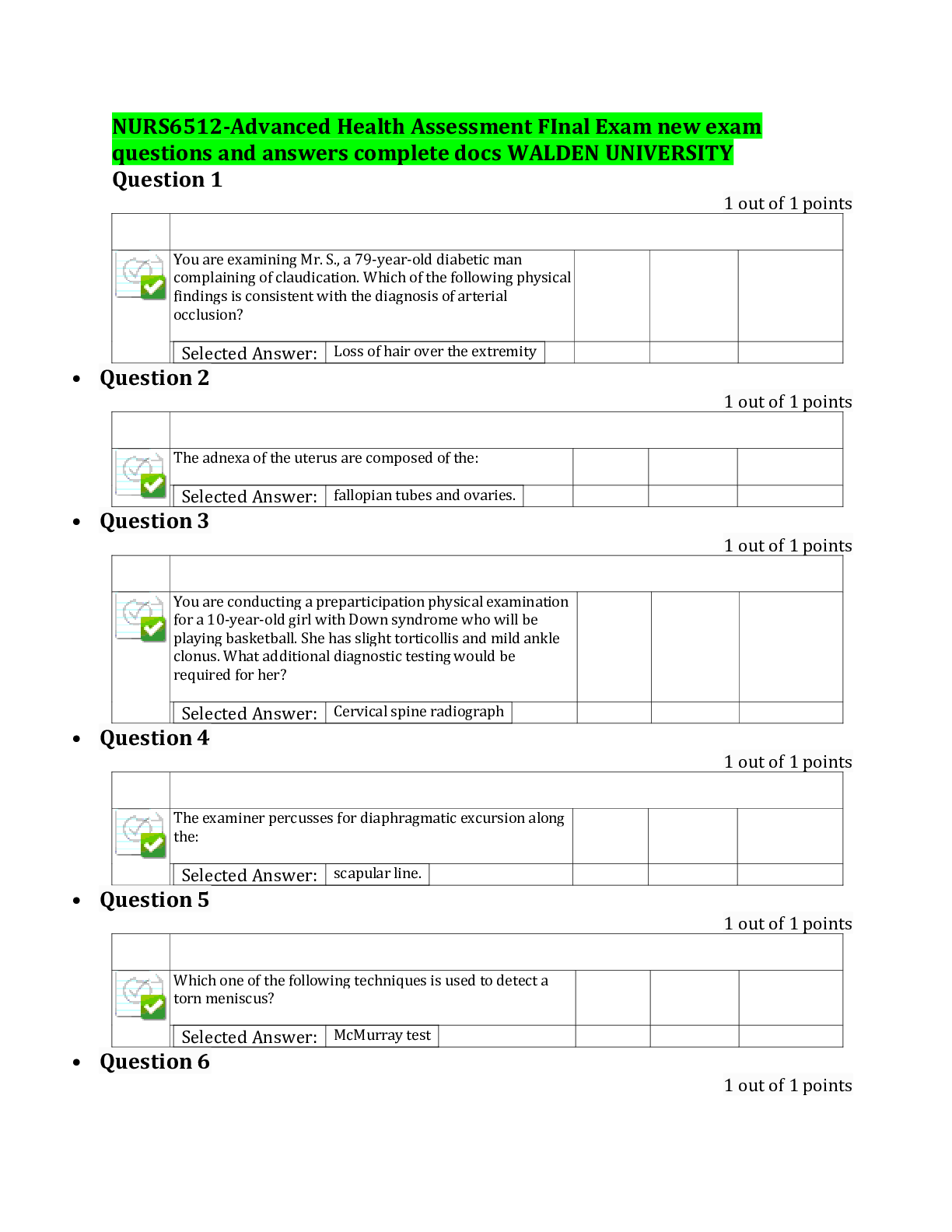
*NURSING > EXAM > Hesi, fundandamental and mother child_Question And Answers Complete Solutions (2020). (All)
Hesi, fundandamental and mother child_Question And Answers Complete Solutions (2020).
Document Content and Description Below
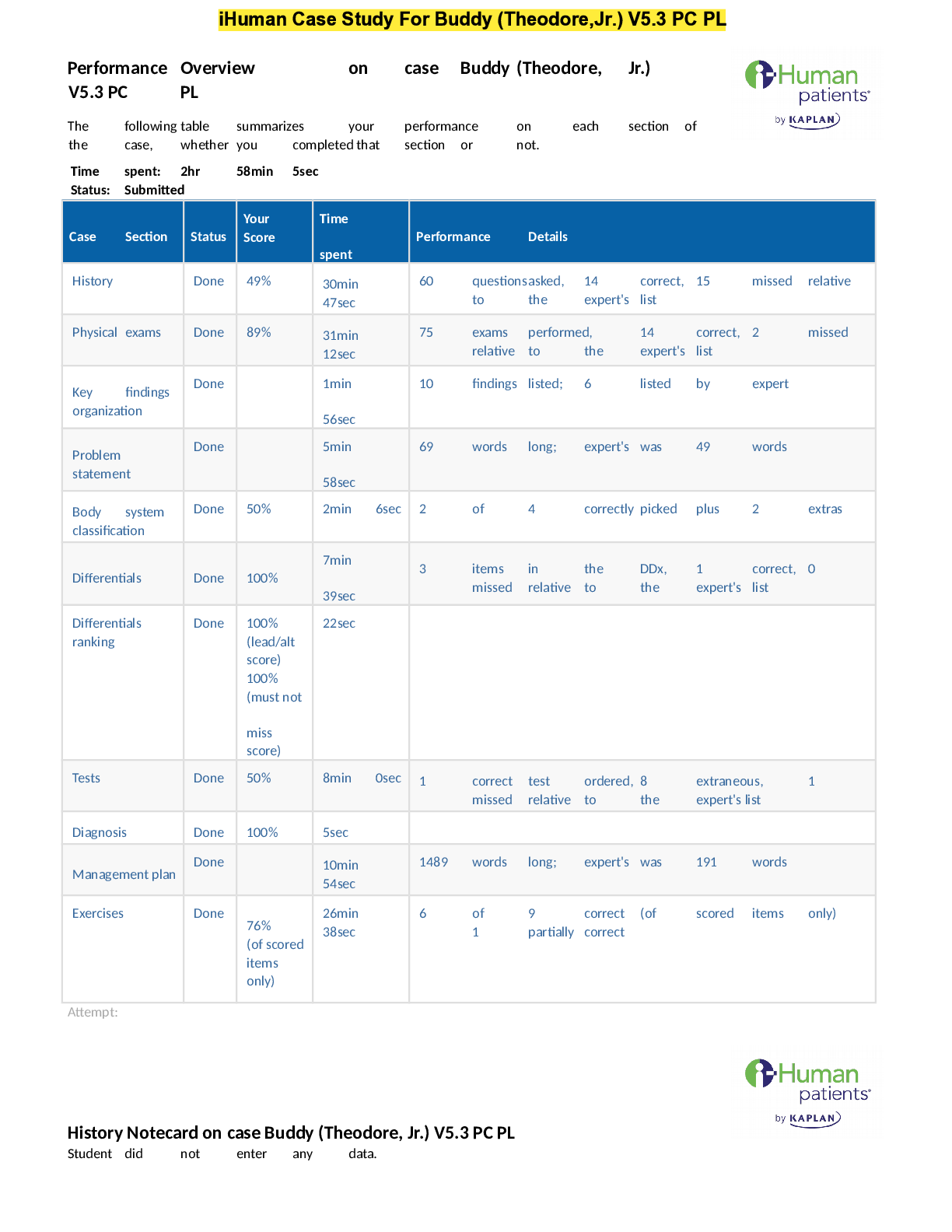
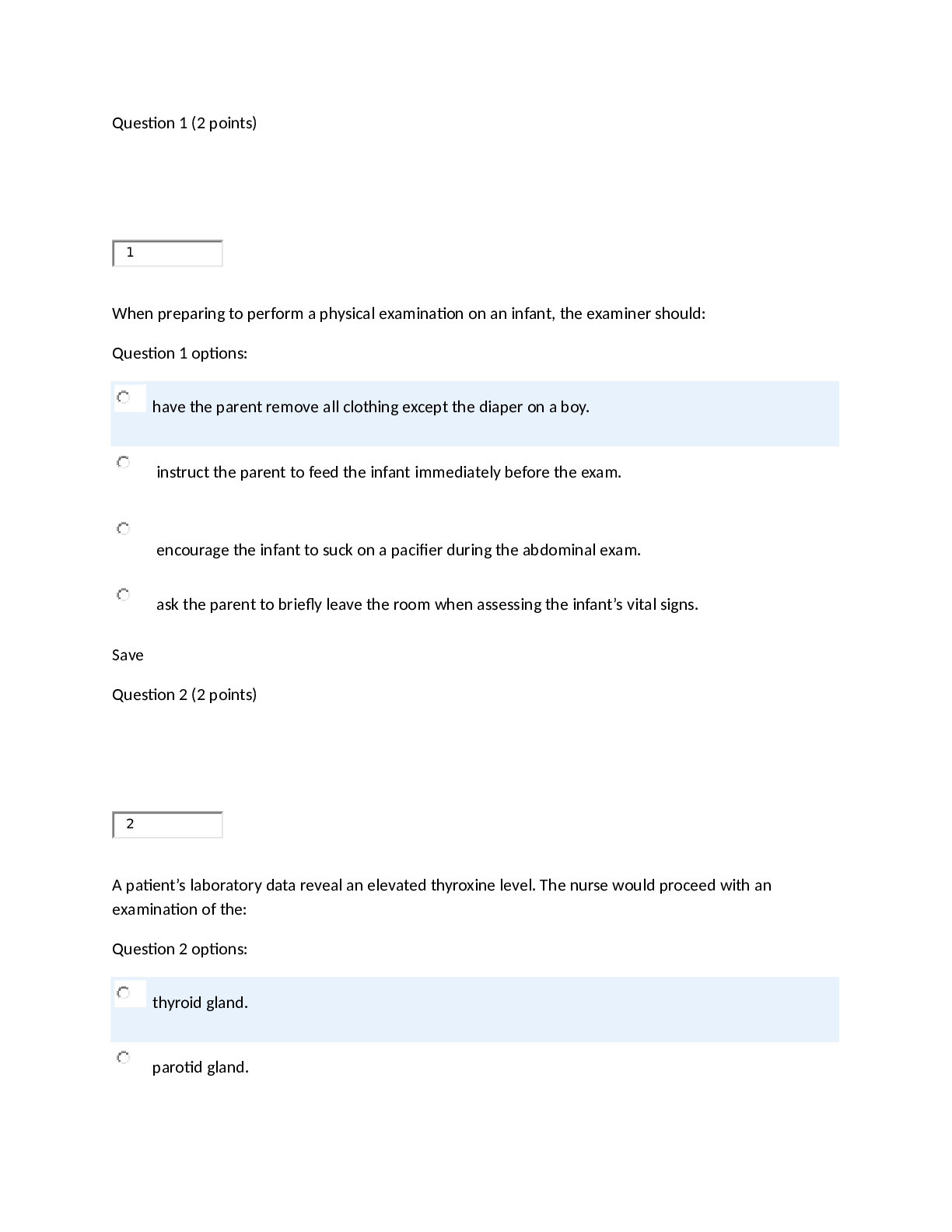
Hesi, Nursing 240- Fundamental and mother child- Verified Answers A nurse on the psychiatric unit of the hospital has been assigned four clients for the shift. The assignment includes an 84-year-old c... lient who is severely depressed, a 73-year-old client who is being discharged, a 53-year-old client who was admitted for lithium toxicity, and a 48-year-old client who has panic attacks. Which client should the nurse evaluate first after receiving report? 1 84-year-old client 2 73-year-old client 3 53-year-old client 4 48-year-old client The 53-year-old client should be evaluated first because of the severity of adaptations associated with lithium toxicity. A severely depressed client has a low energy level and is not at the greatest risk at this time. A client who is stable enough to be discharged does not need immediate attention. Clients with panic attacks usually seek immediate attention when it is needed. A young female client admitted to the trauma center after being sexually assaulted continues to talk about the rape. Toward what goal should the primary nursing intervention be directed? 1 Getting her involved with a rape therapy group 2 Remaining available and supportive to limit destructive anger 3 Exploring her feelings about men to promote future relationships 4 Providing a safe environment that permits the ventilation of feelings The client needs to be able to express her current feelings. Providing an environment in which she feels safe will encourage this expression of feelings. It is too soon after the assault to discuss this topic in a group. Although the nurse should be available and supportive, feelings of anger are usually not the initial response. It is too soon after the assault to discuss her feelings about men and future relationships. A client is dying. Hesitatingly, his wife says to the nurse, "I'd like to tell him how much I love him, but I don't want to upset him." Which is the best response by the nurse? 1 "You must keep up a strong appearance for him." 2 "I think he'd have difficulty dealing with that now." 3 "Don't you think he knows that without your telling him?" 4 "Why don't you share your feelings with him while you can?" It is difficult to work through a loss; however, encouraging the sharing of feelings helps both parties to feel better about having to let go. The response "You must keep up a strong appearance for him" impedes the work of acceptance of one's finality and the use of the remaining time to the best advantage. There is no evidence to suggest that the client cannot cope with these emotions; the response "I think he'd have difficulty dealing with that now" denies that this is a time for closeness and honesty. The response "Don't you think he knows that without your telling him?" is demeaning, closes off communication, and does not foster the expression of feelings. A nonviolent client on the psychiatric unit suddenly refuses to take the prescribed antipsychotic medication. What should the nurse do? 1 Honor the client's decision and document the behavior and all interventions 2 Use an authoritarian approach to induce the client to take the prescribed medication 3 Call the health care provider and request that the client be discharged against medical advice 4 Start proceedings to have the client declared incompetent and seek a court order permitting medication A client has the right to refuse treatment and should not be forcibly medicated unless the client is deemed dangerous to him- or herself or others. An authoritarian approach is not therapeutic and may compromise the nurse-client relationship. Calling the health care provider is premature; first the nurse should attempt therapeutic interventions to meet the client's needs. Starting proceedings to have the client declared incompetent is appropriate for a client who is considered to be dangerous to him- or herself or others, or incompetent to evaluate necessary treatment. STUDY TIP: When forming a study group, carefully select members for your group. Choose students who have abilities and motivation similar to your own. Look for students who have a different learning style than you. Exchange names, email addresses, and phone numbers. Plan a schedule for when and how often you will meet. Plan an agenda for each meeting. You may exchange lecture notes and discuss content for clarity or quiz one another on the material. You could also create your own practice tests or make flash cards that review key vocabulary terms. Which psychotherapeutic theory uses hypnosis, dream interpretation, and free association as methods to release repressed feelings? 1 Behaviorist model 2 Psychoanalytical model 3 Psychobiological model 4 Social-interpersonal model The psychoanalytical model studies the unconscious and uses the strategies of hypnosis, dream interpretation, and free association to encourage the release of repressed feelings. The behaviorist model holds that the self and mental symptoms are learned behaviors that persist because they are consciously rewarding to the individual; this model deals with behaviors on a conscious level of awareness. The psychobiological model views emotional and behavioral disturbances as stemming from a physical disease; abnormal behavior is directly attributed to a disease process. This model deals with behaviors on a conscious level of awareness. The social-interpersonal model affirms that crucial social processes are involved in the development and resolution of disturbed behavior; this model deals with behavior on a conscious level of awareness. A depressed client has been taking Paroxetine (Paxil) 20 mg by mouth once a day for 4 weeks. The practitioner concludes that there is no clinical improvement in the client's condition and increases the daily dose to 30 mg. The medication is supplied in an oral suspension of 10 mg/5 mL. How many milliliters of Paxil solution should the nurse instruct the client to take? Record your answer using a whole number. __________ mL Solve the problem with the use of ratio and proportion: Desired 30 mg :: x mL Have 10 mg 5 mL 10 x = 30 x 5 x = 150 ÷ 10 x = 15 mL Test-Taking Tip: Do not fret over any one question for too long. If you are having trouble, skip the question and go back to it when you have finished answering the other questions. A parent of a 13-year-old adolescent with recently diagnosed Hodgkin disease tells a nurse, "I don't want her to know about the diagnosis." How should the nurse respond? 1 "It's best for your child to know the diagnosis." 2 "Did you know that the cure rate for Hodgkin disease is high?" 3 "Would you like someone with Hodgkin disease to talk with you?" 4 "Let's talk about how you're feeling about your child's diagnosis." Initiating a conversation about the client's feelings does not prejudge the parent; it encourages communication. Stating that it is best for the child to know the diagnosis disregards the parent's feelings and cuts off further communication. Asking the client about the cure rate may stop communication and does not recognize the parent's concerns. Offering to have someone with Hodgkin disease speak to the client is premature and does not recognize the parent's concerns. A client who is to undergo dilation and curettage, and conization of the cervix for cancer appears tense and anxious. What is the best approach for the nurse to support the client emotionally? 1 Explaining that these procedures are considered minor surgery 2 Asking whether something is troubling the client and whether she'd like to talk about it 3 Stating that the procedures are routine and asking what the client is really worried about 4 Explaining that everybody is fearful before the surgery even though there is little reason to worry Asking whether the client wants to talk about what's troubling her acknowledges that the client is anxious and, by means of indirect questioning, helps facilitate communication. Saying that these procedures are considered minor surgery denies the client's feelings. The client has not indicated that she is upset, and she may be unaware of or unable to verbalize the actual cause of the emotions. Saying that there is little reason to worry is false reassurance and cuts off communication. A client in the hyperactive phase of a mood disorder, bipolar type, is receiving lithium. A nurse sees that the client's lithium blood level is 1.8 mEq/L. What is the most appropriate nursing action? 1 Continuing the usual dose of lithium and noting any adverse reactions 2 Discontinuing the drug until the lithium serum level drops to 0.5 mEq/L 3 Asking the health care provider to increase the dose of lithium because the blood lithium level is too low 4 Holding the drug and notifying the health care provider (prescribing provider) immediately because the blood lithium level may be toxic The lithium level should be maintained between 0.5 and 1.5 mEq/L. The lithium level is currently unsafe but does not need to drop to 0.5 mEq/L before being resumed. Continuing the drug and asking the health care provider to prescribe a higher dosage are both unsafe options. An 18 year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her two roommates after being found unconscious in the bathroom. Laboratory tests are ordered. The nurse reviewing the findings notes that the urinalysis is positive for flunitrazepam (Rohypnol). The nurse knows that flunitrazepam is often used: 1 As a date rape drug 2 To control symptoms of psychosis 3 To control symptoms of bipolar mania In4 To treat hangover symptoms after excessive alcohol consumption Rohypnol (flunitrazepam), illegal in the United States, has been used in date rapes; the victim is attacked after consuming a drink spiked with the drug. Flunitrazepam is not used to treat psychosis, mania, or hangover symptoms. Test-Taking Tip: Watch for grammatical inconsistencies. If one or more of the options is not grammatically consistent with the stem, the alert test taker can identify it as a probable in option. When the stem is in the form of an incomplete sentence, each option should complete the sentence in a grammatically way. 4. In the second stage of labor the nurse should plan to discourage a client from holding her breath longer than 6 seconds while pushing with each contraction. What complication does this prevent? 1 Fetal hypoxia 2 Perineal lacerations 3 Carpopedal spasms In4 Maternal hypertension Prolonged breath holding at this stage of labor can result in decreased placental/fetal oxygenation, which could lead to fetal hypoxia. Perineal lacerations occur with rapid, uncontrolled expulsion of the fetus. Carpopedal spasms and maternal hypertension are not caused by prolonged holding of the breath. A nurse is aware that after the administration of alprazolam (Xanax) is started, it is important to observe the client for side effects. What is the nurse's initial action? 1 Measuring the client's urine output 2 Examining the client's pupils daily 3 Checking the client's blood pressure In 4 Monitoring the abdomen for distention Orthostatic hypotension is a common side effect of alprazolam (Xanax) that occurs early in therapy. Central nervous system depression is not an early side effect, but it may occur after prolonged use. An alteration in urine output is not a common side effect, but it may occur after prolonged use. Distention is not a common side effect, but distention from constipation may occur after prolonged use. Test-Taking Tip: Identifying content and what is being asked about that content is critical to your choosing the response. Be alert for words in the stem of the item that are the same or similar in nature to those in one or two of the options. Example: If the item relates to and identifies stroke rehabilitation as its focus and only one of the options contains the word stroke in relation to rehabilitation, you are safe in identifying this choice as the response. A 6-year-old child is found to have type 1 diabetes. In light of the child's cognitive developmental level, which explanation of the illness is most appropriate? 1 "Diabetes is caused by not having any insulin in your body." In2 "Diabetes will require you to take insulin shots for the rest of your life." 3 "You'll learn how to give yourself insulin now that you have diabetes." 4 "Taking insulin for your diabetes is like getting new batteries for your superhero toys." The child is in Piaget's stage of preoperational thought, which is manifested by magical thinking; therefore teaching should also employ magical thinking. "Diabetes is caused by not having any insulin in your body" is too technical and does not take into account the child's preoperational stage of development. This statement is appropriate for an adolescent in the formal operational stage of cognitive development. "Diabetes will require you to take insulin shots for the rest of your life" is too direct and does not consider the child's cognitive developmental stage of preoperational thought. This statement is appropriate for an adolescent in the formal operational stage of cognitive development. Also, the use of the word "shots" may precipitate anxiety. "You will be taught how to give yourself insulin now that you have diabetes" is too direct and does not consider the child's cognitive developmental stage of preoperational thought. This statement is appropriate for an adolescent in the formal operational stage of cognitive development. 1. A client is scheduled for amniocentesis. What should the nurse do before the procedure? 1 Give the client the prescribed sedative 2 Remind the client to empty her bladder 3 Prepare the client for an intravenous infusion 4 Encourage the client to drink three glasses of water An empty bladder reduces the risk of bladder puncture during the procedure. Sedation is not necessary. An intravenous line is not necessary. The client is encouraged to drink three glasses of water before a sonogram, not an amniocentesis. A woman has just received the news that she is pregnant. She is ambivalent about the pregnancy because she had planned to go back to work when her youngest child started school next year. What developmental task of pregnancy must the woman accomplish in the first trimester of pregnancy? 1 Recognize her ambivalence 2 Accept that she is pregnant 3 Prepare for the birth of the baby 4 Recognize the fetus as an individual separate from the mother The developmental task of the first trimester is accepting the reality of the pregnancy. Ambivalence is a normal emotion associated with early pregnancy. It is not a developmental task. Preparing for the birth is a developmental task of the third trimester. Recognizing the fetus as a separate individual from the mother is a developmental task of the second trimester. Test-Taking Tip: Make certain that the answer you select is reasonable and obtainable under ordinary circumstances and that the action can be carried out in the given situation. A married male client with three children has lost his job and states that he feels useless. He is tearful, upset, and embarrassed. What is an appropriate objective of care for this client? 1 Limiting tearfulness 2 Increasing self-esteem 3 Controlling feelings of sadness 4 Promoting acceptance by others The loss of a job can precipitate negative feelings about the self and decrease self-esteem. Feelings should be expressed, not limited; attempting to decrease a client's crying often ends up worsening it. Crying is not necessarily an expression of sadness; other feelings are involved. The focus should be on the client's self-acceptance, not acceptance by others. Test-Taking Tip: Do not read too much into the question or worry that it is a "trick." If you have nursing experience, ask yourself how a classmate who is inexperienced would answer this question from only the information provided in the textbooks or given in the lectures. A health care provider prescribes oxazepam (Serax) for a client who is beginning to experience withdrawal symptoms while undergoing detoxification. What are the primary reasons that oxazepam is given during detoxification? 1 Prevents injury and protects the client when seizures occur 2 Enables the client to sleep and eat better during periods of agitation 3 Encourages the client to cooperate with and accept treatment for alcoholism 4 Reduces the anxiety-tremor state and prevents more serious withdrawal symptoms Oxazepam (Serax) potentiates the actions of γ-aminobutyric acid, especially in the limbic system and , CVMPL;CVKE5/MF4,HMN6N ,’KUJ7YTH]./L,Nreticular formation and thus minimizes withdrawal symptoms. This drug helps reduce the risk for seizures but does not prevent injury or protect the client during a seizure. Enabling the client to sleep and eat better during periods of agitation is not the purpose of the drug. The ability of the client to accept treatment depends on the client's readiness to accept the reality of the problem. 80%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 6. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? A nurse is aware that a co-worker's mother died 16 months ago. The co-worker cries every time someone says the word "mother" and when the mother's name is mentioned. What does the nurse conclude about this behavior? 1 It is an expected response. 2 Most people cry when their mother dies. 3 The co-worker may need help with grieving. 4 The co-worker was extremely attached to the mother. Crying is a release, but the individual should have developed effective coping mechanisms by this time. The co-worker may need help with the grieving process. Excessive crying 16 months after the death of a loved one is not an expected response. People express grief in a variety of ways, not necessarily by crying. Concluding that the co-worker was extremely attached to the mother is an assumption and is not a valid conclusion. 84%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 7. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? 7. What prenatal teaching is applicable for a client who is between 13 and 24 weeks' gestation? 1 Infant care, travel to the hospital, and signs of labor 2 Growth of the fetus, personal hygiene, and nutritional guidance 3 Interventions for nausea and vomiting, urinary frequency, and anticipated care 4 Danger signs of preeclampsia, relaxation breathing techniques, and signs of labor Awareness of the fetus as an individual and the body changes of pregnancy lead the client seek information about fetal growth, body changes, and nutrition . Interventions for nausea and vomiting, urinary frequency, and anticipated care are appropriate for the first trimester. Information on infant care, travel to the hospital, signs of labor, signs of preeclampsia, and relaxation breathing techniques is appropriate in the last trimester. 73%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 8. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? 8. When a client at 39 weeks' gestation arrives at the birthing suite she says, "I've been having contractions for 3 hours, and I think my water broke." What will the nurse do to confirm that the membranes have ruptured? 1 Take the client's oral temperature 2 Test the leaking fluid with nitrazine paper 3 Obtain a clean-catch urine specimen 4 Inspect the perineum for leaking fluid Nitrazine paper will turn dark blue if amniotic fluid is present; it remains the same color in the presence of urine. Temperature assessment is not specific to ruptured membranes at this time; vital signs are part of the initial assessment. Although this may be done as part of the initial assessment; a urine test is unrelated to leakage of amniotic fluid. Inspecting the vagina for leaking fluid will not confirm rupture of the membranes. 75%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 9. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? 9. When working with clients who use manipulative socially acting-out behaviors, the nurse should be: 1 Strict, punishing, and restrictive 2 Sincere, cautious, and consistent 3 Supportive, accepting, and friendly 4 Sympathetic, nurturing, and encouraging A sincere, cautious, and consistent attitude limits this individual's ability to manipulate both situations and staff members. A strict, punishing, and restrictive approach may create a power struggle and limit the development of a therapeutic nurse-client relationship. When accepting the person, the nurse should not support negative behavior; a friendly attitude may encourage further problem behavior. A sympathetic, nurturing, and encouraging approach may encourage the client to continue in her lifestyle rather than learn appropriate ways to relate to others. 75%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 10. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? 10. A male nurse is caring for a client. The client states, "You know, I've never had a male nurse before." What is the best reply by the nurse? 1 "Does it bother you to have a male nurse?" 2 "How do you feel about having a male nurse?" 3 "There aren't many male nurses; we're a minority." 4 "You sound upset. I'll get a female nurse to care for you." Inquiring neutrally about the client's feelings about having a male nurse encourages the client to express and explore feelings in an open, nonjudgmental way. Asking the client whether having a male nurse is disturbing puts the client on the defensive. Stating that there aren't many male nurses does not encourage further conversation, and the client will not have the opportunity to express feelings; this response is focused on the nurse rather than on the client. Immediately volunteering to get a female nurse puts the client on the defensive rather than encouraging verbalization of feelings. 83%of students nationwide answered this question ly. View Topics 11. Confidence: Nailed it Stats Issue with this question? 11. A 14-year-old emancipated minor at 22 weeks' gestation comes in for her second prenatal examination. As she enters the examination room with her mother, she tells the nurse that she does not want her mother present for the examination. What should the nurse say? 1 "Your mother needs to be present for the examination." 2 "What's the problem with your mother being present?" 3 "I'm sure that your mother wants to be with you for support." 4 Telling the mother, "I'm sorry, but I need to ask you to stay in the waiting area." In many states a minor who is self supporting and living away from home, providing military service, married, pregnant, or a parent is considered an emancipated minor . The emancipated minor assumes most responsibilities before the age of 18 years. An emancipated minor is entitled to confidentiality in dealings with healthcare providers. 1. Which statement by the client indicates to the nurse that the teaching about taking an antidepressant medication has been understood? 1 "I need to take every dose of my medication as prescribed." 2 "I need to discontinue the medication if I have side effects." 3 "I don't have to be concerned about taking my medications." 4 "I can double the dose of the medication if I still feel depressed." The client should be encouraged to follow the medical regimen to maximize response to drug therapy. The client needs further teaching. The health care provider should be notified of side effects. The drug should not be discontinued without the health care provider's supervision. The client should be concerned about taking the medication. The health care provider should make the decision to increase the dosage. STUDY TIP: Regular exercise, even if only a 10-minute brisk walk each day, aids in reducing stress. Although you may have been able to enjoy regular sessions at the health club or at an exercise class several times a week, you now may have to cut down on that time without giving up a set schedule for an exercise routine. Using an exercise bicycle that has a book rack on it at home, the YMCA, or a health club can help you accomplish two goals at once. You can exercise while beginning a reading assignment or while studying notes for an exam. Listening to lecture recordings while doing floor exercises is another option. At least a couple of times a week, however, the exercise routine should be done without the mental connection to school; time for the mind to unwind is necessary, too. A depressed client has been receiving venlafaxine (Effexor) 25 mg three times a day by mouth. The health care provider increases the dose to 37.5 mg three times a day by mouth. The pharmacy supplies scored 25-mg tablets of Effexor. How many tablets should the nurse administer? Record your answer using one decimal place. _________ tablets Solve the problem by using ratio and proportion. Desire 37.5 mg x tablets ------------------- = --------- Have 25 mg 1 tablet 25x = 37.5 x = 37.5 ÷ 25 x = 1.5 tablets A nurse leads an assertiveness training program for a group of clients. Which statement by a client indicates that the treatment has been effective? 1 "I know that I should put the needs of others before mine." 2 "I won't stand for it, so I told my boss he's a jerk and to get off my back." 3 "It annoys me when people call me 'sweetie,' so I told him not to do it anymore." 4 "It's easier for me to agree up front and then do just enough so that no one notices." Announcing that "sweetie" is annoying is an assertive statement; it clearly indicates what the problem is and sets limits on undesired behavior without being demeaning. Stating that the client should put the needs of others before the client's needs is nonassertive or passive and denies the individual's own needs and desires. Stating that the client won't stand for someone else's behavior and calling the person a jerk is an aggressive statement that is demeaning and intimidating. Stating that it's easier for the client to agree up front and then do just enough so no one notices is a passive-aggressive response that avoids direct, honest confrontation in favor of devious manipulation. Test-Taking Tip: Do not select answers that contain exceptions to the general rule, controversial material, or degrading responses. What should a nurse consider about the past life of clients who have immigrated to this country? 1 It affects all of their inherited traits. 2 There will be little impact on their lives today. 3 It is important that their values be ascertained first. 4 How they will interact is permanently established. Past experiences are important and must be recognized because they help set the individual's values throughout life. Past experiences will not affect inherited traits. Past experiences play an important role in an individual's life. Nothing establishes how an individual responds forever; new experiences continue to influence future responses. Which relationship is of most concern to the nurse because of its importance in the formation of the personality? 1 Peer relationships 2 Sibling relationships 3 Spousal relationships 4 Parent-child relationships Children base their own worth on the feedback they receive from their parents. This sense of worth sets the basic ego strengths and is vital to the formation of the personality. Peer groups come later in a child's development, but the parent-child relationship is still the most important. Although sibling relationships are important, they are not as important as the parent-child relationship. Spousal relationships come later in life, after the basic personality has been formed. A client at 35 weeks' gestation is experiencing contractions. Her cervix is dilated 2 cm. The nurse teaches the client that sexual activity, particularly intercourse, should be: 1 Avoided to limit the onset of labor 2 Permitted if contractions are irregular 3 Confined to the side-lying position 4 Allowed if penile penetration is shallow A client who is experiencing preterm contractions with the cervix dilated 2 cm should avoid coitus, regardless of position; prostaglandins in semen may stimulate labor, and penile contact with the cervix may increase myometrial contractility. A 28-year-old woman comes into the clinic and tells the nurse that she fears that she is infertile because she has been trying to become pregnant for 2 years. While collecting the health history the nurse learns that the client experiences irregular and infrequent menstrual periods. The client is overweight and has severe acne and alopecia. The health care provider diagnoses polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Which of the following interventions is the most important? 1 Consoling the client over her inability to have children 2 Discussing weight loss, exercise, and a balanced low-fat diet 3 Providing information to the client on how to prepare for surgery 4 Informing client that there are no long-term complications of PCOS Weight loss, exercise, and a balanced low-fat diet can reduce insulin and androgen levels related to PCOS. Meeting with a dietitian may be helpful. Surgery is not necessary at this time. The health care provider would most likely prescribe hormones, other medications, or both. If pregnancy does not occur, surgery is an option. Pregnancy may be possible with hormones, other medications, or both. Early detection of PCOS is important because the condition can lead to type 2 diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and ovarian, breast, and endometrial cancers. Encourage treatment compliance, and encourage positive lifestyle changes. A client in active labor starts screaming, "The baby is coming! Do something!" What is the first nursing action? 1 Notifying the practitioner of the imminent birth 2 Telling the client that it is too soon and encouraging her to pant 3 Checking the perineal area for the presenting part 4 Helping the client hold her knees together and explaining what to expect The first action by the nurse should be to confirm whether birth is imminent by checking the perineal area to determine whether the presenting part is emerging. Confirming the client's sensation is the priority; the nurse should remain with the client and ask a colleague to call the practitioner if birth is imminent. Stating that birth is not imminent demeans the client, and she may be . Holding the knees together is contraindicated. If birth is imminent this could cause injury to the fetus, and if it is not imminent this position is uncomfortable and unnecessary. The nurse is conducting teaching for a client being discharged after an abdominal hysterectomy. Which statement by the client indicates a need for further teaching? 1 "I know not to lift anything heavier than 5 lb." 2 "I'll limit my stair climbing to four times a day." 3 "I'll avoid crossing my legs at the knees when I sit." 4 "I'm glad I'll be able to get back into my jogging routine next week." Discharge instructions after abdominal hysterectomy include avoiding jogging, aerobic exercise, participating in sports, and other any strenuous activity for 2 to 6 weeks after the surgery. The statement indicating that the client plans to start jogging again by next week means that the client requires more teaching. Stair climbing should be limited to fewer than five times per day. Nothing heavier than 5 to 10 lb should be lifted. The client should not cross her legs at the knees when sitting. Those three statements by the client are accurate and indicate understanding of the teaching. A nurse is assigned an adolescent who gave birth 12 hours ago. She continually talks on the phone to her friends and does not respond when her new baby cries. What is the best immediate intervention? 1 Calling social service for a consult 2 Calling the psychiatric team for an intervention 3 Calling her mother and having her speak with the client 4 Modeling appropriate behaviors that encourage infant bonding All women go through several phases of adapting to the role of mother. An adolescent may still need time to adjust to her new role, especially if she has just given birth in the past day. By modeling appropriate behavior, the nurse demonstrates appropriate maternal skills to the adolescent. This will assist her as she makes the transition into her new role as a mother. If this behavior continues and does not improving before discharge, social service may need to get involved, but a consult is not needed in this early phase. A psychiatric consult is not necessary because this is not a psychiatric illness. The adolescent's mother is an important part of the plan, especially if the adolescent is going home to her house, but the relationship between the two needs to be assessed to see what role she will play in this new mother-child relationship. Test-Taking Tip: After you have eliminated one or more choices, you may discover that two of the options are very similar. This can be very helpful, because it may mean that one of these look-alike answers is the best choice and the other is a very good distractor. Test both of these options against the stem. Ask yourself which one completes the incomplete statement grammatically and which one answers the question more fully and completely. The option that best completes or answers the stem is the one you should choose. Here, too, pause for a few seconds, give your brain time to reflect, and recall may occur. A terminally ill client tells the nurse, "I would love to learn to speak German before I die." The nurse's response to the client's desire to learn a foreign language should be based on an understanding that: 1 Activities that support the client's denial should not be encouraged 2 Clients should be encouraged to set meaningful goals for themselves In3 Energies expended on such an activity would not justify the outcome 4 The client's time should be focused on goals that are easily attainable The client's goal is meaningful, and the nurse should do everything possible to help the client achieve it. There is no reason to dissuade the client from a meaningful goal despite its difficulty. The evidence does not demonstrate that the client is in denial. If the client wants to work toward a goal, the energy expenditure is justified. Test-Taking Tip: Start by reading each of the answer options carefully. Usually at least one of them will be clearly wrong. Eliminate this one from consideration. Now you have reduced the number of response choices by one and improved the odds. Continue to analyze the options. If you can eliminate one more choice in a four-option question, you have reduced the odds to 50/50. While you are eliminating the wrong choices, recall often occurs. One of the options may serve as a trigger that causes you to remember what a few seconds ago had seemed completely forgotten. What drug should a nurse anticipate that the health care provider will prescribe for a client demonstrating clinical manifestations associated with an opioid overdose? 1 Naloxone In2 Methadone 3 Epinephrine 4 Amphetamine Naloxone is a narcotic antagonist that displaces opioids from receptors in the brain, thereby reversing respiratory depression. Methadone is a synthetic opioid that causes central nervous system depression; it will add to the problem of overdose. Epinephrine and amphetamine will have no effect on respiratory depression related to opioid overdose. 1. A 1-day-old newborn has just expelled a thick, greenish-black stool. The nurse determines that this is the first stool. What should the nurse do next? 1 Document the stool in the infant's record 2 Assess the infant for an intestinal obstruction 3 Send the stool to the laboratory per protocol In4 Notify the practitioner that a tarry stool has been passed The neonate's first stool, which is thick and greenish-black, is called meconium; the appearance of meconium is an expected occurrence that should be documented. This stool is expected; there is no reason to suspect intestinal obstruction. Meconium stool on the first day of life is expected and does not require further examination. Meconium is not indicative of bleeding; it contains bile and other waste products produced by the fetus. Passage of meconium does not require notification of the practitioner. Test-Taking Tip: Make certain that the answer you select is reasonable and obtainable under ordinary circumstances and that the action can be carried out in the given situation. A newborn has small, whitish, pinpoint spots over the nose that are caused by retained sebaceous secretions. When documenting this observation, a nurse identifies them as: 1 Milia In2 Lanugo 3 Whiteheads 4 Mongolian spots Milia are common, are not indicative of illness, and eventually disappear. Lanugo is fine, downy hair. Whiteheads are a lay term for milia; the term is not used in documentation. Mongolian spots are bluish-black areas on the buttocks that may be present on dark-skinned infants. The nurse assures a breastfeeding mother that one way she will know that her infant is getting an adequate supply of breast milk is if the infant gains weight. What behavior does the infant exhibit if an adequate amount of milk is being ingested? In1 Has several firm stools daily 2 Voids six or more times a day 3 Spits out a pacifier when offered 4 Awakens to feed about every four hours The presence of at least six to eight wet diapers each day indicates sufficient breast milk intake. Several firm stools daily may indicate an inadequate amount of fluid ingestion; the stools of breastfeeding neonates should be soft to loose. Spitting out a pacifier is not an indication of adequate milk consumption; some infants need extra sucking stimulation. Awakening to feed every 4 hours is not a reliable indicator of adequate breast milk intake; sleep patterns vary. A nurse plans to administer vitamin K to a newborn. What site should the nurse use for the injection? 1 Deltoid muscle 2 Rectus femoris 3 Vastus lateralis In4 Gluteus maximus The vastus lateralis is the most appropriate muscle for a newborn's intramuscular injection because it is well developed and there is little danger of nerve injury. The deltoid muscle is too small for a newborn's intramuscular injection. The rectus femoris muscle is not used; it is not as large as the vastus lateralis in a newborn. The sciatic nerve in the newborn is near the outer aspect of the gluteus maximus and might be injured if this site were used for an injection. A mother is inspecting her newborn girl for the first time. The infant's breasts are edematous, and she has a pink vaginal discharge. How should the nurse respond when the mother asks what is wrong? 1 "You seem very concerned. I don't see anything unusual." 2 "Your baby appears to have a problem. I'll notify the pediatrician." 3 "The swelling and discharge will go away. It's nothing to worry about." 4 "The swelling and discharge are expected. They're a response to your hormones." This response emphasizes that the findings are to be expected and explains why they occur; this may relieve the client's anxiety. Claiming not to see anything unusual denies that there is anything to explain to the mother and is somewhat belittling. Calling the pediatrician is not necessary; these findings are expected. The comment that the swelling and discharge will go away tells the mother that the findings are expected but provides no explanation and is somewhat belittling. Test-Taking Tip: Do not select answers that contain exceptions to the general rule, controversial material, or degrading responses. A newborn's total body response to noise or movement is often distressing to the parents. What should the nurse explain about this response? 1 This automatic response probably signifies hunger. 2 This reflexive response is an expected part of development. 3 It is an involuntary response that will remain for the first year of life. 4 It is a voluntary response that indicates insecurity in a new environment. This is the Moro reflex, which indicates an intact nervous system. The Moro reflex has no relationship to hunger. The Moro reflex disappears after the third month of life; if it persists, a neurological disturbance may be present. This reflex is an involuntary response to environmental stimuli. How should a nurse screen the newborn of a diabetic mother for hypoglycemia? 1 Testing for glucose tolerance 2 Drawing blood for a serum glucose determination 3 Arranging for a fasting blood glucose determination 4 Testing heel blood with the use of a glucose-oxidase strip Glucose-oxidase strips are used by nurses to screen infants for hypoglycemia. The glucose tolerance test and serum glucose determination are not used to screen newborns for hypoglycemia. Fasting blood glucose levels are not used routinely to screen newborns for hypoglycemia. A health care provider determines that a fetus is in a breech presentation. For which complication should the nurse monitor the client? 1 Rapid dilation of the cervix, indicating precipitate labor 2 Stronger contractions, indicating progression of the labor 3 Nonreassuring fetal signs, indicating prolapse of the cord 4 Cessation of contractions, indicating primary uterine inertia The feet or buttocks are not effective in blocking the cervical opening, and the cord may slip through and become compressed. Rapid dilation and precipitate labor are more likely to occur if the fetus is in a cephalic presentation. Stronger contractions, indicating progression of labor, is an expected occurrence. Uterine inertia may result from fatigue or cephalopelvic disproportion and is not related directly to fetal presentation. Test-Taking Tip: A psychological technique used to boost your test-taking confidence is to look into a mirror whenever you pass one and say out loud, "I know the material, and I'll do well on the test." Try it; many students have found that it works because it reduces "test anxiety." A new mother exclaims to the nurse, "My baby looks like a Conehead!" How should the nurse respond? 1 "Are you disappointed in how your baby looks?" 2 "Don't worry —your baby's head will be round in a few days." 3 "Is there anyone in your family whose head shape is similar to your baby's?" 4 "This often happens as the baby's head moves down the birth canal—the bones move for easier passage." The shape of the newborn's head is most likely the result of "molding." As the baby's head moves down the birth canal, the bones move for easier passage of the head through the birth canal. The mother needs information that is straightforward and understandable. Telling the client that this often happens as the baby's head moves down the birth canal is accurate information. Asking whether the mother is disappointed in her baby's appearance is an assumed reflection of the mother's feelings and does not address her concern; the nurse should recognize that the mother is disappointed and offer an explanation. Telling the mother that her baby's head will be round in a few days may add to the mother's anxiety because the reason for the infant's appearance has not been explained. It will take several days to determine whether the head is malformed. Asking whether anyone else in the client's family has a similarly shaped head may add to the mother's anxiety. On the second day of life, minutes after drinking 2½ ounces of formula, a newborn regurgitates about half an ounce. The mother remarks, "My baby spits up after every feeding." What should the nurse do next? 1 Reassure the mother that many babies spit up some milk at first 2 Suggest that she hold her baby upright for 30 minutes after feeding 3 Feed a small amount of fresh formula when the baby returns to the nursery 4 Teach the mother how to prop the baby in an infant seat for 1 hour after feeding Holding the infant upright enables gravity to move the feeding through the pyloric sphincter, minimizing regurgitation. Although it is common for infants to regurgitate, this response will not enhance feedings. The infant has had enough formula and does not require more during this feeding. A newborn should not be propped up after feeding because pressure of the abdomen on the stomach puts pressure on the esophagus, which could precipitate regurgitation. Test-Taking Tip: Avoid selecting answers that state hospital rules or regulations as a reason or rationale for action. What should the nurse do to enhance a neonate's behavioral development? 1 Keep the infant awake for longer periods of time before each feeding 2 Touch and talk to the infant hourly, starting at least 3 hours after birth 3 Encourage parental contact with the baby for 15-minutes every 4 hours 4 Help the parents stimulate their awake baby through touch, sound, and sight Stimuli are provided by way of all the senses; because the infant's behavioral development is enhanced through parent-infant interactions, these interactions should be encouraged. Infants require interactions soon after birth and consistently thereafter, but interactions should occur during the infant's regular waking periods. A nurse is assessing a newborn for signs of hyperbilirubinemia (pathological jaundice). What clinical finding confirms this complication? 1 Muscle irritability within 1 hour of birth 2 Neurological signs during the first 24 hours 3 Jaundice that develops in the first 12 to 24 hours 4 Jaundice that develops between 48 and 72 hours after birth The development of jaundice in the first 24 hours indicates hemolytic disease of the newborn. Neurological signs may or may not be present during the first 24 hours; they are dependent on the bilirubin level. Muscle irritability may or may not be present during the first 24 hours; usually it develops later. Serum bilirubin is expected to accumulate in the neonatal period because of the short life span of fetal erythrocytes, reaching a level of 7 mg/100 mL the second to third day when jaundice appears (physiological jaundice). A nurse who is caring for a 32-week appropriate-for-gestational-age (AGA) neonate establishes a list of objectives for the infant. What objective should receive the highest priority? 1 Prevent infection 2 Promote attachment 3 Maintain respirations 4 Support body temperature If the airway is not patent and gas exchange is inadequate, life cannot be sustained; therefore this is the top priority. Although preventing infection is important because the infant lacks immunity from the mother, life will not be sustained without oxygen. Although infant-parent attachment is important, life will not be sustained without oxygen. Although body temperature is important because the infant is lacking brown fat and other defense mechanisms needed to maintain temperature, life will not be sustained without oxygen. During a follow-up appointment, a client at 21 weeks' gestation is found to have hyperemesis gravidarum. The client says, "Why is this happening to me? I don't know whether I can continue like this." What is the best response by the nurse? 1 "Are you saying that you want to schedule an abortion?" 2 "This must be physically and emotionally challenging for you." 3 "We're doing the best we can here, so please be patient with us." 4 "There are dietary changes and medications available that can ease the nausea." An open-ended question validates what the client is experiencing and will encourage further client expression. It is not clear that the client has expressed a desire to have an abortion. It is important to open the lines of communication so the client may express her concerns. Becoming defensive is not in the best interest of the client. This would close down communication. It is true that there are dietary and medication options that can help, but validation of the client's feeling and encouraging open expression is the first priority; only after this is done will the client be ready to listen. A new mother who has begun breastfeeding asks for assistance removing the baby from her breast. What should the nurse teach her? 1 "Pinch the baby's nostrils gently to help release the nipple." 2 "Let the baby nurse as long as desired without interruption." 3 "Pull your nipple out of the baby's mouth when the baby falls asleep." 4 "Insert your finger in the corner of the baby's mouth to break the suction." Inserting a finger into the corner of the baby's mouth is painless and will help prevent damage to the mother's nipple. Pinching the baby's nostrils is somewhat cruel; breaking suction with a finger is less traumatic. The mother may need to remove the baby from the breast before the baby is ready to let go, and the mother should be taught how to do this. Pulling without first breaking the suction may inflict trauma on the nipple. A nonstress test (NST) is scheduled for a client with mild preeclampsia. During the test, the client asks the nurse what it means when the fetal heart rate goes up every time the fetus moves. What should the nurse consider before responding? 1 These accelerations are a sign of fetal well-being. 2 These accelerations indicate fetal head compression. 3 Umbilical cord compression is causing these accelerations. 4 Uteroplacental insufficiency is causing these accelerations. The NST is performed before labor begins. Accelerations with movement and a baseline variability of 5 to 15 beats/min indicate fetal well-being. This reactive NST is considered positive. Early decelerations are associated with fetal head compression during a contraction stress test (CST) or during labor. Variable decelerations are associated with cord compression during a CST or during labor. Late decelerations during a CST or during labor are associated with uteroplacental insufficiency. A nurse is caring for four clients, each with a different medical condition. Which condition should the nurse anticipate will result in the client's being instructed by the health care provider not to breastfeed? 1 Mastitis 2 Inverted nipples 3 Herpes genitalis 4 Human immunodeficiency virus Breastfeeding by a mother infected with HIV is contraindicated because breast milk can transmit the virus to the infant. Breastfeeding by a mother with mastitis is not always contraindicated; during antibiotic treatment the mother can maintain lactation by pumping the breasts and discarding the milk. Once the infection has resolved, breastfeeding may be resumed. Breastfeeding is not contraindicated with inverted nipples because a breast shield can provide mild suction to help evert the nipples. Breastfeeding is not contraindicated in a client with genital herpes. The newborn may contract the infection during a vaginal birth, not in breast milk. Test-Taking Tip: Look for answers that focus on the client or are directed toward feelings. A client who underwent mastectomy because of breast cancer is now undergoing chemotherapy, which has caused hair loss. The client states, "I feel like I've lost my sense of power." What is the nurse's best response? 1 "Hair does not empower a person." 2 "Losing power seems important to you." 3 "Knowledge is power; I'll give you some pamphlets to read." 4 "Hair loss is common; it will grow back, so you shouldn't worry." Stating that the loss of power seems important to the client provides an opportunity for the client to discuss her feelings. Stating that hair doesn't empower a person is confrontational and may cut off further communication. Offering to get the client some pamphlets dismisses the client's concern and does not promote the client's further verbalization of feelings. Stating that hair loss is common and the client shouldn't worry dismisses the client's concerns and cuts off further communication. What is the most important parameter for the nurse to monitor during the first 24 hours after the birth of an infant at 36 weeks' gestation? 1 Duration of cry 2 Respiratory distress 3 Frequency of voiding 4 Decreased temperature Respiratory distress is a common response in the preterm infant, related to possible immaturity of the newborn's respiratory tract, manifesting as a small lumen, weakness of the respiratory musculature, paucity of functional alveoli, or insufficient calcification of the bony thorax. The tone of the cry is more pertinent than its duration. Frequency of voiding is not the priority because the newborn's intake is limited during the first 24 hours. The temperature of the preterm infant is expected to decrease because of immature thermoregulation. The nurse administers the prescribed vitamin K intramuscularly to a newborn immediately after birth to: 1 Promote the synthesis of prothrombin 2 Facilitate the growth of intestinal flora 3 Limit an increase in the serum bilirubin level 4 Decrease the level of calciferol until the kidneys have matured Vitamin K stores are almost absent in the newborn because the intestinal flora that produce this vitamin are not present; vitamin K is an essential precursor of prothrombin, which is part of the clotting mechanism. The intestinal flora develop as the newborn is exposed to extrauterine living conditions. An increased serum bilirubin level may occur in the newborn because of the rapid breakdown of red blood cells and the immature liver's inability to conjugate such large amounts; it is not related to vitamin K. A newborn's kidneys operate at a functional level appropriate to the needs of a healthy newborn, and kidney maturity and calciferol are not related to vitamin K. A client being prepared for surgery because of a ruptured tubal pregnancy complains of feeling lightheaded. Her pulse is rapid, and her color is pale. What condition does the nurse anticipate as a common complication of a ruptured tubal pregnancy? 1 Shock 2 Anxiety 3 Infection 4 Hyperoxygenation Hemorrhage can result from a ruptured tubal pregnancy and shock may ensue. Although the client may be very anxious, the signs and symptoms are those of hemorrhagic shock. There are no data, such as fever or a rising white blood cell count, to support the conclusion that the client has an infection. The data do not support a hyperoxygenated state. A nurse is caring for several pregnant clients in the prenatal clinic. Which client causes the most concern because of her predisposition to placenta previa? 1 19 years old, gravida 1, para 0 2 25 years old, gravida 2, para 1 3 30 years old, gravida 6, para 5 In4 40 years old, gravida 2, para 1 Multiple past pregnancies tend to deplete the ability of the endometrial lining in the fundal portion of the uterus to support the placenta; the placenta then implants in the lower segment. Primigravidas are least prone to placenta previa; the endometrium is receptive to normal implantation. Two pregnancies have not significantly compromised the endometrium; abnormal implantation is less likely to occur. Age is not known to be a significant factor. A nurse in the clinic determines that a 4-day-old neonate who was born at home has a purulent discharge from the eyes. What condition does the nurse suspect? 1 HIV infection 2 Chlamydia trachomatis infection In3 Retinopathy of prematurity (retrolental fibroplasia) 4 A reaction to the ophthalmic antibiotic instilled after birth Chlamydia trachomatis infection occurs 3 to 4 days after birth; if it is not treated prophylactically with an antibiotic at birth or within 3 days, chronic follicular conjunctivitis with conjunctival scarring will occur. HIV infection in the newborn does not manifest with conjunctivitis. The high oxygen concentrations given to severely compromised preterm infants cause vasoconstriction of retinal capillaries, which can lead to blindness; there are no data to indicate that this infant was preterm, severely compromised, or received oxygen. A chemical conjunctivitis occurs within the first 48 hours and is not purulent. Test-Taking Tip: Watch for grammatical inconsistencies. If one or more of the options is not grammatically consistent with the stem, the alert test taker can identify it as a probable in option. When the stem is in the form of an incomplete sentence, each option should complete the sentence in a grammatically way. A new mother asks a nurse how to care for her baby's umbilical cord stump. What should the nurse teach the mother? In1 Expect a moderate amount of drainage. 2 Provide sponge baths until the stump falls off. 3 Keep the area moist with sterile normal saline. 4 Cover the site with a small sterile dressing twice a day. The infant is given sponge baths instead of being immersed in a tub of water because the moisture will retard drying of the cord stump and will delay its falling off. Drainage is indicative of infection; the cord stump should be dry. Moisture slows the drying process and promotes bacterial growth. Keeping the cord stump covered delays drying. Test-Taking Tip: After you have eliminated one or more choices, you may discover that two of the options are very similar. This can be very helpful, because it may mean that one of these look-alike answers is the best choice and the other is a very good distractor. Test both of these options against the stem. Ask yourself which one completes the incomplete statement grammatically and which one answers the question more fully and completely. The option that best completes or answers the stem is the one you should choose. Here, too, pause for a few seconds, give your brain time to reflect, and recall may occur. 1. A nurse is reviewing the laboratory report of a newborn whose hematocrit level is 45%. What value denotes a healthy infant? 1 Less than 40% In2 More than 75% 3 Between 45% and 65% 4 Between 65% and 75% The expected hematocrit level for a healthy newborn is between 45% and 65%. Less than 40% is below the expected level and is considered anemia. More than 75% is high and is considered polycythemia. Between 65% and 75% is above the expected range. While mopping the kitchen floor, a client at 37 weeks' gestation experiences a sudden sharp pain in her abdomen with a period of fetal hyperactivity. When the client arrives at the prenatal clinic, the nurse examines her and detects fundal tenderness and a small amount of dark-red bleeding. What does the nurse conclude is the probable cause of these clinical manifestations? 1 True labor 2 Placenta previa 3 Partial abruptio placentae In4 Abdominal muscular injury Typical manifestations of abruptio placentae are sudden sharp localized pain and small amounts of dark-red bleeding caused by some degree of placental separation. True labor begins with regular contractions, not sharp localized pain. There is no pain with placenta previa, just the presence of bright-red bleeding. There are no data to indicate that the client sustained an injury. A client in the 38th week of gestation exhibits a slight increase in blood pressure. The health care provider advises her to remain in bed at home in a side-lying position. The client asks why this is important. What is the nurse's response regarding the advantage of this position? 1 It increases blood flow to the fetus. In2 Decreases intra-abdominal pressure. 3 It increases the mean arterial pressure. 4 It prevents the development of thrombosis. The side-lying position decreases blood pressure and moves the gravid uterus off the great vessels of the lower abdomen, increasing venous return, improving cardiac output, and promoting kidney and placental perfusion. The side-lying position does not influence intra-abdominal pressure. While a pregnant woman is on bedrest the blood pressure decreases. The side-lying position does not prevent thrombosis; bedrest and immobility may increase the risk of thrombosis. While being admitted for a lumpectomy the client begins to cry and says, "I found the lump a few months ago, but I didn't go to the doctor because of what it could be." How should the nurse reply? 1 "This has been frightening for you." 2 "About 80% of breast lumps are benign." 3 "Cry as long as you like and get it out of your system." 4 "More than 95% of breast lumps are discovered by the woman herself." The response involves the use of reflective technique to acknowledge the client's feelings. Providing statistics does not acknowledge the client's feelings and may cut off communication. Providing false reassurance that crying will ease her concerns is inappropriate. A client has a cesarean birth. What is the most important nursing intervention to prevent thromboembolism on the client's first postpartum day? 1 Providing oxygen therapy 2 Administering pain medication 3 Encouraging frequent ambulation 4 Recommending an increase in oral fluids Ambulation involves muscle contractions that promote an increase in circulation in the legs. During pregnancy, hypercoagulation is associated with an increase in clotting factors and fibrinogen, which increases the risk for thromboembolism. Oxygen therapy will not prevent thromboembolism. Relieving pain does not prevent thromboembolism, but pain medication may be needed to help the client tolerate ambulation. Increasing fluid intake will not prevent thromboembolism. A nurse who is caring for a client in labor uses nitrazine paper to test the pH of the client's leaking vaginal fluid. What color will the nitrazine paper turn if the leakage is amniotic fluid? 1 Red 2 Blue 3 Purple 4 Yellow Amniotic fluid is alkaline (pH of 7-7.50) and turns nitrazine paper blue. Amniotic fluid does not change nitrazine paper red. Amniotic fluid does not change nitrazine paper purple. Yellow in the nitrazine paper usually indicates intact membranes. Test-Taking Tip: A psychological technique used to boost your test-taking confidence is to look into a mirror whenever you pass one and say out loud, "I know the material, and I'll do well on the test." Try it; many students have found that it works because it reduces "test anxiety." An infant is born with a bilateral cleft palate. Plans are made to begin reconstruction immediately. What nursing intervention should be included to promote parent-infant attachment? 1 Demonstrating positive acceptance of the infant 2 Placing the infant in a nursery away from view of the general public 3 Explaining to the parents that the infant will look normal after the surgery 4 Encouraging the parents to limit contact with the infant until after the surgery By demonstrating acceptance of the infant, without regard for the defect, the nurse acts as a role model for the parents, thereby encouraging their acceptance. Infants with cleft palates can remain in the newborn nursery; they should not be hidden. Telling the parents that the child will look normal after surgery is false reassurance; it does not promote parent-infant attachment behaviors. Encouraging the parents to limit contact will delay attachment; the parents should be encouraged to have frequent contact with their infant. Test-Taking Tip: Do not worry if you select the same numbered answer repeatedly, because there usually is no pattern to the answers. A nurse is giving discharge instructions to a new mother. What is the most important instruction to help prevent postpartum infection? 1 "Don't take tub baths for at least 6 weeks." 2 "Wash your hands before and after changing your sanitary napkins." 3 "Douche with a dilute antiseptic solution twice a day and continue for a week." 4 "Tampons are better than sanitary napkins for inhibiting bacteria in the postpartum period." Infection is most commonly transmitted through contaminated hands. Tub baths are permitted. Douching is contraindicated. Tampons are contraindicated in the postpartum period until the cervix has closed completely; they may promote infection when used too early. An infant has surgery for repair of a myelomeningocele. For which early sign of impending hydrocephalus should the nurse monitor the infant? 1 Frequent crying 2 Bulging fontanels 3 Change in vital signs 4 Difficulty with feeding After closure, spinal fluid may accumulate and reach the brain, increasing intracranial pressure (ICP) and causing the fontanels to bulge. Frequent crying may be a typical pattern for the neonate; it does not, in and of itself, indicate changes in ICP. Changes in vital signs are not among the early signs of increasing ICP in an infant. Difficulty with feeding can indicate changes in ICP but is not one of the first signs. A new mother asks the nurse whether she may wash her baby in a tub after they go home. What is the nurse's best response? 1 "Yes, as long as [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 47 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$20.00
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 19, 2020
Number of pages
47
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 19, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
59

















.png)