopes upward. 267) The only goods you consume are pizza and soda. Both are normal goods. You consider pizza and soda to be substitutes. Which of the following will lead you to eat more pizza? 267) A) The price of a soda rises. B) The price of a soda falls. C) pizza falls. D) Both answers A and C are correct. 268) The only goods you consume are pizza and soda. Both are normal goods. For you, pizza and soda are substitutes. Which of the following leads you to buy more of both goods? 268) A) The price of a pizza falls. B) Your income increases. C) soda falls. D) Both answers A and B are correct. G.KAZAR269) Michael consumes only steak and lobster. Suppose that the price of steak rises. After Michael is back at equilibrium, compared to the situation when steak was cheaper, the marginal utility from the last steak will 269) A) not have changed. B) have decreased. C) have increased. D) not be comparable with the marginal utility before the price hike. 270) Lucy buys only magazines and CDs. Both are normal goods. Lucy's income decreases, but the prices of magazines and CDs do not change. Marginal utility theory predicts that Lucy will ________. 270) A) increase her marginal utility from both magazines and CDs by buying more magazines and CDs B) buy more magazines and more CDs C) substitute magazines for CDs D) buy fewer magazines and fewer CDs 271) Sheila's Sports Shop is a very popular sporting goods store, which has a yearly revenue of $600,000. Sheila runs the business herself. Her alternative employment options are to be a college swimming coach for $50,000 per year or a construction worker for $40,000 per year. Sheila spends $230,000 purchasing goods for resale to her customers. She also has four employees, who each earn $25,000 per year. Sheila owns the building that her Sports Shop is housed in and she could have rented it out for $20,000 per year. Sheila's economic profit is equal to 271) A) $250,000 per year. B) $270,000 per year. C) 160,000 per year. D) 00,000 per year. 272) Which of the following statements does NOT correctly characterize normal profit? 272) A) It is part of a firm's opportunity cost. B) the average return for supplying entrepreneurial ability. C) equal to a firm's total revenue minus its opportunity cost. D) None of the above because all the statements correctly characterize normal profit. 273) Sheila's Sports Shop is a very popular sporting goods store, which has a yearly revenue of $600,000. Sheila runs the business herself. Her alternative employment options are to be a college swimming coach for $50,000 per year or a construction worker for $40,000 per year. Sheila spends $230,000 purchasing goods for resale to her customers. She also has four employees, who each earn $25,000 per year. Sheila owns the building that her Sports Shop is housed in and she could have rented it out for $20,000 per year. Sheila's costs for resources bought in the market equal 273) A) $350,000 per year. B) $330,000 per year. C) 200,000 per year. D) 70,000 per year. 274) A firm's opportunity costs ________. 274) A) include the cost of using resources owned by the firm B) rease when economies of scope exist C) do not include any opportunity costs for resources the owner suppliers D) equal the costs of resources it buys from others in the market G.KAZAR275) Bud opened a flower shop. He rented a building for $9,000 a year. To buy equipment for the store, he withdrew $10,000 from his savings account, which earned an annual interest rate of 3 percent. During the first year of operation, Bud paid $4,000 for utilities and $12,000 to his suppliers. The store's total annual revenue was $55,000. The market value of the store's equipment at the end of the year was $8,000. If Bud had not started this business, he would have continued to work as an employee at another flower shop for $30,000 a year. During the first year of operation, Bud 275) A) received an economic profit of $30,000. B) incurred an economic loss of $12,300 C) 20,000. D) 2,300 276) Economic depreciation is the 276) A) return that an entrepreneur can expect to receive on average. B) forgone return on the funds used to buy capital. C) irm's opportunity cost of using its own capital. D) change in the market value of capital over a given period. 277) Which of the following constrain (that is, limit) a firm's profits? I. its technology II. its information III. the market in which it operates 277) A) I only B) I and II C) II and III D) I, II and III 278) The implicit rental rate for capital includes the 278) A) amount paid for the use of a piece of capital equipment owned by someone else. B) firm's normal profit. C) total value of a piece of capital equipment. D) interest income forgone by purchasing the piece of capital equipment. 279) Ed is a freelance writer who could work for a newspaper at $25,000 a year but instead works for himself for $41,000 a year. His only business expenses are $1,000 for writing materials and $12,000 for rent. Ed's normal profit is $1,000. Ed's economic profit from working as a freelance writer is 279) A) $25,000. B) $15,000. C) $1,000. D) $2,000. 280) Lucinda starts a business consulting company. She makes all the business decisions and bears the risk of running the business. The typical payment for Lucinda's work is ________. 280) A) a normal profit B) ll the revenue greater than her opportunity cost C) n economic profit D) ll the revenue greater than the capital investment 281) Over a given period, economic depreciation is the change in capital equipment's 281) A) market value. B) rate of return. C) output. D) cost of maintenance. 282) Sue owns a baking company. The company's total revenue for a month is $4000. The monthly costs of resources bought in the market and of resources owned by the firm are $2000 and monthly costs of resources supplied by the owner are $1000. Sue's economic profit for the month is equal to 282) A) $1000. B) $3000. C) $2000. D) $4000. G.KAZAR283) A firm's market constraints include the conditions under which it can 283) A) convert inputs into outputs. B) produce the inputs to production. C) buy its inputs and sell its outputs. D) issue stock. 284) An electrician quits her current job, which pays $40,000 per year. She can take a job with another firm for $45,000 per year or work for herself. The opportunity cost of working for herself is 284) A) $45,000. B) $85,000. C) $40,000. D) $5,000. 285) Sheila's Sports Shop is a very popular sporting goods store, which has a yearly revenue of $600,000. Sheila runs the business herself. Her alternative employment options are to be a college swimming coach for $50,000 per year or a construction worker for $40,000 per year. Sheila spends $230,000 purchasing goods for resale to her customers. She also has four employees, who each earn $25,000 per year. Sheila owns the building that her Sports Shop is housed in and she could have rented it out for $20,000 per year. Sheila's costs for the resources that she supplies to the business equal 285) A) $90,000 per year. B) $330,000 per year. C) 70,000 per year. D) 0 per year. 286) Which of the following is part of a firm's opportunity costs? I. wages II. utility costs III. interest on a bank loan IV. interest forgone on funds used to buy capital equipment 286) A) I, II and III B) III and IV C) I and II D) I, II, III and IV 287) The most important goal of the firm is to 287) A) maximize its sales volume. B) maximize its profits. C) inimize its costs. D) revenues. 288) Heidi quit her job as a chef making $40,000 per year to start her own restaurant. The first year, Heidi's restaurant earned $100,000 in revenue. Heidi pays $50,000 per year in wages to the waitresses and hostess and $20,000 per year to buy food. What is Heidi's profit as measured by an accountant for the year? 288) A) $30,000 B) $80,000 C) $50,000 D) -$10,000 289) ________ is the change in market value of capital over a given period. 289) A) Accounting depreciation B) Accounting implicit rental cost C) Implicit rental rate D) Economic depreciation 290) The average return for supplying entrepreneurial ability is the entrepreneur's 290) A) economic profit. B) explicit profit. C) normal profit. D) accounting profit. 291) Among the opportunity costs of a firm are all of the following EXCEPT 291) A) normal profits. B) costs of resources bought in markets, such as labor. C) economic profits. D) the owner's forgone wage. G.KAZAR292) Economic profit is the difference between total revenue and 292) A) interest costs of production. B) the normal profit. C) opportunity costs of production. D) costs of resources bought in markets. 293) The implicit rental rate for capital is 293) A) an opportunity cost. B) part of the firm's normal profit. C) accounting cost. D) cost that is irrelevant to the business. 294) Mr. Sweet opened a candy store. He rented a building for $30,000 a year. During the first year of operation, Sweet paid $40,000 to his employees, $10,000 for utilities, and $20,000 for goods he bought from other firms. His total revenue was $135,000. Sweet's best alternative to running this candy store is to work for Wal-Mart as a sales associate for $15,000 a year. What is Sweet's economic profit? 294) A) $35,000 B) zero C) $20,000 D) -$20,000 295) Mr. Sweet opened a candy store. He rented a building for $30,000 a year. During the first year of operation, Sweet paid $40,000 to his employees, $10,000 for utilities, and $20,000 for goods he bought from other firms. His total revenue was $135,000. Sweet's best alternative to running this candy store is to work for Wal-Mart as a sales associate for $15,000 a year. What is Sweet's total opportunity cost? 295) A) $115,000 B) $135,000 C) $100,000 D) $15,000 296) Joe quits his job as an insurance agent and opens his own sporting goods store. If his profits as measured by his accountant are greater than zero, then 296) A) his opportunity costs must be zero. B) e made a good move because he is earning above normal profits. C) is economic profit must be greater than zero. D) There is not enough information to determine his economic profit, if any. 297) If instead of working on his own as a consultant making $25,000, Joe takes a job at a bank, the $25,000 is 297) A) an accounting profit. B) a depreciation. C) loss. D) opportunity cost. 298) Greg, a landscaper, is planning on opening his own landscaping company. He currently earns $40,000 per year working for his uncle but he will need to quit that job. He plans to use $10,000 in savings to pay for the equipment he needs, though even after use he could sell the equipment for what he paid, $10,000. The current interest rate on savings is 5 percent. What is the total opportunity cost incurred by Greg in running his own business? 298) A) $10,000 B) $40,500 C) $50,000 D) $40,000 299) Any method of producing a good or service is ________. It ________ the maximum profit that a firm can make. 299) A) an information constraint; always increases B) technology; limits C) n information constraint; limits D) a technology; always increases G.KAZAR300) A firm's basic goal is best described as 300) A) maximizing profit. B) maximizing total revenue. C) sales. D) inimizing total cost. 301) Emma owns a firm that produces umbrellas. Currently, Emma produces 2,500 umbrellas a day. Emma cannot produce more umbrellas in a day unless she purchases another machine or else hires more workers. Emma is ________ efficient. 301) A) capital and labor B) economically C) ost D) technologically 302) A company does not need to know the price of each resource it employs if it wants to determine whether or not it is achieving 302) A) accounting efficiency. B) managerial efficiency. C) economic efficiency. D) technological efficiency. Techniques for making 100 pizzas Options Labor (workers) Capital (units) 1 23 2 2 10 5 3 8 5 4 5 10 303) Labor costs $20 per worker and capital costs $100 per unit. Then, according to the above table, which of the following options for pizza production is technologically efficient? 303) A) Option 2 B) 4 C) 1 D) All of the above listed options are technologically efficient. Technique Number of workers Units of capital A 1 3 B 1 5 C 2 3 D 3 2 304) The table above shows four methods for producing 10 computer desks a day. If the cost of a worker is $50 a day and the cost of capital is $150 a day, ________ economically efficient . 304) A) method A is B) method B is C) method D is D) method A or C is 305) Technological efficiency occurs when the firm produces a given output 305) A) at the greatest cost. B) at the least cost. C) by using the least amount of inputs. D) by using the maximum amount of inputs. G.KAZAR306) A method that is technologically inefficient 306) A) means that it uses too much labor and too little capital. B) ight or might not be economically efficient. C) results from failure to calculate the ratio of the cost of labor to the cost of capital. D) can never be economically efficient. Technique Capital (units) Labor (units) A 110 10 B 90 20 C 80 15 D 75 20 307) The above table gives techniques that Fatz Confectionery can use to produce 2,000 pounds of candy. Which technique is technology inefficient? 307) A) A B) B C) C D) D 308) Which of the following statements is correct? 308) A) Technological efficiency depends on the relative costs of resources. B) Economic efficiency depends only on production methods. C) A firm can be economically efficient without being technologically efficient. D) Economic efficiency occurs when the firm produces a given output at the least cost. 309) Economic efficiency necessarily occurs when the firm 309) A) produces a given output by using the least inputs. B) at least cost. C) earns an economic profit. D) normal profit. Methods for making 2,000 CDs per day Method Capital (units) Labor (workers) A 12 200 B 20 80 C 70 10 D 30 85 310) In the table above, if the cost of capital is $20 per day and an hour of labor is $15 per day, which method is economically efficient? 310) A) A B) B C) C D) D G.KAZARTechnique Number of workers Units of capital A 1 3 B 1 5 C 2 3 D 3 2 311) The table above shows four methods for producing 10 computer desks a day. Of the four methods, ________ technologically inefficient. 311) A) B and C are B) D is C) A and B are D) B is 312) When Acme Inc. produces a certain amount of output by using the least amount of inputs, Acme Inc. definitely 312) A) achieves economic efficiency. B) minimizes labor costs. C) aximizes profits. D) technological efficiency. Technique Capital (units) Labor (units) A 70 20 B 80 60 C 120 20 D 5 180 313) The above table gives techniques Jitters Coffee Company can use to package 5,000 pounds of coffee. If the cost of capital is $50 per unit and the cost of labor is $100 per unit, the economically efficient technique for packaging 5000 pounds of coffee is 313) A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. 314) The accountant for Muzhi's Sushi claims that Muzhi has accomplished "economic efficiency." This means that Muzhi's Sushi 314) A) produces a given output using the least inputs. B) has a normal profit greater than an economic profit. C) n economic profit greater than a normal profit. D) produces a given output at the lowest cost. Technique Capital (units) Labor (units) W 25 30 X 35 10 Y 25 25 Z 45 5 315) The table above shows techniques that can be used to produce 100 shirts. If the price of an hour of labor is $20 and the price of a unit of capital is $8, then the economically efficient technique is 315) A) W. B) X. C) Y. D) Z. G.KAZARProduction Information for Scully's Splendid Spacecrafts Technique to produce 50 space crafts Units of capital (thousands) Hours of labor (thousands) W 4 28 X 4 16 Y 8 4 Z 10 1 316) In the above table, if the price of labor is $10 per hour and the price of capital is $20 per unit, which method of producing 50 space crafts is economically efficient? 316) A) Technique W B) Technique X C) Technique Y D) Technique Z Techniques for making 100 automobiles Method Labor (workers) Capital (units) A 50 500 B 20 700 C 6 0400 317) The table above shows three production methods to produce 100 automobiles per day. If the price of labor is $20 per unit and the price of capital is $100 per unit, which of the three methods is economically efficient? 317) A) Method A only. B) B only. C) C only. D) All three methods are economically efficient. 318) A firm that is maximizing its profit 318) A) is economically efficient but might be technologically inefficient. B) technologically efficient but might be economically inefficient. C) might be economically inefficient and/or technologically inefficient. D) is economically efficient and technologically efficient. Techniques that produce 100 sweaters Technique Labor (hours) Capital (machines) A 10 35 B 25 25 C 10 60 D 30 20 319) Using the data in the above table, if the price of an hour of labor is $20 and the price of a unit of capital is $10, then the most economically efficient technique for producing 100 sweaters is 319) A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. G.KAZARTechniques for making 100 automobiles Method Labor (workers) Capital (units) A 50 500 B 20 700 C 6 0400 320) The table above shows three production methods to produce 100 automobiles per day. Which of the three methods is technologically efficient? 320) A) Method A only B) B only C) C only D) A, B and C are all technologically efficient. Technique Capital (units) Labor (units) W 25 30 X 35 10 Y 25 25 Z 45 5 321) The table above shows techniques that can be used to produce 100 shirts. The technique that is NOT technologically efficient is 321) A) W. B) X. C) Y. D) Z. 322) Technological efficiency necessarily means producing 322) A) with the highest level technology available. B) at minimum cost. C) without using more inputs than necessary. D) technology itself. 323) Which of the following is a correct statement? 323) A) Technological efficiency depends on the costs of resources while economic efficiency depends on only production methods. B) Economic efficiency definitely occurs when a firm cannot increase production without using more resources. C) Technological efficiency depends only on production methods, while economic efficiency depends on the costs of resources. D) all of the above 324) Which of the following statements is true? I. A firm that is not economically efficient does not maximize profit. II. Economic efficiency depends on the relative costs of resources. III. A technological efficient firm is also economically efficient. 324) A) I only B) I and II C) II and III D) II only G.KAZAR325) Firm A can produce a unit of output with 10 hours of labor and 5 units of material. Firm B can produce a unit of output with 5 hours of labor and 10 units of material. Firm C can produce a unit of output with 10 hours of labor and 10 units of material. If the prices of labor and material are $10 per hour and $5 per unit, respectively, which of these firms is the most technologically efficient? 325) A) firm A only B) B only C) C only D) Firms A and B could both be technologically efficient. Method Labor required (person-hours) Capital required (machine-hours) T-1 200 100 T-2 150 150 T-3 150 130 T-4 100 200 326) The table below shows four alternative techniques for assembling a car. Which of the four techniques for assembling a car cannot be economically efficient with any input prices ? 326) A) T-1 B) T-2 C) T-3 D) T-4 327) The table below shows four alternative techniques for assembling a car. The cost of labor is $20 per hour, and the cost of capital is $10 per hour. Which of the four techniques for assembling a car is not technologically efficient? 327) A) T-1 B) T-2 C) T-3 D) T-4 328) Economic efficiency occurs when the firm produces a given output 328) A) by using the least amount of inputs. B) at the least cost. C) maximum amount of inputs. D) greatest cost. Technique Capital (units) Labor (units) A 70 20 B 80 60 C 120 20 D 5 180 329) The above table gives techniques Jitters Coffee Company can use to package 5,000 pounds of coffee. Which technique(s) is (are) technologically inefficient? 329) A) A B) C C) B, C, and D D) B and C G.KAZARTechniques that produce 100 sweaters Technique Labor (hours) Capital (machines) A 10 35 B 25 25 C 10 60 D 30 20 330) In the above table, the technique that is never economically efficient is 330) A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. 331) Which of the following are types of economic markets? I. perfectly competitive II. oligopoly III. monopoly IV. multilateral 331) A) II and III B) I, II and III C) I and IV D) I and II 332) A market structure in which many firms are selling an identical product is called 332) A) perfect competition. B) oligopoly. C) monopolistic competition. D) monopoly. 333) A market with the characteristics of many firms selling an identical product, many buyers, and no restrictions on entry or exit to the market is 333) A) an oligopolistic market. B) a monopoly market. C) istically competitive market. D) perfectly competitive market. 334) The market for wheat is an example of 334) A) a perfectly competitive market. B) a monopoly market. C) n oligopolistic market. D) istically competitive market. 335) Under ________ there are many firms selling identical products. 335) A) monopoly B) perfect competition C) istic competition D) oligopoly 336) Which of the following pairs of market types are both characterized by having a large number of firms? 336) A) monopoly and monopolistic competition B) oligopoly C) perfect competition and monopolistic competition D) oligopoly 337) Under ________, there are many firms selling slightly different products. 337) A) monopoly B) oligopoly C) istic competition D) perfect competition G.KAZAR338) In a market where firms are successful in convincing their customers that their product is different from their competitors' product but otherwise have no barriers to entry would be best characterized by 338) A) perfect competition. B) monopolistic competition. C) a monopoly. D) an oligopoly market. 339) Which market type has characteristics as follows: large number of firms, differentiated product? 339) A) oligopoly B) monopolistic competition C) y D) perfect competition 340) A market structure in which many firms compete by making similar but slightly different products is called 340) A) perfect competition. B) oligopoly. C) monopolistic competition. D) monopoly. 341) In a given market, a large number of firms sell a similar product. Consumers think that each firm's product is somewhat different from that of its competitors. This market is 341) A) perfectly competitive. B) equivalent to an oligopoly because consumers think the products are different. C) monopoly because consumers think the products are different. D) monopolistically competitive. 342) The market structure in which a large number of firms compete by making similar but slightly different products is called 342) A) monopolistic competition. B) monopoly. C) perfect competition. D) oligopoly. 343) In monopolistic competition, there are ________. 343) A) many firms selling products for which no good substitutes exist B) , each selling an identical product C) selling similar but slightly different products D) a small number of firms, each selling an identical product 344) A market structure in which a small number of firms compete is called 344) A) perfect competition. B) oligopoly. C) monopoly. D) monopolistic competition. 345) Under oligopoly, there are ________ firms selling products that are ________. 345) A) many; either identical or different B) a few; identical C) either identical or different D) different 346) Coca Cola and Pepsi, which together account for about 85 percent of the soft drink market, are best described as being in 346) A) a monopoly market. B) an oligopolistic market. C) istically competitive market. D) perfectly competitive market. 347) The air travel market, which is dominated by a few large firms, is an example of 347) A) a perfectly competitive market. B) a monopolistically competitive market. C) y market. D) n oligopolistic market. G.KAZAR348) A market structure in which one firm produces a good or service that has no close substitutes is called 348) A) monopolistic competition. B) perfect competition. C) oligopoly. D) y. 349) Which market type has characteristics as follows: one firm, good or service produced has no close substitutes, barriers to entry prevent new firms from entering into the industry? 349) A) monopoly B) perfect competition C) istic competition D) oligopoly 350) Kansas Power and Light, the only supplier of electricity in Kansas, is an example of a firm in what type of market? 350) A) an oligopolistic market B) a monopoly market C) perfectly competitive market D) istically competitive market 351) Which of the following factors is fixed in the long run? 351) A) Land B) Entrepreneurship C) Capital D) None of the above because all factors are variable in the long run. 352) The long run is a period of time in which 352) A) all factors of production are variable. B) some but not all factors of production are variable. C) fixed. D) all factors of production are fixed. 353) Which of the following statements is correct? 353) A) Long-run decisions are easily reversed. B) A firm does not need to take into account its sunk cost when making current decisions. C) In the long run, a firm can change its plant but not the quantity of its labor. D) Short-run decisions are not easily reversed. 354) The short run is a period of time in which 354) A) prices and wages are fixed. B) nothing the firm does can be altered. C) the amount of output is fixed. D) quantity of at least one factor of production is fixed. 355) A period of time in which the quantity of at least one factor of production used by a firm is fixed is called the 355) A) short run. B) market period. C) long run. D) intermediate run. 356) In economics, the short run is the time frame in which the quantities of ________ and the long run is the period of time in which ________. 356) A) some factors of production are variable; the quantities of all factors of production are fixed B) all factors of production are variable but technology is fixed; technology is variable C) some factors of production are fixed; the quantities of all factors of production can be varied D) all factors of production are fixed; the quantities of all factors of production can be varied G.KAZAR357) All the decisions made by people who operate firms have one overriding objective, which is to ________. 357) A) make maximum attainable profit B) maximize the quantity that the firm sells C) firm's market share D) firm's total revenue 358) In the short run, 358) A) no factors of production are fixed. B) labor usage must remain fixed. C) all factors of production are fixed. D) a firm's plant is fixed. 359) The long run is a time period in which 359) A) all factors of production are fixed. B) variable. C) one year or less elapses. D) there is at least one fixed factor of production and at least one variable factor of production. 360) After constructing a new factory, the cost of building the factory is a 360) A) variable cost. B) past cost. C) sunk cost. D) None of the above answers are correct. 361) A cost that has already been made and cannot be recovered is called a 361) A) fixed cost. B) sunk cost. C) marginal cost. D) variable cost. 362) Economists define the short run as a period of time so short that 362) A) the amount of output cannot be changed at all. B) at least one factor of production cannot be varied. C) only one factor of production can be varied. D) the amount of output cannot be changed except under diminishing marginal returns. 363) The long run is a time frame in which 363) A) the quantities of all factors of production can be varied. B) all costs are sunk costs. C) the quantities of all factors of production are fixed. D) the quantities of some factors of production are fixed and the quantities of other factors of production can be varied. 364) An example of a variable factor of production in the short run is 364) A) an employee. B) land. C) capital equipment. D) building. 365) A period of time in which the quantity of all factors of production used by a firm can be varied is called the 365) A) market period. B) long run. C) variable run. D) short run. 366) The short run is a time frame in which 366) A) at least one factor of production is fixed. B) ll factors of production are fixed. C) t least one factor of production can be varied. D) ll factors of production can be varied. G.KAZAR367) An example of a short-run fixed factor of production is 367) A) electricity. B) labor. C) postage for mailing. D) capital equipment. 368) The short run is a time period during which 368) A) at least one factor of production is fixed. B) all factors of production are fixed. C) variable. D) firm can earn a normal profit. 369) In the long run, a firm can vary 369) A) its capital but not its labor. B) both its labor and its capital. C) labor but not its capital. D) neither its labor nor its capital. 370) In the short run, 370) A) all factors of production are variable. B) the size of the plant is fixed. C) all factors of production are fixed. D) some firms experience increasing returns to scale. 371) Increasing marginal returns to labor might occur at low levels of labor input because of 371) A) differing factor proportions. B) ecreasing use of machinery and increasing use of technology. C) increasing average costs. D) specialization of tasks. Jefferson's Cleaners Labor (workers) Total product (suits cleaned per day) 0 0 1 12 2 26 3 46 4 60 5 73 6 84 7 94 8 102 9 109 372) Based on the data in the above table, at what level of output does the marginal cost start to rise at Jefferson's Cleaners? 372) A) 47 suits per day B) 74 suits per day C) 85 suits per day D) 45 suits per day G.KAZARLabor (workers per day) Total product (pizzas per day) 0 0 1 10 2 25 3 37 4 45 5 50 373) Based on the production data for Pat's Pizza Parlor in the above table, which worker has the largest marginal product? 373) A) Worker 1 B) Worker 2 C) Worker 3 D) Worker 4 Labor (workers) Total product (books sold per hour) 0 0 1 10 2 24 3 40 4 58 5 73 6 83 7 87 8 89 9 90 10 90 374) The above table shows the short-run total product schedule for the campus book store. What is the marginal product (MP) of going from 5 to 6 employees at the book store? 374) A) between 11 and 14 books sold B) 10 books sold C) 13.83 books sold D) 83 books sold 375) Diminishing marginal returns occurs when 375) A) a variable unit is increased and its marginal product falls. B) input is increased and output decreases. C) ll inputs are increased and output increases by a smaller proportion. D) decreases. G.KAZARLabor (workers) Total product (books sold per hour) 0 0 1 10 2 24 3 40 4 58 5 73 6 83 7 87 8 89 9 90 10 90 376) The above table shows the short-run total product schedule for the campus book store. What is the average product (AP) of the 4th employee? 376) A) 14.5 books sold B) 58 books sold C) 18 books sold D) 13.3 books sold 377) Average product equals the 377) A) total amount of output produced divided by the quantity of labor employed. B) . C) divided by price of the output. D) increase in output that results from a one-unit increase in the quantity of labor employed with all other inputs remaining the same. Labor (workers) Total product (units per day) 0 0 1 3 2 12 3 19 4 23 5 25 378) Using the data in the above table, if the firm employs 3 workers, total product (measured in units per day) and average product and marginal product of the third worker (measured in units per worker) are 378) A) 19, 6 1/3, and 7 respectively. B) 19, 3, and 9 respectively. C) 9 respectively. D) 3, 19, and 6 1/3 respectively. G.KAZAR379) Which of the following statements regarding the marginal product curve is FALSE? 379) A) Increasing marginal returns occur only when the total product increases as the number of workers increases. B) Increasing marginal returns is due to greater efficiency from specialization in the production process. C) Along the marginal product curve, increasing marginal returns occur first and then diminishing marginal returns. D) The law of diminishing returns applies in the short run. 380) Total product divided by the total quantity of labor employed equals the 380) A) average product of labor. B) average variable cost. C) total cost. D) marginal product of labor. Labor (workers per day) Total product (pizzas per day) 0 0 1 10 2 25 3 37 4 45 5 50 381) Based on the production data for Pat's Pizza Parlor in the above table, which of the following pair of workers have the same average product? 381) A) 2 and 5 B) 1 and 2 C) 2 and 4 D) 1 and 5 382) If a firm's marginal product of labor is greater than its average product of labor, then an increase in the quantity of labor it employs definitely 382) A) increases its total product. B) decreases its average product of labor. C) oes not change its average product of labor. D) increases its marginal product of labor. 383) When the total product curve is drawn in a figure that measures employment along the horizontal axis, it is a graph that shows the 383) A) minimum cost of producing a given amount of output using different techniques. B) aximum output attainable for each quantity of labor employed. C) inimum output attainable for each quantity of labor employed. D) aximum profit attainable for each unit of output sold per unit of labor employed. 384) The law of diminishing returns makes it clear that as more a variable input is employed, in the ________ the marginal product of the variable input eventually will ________. 384) A) short run; rise B) short run; fall C) long run; rise D) long run; fall G.KAZARLabor (workers per day) Quantity (T shirts per day) 0 0 1 10 2 22 3 30 4 34 5 35 385) The table above shows some data that describe Tom's T-Shirts' total product when Tom has 1 sewing machine. An increase in the number of workers from 1 to 2 a day increases average product of labor from ________ T shirts per worker and marginal product of labor is ________ T shirts per worker. 385) A) 10 to 22; 12 B) 10 to 11; 22 C) 10 to 22; 22 D) 10 to 11; 12 386) In the figure above, the marginal product of the second worker is 386) A) 10 units. B) 1 units. C) 2 units. D) 5 units. G.KAZARLabor (workers) Total product (units) Marginal product Average product 0 0 1 3 2 4.5 3 14 4 3 5 19 6 1 387) The above (incomplete) table provides information about the relationships between labor and various product measures. The total product that can be produced with 6 units of labor is 387) A) 19. B) 20. C) More information is needed to answer the question. D) None of the above answers is correct. 388) In the above figure, the average product of labor at point c is 388) A) 2. B) 10. C) 5. D) None of the above answers is correct. 389) In the above figure, after the second worker is hired, the marginal product of labor is 389) A) constant. B) diminishing. C) increasing. D) zero. G.KAZARTotal Product, Marginal Product, Average Product Labor (workers per day) Total product (units per day) Marginal product Average product 0 0 0 0 1 2 2 2 2 8 3 12 4 15 5 16 1 390) In the above table, the marginal product of the third worker is 390) A) 1. B) 2. C) . D) 4. 391) The marginal product and average product curves 391) A) do not intersect at any predictable point. B) intersect at the maximum point of the average product curve. C) never intersect. D) intersect at the maximum point of the marginal product curve. 392) In the above figure, the most efficient way to produce 10 units is to hire 392) A) 5 workers. B) 2 workers. C) 1 worker. D) workers. G.KAZARLabor (workers) Total product (units per hour) 0 0 1 8 2 20 3 34 4 46 5 56 6 64 78 74 9 75 393) In the above table, diminishing marginal returns start to occur when the 393) A) 4th worker is employed. B) 5th worker is employed. C) 6th worker is employed. D) 3rd worker is employed. Labor (workers) Total product (units per day) 0 0 1 3 2 12 3 19 4 23 5 25 394) Using the data in the above table, if the firm employs 5 workers, total product (measured in units per day) and average product and marginal product of the fifth worker (measured in units per worker) are 394) A) 23, 5.00, and 4 respectively. B) 25, 5.75, and 4 respectively. C) D) 00, and 2 respectively. G.KAZARDecent Donuts Labor (workers) Total product (dozens of donuts per day) 0 0 1 12 2 26 3 44 4 64 5 86 6 110 7 122 8 125 9 127 10 128 395) Based on the data in the table above, when Decent Donuts hires eight workers, the 395) A) marginal product of labor is greater than the average product. B) equal to the average product. C) average product of labor is greater than the marginal product. D) marginal product of labor is not defined. 396) The law of diminishing returns implies that, with the quantity of capital fixed, as the use of labor rises, 396) A) total product will fall eventually. B) he total product of labor will fall below the marginal product of labor. C) marginal product of labor will fall eventually. D) production process will become technologically inefficient eventually. 397) Most total product curves have 397) A) output increasing at an increasing rate as labor is added. B) first increasing and then decreasing marginal returns to labor. C) output first increasing and then decreasing as labor is added. D) first decreasing and then increasing marginal returns to labor. 398) When the marginal and average products of labor are equal to each other, the 398) A) total product must be at its maximum value. B) average product must be at its maximum value. C) marginal product must be at its maximum value. D) None of the above answers is correct 399) The average product of labor is 399) A) the inverse of the average product of capital. B) slope of the curve showing the marginal product of labor. C) otal product divided by the total quantity of labor employed. D) he slope of the curve showing the total product of labor. 400) At that amount of output where diminishing marginal returns first sets in, 400) A) marginal product will begin to decline. B) average product will begin to decline. C) total product will begin to decline. D) ll of the above G.KAZARJefferson's Cleaners Labor (workers) Total product (suits cleaned per day) 0 0 1 12 2 26 3 46 4 60 5 73 6 84 7 94 8 102 9 109 401) Using the data in the above table, which worker hired at Jefferson's Cleaners is the first to show diminishing marginal returns? 401) A) the second B) the fourth C) the third D) the fifth Labor (workers) Total product (books sold per hour) 0 0 1 10 2 24 3 40 4 58 5 73 6 83 7 87 8 89 9 90 10 90 402) The above table shows the short-run total product schedule for the campus book store. With which employee do diminishing marginal returns set in? 402) A) the 2nd employee B) the 5th employee C) 9th employee D) 6th employee 403) In general, increasing marginal returns occur 403) A) as output expands at low levels of production. B) high levels of production. C) through the entire range of production. D) whenever the slope of the total product curve is positive. G.KAZAR404) The average product of labor is equal to the 404) A) total number of workers hired divided by the total product. B) product divided by the total number of workers hired. C) slope of the marginal product of labor curve. D) Both answers B and C are correct. Labor (workers) Total product (shirts) 0 0 1 50 2 120 3 180 4 220 5 250 405) The table above shows the short-run product schedule for Virginia's Tee-Shirts. The worker for whom the law of diminishing returns initially occurs is the ________ worker. 405) A) 3rd B) 2nd C) 5th D) 4th 406) At point e in the above figure, the marginal product of labor 406) A) equals the average product of labor. B) is less than the average product of labor. C) at its maximum. D) is greater than the average product of labor. G.KAZAR407) The law of diminishing returns states that as 407) A) a firm uses more of a variable input, given the quantity of fixed inputs, the firm's average total cost will decrease eventually. B) a firm uses more of a variable input, given the quantity of fixed inputs, the marginal product of the variable input eventually diminishes. C) the size of a plant increases, the firm's fixed cost increases. D) decreases. 408) The marginal product of labor is the increase in total product from a 408) A) one unit increase in the quantity of labor, while holding the quantity of other inputs constant. B) one percent increase in the wage rate, while also increasing the price of other inputs by one percent. C) one unit increase in the quantity of labor, while also increasing the quantity of other inputs by one unit. D) one dollar increase in the wage rate, while holding the price of other inputs constant. 409) A firm's total product curve shows 409) A) that in the long run the firm must adjust the quantity of all the resources it employs. B) how the cost of the fixed resources change when output changes. C) that inefficiency is not possible. D) how the amount of output changes when the quantity of labor changes. 410) When the average product of labor is greater than the marginal product of labor, 410) A) the average product of labor is decreasing as labor increases. B) marginal product of labor must be increasing as labor increases. C) re must be increasing marginal returns. D) None of the above answers is correct Output (T shirts per hour) Total cost (dollars) Total variable cost (dollars) 4 42 22 5 50 30 6 60 40 411) The table above gives the cost of producing T-shirts. The total fixed cost is ________ and the marginal cost of increasing production from 5 to 6 T shirts is ________. 411) A) $10.40; $8 B) $20; $6 C) unable to be determined; $8 D) $20; $10 412) Which of the following statements is correct? 412) A) As output increases, total cost increases and total fixed cost decreases. B) Total fixed cost plus total variable cost equals total cost. C) As output increases, total cost and total fixed cost increase but not necessarily by the same amount. D) As output increases, total cost and total fixed cost increase by the same amount. G.KAZARLabor (workers per week) Output (units per week) 0 0 1 20 2 50 3 70 4 85 5 95 6 100 413) The table above gives a firm's total product schedule. Suppose labor is the only variable factor of production. The price of labor is $500 per week and total fixed costs are $600 per week. What is the total cost of producing 70 units? 413) A) $2,100 B) $1,700 C) $2,300 D) $1,900 414) In the above figure, the relationship between costs indicates that the distance between curves 414) A) A and B is equal to the fixed cost. B) A and B is equal to the variable cost. C) B and C fixed cost. D) B and C average total cost. 415) Total fixed cost is the sum of all 415) A) the marginal costs of the different factors of production. B) costs associated with the production of goods. C) that rise as output increases. D) of the firm's fixed factors of production. G.KAZAROutput (pies) Total variable cost (dollars) Total cost (dollars) 0 0 300 100 400 200 1,000 300 1,800 400 2,800 416) The above table gives some of the costs of the Delicious Pie Company. What is the average variable cost of producing 300 pies? 416) A) $5 B) $1,800 C) $6 D) More information is needed to calculate the average variable cost. 417) Which of the following curves is not U-shaped? 417) A) average variable cost curve B) average total cost curve C) fixed cost curve D) marginal cost curve 418) In the figure above, curve A is the ________ curve. 418) A) average variable cost B) average total cost C) fixed cost D) marginal cost G.KAZARLabor (workers) Total product (books sold per hour) 0 0 1 10 2 24 3 40 4 58 5 73 6 83 7 87 8 89 9 90 10 90 419) The above table shows the total product schedule for the campus book store. If employees are paid $6 per hour and there are no other variable costs, then what is the marginal cost (MC) per book of increasing book sales from 83 to 87 books per hour? 419) A) $6.00 B) $2.07 C) $4.00 D) $1.50 Output (tents) Total fixed cost (dollars) Total variable cost (dollars) Total cost (dollars) 0 50 0 50 1 50 25 75 2 50 45 95 3 50 70 120 4 50 115 165 420) The above table shows some cost data for Tracey's Tents. What is the average total cost when output is 3? 420) A) $50 B) $40 C) $30 D) $120 G.KAZARQuantity (barrels of pickles) Total variable cost (dollars) 0 0 1 20 2 35 3 50 4 75 5 110 6 160 421) The above table gives some cost data for Peter's Pickles. Peter's fixed cost is $20. The average total cost (ATC) when 5 barrels of pickles are produced is 421) A) $35. B) $26. C) $22. D) There is not enough information to answer the question. 422) In the figure above, when 40 units are produced the average fixed cost is 422) A) $8. B) $12. C) $20. D) $4. 423) Marginal cost is the increase in total ________ that results from a one-unit increase in ________. 423) A) variable cost; the variable input B) cost; output C) fixed cost; the fixed input D) fixed cost; output G.KAZAR424) The marginal cost curve passes through the ________ points of the ________ cost curve and the ________ cost curve. 424) A) minimum; average total; average variable B) fixed C) variable; average fixed D) aximum; total cost; total variable Output (units) Total cost (dollars) Average variable cost (dollars) Marginal cost (dollars) 0 10 3 80 9 20 14 290 17 380 425) The above (incomplete) table provides information about the relationships between output and various cost measures. The marginal cost per unit when increasing output from 14 to 17 units is 425) A) $380. B) $20. C) $30. D) None of the above answers is correct. 426) In the above figure, the total fixed cost curve is curve 426) A) A. B) B. C) C. D) none of the curves in the figure 427) In the above figure, the total cost curve is curve 427) A) A. B) B. C) C. D) none of the curves in the figure G.KAZAR428) In the figure above, curve C is the ________ curve. 428) A) average variable cost B) marginal cost C) fixed cost D) total cost 429) Some of the cost curves for Ike's Ice Cream Kitchen are given in the above figure. At which of the following levels of output does the marginal product of labor equal the average product of labor? 429) A) at 60 gallons B) at 10 gallons C) at 40 gallons D) at 0 gallons G.KAZARLabor (workers per hour) Total product (baseball hats per hour) 0 0 1 4 2 10 3 18 4 25 5 30 430) The table above gives production information for Bob's Baseball Cap Company. Bob's total cost when zero caps are produced is $200 and workers cost $10 per hour. The marginal cost per hat of producing 30 hats per hour (instead of 25) is 430) A) $240.00 per hat. B) $8.33 per hat. C) $2.00 per hat. D) $250.00 per hat. Cost schedule Labor (workers) Output (units per day) Total variable cost (dollars) Total cost (dollars) 0 0 0 30 1 3 20 50 2 8 40 70 3 12 60 90 4 14 80 110 5 15 100 130 431) In the above table, the average total cost of producing 14 units of output is 431) A) $6.75. B) $5.71. C) $7.00. D) $7.86. 432) The vertical distance between a firm's total cost (TC) and its total variable cost (TVC) curves 432) A) is equal to the total fixed cost, TFC. B) decreases as output decreases. C) average variable cost, AVC. D) marginal cost, MC. G.KAZARDecent Donuts Labor (workers) Total product (dozens of donuts per day) 0 0 1 12 2 26 3 44 4 64 5 86 6 110 7 122 8 125 9 127 10 128 433) Use the data in the table above and suppose that labor is the only variable factor of production. When 122 dozen donuts are produced at Decent Donuts, the MC curve 433) A) shows the effect of increasing marginal returns. B) has a positive slope. C) Both answers A and B are correct. D) Neither answer A nor B is correct. Labor (workers per day) Output (units per day) 0 0 1 10 2 15 3 18 4 20 5 21 434) Cindy's Sweaters' production function is shown in the above table. Cindy rents two knitting machines for $30 a day each and hires workers at a wage rate of $40 a day. If Cindy produces 18 sweaters per day, what is her average total cost? 434) A) $10.00 B) $11.00 C) $13.33 D) $6.67 435) Which of the following shifts the AVC curve upward at Barney's Bagel Bakery? 435) A) an increase in the fixed amount of local property tax that Barney pays on the building he owns and uses B) an increase in the hourly wage that Barney pays his workers C) Barney's daily output from hiring more workers D) ll of the above G.KAZAR436) Fernando charges the restaurant Flaming Fernando's $1,000 annually for use of his name. If Fernando increases the fee for use of his name, 436) A) the restaurant's average fixed cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves shift upward. B) and average total cost curves shift upward. C) the restaurant's average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves shift upward. D) the restaurant's average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost curves all shift upward. 437) In the above figure, curve D slopes downward because 437) A) there are diminishing returns. B) all costs decrease as output increases. C) verage fixed costs decrease as output increases. D) there are decreasing marginal costs. 438) Increasing marginal returns means that as the firm expands its output, its 438) A) long-run average total cost decreases. B) short-run average total cost decreases. C) - increases. D) - increases. G.KAZARCost schedule Labor (workers) Output (units per day) Total variable cost (dollars) Total cost (dollars) 0 0 0 30 1 3 20 50 2 8 40 70 3 12 60 90 4 14 80 110 5 15 100 130 439) In the above table, the average fixed cost of producing 15 units of output is 439) A) $0.50. B) $2.00. C) $8.66. D) $6.66. 440) A firm's average total cost is $60, its average variable cost is $30, and its total fixed cost is $600. Its output is 440) A) 20 units. B) 30 units. C) 50 units. D) 40 units. 441) A firm's average variable cost is $60, its total fixed cost is $3,000, and its output is 600 units. Its average total cost is 441) A) more than $64. B) less than $58. C) between $58 and $62. D) between $62 and $64. 442) As output increases, marginal cost will eventually 442) A) decrease because of the law of diminishing returns. B) increase because of the law of diminishing returns. C) increasing returns. D) decrease because of the law of increasing returns. 443) If marginal cost is less than average total cost, then ________ is ________. 443) A) marginal cost; rising B) marginal cost; falling C) average total cost; falling D) average variable cost; falling Labor (workers per day) Output (units per day) 0 0 1 10 2 15 3 18 4 20 5 21 444) Cindy's Sweaters' production function is shown in the above table. Cindy rents two knitting machines for $30 a day each and hires workers at a wage rate of $40 a day. If Cindy produces 20 sweaters per day, what is her average fixed cost of production? 444) A) $8.00 B) $3.33 C) $3.00 D) $11.00 G.KAZAR445) Marginal cost ________ as the quantity produced is increased. 445) A) always decreases B) first decreases and then increases C) increases D) increases and then decreases 446) A company could produce 100 units of a good for $320 or produce 101 units of the same good for $324. The $4 difference in costs is 446) A) the marginal cost of producing the 101st unit. B) neither the marginal benefit nor the marginal cost of producing the 101st unit. C) the marginal benefit of producing the 101st unit. D) both the marginal benefit and the marginal cost of producing the 101st unit. Output (pies) Total variable cost (dollars) Total cost (dollars) 0 0 300 100 400 200 1,000 300 1,800 400 2,800 447) The above table gives some of the costs of the Delicious Pie Company. What is the total fixed cost of producing 100 pies? 447) A) $300 B) $700 C) $400 D) More information is needed to calculate the total fixed cost. Labor (workers) Output (units) Total fixed cost, TFC (dollars) Total variable cost, TVC (dollars) Total cost, TC (dollars) 0 0 20 0 20 1 4 20 25 45 2 9 20 50 70 3 13 20 75 95 4 16 20 100 120 5 18 20 125 145 448) Using the data in the above table, when the firm increases its output from 4 to 9 units, the marginal cost of a unit is 448) A) $6.00 a unit. B) $5.00 a unit. C) $4.00 a unit. D) $7.00 a unit. G.KAZARLabor (workers) Output (frijoles) Total cost (dollars) 0 0 1,000 5 1000 3,000 10 3000 5,000 15 4000 7,000 20 4500 9,000 449) The above table gives some production and cost information for Flaming Fernando's, a restaurant that sells Fiery Frijoles. What is the average total cost of producing 4,500 frijoles? 449) A) $9000 B) $2 C) $225 D) More information is needed to determine the answer. 450) The above table gives some production and cost information for Flaming Fernando's, a restaurant that sells Fiery Frijoles. What is the average variable cost of producing 1,000 frijoles? 450) A) $3 B) $2 C) $1 D) More information is needed to determine the answer. G.KAZARAnswer Key Testname: UNTITLED1 [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 137 pages
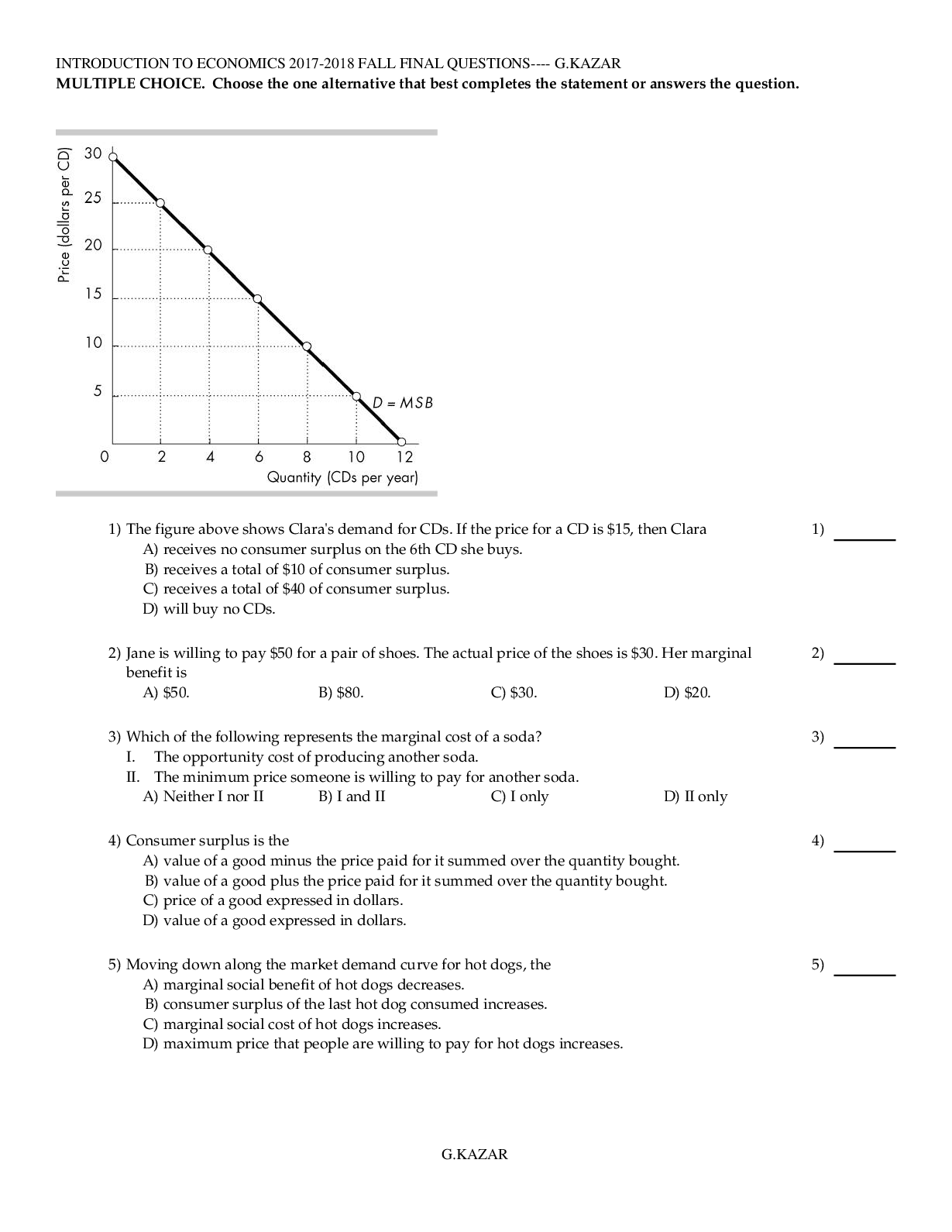
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 16, 2020
Number of pages
137
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 16, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
154



















.png)
.png)
.png)

