Physics > GIZMOS > Student Exploration: Free-Fall Laboratory Vocabulary: acceleration, air resistance, free fall, inst (All)
Student Exploration: Free-Fall Laboratory Vocabulary: acceleration, air resistance, free fall, instantaneous velocity, terminal velocity, velocity, vacuum
Document Content and Description Below
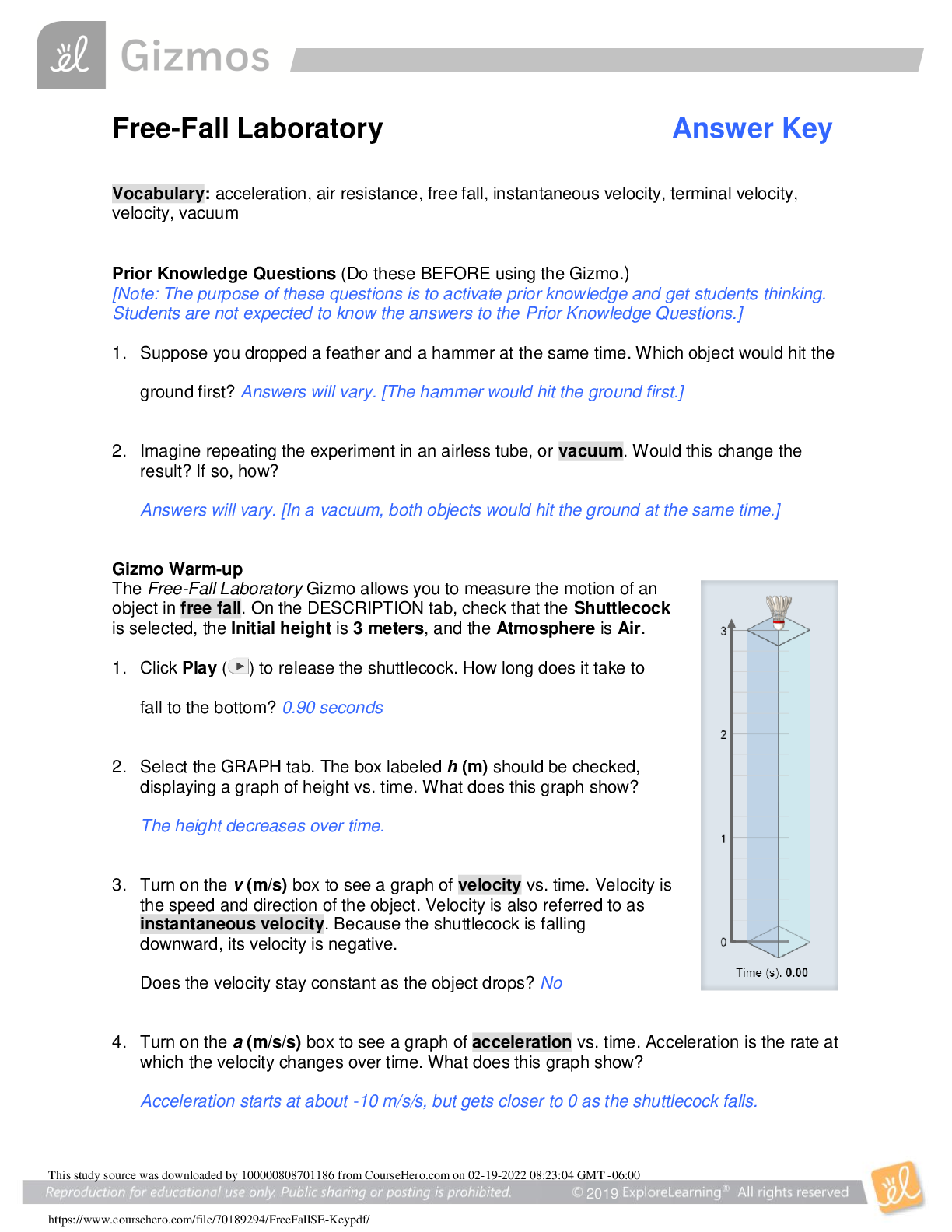
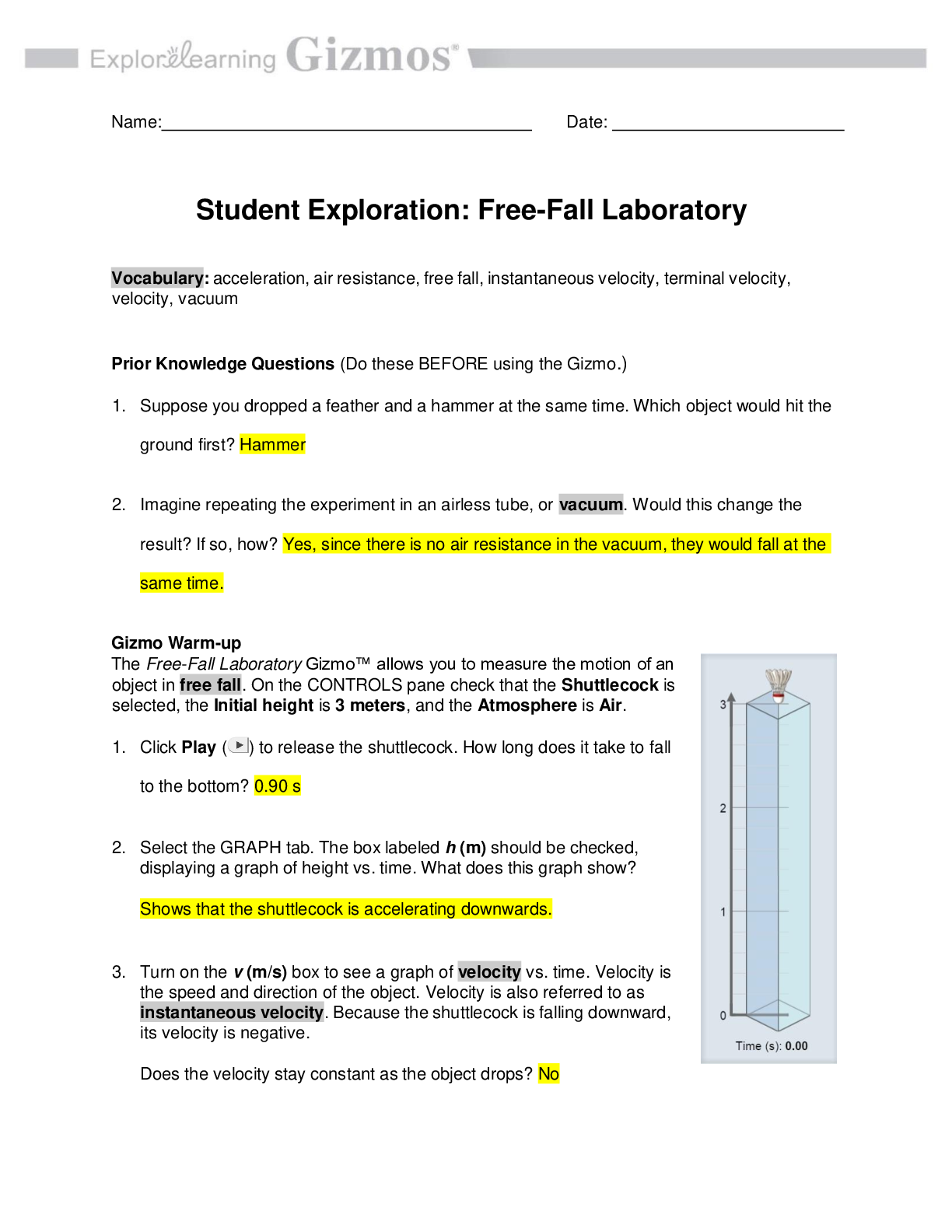
Vocabulary: acceleration, air resistance, free fall, instantaneous velocity, terminal velocity, velocity, vacuum Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. Suppose you droppe... d a feather and a hammer at the same time. Which object would hit the ground first? I believe the hammer falls faster since it weighs more. 2. Imagine repeating the experiment in an airless tube, or vacuum. Would this change the result? If so, how? The result would be different since there will be no air the feather won’t glide; it will do a free fall. They would fall at the same time. Gizmo Warm-up The Free-Fall Laboratory Gizmo allows you to measure the motion of an object in free fall. On the DESCRIPTION tab, check that the Shuttlecock is selected, the Initial height is 3 meters, and the Atmosphere is Air. 1. Click Play ( ) to release the shuttlecock. How long does it take to fall to the bottom? 0.90s 2. Select the GRAPH tab. The box labeled h (m) should be checked, displaying a graph of height vs. time. What does this graph show? It shows that the shuttlecock is accelerating downwards. 3. Turn on the v (m/s) box to see a graph of velocity vs. time. Velocity is the speed and direction of the object. Velocity is also referred to as instantaneous velocity. Because the shuttlecock is falling downward, its velocity is negative. Does the velocity stay constant as the object drops? No 4. Turn on the a (m/s/s) box to see a graph of acceleration vs. time. Acceleration is the rate at which the velocity changes over time. What does this graph show? 2019 Activity A: Falling objects Get the Gizmo ready: • Click Reset ( ). • Select the DESCRIPTION tab. Question: What factors affect how quickly an object falls? 1. Observe: Drop each item through Air from a height of 3 meters. Record how long it takes to fall below. For the tennis ball, try to click Pause ( ) when it hits the ground. Shuttlecock Cotton ball Tennis ball Rock Pebble 0.71 0.79 0.80 2. Form a hypothesis: Why do some objects fall faster than others? Some objects fall faster since they weight more. 3. Predict: A vacuum has no air. How do you think the results will change if the objects fall through a vacuum? Both items will fall at the same time. 4. Experiment: On the Atmosphere menu, select None. Drop each item again, and record the results below. Shuttlecock Cotton ball Tennis ball Rock Pebble 0.78 0.78 0.78 0.78 0.78 5. Analyze: What happened when objects fell through a vacuum? They all touched the bottom at the same time. 6. Draw conclusions: Objects falling through air are slowed by the force of air resistance. Which objects were slowed the most by air resistance? Why do you think this is so? The shuttlecock and cotton ball were slowed the most by air resistance. This is due to (Activity A continued on next page) 7. Calculate: Select the Shuttlecock. Check that the Initial height is 3 meters and the Atmosphere is None. Click Play and wait for the Shuttlecock to fall. Select the BAR CHART tab and turn on Show numerical values. A. How long did it take the shuttlecock to fall to the bottom? 0.78 B. What was the acceleration of the shuttlecock during its fall? -9.81 C. What was the velocity of the shuttlecock when it hit the bottom? -7.68 (Note: This is an example of instantaneous velocity.) D. What is the mathematical relationship between these three values? 8. Make a rule: If the acceleration is constant and the starting velocity is zero, what is the relationship between the acceleration of a falling body (a), the time it takes to fall (t), and its instantaneous velocity when it hits the ground (v)? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 06, 2021
Number of pages
6
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 06, 2021
Downloads
1
Views
300

.png)