Medical Studies > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Ultimate Medical Academy, Tampa - MEDICAL BI 2020-Surgery-II. Contains 201 Questions, (MCQ), And Cli (All)
Ultimate Medical Academy, Tampa - MEDICAL BI 2020-Surgery-II. Contains 201 Questions, (MCQ), And Clinical Summaries WIth Descriptions of Procudures. Answers Provided at the end of the document.
Document Content and Description Below
2020 Surgery Section Part II Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What is the symptomatic term for hives? a. Rash c. Urticaria... b. Eruption d. Dermatitis ____ 2. Melanin is found in what layer of the epidermis? a. Epithelium c. Dermal b. Squamous d. Basal ____ 3. What term relates to the connecting of the skin to the underlying muscles? a. Dermis c. Hypodermis b. Epidermis d. Sebaceous ____ 4. What term best describes a mass of hyperplastic scar tissue? a. Keliod c. Dermatofibroma b. Pilonidal Cyst d. Congenital nevus ____ 5. What is commonly known as a boil of the skin? a. Abscess c. Carbuncle b. Furuncle d. Impetigo ____ 6. What are the layers of the skin? a. Epidermis and Dermis b. Epidermis, Dermis and Fascia c. Epidermis, Dermis, Subcutaneous Tissue and Fascia d. Epidermis and Fascia ____ 7. What is the correct diagnostic code to report for treatment of a melanoma in-situ of the left arm? a. 173.6 c. 172.6 b. 232.6 d. 238.2 ____ 8. A patient is taken to surgery for the removal of a squamous cell carcinoma of the right thigh. Pathology indicated that this carcinoma is a metastasis of a previous squamous cell carcinoma of the trunk. What is the correct diagnostic code for today’s procedure? a. 173.7 c. 198.5 b. 198.2 d. 173.5 ____ 9. What would be the correct diagnostic code to report an open wound of the right leg related to a non-healing operative wound of squamous cell carcinoma? a. 173.7 c. 890.0 b. 998.59 d. V10.83 ____ 10. A patient presented to the office with a suspicious lesion of the nose. The physician took a biopsy of the lesion and pathology determined the lesion to be a dysplastic nevus. What is the correct diagnosis code to report? a. 173.3 c. 239.2 b. 216.3 d. 238.2 ____ 11. Joe has a terrible problem with ingrown toenails. He goes to the podiatrist to have a nail removed along with the nail matrix. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 11730 c. 11752 b. 11750 d. 11720 ____ 12. What CPT® code(s) would best describe the treatment of 9 plantar warts removed and 6 flat warts all destroyed with cryosurgery during the same office visit? a. 17110, 17111-52 c. 17110, 17003 b. 17110 d. 17111 ____ 13. What CPT® code(s) describe the destruction of 16 lesions using cryosurgery to the upper torso on a patient diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum? a. 17000, 17003 x 2 c. 17004 b. 17110, 17003 d. 17111 ____ 14. While whittling a piece of wood, the patient sustained an avulsion injury to a portion of his left index finger and underwent formation of a direct pedicle graft with transfer from his left middle finger. Immobilization was accomplished with a plaster splint. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 15574 c. 15750 b. 15740 d. 15758 ____ 15. A patient presents to the physician with multiple burns. After examination the physician determines the patient has 3rd degree burns of the anterior portion of his left leg, below the knee extending to the foot (4.5%). He also has 3rd degree burns of the anterior portion of the left side of his chest (4.5%). The patient has 2nd degree burns of the posterior portion of his back and left arm (13.5%). What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 945.29, 945.19, 948.31 b. 942.34, 945.31, 948.31 c. 945.10, 945.13, 942.12, 943.30, 942.24, 948.31 d. 945.39, 942.32, 942.24, 943.20, 948.20 ____ 16. A patient presents to the physician to discuss their acne and ask the physician about a suspicious lesion of their left ear. The patient and physician discuss further treatment of the acne and agree to take a biopsy of the lesion of the ear. Billing was sent prior to receiving the pathology report. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 706.1, 238.2 c. 706.1, 239.2 b. 706.1 d. 706.1, 173.2 ____ 17. The patient is here to see us in follow-up for a keloid that was excised from his neck in November of last year. He believes that it’s coming back. He does have a recurrence of the keloid on the superior portion of the scar. Since the keloid is still small, the options of an injection or radiation to the area were discussed.It was agreed that our next course should be a Kenalog injection. The risks associated with the procedure were discussed with the patient. Informed consent was obtained. The area was infiltrated with 1.5 cc of medication. This was a mixture of 1 cc of 40-mg Kenalog and 0.5 cc of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine. He tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 11900, 11901 x 7, J3301, 706.1 c. 11901, J3301, 701.4 b. 11900, J3301, 701.4 d. 11901 x 8, J3301, 238.2 ____ 18. A patient presents with a recurrent seborrheic keratosis of the left cheek. The area was marked for a shave removal. The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic, prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. The lesion measuring 1.8 cm was shaved using an 11-blade. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using light pressure. The specimen was sent for permanent pathology. The patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 11200 c. 11442 b. 11312 d. 11642 ____ 19. The patient has a suspicious lesion of the left jaw line. Clinical diagnosis of this lesion is unknown, but due to the appearance malignancy is a realistic concern. The lesion was excised into the subcutaneous fat measuring .8 cm and margins of .1 cm on each side. Hemostasis was achieved using light pressure. The wound was closed in layers using 5.0 monocryl and 6.0 Prolene. Pathology revealed this lesion to be a benign nevus with clear margins. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 13131, 11441-51, 173.3 c. 12051, 11441-51, 216.3 b. 13131, 11441-51, 172.3 d. 12051, 11641-51, 216.3 ____ 20. Patient has a suspicious lesion of the right axilla. The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic and prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. With the use of a 3 mm punch tool the lesion was excised and closed with 5.0 Prolene suture. Pathology report indicated this was a seborrheic keratosis. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 11100, 702.19 c. 11400, 702.11 b. 11400, 702.19 d. 11100, 702.11 ____ 21. The patient is here to see us about some skin tags of her neck and both underarms. She has had these lesions for some time and they are irritated by her clothing, they itch and at times have burning sensation to them. We discussed the treatments options along with the risks. Informed consent was obtained and we proceeded. We removed 16 skin tags from the right axilla, 16 skin tags from the left axilla, 10 from the right neck and 17 from the left neck. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 11057, 216.5, 216.4 c. 11200, 11201 x 4, 11201-52, 701.9 b. 11200, 216.5, 216.4 d. 11200, 11201 x 5, 701.9 ____ 22. Patient presents to the physician for the removal of a squamous cell carcinoma of the right cheek. After the area being prepped and draped in a sterile fashion the surgeon measured the lesion, documenting the size of the lesion to be 2.3 cm in its’ largest diameter, additional the physician took margins of 2mm on each side of the lesion. The patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 11642, 12013 c. 11643, 12013 b. 11643 d. 11442 ____ 23. Patient is diagnosed with actinic keratosis of the chest and arms, presents to her physician office for the destruction of these lesions. Using cryosurgery the physician destroys 7 lesions on the right arm, 4 lesions on the left forearm and 8 lesions on the chest. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 17000, 17003 x 18, 239.2 c. 17004, 702.0 b. 17003 x 19, 238.2 d. 17000, 17003 x13, 17004, 702.0 ____ 24. The patient is diagnosed with superficial basal cell carcinoma of the neck and cheek. After discussion with the physician about different treatment options the patient decides to have these lesions destroyed using cryosurgery. Consent is obtained and the areas are prepped in a sterile fashion. With the use of cryosurgery the physician destroys the lesion on the neck measuring 2.3 cm and the lesion on the cheek measuring 0.8 cm. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 17272, 17281-51 c. 17273, 17281-51, 11623-51, 11641-51 b. 17273, 17281-51 d. 11623, 11641-51 ____ 25. Patient is a 69-year-old woman with a biopsy proved squamous cell carcinoma of her left forearm measuring 2.3 cm in greatest diameter. The area was marked with 4 mm gross normal margins. This area was removed as drawn, and the surgeon then incised his planned rhomboid flap, elevating the full-thickness flap into the defect and closing the sites in layers using 3-0 Monocryl, 4-0 Monocryl and 5-0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedure well. Final measurements were 2.7 cm x 2.1 cm. a. 14020 c. 13101, 11603-51 b. 14020, 11603-51 d. 15100, 11603-51 ____ 26. A 50-year-old female has telangiectasias of the face on both cheeks. She is very bothered by this and presents to have them destroyed via laser. The physician lasers 2 lesions on each cheek. a. 17106 c. 17000, 17003 b. 17110 d. 17263 ____ 27. Meredith has breast cancer on the left side, diagnosed with an excisional biopsy last week. Today she is having a radical mastectomy, Urban type, and concurrently a single pedicle TRAM flap reconstruction with supercharging. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 19367-LT, 19307-LT, 51-LT c. 19368-LT, 19306-51-LT b. 19305-LT, 19367-51-LT, 19368-51-LT d. 19367-LT, 19302-51-LT ____ 28. A 14-year-old boy was thrown against the window of the car on impact. The resulting injury was a star shaped pattern cut into the top of his head. On presentation to the ED, the MD on call for plastic surgery was asked to evaluate the injury and repair it. The surgeon performed an expanded problem focused H&P. Medical Decision Making was moderate. The total length of the intermediate repair was 5+ 4+ 4+ 5 cm. The star like shape allowed the surgeon to pull the wound edges together nicely in a natural Y plasty in two spots. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for the repair? a. 14041 c. 13121 b. 14040 d. 12035 ____ 29. A 63-year-old patient arrives for skin tag removal. As previously noted in her other visit, she has 3 located on her face, 4 on her shoulder and 15 on her back. The physician removes all the skin tags with no complications. What is the appropriate CPT® code(s) for this encounter? a. 11201 c. 11200, 11201-52 b. 11201, 11201-51 d. 11200, 11201 ____ 30. A 45-year-old male with a previous biopsy positive for malignant melanoma, presents for definitive excision of the lesion. After induction of general anesthesia the patient is placed supine on the OR table, the left thigh was prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. IV antibiotics are given as patient had previous MRSA infection. The previous excisional biopsy site on the left knee had measured approximately 4 cm and was widely elipsed with a 1.5 cm margin.. The excision was taken down to the underlying patellar fascia. Hemostasis was achieved via electrocautery. The resulting defect was 11cm x 5cm. Wide advancement flaps were created inferiorly and superiorly using electrocautery. This allowed the skin edges to come together without tension. The wound was closed using interrupted 2-0 monocryl and 2 retention sutures were placed using #1 Prolene. Skin was closed with a stapler. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 27328 c. 14301, 27328-51 b. 14301 d. 15738, 11606-51 ____ 31. Patient is an 81-year-old male with a biopsy proven basal cell carcinoma of this posterior neck just near his hairline; additionally the patient had two additional areas of concern on his cheek. Informed consent was obtained and the areas were prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. Attention was first directed to the basal cell carcinoma of the neck, I excised the lesion measuring 2.6 cm as drawn down to the subcutaneous fat. With extensive undermining of the wound I closed in layers using 4.0 monocryl, 5.0 Prolene and 6.0 Prolene; the wound measured 4.5cm. Attention was then directed to the other two suspicious lesions on his cheek; after administering local anesthesia I proceeded to take a 3mm punch biopsy of each lesion and was able to close with 5.0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedures well. Pathology later showed the basal cell carcinoma was completely removed and the biopsies indicated actinic keratosis. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 13132, 11623-51, 11100-59, 11101 c. 12042, 11623-51, 11100-59, 11101 b. 13131, 11622-51, 11100-59, 11100-59 d. 13132, 11623-51, 11440-51, 11440-51 ____ 32. Patient is a 53-year-old female who yesterday underwent Mohs surgery with Dr. Smith to remove basal cell carcinoma of her scalp. Due to the size of the defect Dr. Smith requested a Plastic Surgeon to reconstruct the site. Dr. Jones discussed with the patient his planned closure which was a Ying-Yang type flap. The patient agreed and we proceeded. The area was prepped and draped in a sterile fashion being careful to keep the betadine solution out of the open wound. Wound preparation was done by excising an additional 1 mm margin to freshen the wound and excising the wound deep sting superficial to the galea. Starting on the right Dr. Jones incised his planned flap, elevating the flap with full-thickness and subcutaneous fat, staying superior to the galea; then Dr. Jones incised his planned flap on the left elevating the flap with full-thickness and subcutaneous fat. Both flaps were rotated together and the wound was temporarily closed using the skin stapler. Once it was determined that there was minimal tension on the wound; the galea was approximated using 4.0 Monocryl. The wound was then closed in layers using 5-0 Monocryl and a 35R skin stapler. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved through-out the procedure with the Bovie cautery. Final measurements of the wound were 36.25 cm squared. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 14021-22 c. 14301 b. 14021, 15004-51 d. 14301, 15004-51 ____ 33. Patient presents to the emergency department with multiple lacerations due to a knife fight at the local bar. After examination it was determined that these lacerations could be closed using local anesthesia. The areas were prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. The surgeon documented the following closures; 7.6 cm simple closure of the right forearm; 5.7 intermediate closure of the upper right arm; 6.5 simple closure of the right wrist; 4.7 complex closure of the right neck; 10.3 intermediate closure of the upper chest; 8.9 cm intermediate closure of the right abdominal area; 4.2 complex closure of the right ear and 3.9 intermediate closure of the right cheek. a. 13152, 13132, 12036, 12052, 12005 b. 13132, 13131, 12052, 12034, 12034, 12002, 12032, 12004 c. 13132, 13152, 12047 d. 13152, 13131, 12036, 12004 ____ 34. Patient presents to the operative suite with a biopsy proven squamous cell carcinoma of the left ankle. A decision was made to remove the lesion and apply a split thickness skin graft on the site. The lesion was excised as drawn and documented as measuring 2.4 cm with margins. Using the Padgett dermatone the surgeon harvested a split-thickness skin graft from the left thigh, which was meshed 1.5 x 1 and then inset into the ankle wound using a skin stapler. Xeroform bolster was then placed of the skin graft using Xeroform and 4-0 nylon and the lower extremity were wrapped with bulky cast padding and double Ace wrap. The skin graft donor site was dressed with OpSite. The surgeon noted the skin graft measured 4.0 cm squared in total. a. 15100, 11603-51, 173.7 c. 15120, 13100-51, 216.7 b. 15100, 173.7 d. 15240, 11603-51, 173.7 ____ 35. Patient presents with a suspicious lesion on her left arm. With the patient’s permission the physician marked the area for excision. The lesion measured 0.9 cm. The wound measuring 1.2 cm was closed in layers using 4-0 Monocryl and 5-0 Prolene. Pathology later reported the lesion to be a sebaceous cyst. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 11401, 216.6 c. 13121, 11401-51, 216.6 b. 12031, 11401-51, 706.2 d. 11402, 706.2 ____ 36. Operative Report: Pre-Operative Diagnoses: Basal Cell Carcinoma, forehead Basal Cell Carcinoma, right cheek Suspicious lesion , left nose Suspicious lesion, left forehead Post-Operative Diagnoses: Basal Cell Carcinoma, forehead with clear margins Basal Cell Carcinoma, right cheek with clear margins Compound nevus, left nose with clear margins Epidermal nevus, left forehead with clear margins INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 47-year-old white man with a biopsy-proven basal cell carcinoma of his forehead and a biopsy-proven basal cell carcinoma of his right cheek. We were not quite sure of the patient’s location of the basal cell carcinoma of the forehead whether it was a midline lesion or lesion to the left. We felt stronger about the midline lesion, so we marked the area for elliptical excision in relaxed skin tension lines of his forehead with gross normal margins of 1-2 mm and I marked the lesion of the left forehead for biopsy. He also had lesion of his left alar crease that we marked for biopsy and then a large basal cell carcinoma of his right cheek, which was more obvious. This was marked for elliptical excision with gross normal margins of 2-3 mm in the relaxed skin tension lines of his face. I also drew a possible rhomboid flap that we would use if the wound became larger. He observed all these margins in the mirror, so he could understand the surgery and agree on the locations, and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: All four areas were infiltrated with local anesthetic. The face prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I excised the lesion of the forehead measuring 6-mm and right cheek measuring 1.3 cm as I had drawn them and sent in for frozen section. The biopsies were taken of the left forehead and left nose using a 2-mm punch, and these wounds were closed with 6-0 Prolene. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved of those wounds using Bovie cautery. I closed the cheek wound first. Defects were created at each end of the wound to facilitate primary closure and because of this I considered a complex repair and the wound was closed in layers using 4-0 Monocryl, 5-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene, with total measurement of 2.1 cm. The forehead wound was closed in layers using 5-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene, with total measurement of 1.0 cm. Loupe magnification was used and the patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 13121, 12051-51, 11642-51, 11640-51, 11100-58, 11100, 173.3, 232.3, 238.2, 216.3 b. 13131, 12051-51, 11642-51, 11641-51, 11100-59, 11101, 173.3, 216.3 c. 13131, 12052-51, 11442-51, 11440-51, 11100-59, 11101, 173.2, 173.4, 216.2, 216.3 d. 12053, 11643-51, 11100-58, 11101, 172.3, 173.3, 238.2, 239.2 ____ 37. Operative Report Pre-Operative and Post-Operative Diagnosis: Squamous cell carcinoma, left leg Open wound, right leg Personal history of squamous cell carcinoma, right leg INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is an 81-year-old white man with a biopsy-proven squamous cell carcinoma of his left leg. I marked the areas for excision with gross normal margins of 5 mm, and I drew my planned skin graft donor site from his left lateral thigh. He also had an open wound of his right leg from a squamous cell carcinoma I had excised four months ago and the skin graft had not taken. So we plan on re-skin grafting that area. The patient is aware of all of these markings, and he understood the surgery and the location, and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The patient was taken to the operating room. IV Ancef was given. I used plain lidocaine for his local anesthetic throughout the procedure until the skin grafts were inset. The anterior of his leg and the thigh were infiltrated with local anesthetic. Both upper extremities were prepped and draped circumferentially, which included the left thigh on the left side. I excised the lesion of his left leg as drawn into the subcutaneous fat. Hemostasis achieved with the Bovie cautery. I then excised the wound of his right leg to lower the bacterial counts. I took a 1-2 mm margin around the wound and excised the granulation tissue as well. Hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. I then changed gloves. A split-thickness skin graft was harvested from the left thigh using the Zimmer dermatome. This was meshed one and a half times one. By this time, the pathology had returned showing that the margins were clear. The skin grafts were inset on each leg wound using the skin stapler. Xeroform and gauze bolster was placed over the skin graft using 4-0 nylon. The skin graft donor site was dressed with OpSite. The legs were further dressed with heavy cast padding and the double Ace wrap. The patient tolerated the procedure well. PROCEDURES: Excision squamous cell carcinoma, left leg with excised diameter of 2.5 cm, repaired with a split-thickness skin graft measuring 5.1 cm squared. Excisional preparation of right leg wound repaired with a split-thickness skin graft measuring 3.2 cm squared. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 15100, 11603, 15002, 173.7, 996.52, V10.83 b. 15100-RT, 15100-LT, 11603, 15002, 173.7, 996.52, V10.83 c. 15100-LT, 11403, 15100-RT, 173.7, V10.82 d. 15100-50, 11603, 890.0, 173.7, 996.52 ____ 38. The patient is seen in follow-up for the excision of the basal cell carcinoma of his nose. I examined his nose noting the wound has healed well. His pathology showed that the margins were clear. He has a mass of his forehead that he says is from a piece of sheet metal that injured his forehead. He has an x-ray print that shows a foreign body, so we have offered to remove that. After obtaining consent we proceeded. The area was infiltrated with a local anesthetic. I had drawn for him how I would incise over the foreign body. He observed this in the mirror so he could understand the surgery and agree on the location. I incised a thin ellipse over the mass to give me better access to it and then the mass was removed. There was a capsule around this, what appeared to be a black-colored metal that was stained, and I felt that could potentially cause a permanent black mark on his forehead, so I offered to excise that and he wanted me to do so, so I went ahead and removed the capsule with the stain and that removed all the black stain that I could see, because of this I consider this to be a complicated procedure. Hemostasis was achieved with light pressure. The wound was closed in layers using 4-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 10121, 709.4, V90.10 c. 10121, 729.6, V90.10 b. 11010, 709.4, V90.10 d. 11010, 729.6, V90.10 ____ 39. The patient is here because the cyst of her chest has sort of come to a head and is still painful even though she has been on antibiotics for a week. I offered to drain that for her. After obtaining consent, we infiltrated the area with 1 cc of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine, prepped the area with Betadine and opened the cyst in the relaxed skin tension lines of her chest, and removed the cystic material. There was no obvious purulence. We are going to have her clean this with a little Q-tip. We will let that heal on its own and eventually excise it. I will have her come back a week from Tuesday and we are going to reschedule her surgery. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 10040, 706.1 c. 10061, 706.2 b. 10060, 706.2 d. 10160, 996.54 ____ 40. The patient is here in follow-up for the left capsulectomy. She had developed a seroma. It has been present for about a week. It has been about the same volume. It does not hurt her any. She has not had any fever. She has not had any trouble breathing. PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: On examination she does have a seroma present and I have offered to aspirate the area. I have told her that we usually try this for a few times and then if it has not resolved, usually we give up and let it resolve on its own. One of the risks in doing this is pneumothorax, so we do not want to push it too hard. We prepped her left chest with Betadine and with a 16-gauge needle sterilely aspirated 60 cc of serosanguinous fluid. It was not cloudy at all. She had no trouble with her procedure and no difficulty breathing. We are going to see her next week. She has asked if she can go ahead and be fitted for a prosthesis and I am going to give her a prescription for one as long as she does not have the seroma when she goes to get fitted I think it is fine. She is going to try to get a Spandex-type top to get some compression to the area. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for the procedure? a. 10160-78, 998.13 c. 10140-78, 906.3 b. 10180-58, 998.12 d. 10140-58, 729.91 ____ 41. Operative Report PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Basosquamous cell carcinoma, scalp. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Basosquamous cell carcinoma, scalp. PROCEDURE PERFORMED: Excision of basosquamous cell carcinoma, scalp with Yin-Yang flap repair ANESTHESIA: Local, using 4 cc of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine. COMPLICATIONS: None. ESTIMATED BLOOD LOSS: Less than 5 cc. SPECIMENS: Basosquamous cell carcinoma, scalp sutured at 12 o’clock, anterior tip INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 43-year-old white man with a biopsy-proven basosquamous cell carcinoma of his scalp measuring 2.1 cm. I marked the area for excision with gross normal margins of 4 mm and I drew my planned Yin-Yang flap closure. The patient observed these markings in two mirrors, so he can understand the surgery and agreed on the location and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic. The patient was placed prone, his scalp and face were prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I excised the lesion as drawn to include the galea. Hemostasis was achieved with the Bovie cautery. Pathologic analysis showed the margins to be clear. I incised the Yin-Yang flaps and elevated them with the underlying galea. Hemostasis was achieved in the donor site using Bovie cautery. The flap rotated into the defect with total measurements of 2.9 cm x 3.2 cm. The donor sites were closed and the flaps inset in layers using 4-0 Monocryl and the skin stapler. Loupe magnification was used. The patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 14060, 172.3 c. 14041, 172.4 b. 14040, 173.4 d. 14020, 173.4 ____ 42. The patient is coming in for removal of fatty tissue of the posterior iliac crest, abdomen, and the medial lateral thighs. Suction-assisted lipectomy was then undertaken in the left posterior iliac crest area and this was continued on the right and then the lateral trochanteric and posterior aspect of the medial thighs. The medial thighs were suctioned followed by the abdomen. The total amount infused was 2300 cc and the total amount removed was 2400 cc. The incisions were closed and a compression garment was applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 15830, 15832 c. 15830, 15839, 15847 b. 15877, 15879 d. 15877, 15878 ____ 43. Operative Report PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Diabetic foot ulceration. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Diabetic foot ulceration. OPERATION PERFORMED: Debridement and split thickness autografting of left foot ANESTHESIA: General endotracheal. INDICATIONS FOR PROCEDURE: This patient with multiple complications from Type II diabetes has developed ulcerations which were debrided and homografted last week. The homograft is taking quite nicely, the wounds appear to be fairly clean; he is ready for autografting. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: After informed consent the patient is brought to the operating room and placed in the supine position on the operating table. Anesthetic monitoring was instituted, internal anesthesia was induced. The left lower extremity is prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. Staples were removed and the homograft was debrided from the surface of the wounds. One wound appeared to have healed; the remaining two appeared to be relatively clean. We debrided this sharply with good bleeding in all areas. Hemostasis was achieved with pressure, Bovie cautery, and warm saline soaked sponges. With good hemostasis a donor site was then obtained on the left anterior thigh, measuring less than 100 cm2. The wounds were then grafted with a split-thickness autograft that was harvested with a patch of Brown dermatome set at 12,000 of an inch thick. This was meshed 1.5:1. The donor site was infiltrated with bupivacaine and dressed. The skin graft was then applied over the wound, measured approximately 60 cm2 in dimension on the left foot. This was secured into place with skin staples and was then dressed with Acticoat 18's, Kerlix incorporating a catheter, and gel pad. The patient tolerated the procedure well. The right foot was redressed with skin lubricant sterile gauze and Ace wrap. Anesthesia was reversed. The patient was brought back to the ICU in satisfactory condition. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 15220-58, 15004-58, 707.15, 250.80 b. 15120-58, 15004-58, 250.80, 707.15 c. 15950-78, 15004-78, 250.00, 707.14 d. 11044-78, 15120-78, 15004-78, 250.80, 707.15 ____ 44. Operative Report Diagnosis: Basal Cell Carcinoma Procedure: Mohs micrographic excision of skin cancer. Site: face left lateral canthus eyelid Pre-operative size: 0.8 cm Indications for surgery: Area of high recurrence, Area of functional and/or cosmetic importance Discussed procedure including alternative therapy, expectations, complications, and the possibility of a larger or deeper defect than expected requiring significant reconstruction. Patient’s questions were answered. Local anesthesia 1:1 marcaine and 1% lidocaine with epinephrine. Sterile prep and drape. Stage 1: The clinically apparent lesion was marked out with a small rim of normal appearing tissue and excised down to subcutaneous fat level with a defect size of 1.2 cm. Hemostasis obtained and a pressure bandage placed. The tissue was sent for slide preparation. Review of the slides show clear margins for the site. Repair: Complex repair. Repair of Mohs micrographic surgical defect. Wound margins were extensively undermined in order to mobilize tissue for closure. Hemostasis was achieved. Repair length 3.4 cm. Narrative: Burrows triangles removed anteriorly (medial) and posteriorly (lateral). A layered closure was performed. Multiple buried absorable sutures were placed to reappose deep fat. The epidermis and dermis were reapposed using monofilament sutures. There were no complications; the patient tolerated the procedure well. Post-procedure expectations (including discomfort management), wound care and activity restrictions were reviewed. Written Instructions with urgent contact numbers given, Follow-up visit and suture removal in 3-5 days What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 13152, 11642-51, 173.3 c. 17313, 13152-51, 173.1 b. 17311, 17312, 13152-51, 173.3 d. 17311, 13152-51, 173.1 ____ 45. PREOPERATIVE & POSTOPERATIAVE DIAGNOSES: 1. Macromastia. 2. Back pain. 3. Neck pain. 4. Shoulder pain. 5. Shoulder grooving 6. Intertrigo. NAME OF PROCEDURE: 1. Right breast reduction of 1950 g. 2. Right free-nipple graft. 3. Left breast reduction of 1915 g. 4. Left free-nipple graft. INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 43-year-old female with macromastia and associated back pain, neck pain, shoulder pain, shoulder grooving and intertrigo. She desired a breast reduction. Because of the extreme ptotic nature of her breasts, we felt that she would need a free-nipple graft technique. In the preoperative holding area, we marked her for this free-nipple graft technique of breast reduction. The patient observed these markings so she could understand the surgery and agree on the location, and we proceeded. The patient also was morbidly obese with a body mass index of 54. Because of this, we felt that she met the criteria for DVT prophylaxis, which included Lovenox injection. The patient understood that this would increase her risk of bleeding. She also made it known that she is a Jehovah's Witness and refused blood products, but she did understand that her risk of bleeding would significantly increase and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The patient was given 40 mg of subcu Lovenox in the preoperative holding area. She was then taken to the operating room. Bilateral thigh-high TED hose, in addition to bilateral pneumatic compression stockings throughout the procedure. IV Ancef 1 g was given. Anesthesia was induced. Both arms were secured on padded arm boards using Kerlix rolls. A similar body bear hugger was placed. The chest and abdomen were prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I began by circumscribing around each nipple-areolar complex using a 42-mm areolar marker. On each side the free-nipple grafts were harvested. They were marked to be side specific and they were stored on the back table in moistened lap sponges. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using Bovie cautery. The tail of the apex of each breast was then deepithelialized using the scalpel. I then amputated the inferior portion of the breast from the right side. Again, meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. There were also large feeder vessels that were divided and ligated using either a medium Ligaclip or 3-0 silk tie sutures. I then moved to the left and again amputated the inferior portion of the breast. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. Each of these wounds were then temporarily closed using the skin stapler. The patient was then sat up. I felt that we had achieved a very symmetrical result. The new positions for the nipple-areolar complexes was marked with a 42-mm areolar marker and methylene blue. The patient was then placed in the supine position and the new positions for the nipple-areolar complexes were deepithelialized using the scalpel. Meticulous hemostasis was then achieved again using the Bovie cautery. The free-nipple grafts were then retrieved from the back table. They were each defatted using scissors and they were placed in an onlay fashion on the appropriate side, and each were inset using 5-0 plain sutures. Vents were made in the skin graft to allow for the egress of fluid on each side, and then a vertical mattress suture was used tied over a piece of Xeroform in critical areas of each of the nipple-areolar complexes. A Xeroform bolster wrapped over a mineral oil-moistened sponge was affixed to each of the nipple-areolar complexes using 5-0 nylon suture. The vertical and transverse incisions were then closed using 3-0 Monocryl, both interrupted and running suture, and 5-0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedure well. Again, meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. She was then given another 1 g of Ancef at the 2-hour mark by our anesthesiologist, and she was taken to the recovery room in good condition. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 19316-50, 19355-59, 50 c. 19318-50, 19355-59, 50 b. 19318-50, 19350-59, 50 d. 19340-50, 19350-59, 50 ____ 46. Operative Report PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Congenital left breast deformity. POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Congenital left breast deformity. PROCEDURE PERFORMED: Placement of left breast implant using mentor catalog #, lot #, serial #, 425 cc smooth round moderate profile implant filled with 475 cc of normal saline for breast reconstruction. INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is a 34-year-old female who approximately 15 to 16 years ago had a left breast implant placed for breast reconstruction for her congenitally underdeveloped left breast. This implant ruptured and in late September 2008, I performed a capsulectomy and exchanged her ruptured implant for a new implant. About a week after surgery, the patient developed an infection and because of that infection, her implant had to be removed. The patient’s infection has completely resolved and she is now ready to have her implant replaced. In the preoperative holding area, I marked her for the ideal position of this implant and performed a breast exam that did not show that there was no mass in either breast and no mass in axillae and we proceeded. We did discuss with the patient that even though her original implant was placed in subglandular position I felt that it would be beneficial to place the implant behind her pectoralis major muscle that is in submuscular position today and the patient agreed on this and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The patient was given 1 g of IV vancomycin. The patient was taken to the operating room; general anesthesia was induced bilateral pneumatic compression stockings were worn throughout the procedure. A lower body Bair Hugger was placed. Both arms were secured to padded armboard using Kerlix roll. The neck, chest, axillae, and upper abdomen were prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I began by incising the central portion of her previous scar. I then dissected down to the pectoralis major muscle. A submuscular plane was developed through a lateral approach and the inferior and medial origin of the muscle was partially divided using the Bovie cautery. Meticulous hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. There were no signs of infection nor were there any pockets of seroma fluid or hematoma. The wound was carefully inspected. Meticulous hemostasis had been achieved. Gloves were then changed. The implant was opened. The air was evacuated. It was placed in the submuscular pocket and the wound was temporarily closed using a skin stapler. The implant was then filled to its maximum volume and that was 475 cc of normal saline. The patient was then sat up. I then adjusted the volume and ultimately did feel that she needed a 475 cc for the breast symmetry with her contralateral breast. Once I was satisfied with the position of the implant, the patient was then placed supine. Gloves were changed again. The fill tube was removed and I then secured the filled valves digitally and the deepest layer of breast tissue was closed using 3-0 Vicryl in running suture and the skin was closed in three layers using 4-0 Monocryl, 5-0 Monocryl, and 5-0 Prolene. The wound was dressed with Xeroform and gauze. The patient tolerated the procedure well. She was taken to recovery room in good condition. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 19325-LT, 611.83 c. 19316-LT, 611.83 b. 19340-LT, 757.6 d. 19342-LT, 757.6 ____ 47. INDICATIONS FOR SURGERY: The patient is an 82-year-old white man with a biopsy-proven basal cell carcinoma of his right lower eyelid and cheek laterally. I marked the area for rhomboidal excision and I drew my planned rhomboid flap. The patient observed these markings in a mirror, so he can understand the surgery and agreed on the location and we proceeded. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE: The area was infiltrated with local anesthetic. The face prepped and draped in sterile fashion. I excised the lesion as drawn into the subcutaneous fat. Hemostasis was achieved using the Bovie cautery. Modified Mohs analysis showed the margin to be clear. I incised the rhomboid flap as it was drawn and elevated the flap with a full-thickness of subcutaneous fat. Hemostasis was achieved in the donor site and actually the Bovie cautery was not used, the handheld cautery was used. The flap was rotated into the defect. The donor site was closed and flap inset in layers using 5-0 Monocryl and 6-0 Prolene. The patient tolerated the procedure well. The total site measured 1.3 cm x 2.7 cm What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 14020 c. 14040, 14060 b. 14060 d. 11643 ____ 48. A wire placement in the lower outer aspect of the right breast was placed by a radiologist the day prior to this procedure. During this operative session, the surgeon created an incision through the wire track and the wire track was followed down to its entrance into breast tissue. A nodule of breast tissue was noted immediately adjacent to the wire. This entire area was excised by sharp dissection, sent to pathology and returned as a benign lesion. Bleeders were cauterized, and subcutaneous tissues were closed with 3-0 vicryl. Skin edges were approximated with 4-0 subcuticular sutures and adhesive strips were applied. The patient left the operating room in satisfactory condition. What is the correct code for the surgeon’s services? a. 19125 c. 19125, 19295 b. 11400 d. 19120 ____ 49. A malignant lesion of the forehead measuring 1.0 cm was removed. The operative report states that skin margins are 1.1 cm on all sides. Layered closure was performed. How is this coded? a. 11644, 12052-51 c. 11604 b. 11602, 12052-51 d. 11602, 12051-51 ____ 50. A 56-year-old pro golfer is having Mohs micrographic surgery for skin cancer on his forehead. The surgeon takes him back for two sessions. The first session has 4 tissue blocks and the second has 6 tissue blocks, 2 of which have toluidine blue. What is the best way to code for both sessions' service? a. 17311, 17314, 17315, 88314 c. 17311, 17312, 17315 b. 17313, 17314, 17315 d. 17311, 17312, 17315, 88314 ____ 51. A patient is seen in the same day surgery unit for an arthroscopy to remove some loose bodies in the shoulder area. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29805 c. 29807 b. 29806 d. 29819 ____ 52. What hallux valgus surgery includes a tendon transplant? a. Joplin procedure c. Mitchell procedure b. Mayo procedure d. Keller procedure ____ 53. What is the acromion? a. Part of the elbow joint c. Tendon in the shoulder b. Ligament near the knee d. Extension of the scapula ____ 54. Hallux rigidus is condition affecting what part of the body? a. Spine c. Foot b. Ankle d. Knee ____ 55. What is segmental instrumentation? a. Rods attached only at the top and bottom of a spinal fixation device. b. Bone plates in more than one area of the skull c. A spinal fixation device attached in at least three places d. The instruments used in surgery of the metatarsals. ____ 56. A patient has a greenstick fracture of the arm. It is treated by surgically placing a bone plate on the distal radial shaft. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 813.81 c. 813.21 b. 813.31 d. 733.12 ____ 57. In the ICD-9-CM, what would you look for in the alphabetic index, to code a tear of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder? a. Rotator cuff, sprain c. Injury, shoulder b. Sprain, shoulder d. Tear, rotator cuff ____ 58. A patient presents to the ED with back pain and is diagnosed with a lumbar sprain. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 847.2 c. 724.6 b. 846.0 d. 724.2 ____ 59. A patient complains of pain in his foot and heel, and is diagnosed with plantar fasciitis in the sole of his left foot. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 729.5 c. 825.20 b. 728.71 d. 581.3 ____ 60. The patient fell on location and fractured his femoral shaft in three places. He has to have an ORIF of the left femur with an intramedullary nail and interlocking screws. The orthopedist also places the leg in a plaster splint prior to leaving the OR. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 27245 c. 27513 b. 27507 d. 27506 ____ 61. A 44-year-old male with biplanar deformity, acquired limb length discrepancies and tibial nonunion has undergone deformity correction. He now requires exchange of a strut 45 days postoperatively. The intraoperative mounting parameters, deformity parameters, and initial strut settings are inserted into the computer prior to Jim’s discharge and a daily schedule is generated for him to perform the gradual deformity correction necessary. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20696 c. 99024 b. 20697 d. 20692, 20697 ____ 62. A patient is given Xylocaine, a local anesthetic, by injection on the thigh above the site to be biopsied. A small bore needle is then introduced into the muscle, about 3 inches deep, and a muscle biopsy is taken. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for this service? a. 20205 c. 20225 b. 20206 d. 27324 ____ 63. The patient presents today for closed reduction of the nasal fracture. The depressed right nasal bone was elevated using heavy reduction forceps while the left nasal bone was pushed to the midline. This resulted in good alignment of the external nasal dorsum. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for this procedure? a. 21325 c. 21315 b. 21310 d. 21337 ____ 64. A 22-year-old female has a retained Kirschner wire in the left little finger. Using local anesthesia, the left upper extremity was thoroughly cleansed with Betadine. The end portion of the little finger was opened by a transverse incision through the subcutaneous tissue to the bone. The retained Kirschner wire was located within the distal phalanx. It was removed and closed with sutures. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 10120-F4 c. 20670-F4 b. 20680-F4 d. 10121-F4 ____ 65. A 63-year-old man presents with a neck mass to be excised. The neck mass was palpated and an incision was then made and carried down through the dermis with electrocautery. The subcutaneous tissue of the skin was opened encountering an organized mass that has a benign appearance of a lipoma. Using careful blunt and sharp dissection, the mass measuring 5 cm was completely excised around its entire circumference leaving the capsule intact. The mass was then removed from its posterior attachments using electrocautery. What CPT® code(s) should be used for this procedure? a. 11426 c. 11626 b. 21552 d. 21555 ____ 66. A 27-year-old presents with right-sided thoracic myofascial pain. A 25 gauge 1.5 inch needle on a 10 cc controlled syringe with 0.25% bupivacaine was used. After negative aspiration, 2 cc were injected into each point. A total of four points were injected. A total of 8 cc of bupivacaine was used on the rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, and levator scapular muscles. What CPT® code(s) should be used for this procedure? a. 20550 x 4 c. 20552 b. 20553 d. 20552, 20553-51 ____ 67. A 42-year-old with chronic right trochanteric bursitis is scheduled to receive an injection at the Pain Clinic. A 22-gauge spinal needle is introduced into the trochanteric bursa, and a total volume of 8 cc of normal saline and 40 mg of Kenalog was injected. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20610-RT c. 20550-RT b. 27093-RT d. 20605-RT ____ 68. A 63-year-old man sustained a gunshot wound through the right maxillary sinus that penetrated through the right neck. CT scan revealed no hard evidence of arterial injury but a bullet was directly in line with the internal jugular vein. He was sent to the operating room for neck exploration to rule out vascular injury and injury to the aerodigestive tract. A sternocleidomastoid incision was performed and carried down through the platysma muscle. There was no penetration of the internal jugular vein, but a foreign body was identified resting on the internal jugular vein at approximately the level of the angle of the mandible and removed. The parotid gland was noted to have a blast injury near the tail. This was not surgically repaired or resected. Once all bleeding was controlled, a 10 French round drain was placed in the wound. The wound was copiously irrigated. The platysma muscle was closed and the skin was closed with subcuticular closure. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20525 c. 20100 b. 35201 d. 21899 ____ 69. A 66-year-old has sustained a left proximal humerus fracture. Standard deltopectoral approach was used and dissection was carried out down to the fracture site. The fracture site was identified and fragments were mobilized and the humeral head fragments removed. Once this was done, the stem was prepared up to a size 10. A trial reduction was carried out with the DePuy trial stem and implant head. Sutures were placed in key positions for closure of the tuberosities down to the shaft including sutures through the shaft. The shaft was then prepared and cement was injected into the shaft. The implant was placed. Once the cement was hardened, the head was placed on Morse taper and then reduced. A bone graft was placed around the area where the tuberosities were being brought down. The tuberosities were then tied down with a suture previously positioned. This gave excellent closure and coverage of the significant motion at the repair sites. The wound was thoroughly irrigated. The skin was closed with Vicryl over a drain and also staples in the epidermis. A sterile dressing and sling was applied. The patient was taken to recovery in stable condition. No immediate complications. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 23616-LT c. 23615-LT b. 23605-LT d. 23670-LT ____ 70. A 49-year-old presents with an abscess of the right thumb. Physician incises the abscess and purulent sanguinous fluid is drained. The wound is packed with iodoform packing. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 10061-F5 c. 10060-F5 b. 26010-F5 d. 26011-F5 ____ 71. An 85-year-old has developed a lump in her right groin. An incision over the lesion was made and dissected through the skin and subcutaneous tissue going deep into the femoral fascia. Sharp dissection of the mass was performed, free from the surrounding structures. The 3-cm mass was isolated and cultured. The incision was closed, the area was cleaned and dried, and dressing applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 27087 c. 27048 b. 27047 d. 27049 ____ 72. A young female patient was taken to the operative suite, at which time she was placed under appropriate anesthesia. She has been suffering from pain and potential rotator cuff tear of the right shoulder. The right arm was sterilely draped and prepped. Arthroscopic portals were created anteriorly-posteriorly. The joint line was carefully examined. The biceps insertion was noted to be normal. The middle and inferior glenohumeral ligaments were visualized and noted to be normal. The undersurface of the rotator cuff was clearly visualized and also noted to be normal. There was a large anterior spur formation. The burr was introduced through a lateral portal and the anterior lip of the acromion was resected. The undersurface of the clavicle was noted to be quite prominent and part of the impinging process. There was intense bursitis and a bursectomy was performed, allowing for acromial decompression. Spurs were removed from the distal clavicle. All instrumentation was removed, dressing was applied, and the patient was placed in a sling and returned to the recovery room. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 23130, 23120-51 c. 23415 b. 29826, 29824-51 d. 29826 ____ 73. A 14-year-old status post injury over one year ago to her left wrist presented with recurring wrist pain. The patient was taken to the operating room and placed under general anesthesia. She was placed in wrist traction. The radiocarpal joint was entered through sharp skin dissection and blunt dissection into the joint. There was found to be mild synovitis in the dorsal ulnar aspect of the wrist. This was debrided arthroscopically with a shaver. There was a peripheral tear of the triangle fibrocartilage. This area was shaved to promote healing. Using outside-om technique, a PDS suture was placed across the TFCC and into the capsule. There was synovitis within the midcarpal joint, but there was no articular injury. All instruments were removed and the wounds were closed with interrupted nylon sutures. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29844 c. 29847 b. 29845 d. 29846 ____ 74. A 72-year-old female sustained a left radius fracture, resulting in volar angulation, radial shortening and loss of radioulnar inclination. A general anesthetic was administered. A standard dorsal central approach to the wrist was made. The capsule was opened in a T fashion and the malunion site was identified. A series of osteotomes was utilized to open the fracture site back up and then the normal distal radial architecture was restored. The pie-plate was then placed on the distal radius, utilizing a combination of 2.0 and 1.8 screws and threaded pins for the distal segment and 2.7 screws proximally. Fragments were secured, and Norian SRS was packed into the defect and allowed to harden. With this completed, the wounds were copiously irrigated with normal saline. Soft tissue was closed back over the plate and distal radius, and secured with 2-0 Vicryl. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 25400 c. 25607 b. 25405 d. 25609 ____ 75. A patient presented with a closed, displaced supracondylar fracture of the left elbow. After conscious sedation, the left upper extremity was draped and closed reduction was performed, achieving anatomical reduction of the fracture. The elbow was then prepped and with the use of fluoroscopic guidance, two K-wires were directed crossing the fracture site and purchasing the medial cortex of the left distal humerus. Stable reduction was obtained, with full flexion and extension. K-wires were bent and cut at a 90 degree angle. Telfa padding and splint were applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 24535 c. 24582 b. 24538 d. 24566 ____ 76. A patient presented with a right ankle fracture. After induction of general anesthesia, the right leg was elevated and draped in the usual manner for surgery. A longitudinal incision was made parallel and posterior to the fibula. It was curved anteriorly to its distal end. The skin flap was developed and retracted anteriorly. The distal fibula fracture was then reduced and held with reduction forceps. A lag screw was inserted from anterior to posterior across the fracture. A 5-hole 1/3 tubular plate was then applied to the lateral contours of the fibula with cortical and cancellous bone screws. Final radiographs showed restoration of the fibula. The wound was irrigated and closed with suture and staples on the skin. Sterile dressing was applied followed by a posterior splint. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 27814 b. 27792 c. 27766 c. 27823 ____ 77. A 49-year-old female presented with chronic de Quervain’s and has been unresponsive to physical therapy, bracing or cortisone injection. She has opted for more definitive treatment. After induction of anesthesia, the patient’s left arm was prepared and draped in the normal sterile fashion. Local anesthetic was injected using a combination 2% lidocaine and 0.25% Marcaine. A transverse incision was made over the central area of the first dorsal compartment. The subcutaneous tissues were gently spread to protect the neural and venous structures. The retractors were placed. The fascial sheath of the first dorsal compartment was then incised and opened carefully. The underlying thumb abductor and extensor tendons were identified. The tissues were dissected and the extensor retinaculum of the first extensor compartment was incised. The fibrotic tissue was incised and the tendons gently released. The tendons were freely moving. Sub q tissues were closed with 3-0 Vicryl and the skin with 3-0 Prolene subcuticular closure. Steri-strips, Xeroform and dry sterile dressings were applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 25001 c. 25118 b. 25000 d. 25085 ____ 78. This 45-year-old male presents to the operating room with a painful mass of the right upper arm. Upon deep dissection a large mass in the soft tissue of the patient's shoulder was noted. The mass appeared to be benign in nature. With deep blunt dissection and electrocautery, the mass was removed and sent to pathology. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 23076 c. 23075 b. 23066 d. 23030 ____ 79. A six-year-old male suffered a fracture after falling off the monkey bars at school. He fell on an outstretched hand and suffered a transcondylar fracture of the left humerus. After prep and drape, a manipulation was done to achieve anatomic reduction. Once the joint was adequately reduced, skeletal traction was placed distally and proximally to maintain excellent fixation and anatomic reduction. The pins were bent, trimmed and covered with a sterile dressing and a posterior splint was placed on the patient’s arm. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 24516 c. 24535 b. 24530 d. 24538 ____ 80. A 27-year-old triathelete is thrown from his bike on a steep downhill ride. He suffered a severely fractured vertebra at C5. An anterior approach is used to dissect out the bony fragments and strengthen the spine with titanium cages and arthrodesis. The surgeon places the patient supine on the OR table and proceeds with an anterior corpectomy at C5 with discectomy above and below. Titanium cages are placed in the resulting defect and morselized allograft bone is placed in and around the cages. Anterior synthes plates are placed across C2-C3 and C3-C5, and C5-C6. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 22326, 22554-51, 22845, 22851, 20930 c. 63001, 22554-51, 22845, 20931 b. 63081, 22554-51, 22846, 22851, 20930 d. 22326, 22548-51, 22846, 20931 ____ 81. This 45-year-old male presents to the operating room with a painful mass of the right upper arm. General anesthesia was induced. Soft tissue dissection was carried down through the proximal aspect of the teres minor. Upon further dissection a large mass was noted just distal of the IGHL, which appeared to be benign in nature. With blunt dissection and electrocautery, the 4-cm mass was removed en bloc and sent to pathology. Wound was irrigated, repair of the teres minor with subcutaneous tissue was then closed with triple-0 Vicryl. Skin was closed with double-0 Prolene in a subcuticular fashion. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 23076-RT c. 23075-RT b. 23066-RT d. 11406-RT ____ 82. The patient has a torn medial meniscus. An arthroscope was placed through the anterolateral portal for the diagnostic procedure. The patellofemoral joint showed some grade 2 chondromalacia on the patella side of the joint only, and this was debrided with the 4.0-mm shaver. The medial compartment was also entered and a complex posterior horn tear of the medial meniscus was noted. It was probed to define its borders. A meniscectomy was carried out back to a stable rim. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29880, 29879-59 c. 29870, 29879-59 b. 29870, 29877-59 d. 29881, 29877-59 ____ 83. A 3-year-old is brought into the ER crying. He cannot bend his left arm after his older brother pulled it. The physician looks at X-ray diagnosing the patient with a medial dislocated nursemaid’s elbow. The ER physician reduces the elbow successfully. The patient is able to move his arm again. The patient is referred to an orthopedist for follow-up care. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 24640-54, 832.23, E927.0 c. 24640-54, 832.10, E927.8 b. 24565-54, 832.22, E929.8 d. 24600-54, 832.00, E928.8 ____ 84. A 50-year-old male had surgery on his upper leg one day ago and is presenting with serous drainage from the wound. He was scheduled back to the operating room for an evaluation of the hematoma. His wound was explored and there was a hematoma at the base of the wound, which was very carefully evacuated and the wound irrigated with antibacterial solution. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 10140-79, 998.12 c. 10140-76, 998.9 b. 27603-78, 998.59 d. 27301-78, 998.12 ____ 85. A 22-year-old female sustained a dislocation of the right elbow with a medial epicondyle fracture while on vacation. The patient was put under general anesthesia and the elbow was reduced and was stable. The medial elbow was held in the appropriate position and was reduced in acceptable position and elevated to treat non-surgically. A long arm splint was applied. The patient is referred to an orthopedist when she returns to her home state in a few days. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 24575-54, 24615-54-51 c. 24577-54, 24600-54-51 b. 24576-54, 24620-54-51 d. 24565-54, 24605-54-51 ____ 86. A 45-year-old presents to the operating room with a right index trigger finger and left shoulder bursitis. The left shoulder was injected with 1 cc of Xylocaine, 1 cc of Celestone, and 1 cc of Marcaine. An incision was made over the A1 pulley in the distal transverse palmar crease, about an inch in length. This was taken through skin and subcutaneous tissue. The Al pulley was identified and released in its entirety. The wound was irrigated with antibiotic saline solution. The subcutaneous tissue was injected with Marcaine without epinephrine. The skin was closed with 4-0 Ethilon suture. Clean dressing was applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 26055-F6, 20610-76-LT c. 26055-F6, 20610-51-LT b. 20552-F6, 20605-52-LT d. 20553-F6, 20610-51-LT ____ 87. A patient presents with a healed fracture of the left ankle. The patient was placed on the OR table in the supine position. After satisfactory induction of general anesthesia, the patient’s left ankle was prepped and draped. The tourniquet was not positioned or utilized. A small incision about 1 cm long was made in the previous incision. The lower screws were removed. Another small incision was made just lateral about 1 cm long. The upper screws were removed from the plate. Both wounds were thoroughly irrigated with copious amounts of antibiotic containing saline. Skin was closed in a layered fashion and sterile dressing applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20680 c. 20670 b. 20680, 20680-59 d. 20680, 20670-59 ____ 88. A patient is seen in the hospital’s outpatient surgical area with a diagnosis of a displaced comminuted fracture of the lateral condyle, right elbow. An ORIF procedure was performed, which included the following techniques: An incision was made in the area of the lateral epicondyle. This was carried through subcutaneous tissue, and the fracture site was easily exposed. Inspection revealed the fragment to be rotated in two places about 90 degrees. It was possible to manually reduce this quite easily, and the manipulation resulted in an almost anatomic reduction. This was fixed with two pins driven across the humerus. The pins were cut off below skin level. The wound was closed with plain catgut subcutaneously and 5-0 nylon for the skin. Dressings and a long arm cast were applied. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 24579, 29065-51, 812.52 c. 24579, 812.42 b. 24577, 812.42 d. 24575, 812.52 ____ 89. A 47-year-old patient was previously treated with external fixation for a Grade III left tibial fracture. There is now nonunion of the left proximal tibia and he is admitted for open reduction of tibia with bone grafting. Approximately 30 grams of cancellous bone was harvested from the iliac crest. The fracture site was exposed and the area of nonunion was osteotomized, cleaned, and repositioned. Intrafragmentary compression was applied with three screws. The harvested bone graft was packed into the fracture site. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 27724, 733.82, 905.4 c. 27722, 733.81, 905.4 b. 27722, 733.82 d. 27724, 733.82 ____ 90. A Grade I, high velocity open right femur shaft fracture was incurred when a 15-year-old female pedestrian was hit by a car. She was taken to the operating room within four hours of her injury for thorough irrigation and debridement, including excision of devitalized bone. The patient was then reprepped, redraped, and repositioned. Intramedullary rodding was then carried out with proximal and distal locking screws. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 27506, 11044-51, 821.11 c. 27507, 11012, 821.01 b. 27506, 11012-51, 821.11 d. 27507, 11044, 821.10 ____ 91. A 49-year-old female had two previous rotator cuff procedures and now has difficulty with shoulder function, deltoid muscle function, and axillary nerve function. An arthrogram is scheduled to be performed. After preparation, the shoulder was anesthetized with 1% lidocaine about 8 cc without epinephrine. The needle was placed into the shoulder area posteriorly under image intensification. It appeared as if the dye was in the shoulder joint. She was moved and a good return of flow was obtained. The shoulder was then mobilized and there was no evidence of any cuff tear from the posterior arthrogram. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 23350 c. 23350, 73040-26 b. 20610, 73040-26 d. 23350, 20610, 73040-26 ____ 92. A 31-year-old secretary returns to the office with continued complaints of numbness involving three radial digits of the upper right extremity. Upon examination, she has a positive Tinelís test of the median nerve in the left wrist. Anti-inflammatory medication has not relieved her pain. Previous electrodiagnostic studies show sensory mononeuropathy. She has clinical findings consistent with carpal tunnel syndrome. She has failed physical therapy and presents for injection of the left carpal canal. The left carpal area is prepped sterilely. A 1.5 inch 25 or 22 gauge needle is inserted radial to the palmaris longus or ulnar to the carpi radialis tendon at an oblique angle of approximately 30 degrees. The needle is advanced a short distance about 1 or 2 cm observing for any complaints of paresthesias or pain in a median nerve distribution. The mixture of 1 cc of 1% lidocaine and 40 mg of Kenalog is injected slowly along the median nerve. The injection area is cleansed and a bandage is applied to the site. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 20526, J3301 c. 20526, J3303 b. 20551, J3302 d. 20550, J3302 ____ 93. An elderly female presented with increasing pain in her left dorsal foot. The patient was brought to the operating room, at which time she was placed under general anesthesia. A curvilinear incision was centered over the lesion itself. Soft tissue dissection was carried down through to the ganglion. The ganglion was clearly identified as a gelatinous material. It was excised directly off the bone and sent to pathology. There was noted to be a large bony spur at the level of the 1st metatarsal. Using double action rongeurs, the spur itself was removed and sequestrectomy was performed. Following that, a rasp was utilized to smooth the bone surface. The eburnated bony surface was then covered, utilizing bone wax. The wound was irrigated and closed in layers. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 28122, 28090-51 c. 28045, 28090-51 b. 28111, 28092-51 d. 28100, 28092-51 ____ 94. Under general anesthesia, a 45-year-old patient was sterilely prepped. The wrist joint was injected with Marcaine and epinephrine. Three arthroscopic portals were created. The articulating surface between the scaphoid and the lunate clearly showed disruption of the ligamentous structures. We could see soft tissue pouching out into the joint; this was debrided. There was abnormal motion noted within the scapholunate articulation. At this point the C-arm was brought in, arthroscopic instruments were placed in the joint and we confirmed the location of the shaver as a probe in the scapholunate ligament. There was a significant gap between the capitate and lunate. K-wire was utilized from the dorsal surface into the lunate, restoring the space. Further examination revealed gross instability between the capitate and lunate. With the wrist in neutral position, a K-wire was then passed through the scaphoid, through the capitate and into the hamate. This provided stabilization of the wrist joint. Stitches were placed, and a thumb spica cast was applied. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29847 c. 29847, 29847-59 b. 29846 d. 29847, 29846 ____ 95. A 74-year-old male presented with ankle avascular necrosis of the talus with collapse of the body. After general anesthesia and sterile prep, the patient was placed prone. A lateral incision was made. The fibula was dissected and approximately 6 cm of the fibula was removed. There were a lot of free fragments of bone around the subtalar joint and the talus itself. Those bones were removed and there was a large defect consistent with avascular necrosis of the body of the talus. An egg-shaped bur was introduced and the articulating cartilage of the ankle joint was excised and debrided off. The subtalar joint was then approached and resection of the articulating surface of the subtalar joint was completed. A bone graft was prepared on the back table. We made two large blocks to fill the defect in the talus and then additional small fragments of cortical cancellous bone to fill in smaller defects around the talus and ankle itself. Fixation was performed in the calcaneocuboid. The talar screw was inserted, followed by fixation of the talonavicular, tibiotalar and more additional compression. The ankle screws were inserted more proximally. The wound was irrigated and closed in layers. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 28730, 20900-51 c. 28705, 20902-51 b. 28715, 20902-51 d. 28725, 20900-51 ____ 96. The patient is a 17-year-old male who was struck on the elbow by another player’s stick while playing hockey. He is found to have a fracture of the olecranon process. The patient was brought to the OR, anesthetized and intubated. The right upper extremity was prepped with Betadine scrub and draped free in the usual sterile orthopedic manner. The arm was then elevated and exsanguinated and the tourniquet inflated to 250 mm./Hg. A five-inch incision was made with the scalpel on the extensor side of the elbow, beginning distally and proceeding in an oblique fashion up the proximal forearm. Dissection was carried down through subcutaneous tissue and fascia, and bleeding was controlled with electrocautery. We then subperiostally exposed the proximal ulna and olecranon to visualize the fracture site. The fracture could be seen at the base of the olecranon process. We irrigated the site thoroughly and reduced the fracture fragments without difficulty. Extending the elbow, we inserted two smooth K-wires across the fracture site. Next, through a drill hole in the proximal ulnar shaft, we threaded an 18 gauge wire through it and wrapped it around the K-wires in a figure-of-eight manner to further stabilize the fixation. Wires were then twisted and placed into soft tissues. The K-wires in the olecranon were advanced slightly after being bent and cut. Sterile dressing was applied and the patient was placed in a splint. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 24685 c. 24675 b. 24635 d. 24586 ____ 97. This 56-year-old female presented with a degenerative posteromedial meniscal flap tear of the right knee. After appropriate preoperative evaluation, the patient was taken to the operating room where general anesthesia was instituted. The patient was placed supine on the operating table. The right lower extremity was sterilely prepped and draped for arthroscopic surgery. The leg was exsanguinated and the tourniquet inflated. The arthroscope was introduced first through the anterolateral portal with medial suprapatellar portal utilized. The lateral compartment looked fairly good. There were some minimal medial degenerative changes. In the medial compartment there was a full-thickness area of osteochondral degeneration with a flap of cartilage noted. It was possible to remove this with a bleeding bony bed with beveled edges of cartilage. The ligament itself was intact. The retropatellar area was normal with only Grade I chondromalacia changes noted. The medial joint was inspected and there was a tear at the junction of the middle and posterior portions of the meniscus, a flap tear that was based more anteriorly. This was shaved with a combination of small baskets and punches, and the meniscal debrided back to a smooth stable rim. There was additional synovitis in the medial aspect of the intercondylar notch and this was removed with the curved automated meniscal incisor. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29880, 29879-51 c. 29882 b. 29881 d. 29881, 29877-51 ____ 98. This 36-year-old female presents with an avulsed anterior cruciate ligament off the femoral condyle with a complete white on white horizontal cleavage tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus, causing instability. A general endotracheal anesthesia was performed, the patient was placed supine on the operating table and the right lower extremity was prepped with Betadine and draped free. Standard arthroscopic portals were created and the knee was systematically examined and probed. The posterior horn of the medial meniscus was noted to be buckled and frayed. This area was carefully probed and found to be irreparable. It was decided that our best option was to proceed with a limited partial meniscectomy, with the goal being to leave as much viable meniscal tissue as possible. Therefore, a medial infrapatellar portal was developed with a longitudinal stab wound. A series of straight-angled and curved basket punches was used to perform a saucerization of the damaged portion of the meniscus, leaving the intact portion of the medial meniscus in place. Debris was meticulously removed with the 4.0 meniscal cutter. Approximately 50% of the medial meniscus remained. Next, our attention was turned to the ACL repair. Through a 5 cm longitudinal anterior incision, a central one-third tendon bone was harvested. A 10 mm graft was taken and bone plug sculpted. Anterolateral notchplasty was done with a curet and polished with the burr. All debris was removed and instruments were used to ensure proper isometry. The graft was tightened in extension about 2.5 mm and actually lengthened in flexion, and this was considered acceptable. Endoscopic guides were used to create the tibial and femoral tunnels, and the edges were rasped smooth. Using a percutaneous guide pin, the graft was placed retrograde to the knee and secured proximally with an 8 x 25 mm interference screw. The knee was put through range of motion, and with the leg in 30 degrees of flexion with the posterior drawer applied to the proximal tibia, an 8 x 20 mm interference screw was used to secure the bone plug distally. The graft was tight, isometric and without adverse features. The wound was copiously irrigated with Kantrex. Cancellous bone fragments from bone plugs were used to graft the donor site defect in the patella. The paratenon was closed over this to house the graft with a running #1 Vicryl. The edge of the distal bone plug was beveled with the rongeur. The subcutaneous tissue was then closed with triple-0 Vicryl. Skin was closed with double-0 Prolene in a subcuticular fashion. Steri-Strips, sterile dressing, cryo cuff and hinged knee brace were applied. The patient was awakened and taken to the recovery room in satisfactory condition. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29888, 20902, 29880-51 c. 29888, 29881-51 b. 29888, 29882-51, 20924 d. 29889, 29880 ____ 99. This patient presented with internal derangement of the left knee. After satisfactory anesthesia was administered, the left lower extremity was prepped and draped in a sterile fashion. Routine portals were made in the knee. We first looked at the medial compartment, which showed a complex small tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus, which was debrided using a 4.0 meniscal shaver. There was an area of grade 4 chondromalacia on the proximal medial distal femur and this was all the way down to bone. There was also evidence of chondromalacia over the patellofemoral joint of grade 4. Both areas were debrided and drilled with a 0.45 K-wire. Multiple drill holes were placed in an attempt to get some scar tissue to form. The notch area was normal and lateral compartment normal. Following microfracture technique, the knee was irrigated, each portal was closed with 4-0 nylon and the patient was taken to recovery. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 29879, 29881-59-51 c. 29879, 29879-59, 29881-51 b. 29880, 29879-51, 29877-51 d. 29879, 29877-59 ____ 100. A 68-year-old female with long-standing degenerative arthritis in her right knee presented. Risks and benefits were discussed. She was agreeable to the surgery. After adequate anesthesia was obtained, the patient was prepped and draped in usual sterile fashion with DuraPrep and Betadine scrub. The leg was exsanguinated and tourniquet inflated. An anterior incision was made and carried through the skin and bursa, cauterizing all bleeders. The bursa was elevated medially and a medial parapatellar incision was made. The proximal tibia was cleaned. The knee had an 18° flexion contracture. The cruciate ligaments were debrided along with the menisci. The proximal tibial cutting guide was placed and the proximal tibial cut was made. The femoral canal was entered and a 6° cut was made for the anterior jig. The distal cut was made at 6°. The femur measured a size 2. The 2 cutting block was placed and the anterior, posterior and chamfer cuts were made. The notch cut was made and then the trial component was placed with a size 2 tibia and 12 mm spacer and was found to fit beautifully and it tracked well. The patella was cut and measured to be a 32. The holes were drilled and the proximal tibial cuts were made. All the excess meniscal tissue and hypertrophic synovium were debrided. The wound was thoroughly irrigated and the bone dried. The cement was mixed, the size 2 tibia with a 12 mm tibial tray, size 2 femur and a size 32 patella were all cemented in place removing all excess cement. After the cement was hard, the tourniquet was released. The knee was placed through a range of motion and was found to track beautifully. The knee was thoroughly irrigated. The retinaculum was closed with interrupted figure-of-eight 1 Vicryl. The bursa was closed with 1 and 0. The subcutaneous layers were closed with 0 and 2-0 and the skin with staples. Sterile dressing was applied. The patient was taken to the recovery room in stable condition. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 27447 c. 27440 b. 27446 d. 27441 ____ 101. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for open decortication and parietal pleurectomy? a. 32220 c. 32225 b. 32320 d. 32652 ____ 102. What is the largest single mass of lymphatic tissue? a. Spleen c. Peyer’s Patches b. Thymus d. Tonsils ____ 103. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported for spontaneous pneumothorax? a. 860.0 c. 512.8 b. 512.1 d. 860.5 ____ 104. What CPT® code should be reported for a percutaneous needle biopsy of mediastinum? a. 32662 c. 32095 b. 32405 d. 32602 ____ 105. What CPT® code should be reported for a frontal sinusotomy, nonobliterative, with osteoplastic flap, brow incision? a. 31080 c. 31084 b. 31087 d. 31086 ____ 106. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for an emergency endotracheal intubation to save the patient’s life? a. 31502 c. 31603 b. 31500 d. 31600 ____ 107. What is the name of the bony structure separating the nostrils? a. Nasal turbinates c. Nasal membrane b. Nasal septum d. Nasal cartilage ____ 108. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for a major thoracotomy for post-op hemorrhage? a. 32110 c. 32310 b. 32100 d. 32120 ____ 109. Johnny has a penny removed from his left nostril in the doctor’s office. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 30320 c. 30100 b. 30300 d. 30160 ____ 110. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported for RSV, respiratory syncytial virus? a. 754.0 c. 466.0 b. 471.0 d. 079.6 ____ 111. What ICD-9-CM code should be reported for pyopneumothorax with fistula? a. 510.0 c. 512.8 b. 510.9 d. 512.1 ____ 112. A patient presents with wheezing and shortness of breath. After evaluating the patient, the physician determines the patient is suffering from an exacerbation of his asthma. The physician orders nebulizer treatments to be administered in his office. According to the ICD-9-CM guidelines for coding signs and symptoms, what is the correct ICD-9-CM code(s)? a. 493.92 c. 786.07, 786.05 b. 493.91, 786.07, 786.05 d. 493.91 ____ 113. Provide the correct ICD 9-CM code for acute RSV bronchiolitis. a. 466.0 c. 466.11 b. 466.19 d. 466.19, 079.6 ____ 114. The provider performs a diagnostic thoracoscopy followed by the thoracoscopic excision of the pericardial cyst. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 32601, 32662-51 c. 32658 b. 32601, 32661-51 d. 32661 ____ 115. A patient’s nose was hit with a baseball during a high school baseball game. At that time reconstruction was performed, with local grafts. Patient returns now as an adult, discontent with the bony prominence along the bony pyramid and flat look of the tip of the nose. He underwent major repair with osteotomies and nasal tip work. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 30410 c. 30450 b. 30435 d. 30462 ____ 116. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported for postoperative pulmonary edema due to fluid overload from infusion? a. 518.4, 276.69, E873.0 c. 518.81, 276.61, E873.1 b. 518.4, 428.1 d. 518.81, 136.3 ____ 117. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported for COPD with acute bronchitis? a. 491.20 c. 491.8 b. 491.9 d. 491.22 ____ 118. A patient with AML (Acute Myelogenous Leukemia) has just learned his sister is an HLA match for him. Stem cells taken from the donor (the patient’s sister) will be transplanted into the patient to help with his treatment. What CPT® code(s) should be used to report for the harvesting of the stem cells from the donor, his sister? a. 38204 c. 38206 b. 38205 d. 38207 ____ 119. A patient is seen in the OR for the removal of a hepatic adenoma which has invaded the diaphragm. The resection of the diaphragm portion of the mass was repaired with primary sutures. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for the diaphragmatic mass resection? a. 39540 c. 39560 b. 39545 d. 39561 ____ 120. A 43-year-old female is seen in the emergency room with severe epistaxis. She said this is a common occurrence for her during the really cold dry months of winter and this is why she is here for the third time this week. Extensive bilateral posterior cautery and packing is required to control the hemorrhage. What CPT® code(s) should be reported for the procedure? (Note: Do not code the E/M) a. 30905-22 c. 30905-50 b. 30903-50 d. 30906-50 ____ 121. An operative report lists excisional bilateral biopsies of deep cervical nodes and biopsy of right deep axillary nodes as the procedures performed. The pathology report comes back confirming lymphadenitis. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 38520-50, 38505-59, 38740-RT, 59 c. 38510-50, 38525-RT, 51 b. 38510, 38525-59 d. 38520-50, 38525-RT ____ 122. What anatomical section contains all of the thoracic viscera except the lungs? a. Mediastinum c. Coronal plane b. Peritoneum d. Mesentery ____ 123. A surgeon performed a transthoracic median sternotomy for exploration of the space around the lung sacs and for drainage of fluid, caused by pneumonia. What is the appropriate code(s)for this scenario? a. 39000, 32421-51 c. 39010 b. 39220, 32421-51 d. 39400 ____ 124. An 18-month-old patient is seen in the ED unable to breath due to a toy he swallowed which had lodged in his throat. Soon brain death would occur if an airway is not established immediately. The ED physician performs an emergency tracheostomy, transtracheal. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 31601, 348.89 c. 31603, 934.8 b. 31601, 31603, 938 d. 31603, 938 ____ 125. A 20-year-old patient is seen for 5 transbrachial lung biopsies of 2 separate lobes. One biopsy is taken in one lobe and 4 biopsies in another lobe. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 31628 c. 31629, 31632 b. 31628, 31632 d. 31628, 31632 x 2 ____ 126. What CPT® code should be reported for an extrapleural pneumonectomy as well as empymectomy performed during the same surgical session? a. 32035, 32445-51 c. 32445, 32540-51 b. 32440, 32445-59 d. 32440, 32540-59 ____ 127. What CPT® code should be reported for extensive excision of seven nasal polyps? a. 30115 c. 30115 x 7 b. 30110, 30115 x 6 d. 30115, 30115-51 x 6 ____ 128. A patient is seen in the endoscopy suite for a diagnostic maxillary sinusotomy. During the sinusotomy, the physician observes some diseased tissue which needs to be removed. The physician decides to perform a maxillary antrostomy with tissue removal. Bleeding is controlled. The patient tolerated the procedure well. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 31231, 31267 c. 31256 b. 31254, 31256 d. 31267 ____ 129. Most nasal passages have how many turbinates present on the lateral wall of each nasal cavity? a. 2 c. 5 b. 3 d. 6 ____ 130. Where in the respiratory system is the carina located? a. Left bronchus c. Tracheal bifurcation b. Sphenoid sinus d. Inferior turbinate ____ 131. This 25-year-old male presents with deviated nasal septum. The patient undergoes a nasal septum repair and submucous resection. Cartilage from the bony septum was detached and the nasoseptum was realigned and removed in a piecemeal fashion. Thereafter, 4-0 chronic was used to approximate mucous membranes. Next, submucous resection of the turbinates was handled in the usual fashion by removing the anterior third of the bony turbinate and lateral mucosal followed by bipolar cauterization. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 30520, 30140-51 c. 30620, 30999-51 b. 30420, 30140-51 d. 30450, 30999-51 ____ 132. This 45-year-old presents with acute pericarditis. The surgeon makes a small incision between two ribs and enters the thoracic cavity. An endoscope is introduced and the pericardial sac is examined by direct visualization. Using an instrument introduced through the endoscope, the surgeon creates an opening in the pericardial sac for drainage purposes. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 32658 c. 32660 b. 32659 d. 32661 ____ 133. The pulmonologist in a multispecialty group refers a patient to the otolaryngologist in the same group, same tax ID, because they think that the shortness of breath that the patient is experiencing may be due to sinusitis and LPR. The otolaryngologist has never seen this patient. The otolaryngologist works up the patient, capturing a comprehensive history, detailed exam and medical decision making of moderate level. The note indicates that he needs to perform to perform a nasal endoscopy to get a better look at what is going on in the sinuses and a flexible laryngoscopy to determine if laryngopharyngeal (LPR) reflux is contributing to the problems because he could not get adequate visualization on manual exam. The scopes are performed and the otolaryngologist diagnoses chronic pansinusitis and chronic laryngitis/tracheitis and LPR. He prescribes Singulair and Nexium and proposes endoscopic surgery be considered in the future if the current route of treatment does not fully take care of the problems experiencing by the patient. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for the procedure? a. a. 99203-25, 31575, 473.8, 476.1 a. 99203-25, 31231, 478.8, 476.1 c. 99203-25, 31231, 478.8 b. 99203-25, 31575, 31231-51, 476.1 ____ 134. A patient with recurrent pneumothoraces presents for chemopleurodesis. With the help of a thoroscope, a catheter is inserted between the ribs and into the pleural space between the parietal and pleural viscera. Subsequently, 5g o sterile asbestos-free talc was introduced into the pleural space via the placed catheter. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 32650, 512.1 c. 32601, 32560, 512.1 b. 32560, 512.8 d. 32650, 32560, 512.8 ____ 135. A 14-year-old boy presents at the Emergency Department experiencing an uncontrolled epistaxis. Through the nares, the ED physician packs his entire nose via anterior approach with medicated gauze. In approximately 15 minutes the nosebleed stops. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 30903-50, 784.7 c. 30901, 784.7 b. 30901-50, 784.7 d. 30905, 784.7 ____ 136. A 20-year-old female, who returned from spring break in Mexico six days ago, presents to the ED with a high fever for three days, a sore throat, general aches and a miserable cough. The ED physician suspects swine flu and orders a rapid flu test. What ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 488.1 c. 780.60, 462, 786.2 b. 487.1 d. 780.60, 462, 780.96, 786.2 ____ 137. A 78-year-old patient with bilateral, lower lobe lung cancer has been in the hospital for seven days with a tunneled chest tube in place to drain fluid from the pleural space. The chest tube currently is inserted between the 4th and 5th intercostal space on the left side. There is a very bad infection at the insertion site. The physician removes this chest tube and inserts another tube in between the 4th and 5th intrecostal space on the right side to continue fluid drainage. The tube placed today is just like the one removed only sterile. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 32422, 162.9 c. 32552, 32551-50, 162.5. 197.0 b. 32552, 32550, 162.5 d. 32550, 162.3, 162.9 ____ 138. A patient underwent bilateral nasal/sinus diagnostic endoscopy. Finding the airway obstructed the physician fractures the middle turbinates and performs surgical endoscopy with total ethmoidectomy and bilateral nasal septoplasty. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 30930, 31255-51, 30520-51 c. 31231, 30130-51, 31255-50 b. 31255-50, 30520-50, 51 d. 31255, 30520-51 ____ 139. A 55-year-old female smoker presents with cough, hemoptysis, slurred speech, and weight loss. Chest x-ray done today demonstrates a large, unresectable right upper lobe mass, and brain scan is suspicious for metastasis. Under fluoroscopic guidance, a needle biopsy of the lung lesion is performed for histopathology and tumor markers. A diagnosis of small cell carcinoma is made and chemoradiotherapy is planned. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 32405, 77002-26, 786.50, 786.3, 784.5, 783.21 b. 32405, 77002-26, 162.9 c. 32405, 77002-26, 786.6 d. 32405, 77002-26, 162.3 ____ 140. A surgeon performs a high thoracotomy with resection of a single lung segment on a 57-year-old heavy smoker who had presented with a six-month history of right shoulder pain. An apical lung biopsy had confirmed lung cancer. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM code(s) should be reported? a. 32100, 729.5 c. 32503, 162.8 b. 32484, 162.8 d. 19271, 32551-51, 786.50 ____ 141. A 3-year-old girl is playing with a marble and sticks it in her nose. Her mother is unable to dislodge the marble so she takes her to the physician’s office. The physician removes the marble with hemostats. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 30300, 932 c. 30150, 933.0 b. 30310, 932 d. 30300, 933.0 ____ 142. An ICU diabetic patient who has been in a coma for weeks as the result of a head injury, becomes conscious and begins to improve. The physician performs a tracheostomy closure and since the scar tissue is minimal, the plastic surgeon is not needed. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported for this procedure? a. 31820, 250.30, 850.3 c. 31825, 250.30, 959.01 b. 31820, 780.01, 959.01, 250.00, V55.0 d. 31825, 250.00, 850.3, 959.01, V55.0 ____ 143. A 27-year-old girl has been on the lung transplant list for months and today she will be receiving a LT and RT lung from an individual involved in an MVA. This person was DOA at the hospital and is an organ donor. The donor pneumonectomy was performed by physician A, the backbench work by physician B and the transplant of both lungs into the prepped and waiting patient by physician C. What is the correct coding for the removal (physician A), preparation (physician B) and insertion (physician C) of the lungs? a. 32850, 32851 x 2, 32856 c. 32850, 32851-50, 32855 x 2 b. 32850, 32851, 32855 d. 32850, 32853-50, 32856 ____ 144. A patient with laryngeal spasms undergoes therapeutic injection of the vocal cords. Topical anesthesia is administered to the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Using an operating microscope, a direct laryngoscope is inserted into the patient’s mouth. The interior larynx is examined and the surgeon injects the vocal cords at two sites with glycerin. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 31571, 478.75 c. 31571, 478.6 b. 31570, 31571, 478.74 d. 31570, 478.75 ____ 145. A patient with partial vocal cord paralysis requires bilateral removal of the arytenoids cartilage to improve breathing. The laryngoscope with operating microscope is inserted. Adequate visualization is established and the arytenoids cartilage is exposed by excision of the mucosa overlying it. What diagnosis and procedure code(s) should be reported for this procedure? a. 31561, 31600, 478.33 c. 31561, 478.33 b. 31560, 478.30 d. 31560, 69990, 478.0 ____ 146. A patient presents to the emergency department (ED) with a sucking chest wound. The physician on duty performs an immediate tube thoracostomy in order to restore normal breathing to the patient before rushing him to surgery to address other injuries. What CPT® code is used for the thoracostomy? a. 31500 b. 32551 c. 32551, 31500-51 d. It is not coded as it will be bundled with any procedures performed during surgery. ____ 147. A patient with a diagnosis of chronic sphenoidal sinusitis undergoes a bilateral sinusotomy. While the physician examines the diseased sphenoid sinus, she takes a biopsy of the sphenoidal masses and removes the mucosa with several polyps. Transseptal sutures are placed and the intraoral incision is closed in a single layer. The nose is packed and external nasal dressings are placed. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 31050-50, 30115-50, 51, 473.3 c. 31051, 12011 x 2, 473.8 b. 31050, 31051-51, 473.8 d. 31051-50, 473.3, 471.8 ____ 148. A returning two-year-old child is seen in the pediatrician’s office with stridor and a “bark” like cough. The pediatrician examines the child quickly and determines the child has croup. The child is given a neublizer breathing treatment in the office to improve PO2 levels. Medication used is breathable epinephrine. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 94640, 478.75 c. 94642, 786.1, 478.75 b. 94640, 478.75 d. 94644, 786.1, 786.2 ____ 149. The surgeon makes an incision in the neck near the cricothyroid membrane for an emergency tracheostomy for a patient who arrives in the emergency room with tracheal crushing injuries suffered in a car accident in which the patient was riding as the passenger. What CPT® and ICD-9-CM codes should be reported? a. 31600, 862.39, E815.1 c. 31603, 874.02, E819.1 b. 31605, 862.29, E819.1 d. 31612, 862.39, E815.1 ____ 150. A 55-year-old patient presents for a planned partial mastectomy. Two hours prior to going to the OR the surgeon injects the patient with Technetium 99. During the mastectomy a Geiger counter probe is used to isolate the area with the highest concentration of Technetium 99. The lymph node or nodes with the highest concentration represent the first in the lymph node chain off the breast and are biopsied to determine if a lymphadenectomy is necessary. As it turns out, the partial mastectomy and sentinel lymph node biopsy are the only procedures necessary in this operative session. What CPT® code(s) should be reported? a. 19301, 38792-51, 38525-51 c. 19302, 78195, 38792-51, 38525-51 b. 19302, 38790-51 d. 19302 ____ 151. How many layers of tissue does an artery have? a. One c. Three b. Two d. Four ____ 152. The conduction system contains pacemaker cells, nodes, the ____ , and the ____. a. Purkinje fibers and the Bundle of HIS. c. Heart valves and Purkinje Fibers b. Bundle of HIS and Electrical system d. Electrical system and Bundle of HIS ____ 153. What part of the cardiovascular system is responsible for the one way flow of blood through the chambers of the heart? a. Septum c. Bundle of HIS b. Heart valves d. Atria ____ 154. Which main coronary artery bifurcates into two smaller ones? a. Right c. Inverted b. Left d. Superficial ____ 155. What is the term for the divider between the heart chamber walls? a. SA node c. Septum b. Bundle branch d. Mitral ____ 156. A patient suffering from an abdominal aortic aneurysm involving a renal artery undergoes endovascular repair using modular prosthesis with two docking limbs. Select the CPT® cod(s) for this procedure. a. 34805 c. 34803 b. 0078T, 0079T d. 34802 ____ 157. A physician places a centrally inserted, tunneled central venous access device with a subcutaneous pump on a 7 year-old patient. a. 36561 c. 36560 b. 36563 d. 36558 ____ 158. Patient presents to her physician 10 weeks following a true posterior wall myocardial infarction. The patient is still symptomatic. What is the correct ICD-9-CM code for this condition? a. 414.8 c. 410.60 b. 410.62 d. 412 ____ 159. ____ is a term that stands for enlargement of the heart. a. Cardiorenal c. Cardiomegaly b. Angiomegaly d. Valvuloplasty ____ 160. Repair of coronary vessel is called: a. Endarterectomy c. Aortic b. Angioplasty d. Endovascular ____ 161. A physician performs a four-vessel autogenous (one venous, three arterial) coronary bypass on a patient who had a previous CABG two years ago, utilizing the saphenous vein and the left and right internal mammary arteries. Select the CPT® codes for this procedure. a. 33535, 33510-51, 33530, 35600 c. 33535, 33517, 33530, 35600 b. 33534, 33518, 33530 d. 33535, 33517, 33530 ____ 162. A patient presented to the ED and was found to have a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm. He was taken to emergency surgery where a physician performed a direct repair. The physician documented that the aneurysm involved the common iliac. Select the proper CPT® code for this procedure. a. 34800 c. 35103 b. 35092 d. 35102 ____ 163. A patient presents to the hospital for a cardiovascular SPECT study. A single study is performed under stress, but without quantification, with a wall motion study, and ejection fraction. Select the CPT® code(s) for this procedure. a. 78451, 78472 c. 78453 b. 78453, 78472 d. 78451 ____ 164. Intracoronary stents are placed in the right coronary and left anterior descending arteries for a patient with stenosis. Percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty is performed on the left circumflex coronary artery. Choose the correct CPT® codes for this procedure. a. 92980-RC, 92981-LD, 92984-LC c. 92980, 92981 b. 92980 X 2, 92982 d. 92980-RC, 92981-LD, 92982-LC ____ 165. Select the ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes used for pseudoaneurysm, cardiac tamponade and left ventricular failure? a. 442.9, 423.3, 428.1 c. 424.0, 420.99, 428.1 b. 414.10, 420.99, 428.0 d. 441.9, 423.9, 428.0 ____ 166. Physician changes the battery on a patient’s dual chamber permanent pacemaker. a. 33212 c. 33213-52, 33233-51 b. 33213-52 d. 33213, 33233-51 ____ 167. Physician replaces a single chamber permanent pacemaker with a dual chamber permanent pacemaker. a. 33213, 33233-51 c. 33214 b. 33213, 33233-51, 33235-51 d. 33212, 33233-51 ____ 168. Patient presents to his physician’s office. He is diagnosed with benign hypertension and Stage 3 chronic kidney disease. a. 403.10, 585.3 c. 403.10, 585.6 b. 401.1, 585.3 d. 401.1, 585.9 ____ 169. In the cath lab, a physician places a catheter in the aortic arch from a right femoral artery puncture. Fluoroscopic imaging performed by the physician. a. 36215, 75605-26 c. 36200, 75650-26 b. 36200, 75605-26 d. 36215, 75650-26 ____ 170. In the cath lab the following procedures are performed: Catheter placed in the left renal, accessory renal superior to the left renal and one main right renal artery. Radiologic supervision and imaging s performed in all locations. a. 36245, 36245-59, 75724-26 b. 36245, 36424-59, 364245, 59 c. 36245, 36245-59, 36245-59, 75724-26, 72722-26-LT d. 36245-LT, 36245-59-LT, 36245-59-RT, 75724-26, 75774-26 ____ 171. Patient is diagnosed with acute systolic heart failure due to hypertension with CKD stage IV. a. 404.91, 428.21, 585.4 c. 401.9, 403.90, 428.21, 585.4 b. 402.91, 403.90, 428.21, 585.4 d. 403.90, 428.21, 585.4 ____ 172. A patient presents for epicardial placement of a permanent pacemaker via median sternotomy to the right atrium and ventricle. The patient has bundle branch block and nodal dysfunction. a. 33214, 426.51, 427.89 c. 33202, 33213-51, 426.50, 427.81 b. 33203, 33213-51, 426.53, 427.81 d. 33208, 33213-51, 426.50, 427.81 ____ 173. A physician states he performed a comprehensive EP study with induction of arrhythmia in the hospital. The report shows bundle of HIS recording, pacing and recording of the right atrium, and induction of arrhythmia by electrical pacing. a. 93600-26, 93602-26, 93610-26, 93618-26 c. 93620-26, 93621-26 b. 93620-26 d. 93619-26 ____ 174. Due to infections from hemodialysis, the physician replaces a dual chamber cardioverter-defibrillator system with an epicardial dual chamber cardioverter defibrillator system. a. 33249 c. 332214 b. 33249, 33241-51, 33243-51, 33244-51 d. 33244, 33202-51, 33240-51, 33241-51 ____ 175. A physician supervises a patient during a cardiac stress test performed at the hospital and writes the interpretation and report. a. 93015 c. 93016, 93018 b. 93016-26 d. 93016, 93017 ____ 176. Aortography and bilateral extremity angiography was performed. The physician placed the catheter in aorta at level of the renal arteries and injected contrast for the aortography and repositioned the catheter just above the bifurcation for angiography of the extremities. a. 36200, 75630-26 c. 36200, 75625-26, 75710-50-26 b. 36200, 75625-26, 75716-26 d. 36200, 75716-26 ____ 177. Catheter advanced from the right femoral artery into the left and right pulmonary artery. The catheter was further negotiated into the right lower lobe. Pulmonary angiography performed in all locations. a. 36014, 36013-59, 75743 b. 36015, 36013-59, 75743, 75774 c. 36015-RT, 36014-59-LT, 75743-26, 75774-26 d. 36015, 36014-59, 75743 ____ 178. An arterial catheterization is performed by cutdown for transfusion. a. 36600 c. 36625 b. 36620 d. 36640 ____ 179. A PICC with a port is placed for a 45 year-old patient for chemotherapy infusion under fluoroscopic guidance in the hospital. a. 36568, 77001 c. 36570, 77001-26 b. 36571, 77001-26 d. 36571, 77001 ____ 180. A physician inserts a centrally inserted, tunneled central venous access device with a subcutaneous pump on a 7 year-old. a. 36561 c. 36560 b. 36563 d. 36558 ____ 181. The cardiologist advances a 6 French catheter into the left renal artery via a right common femoral puncture. It is selectively catheterized and angiographic films are taken. The catheter was then removed and a diagnostic guiding type, RDC catheter was used and the left renal artery was selectively engaged. A 0.014 Supracore wire was used and the lesion was crossed. A 6.0 X 18 mm balloon expandable Racer stent was introduced. This was expanded around 8 atmospheres of pressure which is nominal. Angiography revealed excellent results with no residual stenosis. a. 36217, 36218, 37205, 37206, 75710-26, 75665-26, 75960-26 b. 36245-LT, 37205, 75960-26 c. 36245, 36245-59, 75710-26, 75658-26, 75960-26, 75962-26 d. 36217-RT, 36217-LT, 37205, 75724-26, 75960-26 ____ 182. Preoperative Diagnosis: Aortic valve stenosis with coronary artery disease associated with congestive heart failure Postoperative Diagnosis: Same Anesthesia: General endotracheal Incision: Median sternotomy Description of Procedure: The patient was brought to the operating room and placed in supine position. After the patient was prepared, median sternotomy incision was carried out and conduits were taken from the left arm as well as the right thigh. She was cannulated after the aorta and atrium were exposed and full heparinization. She went on cardiopulmonary bypass and the aortic cross-clamp was applied Cardioplegia was delivered through the coronary sinuses in a retrograde manner. The patient was cooled to 32 degrees. Iced slush was applied to the heart. The aortic valve was then exposed through the aortic root by transverse incision. The valve leaflets were removed and the #23 St. Jude mechanical valve was secured into position by circumferential pledgeted sutures. At this point, aortotomy was closed. Attention was turned to the coronary arteries. The first obtuse marginal artery was a very large target and the vein graft to this target indeed produced an excellent amount of flow. Proximal anastomosis was then carried out to the foot of the aorta. The radial artery was anastomosed to the left anterior descending artery target in an end-to-side manner. The proximal anastomosis was then carried out to the root of the aorta. The patient came off cardiopulmonary bypass after aortic cross-clamp was released. She was adequately warmed. Protamine was given without adverse effect. Sternal closure was then done using wires. The subcutaneous layers were closed using Vicryl suture. The skin was approximated using staples. a. 33400, 33533, 33510 c. 33405, 33533, 33510, 35500 b. 33405, 33533, 33517, 35600 d. 33411, 33533, 33517, 35600 ____ 183. During an inpatient hospitalization, a patient who suffered a myocardial infarction had a combined right and left heart catheterization. Access was achieved through the right femoral artery and the right femoral vein. Selective catheterization of the coronary arteries and selective catheterization of the left ventricle were followed by injections of contrast and angiography. During the right heart catheterization, angiography of the right atrium was performed. Imaging supervision, interpretation and report for all angiography was done during the cardiac catheterization. Select the CPT® codes for this procedure. a. 93453-26, c. 93460 b. 93460-26, 93565-26 d. 93460, 93565 ____ 184. A 35 year-old patient presented to the ASC for PTA of an obstructed hemodialysis AV graft in the venous anastomosis and the immediate venous outflow. The procedure was performed under moderate sedation administered by the physician that performed the PTA. The physician performed all aspects of the procedure, including radiological supervision and interpretation. Code for all services performed. a. 35460, 99144, 75978-26 c. 35476, 75978-26 b. 35492, 75978-26 d. 35476, 99144, 75978-26 ____ 185. What is included in all vascular injection procedures? a. Catheters, drugs, and contrast material b. Selective catheterization c. Just the procedure itself d. Necessary local anesthesia, introduction of needles or catheters, injection of contrast media with or without automatic power injection, and/or necessary pre-and postinjection care specifically related to the injection procedure. ____ 186. Patient undergoes transcatheter placement of an extracranial vertebral artery stent in the right vertebral artery. a. 0075T c. 35005 b. 35301 d. 0075T-26 ____ 187. Catheter advanced from the right femoral artery into the left and right pulmonary artery. The catheter was further negotiated into the right lower lobe. Pulmonary angiography performed in all locations, including radiologic supervision and interpretation. a. 36015-RT, 36014-59-LT, 75743-26, 75774-26 b. 36015-50, 36014, 75743-26 c. 36014-50, 75741, 75774-26 d. 36015, 36014-59, 75741-26, 75741-59 ____ 188. INDICATIONS FOR CORONARY INTERVENTION: Acute inferior myocardial infarction. Documented mildly occlusive plaque with much clot in the right coronary artery. PROCEDURE: Insertion of temporary pacemaker in the right femoral vein. Primary stenting of the right coronary artery with a 4.5 x 16 mm Express stent. Angio-Seal to the vessels of the right common femoral artery post procedure, and also Angio-Seal of the right common femoral vein. TECHNIQUE: Judkins percutaneous approach from the right groin with Perclose at the arterial puncture site post procedure. CATHETERS: #4-French Angio-Jet catheter device, insertion of a #5-French temporary pacing wire, a 4.5 x 16 mm Express stent. PRESSURES: Aortic Pressure: 107/78 RESULTS: Coronary stenting procedure of the right coronary artery: The right coronary artery was primarily stented with a 4.5 x 16 mm Express stent. It was expanded to 12 atmospheres. There was no residual stenosis. IMPRESSION: Successful Angio-Jet and stenting of the distal right coronary artery with no residual stenosis. Angio-Seal to the right femoral vein post procedure. PROCEDURE: Through the femoral artery sheath the EBU was advanced to the left main. Following this, a PT graphic intermediate wire was used to cross the lesion. Following this, angioplasty of the lesion was performed utilizing a 2.5 x 20 millimeter CrossSail balloon at multiple sites to ten atmospheres. Following this, there was a fair result, however there was a significant stenosis and significant calcification at the area and the decision was made to pursue trying to stent the lesion. Multiple stents were attempted including a 2.5 x 9 millimeter zipper MX and a 2.5 x 13 millimeter Guidant stent. This was abandoned and in switching out to a balloon for further ballooning, the patient became hypertensive and with difficulty in terms of her respiratory status. Angiography revealed an occlusion of the mid left anterior descending and thrombus throughout the proximal left anterior descending extending into the left main. Recheck of ACT showed the ACT to be at eight seconds. This likely represented subtherapeutic range for her anticoagulation. A check of her medications revealed that instead of Angiomax, the patient had been given ReoPro without antithrombotic agent. She was therefore given IV heparin up to 12,000 units and her ReoPro was continued. The lesion was then rewired and an AngioJet was used to try to suction out this area of thrombus. Unfortunately the AngioJet was unable to cross the mid left anterior descending lesion and therefore was somewhat limited in its use for a more distal thrombus, it did suction out the proximal left anterior descending thrombus. At this point, the patient was emergently intubated and multiple pressors were started including dopamine, Levophed, vasopressin and epinephrine. Following this, a laser was attempted to cross the lesion an excimer laser X80 Spectranetics 0.9 Vitesse, however, this laser was unable to cross the lesion. Therefore a long balloon, a 2.0 x 40 millimeter CrossSail balloon was used to cross the lesion and inflate multiple segments of the mid left anterior descending up to a maximum inflation pressure of ten atmospheres. This improved flow, though by no means restored it back to normal. Therefore following this, longer balloon inflations were performed utilizing a 2.0 x 20 millimeter CrossSail balloon up to fourteen atmospheres for one and a half minutes. This did not improve significantly the flow distally and therefore the decision was made to try to stent the mid segment with a 2.5 x 9 millimeter zipper MX stent to a maximum inflation pressure of fourteen atmospheres. This resolved the issue in terms of the mid left anterior descending lesion, however beyond the stent there was continued to be residual stenosis and multiple balloons were used to balloon this up to a 2.5 x 20 millimeter balloon up to fourteen atmospheres. The final result in the left anterior descending revealed a lesion in the mid left anterior descending that was approximately 40 percent, there was TIMI III flow throughout the proximal and mid left anterior descending. However, at the level of the apex, there was TIMI 0 flow. Throughout the angioplasty, the patient had episodes of bradycardia and a temporary pacemaker was placed, and this was removed at the end of the procedure. IMPRESSION: Successful stent to the mid left anterior descending, complicated by thrombotic event in the left anterior descending system. Final result was a successful stent to the mid left anterior descending with residual TIMI 0 flow in the distal left anterior descending. At the end of the case an intra-aortic balloon was placed in the left femoral artery sheath and the patient was sent to the Coronary Care Unit on multiple pressors including epinephrine, vasopressin, Levophed and dopamine. a. 92980-RC, 92981-RC c. 92980-LC, 92981-RC, 92973 b. 92980-RC, 92981-LD, 33967, 92973 d. 92982-RC, 92980-RC, 92973-RC ____ 189. A patient has a complete TTE performed to assess her mitral valve prolapse (congenital). The physician performs the study in his cardiac clinic. a. 93303 c. 9308 b. 93306 d. 93312 ____ 190. A patient has a Transtelephonic rhythm strip pacemaker evaluation for his dual chamber pacemaker started. The physician plans on it being worn for 90 days. After 2 months, the patient no longer wants to wear the device and it is removed. What can the physician report? a. 93293-52 c. 93296 b. 93295 d. 93293 ____ 191. A patient is brought to the operating suite when she experiences a large output of blood in her chest tubes post CABG. The physician that performed the original CABG yesterday is concerned at the post-operative bleeding. He explores the chest and finds a leaking anastomosis site that he resutured. a. 35761 c. 35820-78 b. 35761-78 d. 35241 ____ 192. MAZE procedure is performed on a patient with atrial fibrillation. The physician isolates and ablates the electric paths of the pulmonary veins in the left atrium, the right atrium, and the atrioventricular annulus while on cardiopulmonary bypass. a. 33254 c. 33256 b. 33255 d. 33259 ____ 193. Patient undergoes a mitral valve repair with a ring insertion and an aortic valve replacement, on cardiopulmonary bypass. a. 33464, 33406-51 c. 33430, 33405-51 b. 33426, 33405-51 d. 33468, 33426-51 ____ 194. Patient undergoes a 3 artery CABG. A surgical assistant procures the artery used for the grafts. Code for the assistant surgeon. a. 33535-80 c. 33510-80 b. 33533-80, 35600-80 d. 33517-80, 35600-80 ____ 195. The skin over the left groin was prepped and draped in a sterile fashion and anesthetized with 1% Xylocaine. A 5 French pigtail catheter was placed in the abdominal aorta and a run-off was performed following injection of 80cc of contrast. Oblique DSA images of the iliac circulation were performed following 2 injections, each 15cc. Findings: Abdominal aorta: no signs of renal artery stenosis. There is mild atheromatous change involving the lower abdominal aorta. There are 2 eccentric plaques arising from the distal aorta just above the iliac bifurcation. There are high-grade stenoses involving both proximal iliacs, the right far more pronounced than the left. The right superficial femoral, profunda femoral, popliteal arteries are normal. The trifurcation vessels are unremarkable. On the left, there is an eccentric plaque in the common femoral artery just below the catheter entrance site. This creates approximately 40-50% stenosis at this site. The remainder of the proximal femoral artery is normal. The trifurcation vessels and popliteal artery are normal. a. 36200, 75650, 75625 c. 36200, 75630-26 b. 36215, 75630-26-50 d. 36200, 75625, 75600 ____ 196. PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Heart Block POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Heart Block ANESTHESIA: Local anesthesia NAME OF PROCEDURE: Reimplantation of dual chamber pacemaker DESCRIPTION: The chest was prepped with Betadine and draped in the usual sterile fashion. Local anesthesia was obtained by infiltration of 1% Xylocaine. Then a subfascial incision was made about 2.5 cm below the clavicle and the old pulse generator was removed. Using the Seldinger technique, the subclavian vein was cannulated and through this, the old atrial lead was removed and a new atrial lead (serial # 6662458) was placed in the left atrium, and to the atrial septum. Thresholds were obtained as follows: the P-wave was 1.4 millivolts, atrial threshold was 1.6 millivolts with a resultant current of 3.5 mA, and resistance of 467 ohms. Using a second subclavian stick in the Seldinger technique, the old ventricular lead was removed and a new ventricular lead (serial # 52236984) was inserted and placed into the right ventricular apex. The thresholds were obtained and were as follows: R-wave was 23.5 millivolts. The patient was pacing at 100% at 0.5 volts with resultant current of 0.8 mA and resistance of 480 ohms. When we were satisfied with the thresholds, the leads were connected to the pacemaker generator (serial # 22561587) which was inserted into the previously created pocket. The wound was thoroughly irrigated with antibiotic solution and hemostasis was obtained. The incision was closed in layered fashion with 2-0 Dexon. A compressive dressing was applied and the patient tolerated the procedure very well. He was taken to the recovery room in satisfactory condition. a. 33207, 33206-51, 33236-51 c. 33208, 33238-51, 33241-51 b. 33202, 33233-51 d. 33235, 33208-51, 33233-51 ____ 197. A patient presents for extremity venous study. Complete noninvasive physiologic studies of both lower extremities. a. 92922 c. 93965 b. 93923 d. 93965-50 ____ 198. An electrophysiologist performs the following EP study in the cardiac suite: right atrial and ventricular pacing, recording of the bundle of HIS, right atrial and ventricular recording, and left atrial and ventricular pacing and recording from the left atrium. a. 93600, 93602, 93603, 93610, 93612, 93618, 93621, 93622 b. 93619, 93621 c. 93620, 93621, 93622 d. 93620, 93618, 93621 ____ 199. CLINICAL SUMMARY: The patient is a 41-year-old female with known coronary disease and recent recurrent chest pain, cardiac catheterization demonstrating subtotal occlusion of the diagonal artery at its takeoff from the left anterior descending artery with the diagonal artery taking off within the left anterior descending vessel. PROCEDURE: With informed consent obtained, the patient was prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. With the right groin area infiltrated with 2% Xylocaine and the patient given 2mg of Versed and 50mcg Fentanyl intravenously for conscious sedation and pain control. The right femoral artery was cannulated with a modified Seldinger technique and a 6-French catheter sheath placed. A 6-French JL3.5 catheter with no side holes was utilized as a guiding catheter. After the initial guiding picture had been obtained, the patient was given Angiomax per protocol, and a short Cross-it 100 wire was advanced to the LAD and then into the diagonal vessel. A 2.0. 15-mm-long Maverick balloon was used for dilatation of the diagonal artery ostium with inflation pressure up to 8 atmospheres was applied. Final angiographic documentation was carried out after the patient received 200 mcg of intracoronary nitroglycerine. The guiding catheter was then pulled, the sheath secured in place. The patient is now being transferred to telemetry for post coronary intervention observation and care. RESULTS: The initial guiding picture of the left coronary system demonstrates the high-grade ostial stenosis of the diagonal artery taking off within the LAD. Following the coronary intervention with balloon angioplasty there is complete resolution of the stenosis with less than 10% residual narrowing observed, no evidence for intimal disruption, no intraluminal filling defect, and good antegrade TIMI III flow preserved. CONCLUSION: Successful coronary intervention with balloon angioplasty to the ostial/proximal segment of the second diagonal vessel. a. 92980-LD c. 92980-LD, 92984-LD b. 92982-LD d. 92995 ____ 200. Preoperative Diagnosis: Coronary artery disease associated with congestive heart failure; in addition, the patient has diabetes and massive obesity. Postoperative Diagnosis: Same Anesthesia: General endotracheal Incision: Median sternotomy Indications: The patient had presented with severe congestive heart failure associated with her severe diabetes. She had significant coronary artery disease consisting of a chronically occluded right coronary artery but a very important large obtuse marginal artery coming off as the main circumflex system. She also has a left anterior descending artery which has moderate disease and this supplies quite a bit of collateral to her right system. The decision was therefore made to perform a coronary artery bypass grafting procedure, particularly since she is so symptomatic. The patient was brought to the operating room Description of Procedure: The patient was brought to the operating room and placed in supine position. Myself, the operating surgeon was scrubbed throughout the entire operation. After the patient was prepared, median sternotomy incision was carried out and conduits were taken from the left arm as well as the right thigh. The patient weighs almost three hundred pounds and with her obesity there was some concern as to taking down the left internal mammary artery. Because the radial artery appeared to be a good conduit she would have arterial graft to the left anterior descending artery territory. She was cannulated after the aorta and atrium were exposed and full heparinization. Attention was turned to the coronary arteries. The first obtuse marginal artery was a very large target and the vein graft to this target indeed produced an excellent amount of flow. Proximal anastomosis was then carried out to the foot of the aorta. The left anterior descending artery does not have severe disease but is also a very good target and the radial artery was anastomosed to this target and the proximal anastomosis was then carried out to the root of the aorta. Sternal closure was then done using wires. The subcutaneous layers were closed using Vicryl suture. The skin was approximated using staples. a. 33533, 33510 c. 33533, 33517 b. 33511 d. 33533, 33517, 35600 ____ 201. CLINICAL SUMMARY: The patient is a 55-year-old female with known coronary disease and previous left anterior descending and diagonal artery intervention, with recent recurrent chest pain. Cardiac catheterization demonstrated continued patency of the stented segment but diffuse borderline changes in the ostial/proximal portion of the right coronary artery. PROCEDURE: With informed consent obtained, the patient was prepped and draped in the usual sterile fashion. With the right groin area infiltrated with 2% Xylocaine and the patient given 2 mg of Versed and 50 mcg of fentanyl intravenously for conscious sedation and pain control, the 6-French catheter sheath from the diagnostic study was exchanged for a 6-French sheath and a 6- French JR4 catheter with side holes utilized. The patient initially received 3000 units of IV heparin, and then IVUS interrogation was carried out using an Atlantis Boston Scientific probe. After it had been determined that there was significant stenosis in the ostial/proximal segment of the right coronary artery, the patient received an additional 3000 units of IV heparin as well as Integrilin per double-bolus injection. A 3.0, 16-mm-long Taxus stent was then deployed in the ostium and proximal segment of the right coronary artery in a primary stenting procedure with inflation pressure up to 12 atmospheres applied. Final angiographic documentation was carried out and then the guiding catheter pulled, the sheath upgraded to a 7-French system because of some diffuse oozing around the 6-French-sized sheath, and the patient is now being transferred to telemetry for post coronary intervention observation and care. RESULTS: The initial guiding picture of the right coronary artery demonstrates the right coronary artery to be dominant in distribution, with luminal irregularities in its proximal and mid third with up to 50% stenosis in the ostial/proximal segment per angiographic criteria although some additional increased radiolucency observed in that segment. IVUS interrogation confirms severe, concentric plaque formation in this ostial/proximal portion of the right coronary artery with over 80% area stenosis demonstrated. The mid, distal lesions are not significant with less than 40% stenosis per IVUS evaluation. Following the coronary intervention with stent placement, there is marked increase in the ostial/proximal right coronary artery size with no evidence for intimal disruption, no intraluminal filling defect, and TIMI III flow preserved. CONCLUSION: Successful coronary intervention with drug-eluting Taxus stent placement to the ostial/proximal right coronary artery. a. 92980-RC, 92978-RC c. 92980-RC, 92978-51-RC b. 92980-RC, 92984-RC, 92978-RC d. 92982-RC, 92981-RC, 92978-51-RC [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 67 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 13, 2021
Number of pages
67
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
95







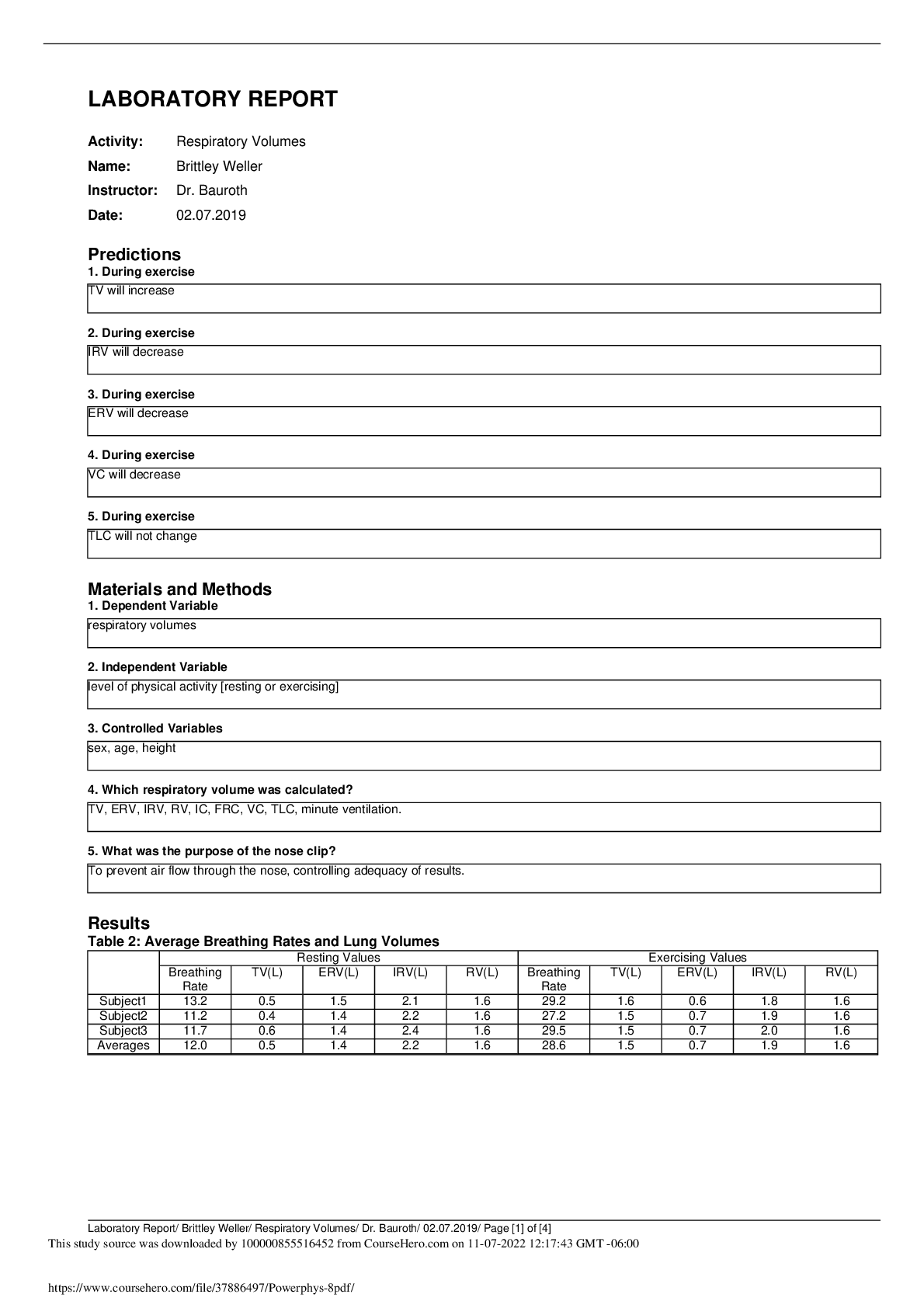
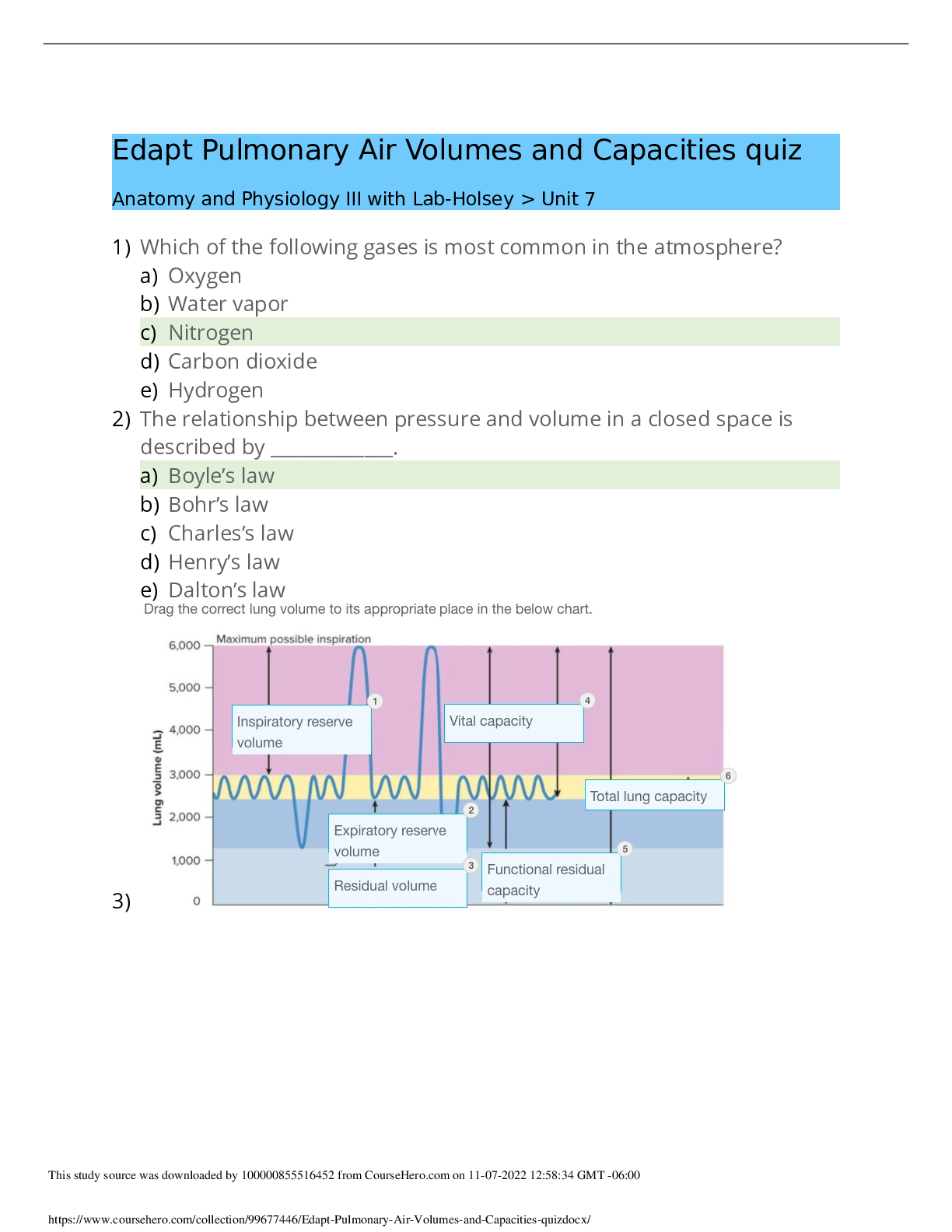





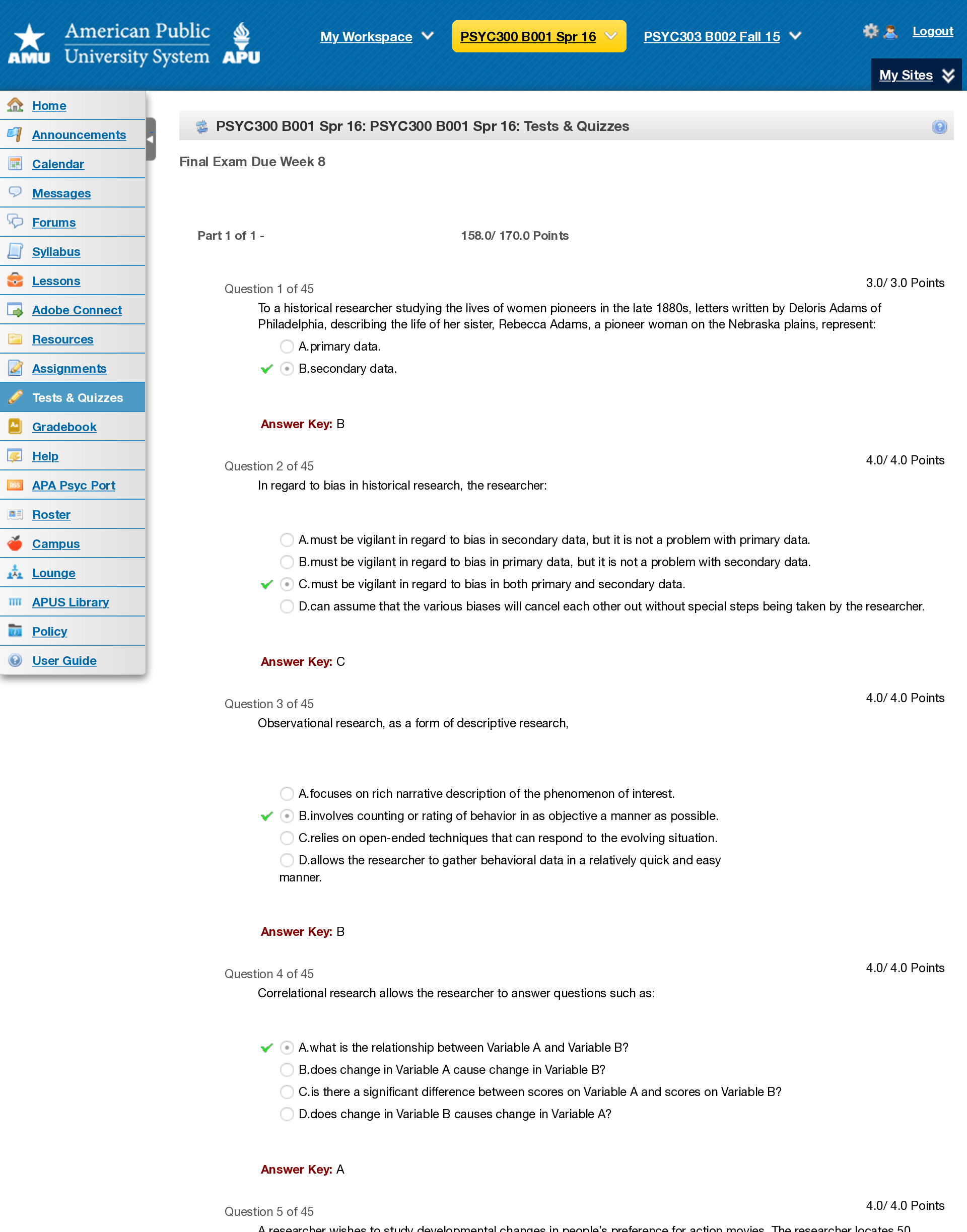
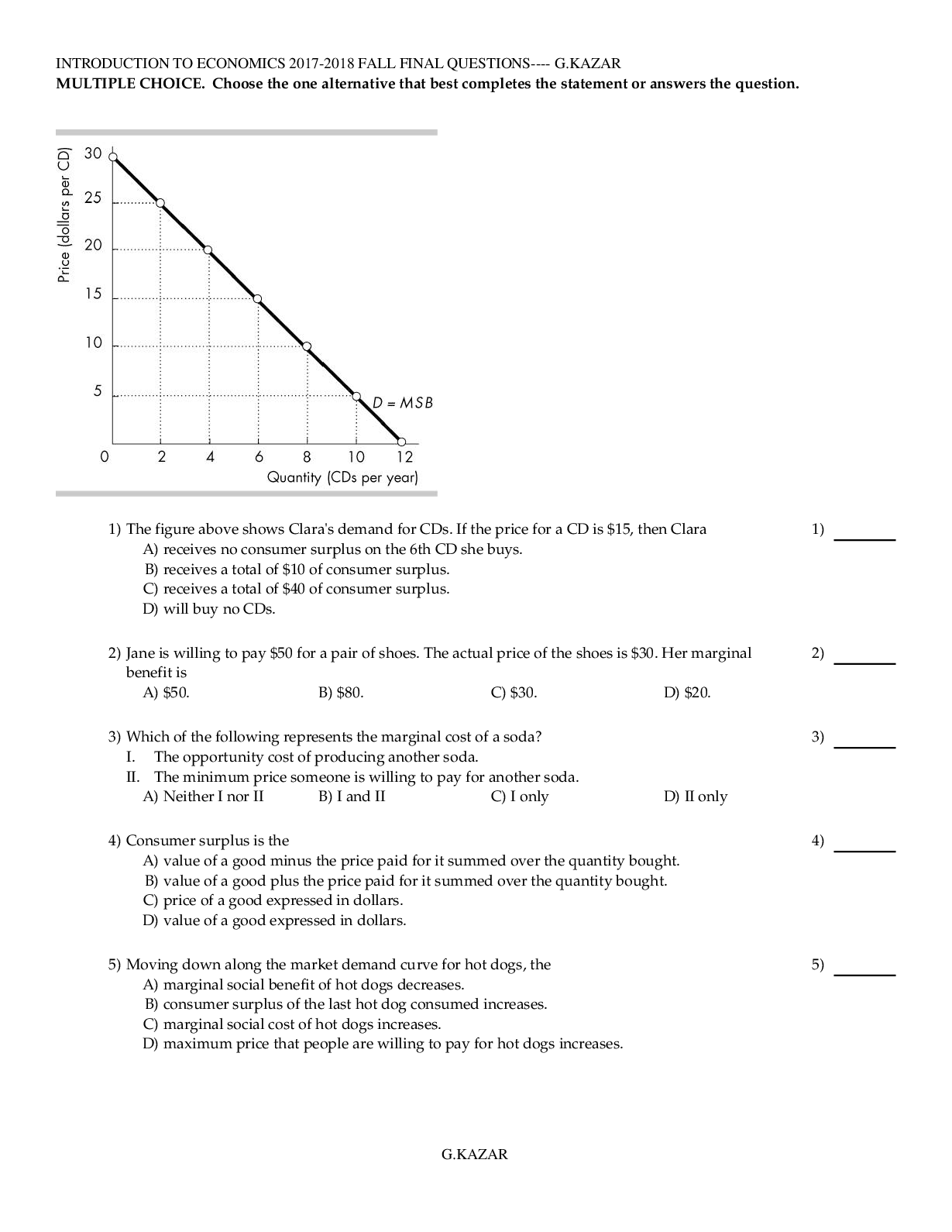
.png)
.png)






