*NURSING > EXAM > NSG 201 Saunders Review Test 2 (Nursing, The American, cognitive ability) GRADED A Questions and Ans (All)
NSG 201 Saunders Review Test 2 (Nursing, The American, cognitive ability) GRADED A Questions and Answer solutions with rationale/ 100% CORRECT.
Document Content and Description Below
1.ID: 9476801282 The nurse is caring for a woman who is starting medroxyprogesterone injections for birth control. What statements by the client would indicate a need for further teaching? Select al... l that apply. A. “I may experience some weight gain.” Incorrect B. “I may not have regular periods while taking this medication.” C. “I should return in approximately 6 months for my next injection.” D. “Because it is highly effective, I can use this medication for many years.” E. “Depression is a side effect, and I should let my doctor know if I experience any mood changes.” Incorrect Rationale: Medroxyprogesterone is an injectable progestin given every 3 months to prevent ovulation and pregnancy. It suppresses ovulation for 15 weeks, and therefore, timing of the next injection is very important and should be no longer than exactly 3 months. Although medroxyprogesterone is highly effective, it should not be taken for more than 2 years due to the risk of osteoporosis. Weight gain, irregular periods, and depression are all known side effects. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic words, “need for further teaching.” These words indicate a negative event query and the need to select the incorrect client statements. Specific knowledge about this medication is needed to answer correctly. Remember that it needs to be given every 3 months and should not be taken for more than 2 years due to the risk of osteoporosis. Review: medroxyprogesterone injections Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Need: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Pharmacology: Reproductive Medications Priority Concepts: Client Education, Reproduction HESI Concepts: Sexuality/Reproduction, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Rosenjack Burchum, Rosenthal (2016), pp. 760-761. Awarded -1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 2.ID: 9476801218 Following thyroid surgery, the nurse notes this response (refer to figure) when taking the client’s blood pressure. On further assessment, which laboratory finding would the nurse expect to find? A. Serum calcium of 8.4 mg/dL (2.1 mmol/L) B. Correct C. Sodium level of 138 mEq/L (138 mmol/L) D. Serum potassium of 5.1 mEq/L (5.1 mmol/L) E. F. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) of 1.5 mU/L Incorrect Rationale: Hypocalcemia is characterized by tetany, or sustained muscle contractions. Chvostek’s sign is facial contractions seen after a light tap of the facial nerve in front of the ear. Trousseau’s sign is carpal contraction when a blood pressure cuff is inflated. These two signs are observed in hypocalcemia. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, thyroid surgery and the signs of hypocalcemia. Use knowledge of signs of muscle contractions and its association with a low calcium level. Note that hypocalcemia is a known complication after thyroid surgery and serum calcium levels should be closely monitored. Review: hypocalcemia. Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Need: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Analyzing Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Fluids & Electrolytes Priority Concepts: Cellular Regulation, Fluid and Electrolytes HESI Concepts: Cellular Regulation, Fluids and Electrolytes Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 298-299). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 3.ID: 9476805570 The charge nurse on a women’s health unit is making a client room assignment. Which clients would be least appropriate to assign to share a room with a woman who is pregnant? Select all that apply. A. A client with hepatitis B Correct B. A client with herpes zoster Correct C. A client with pyelonephritis Incorrect D. A client with hashimotos thyroiditis Incorrect E. A client with a urinary tract infection Rationale: Viral infections such as hepatitis B and herpes zoster can be very serious for the mother and fetus if exposed and clients with these conditions should not share a room with a pregnant client. Pyelonephritis, hashimotos thyroiditis, and urinary tract infections can all have adverse effects on a pregnant woman, however, these are not contagious conditions, and therefore clients with these conditions can safely room share with a pregnant woman. Test taking strategy: Focus on the strategic words least appropriate and select the clients that should not share a room with a pregnant female. Think about the infectious factors of each disorder in the options to answer correctly. Review: risks of pregnancy Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Need: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Maternity: Antepartum Priority Concepts: Care Coordination, Infection HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Infection Reference: McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., pp. 626-628). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded -1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 4.ID: 9476805554 The home health nurse is caring for an older client recovering from pneumonia. A concerned family member believes that the client is no longer capable of caring for self effectively. The nurse conducts an assessment of the client’s basic activities of daily living (BADLs). What activities would the nurse assess? Select all that apply. A. Eating Correct B. Bathing Correct C. Cooking Incorrect D. Dressing Correct E. Taking medications Incorrect F. Balancing a checkbook Rationale: ADL’s are basic activities that assess functional ability. Daily activities such as eating, bathing, and dressing are considered basic every day needs. Activities such as cooking, taking medication, and balancing a checkbook are considered more complex, instrumental activities. Test-taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, basic activities of daily living. Select the answers that require the most basic care for completion. In addition, specific knowledge of those activities that are basic and those that are instrumental will assist in answering correctly. Review: Activities of Daily Living. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Need: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Safety Priority Concepts: Functional Ability, Safety HESI Concepts: Functional Ability, Safety References: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for nursing practice. (p. 12). St. Louis, MO: Mosby. Potter, P., Perry, A. G., Stockert, P. A., & Hall, A. M. (2013). Fundamentals of nursing. (8th ed., pp. 259-260). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 5.ID: 9476807948 The nurse is caring for a client who has recently undergone a right-sided mastectomy for stage 3 breast cancer. When giving report to the next shift, what information would be essential to communicate to the oncoming nurse? Select all that apply. A. Elevate the right arm on a pillow. Correct B. Monitor skin color and for the presence of edema. Correct C. Educate that a medical alert bracelet is being worn. Correct D. Ensure the client refrains from any physical activity. Incorrect E. Take blood pressure measurements on the right side only. Incorrect Rationale: After a mastectomy, the nurse must assess for peripheral tissue perfusion. Therefore it is important to assess skin color and for the presence of edema. Elevation of the extremity will decrease venous pressure and decrease edema. A medical alert bracelet should be worn at all times. A medical alert bracelet should be worn to alert others and prevent anyone from using the affected extremity for blood pressure, intravenous (IV punctures), or blood draws because this could increase the likelihood of infection or decreased tissue perfusion. Although the client should avoid heavy lifting, activity should be encouraged and the client should participate in physical therapy unless contraindicated. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic word essential when considering what information should be included in shift change report. Think about what information would be necessary for safe care of the client to help select the correct answer. Also noting the words, any and only in options 4 and 5 will assist in eliminating these options. Review: mastectomy Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Communication and Documentation Content Area: Adult Health: Oncology Priority Concepts: Care Coordination, Tissue Integrity HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Tissue Integrity Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 1254-1255). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded -1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 6.ID: 9476793886 A client informs the nurse that she has recently started taking the herbal supplement black cohosh for her menopausal symptoms. When reviewing the client’s medical record, what finding would warrant the need for follow-up? Refer to chart. H i s t o r y a n d P h y s i c a l Laboratory Results M e di c at io n s R e n a l I n Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 2.45 mIU/L Gl ipi zi de 5 m g s u f f i c i e n c y or al on ce da ily H e a r t f a i l u r e B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) 204 pg/ml Si m va st at in 4 0 m g on ce da ily A. TSH result B. BNP result C. Heart failure D. Glipizide prescription Correct Rationale: Black cohosh is an herbal product used to treat hot flashes, irritability, and palpitations. It potentiates insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents, and anti- hypertensive agents. Therefore, follow-up would be necessary if the client was taking glipizide, a sulfonlyrea oral hypoglycemic agent. The TSH result is a normal finding. The BNP result would be expected with a known diagnosis of heart failure and additionally would not be affected by black cohosh. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic words need for follow-up when considering what information provided in the chart is important. The options of heart failure and the BNP result are comparable or alike options, and therefore should be eliminated. Next, note that the TSH level is normal to eliminate this option. Review: interactions associated with black cohosh Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Analysis Content Area: Fundamental of Care: Safety Priority Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety References: Hodgson, B., & Kizior, R. (2015). Saunders nursing drug handbook 2015. (p. 1317 ). St. Louis: Saunders. Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 1285). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 7.ID: 9476797805 A client is admitted to hospital for treatment of a respiratory infection. The client was treated with an intravenous (IV) course of ampicillin and is ready to be discharged home on oral antibiotics. What information present in the chart would warrant the nurse to provide further teaching? Hist ory and Phy sica l Labo rator y and Diag nosti c Findi ngs Medi catio ns Ane Ches t X- Ray: norg esti mate mia cons olida tion in left uppe r lobe and ethin yl estra diol oral once daily Poly Cys Pota Metf tic ssiu ormi Ova m n rian level 500 Syn of mg dro 4.5 oral me meq/ twice (PC L daily OS) A. Anemia B. Potassium result C. Chest X-ray result Incorrect D. Norgestimate and ethinyl estradiol prescription Correct Rationale: Broad-spectrum antibiotics such as ampicillin are commonly used to treat upper respiratory infections. These medications can decrease the effectiveness of oral contraceptive medications and the client should be advised to use alternative birth control options. Anemia has no impact on the use of ampicillin. The chest x-ray results, although abnormal, are expected with a respiratory infection. Serum potassium level is within normal limits. PCOS and the use of metformin is not affected by the oral antibiotic. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, provide further teaching. Use knowledge of board spectrum antibiotics to answer correctly. Remember that antibiotics can cause a decrease in the effectiveness of oral contraceptive pills. Review: broad spectrum antibiotics. Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Analysis Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Safety Priority Concepts: Client Education, Safety HESI Concepts: Safety, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Rosenjack Burchum, Rosenthal (2016), pp. 1022, 1024. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 8.ID: 9476797864 The charge nurse is making a client assignment for the upcoming shift. In order to create a safe assignment, the charge nurse plans to assign those clients requiring airborne precautions amongst different nurses. Which clients should be assigned to different nurses? Select all that apply. A. A client with measles. Correct B. A client with C. difficle. C. A client with influenza. Incorrect D. A client with pneumonia. E. A client with tuberculosis. Correct Rationale: Airborne precautions are used for those clients that are diagnosed with or suspected to have a condition spread through airborne transmission. Measles and tuberculosis are transmitted via airborne transmission. A client with influenza should be placed on droplet precautions. A client with C. difficile should be placed in contact and enteric precautions and a client with pneumonia only requires standard precautions. Test Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject of the question, airborne contact precautions. Think about how each disease identified in the options is transmitted in order to help select the correct option. Review: all types of transmission-based precautions Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Infection Control Priority Concepts: Care Coordination, Infection HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Infection References: Ignatavicius, D. M., & Workman, L. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed. p. 440). St. Louis, MO: W.B. Saunders Company. Perry, A., Potter, P., & Ostendorf, W. (2014). Clinical nursing skills & techniques (8th ed., p. 173). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 9.ID: 9476801200 The nurse at an outpatient clinic is performing a health assessment on a 67 year-old client. Her health history includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and diabetes mellitus and she currently has no complaints. On assessment, the client tells the nurse that she has not received any vaccinations other than a tetanus vaccine four years ago. Which routine vaccinations should be recommended given the client’s age? Select all that apply. A. Tetanus vaccine Incorrect B. Shingles vaccine Correct C. Influenza vaccine Correct D. Rotavirus vaccine Incorrect E. Pneumococcal vaccine Correct Rationale: The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends that a healthy individual over the age of 65 years old should receive the shingles vaccine, an annual influenza vaccine, and a pneumococcal vaccine. Rotavirus is given to infants and the client is not due for a tetanus booster. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the data in the question and recall the recommended immunization schedule. Also focus on the client’s age to assist in answering. Review: immunization schedules Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Developmental Stages: Health Assessment/Physical Exam Priority Concepts: Health Promotion, Immunity HESI Concepts: Health Promotion, Immunity Reference: Ignatavicius, D. M., & Workman, L. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed. p. 16). St. Louis, MO: W.B. Saunders Company. Awarded -1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 10.ID: 9476801225 The nurse at a long-term care facility is conducting a medication review of a newly admitted older client with dementia, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and depression. Which medication prescription would warrant the need to contact the health care provider? Select all that apply. A. Lisinopril 10 mg orally once daily. B. Furosemide 20mg orally once daily. C. Fluoxetine 20 mg orally once daily. Correct D. Metformin 500mg orally twice daily. E. Cyclobenzaprine 5mg every 8 hours as needed. Correct Rationale: A close review of medications is necessary for safe care of any client client but because the aging process affects physiological functioning, medication prescriptions for the older client need to be carefully monitored. The use of fluoxetine and cyclobenzaprine are considered inappropriate in the older client according to the Beers criteria and should not be used. All other medications listed would be appropriate. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject of this question, appropriate medication use in the elderly population. Think about physiological changes that occur with aging when selecting the correct option. Also, specific knowledge of medications in the Beers criteria and the classifications of the medications in the options will assist in answering correctly. Review: Beers criteria Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Analysis Content Area: Fundamental of Care: Medications and Administration Priority Concepts: Collaboration, Safety HESI Concepts: Collaboration, Safety References: Ignatavicius, D. M., & Workman, L. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed. p. 20-21). St. Louis, MO: W.B. Saunders Company. Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 74). St. Louis: Mosby. American Geriatrics Society Updated Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults, The American Geriatrics Society 2012 Beers Criteria Update Expert Panel; http://www.americangeriatrics.org/files/documents/beers/2012BeersCriter ia_JAGS.pdf Awarded 1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 11.ID: 9476801253 The nurse is assisting in the examination of a five year old child who was removed from an abusive home. The social worker alerts the nurse that there is a history of violence in the child’s home, which has resulted in the removal of the child and siblings. Which behaviors should the nurse expect the child to express? Select all that apply. A. Smiling during the exam. B. Blaming the abuser for the injury. C. A need to find and protect a sibling. Correct D. Feeling guilty for causing the abuse to occur. Correct E. Aggressive behavior towards the nurse and health care provider. Correct Rationale: In homes where intimate partner violence (IPV) occurs, children are exposed to that violence at the very least and often become additional recipients of that violence. IPV usually predates abuse of the child. Younger children seem to have more behavioral problems when exposed to intra-family violence. For instance, they often have problems with anxiety, depression, and aggression. They often experience many fears and worries that are developmentally inappropriate. Expressing the need to find and protect a sibling is an example of worry that is developmentally inappropriate for a five year old child. Guilt is another aspect that abused children frequently struggle with, as children often blame themselves for abuse. The nurse would expect the child to portray aggressive behaviors out of fear. Due to the history of violence that this child has been subjected to, the nurse would not expect the child to smile and be receptive to the exam, or blame the abuser for the injury. Another issue of concern that the nurse should be aware of is post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Associated features of PTSD may be more detrimental than the violence itself. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “behaviors of an abused child”. Determine which behaviors an abused child would show during interaction with the nurse. Eliminate options 1 and 2, because the child is likely to be afraid and unsure of the nurse and exam. Review: Behaviors of the abused child. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity. Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Leadership/Management Giddens Concepts: Caregiving, Interpersonal Violence HESI Concepts: Developmental/Family Dynamics, Violence References: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for nursing practice. (1st ed., p. 353). St. Louis: Mosby. Hockenberry, M, & Wilson, D. (2015). Wong’s nursing care of infants and children (10th ed. pp. 565-566). St Louis: Mosby. Awarded 3.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 12.ID: 9476797879 The nurse is examining an infant with burns that are suspicious for child abuse. Which findings should the nurse report as highly suspicious for abuse? (Select all that apply). A. A burn mark on the child’s finger. B. Circular burn marks on the infant’s buttocks. Correct C. A bright pink coloring on the infant’s cheeks. D. A dark brown marking on the infant’s lower back. Incorrect E. A stocking pattern of burn marks on the infant’s feet and legs. Correct Rationale: Examination findings for interpersonal violence range from subtle to obvious. Some may manifest as old or new injuries that may seem mild to more significant and may not raise concern. For this reason, it is critical to consider the history in relation to injuries seen. The nurse should also maintain a high degree of awareness for injuries that are not typically seen in the context of day- to-day living—such as unusual patterns of bruising or burn marks. Findings during the physical assessment that would raise suspicion for the nurse are circular burns or burns that occur in a stocking pattern. A burn mark to the finger should be questioned, but is not highly suspicious for child abuse. Bright pink coloring to the checks is typically normal in infants. Dark brown markings located on the lower back or buttocks are known as Mongolian spots. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “highly suspicious signs of child abuse”. Note the word “highly” nad determine which signs are indicative of abuse. Eliminate options 1, 3 and 4 because these findings do not necessarily indicate that child abuse has occurred.. Review: Child Abuse Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Leadership/Management Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Interpersonal Violence. HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Violence Reference: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for nursing practice. (1st ed., p. 354). St. Louis: Mosby. Hockenberry, M, & Wilson, D. (2015). Wong’s nursing care of infants and children (10th ed. p. 562). St Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 13.ID: 9476801241 The nurse is volunteering at a local health fair to educate the public on primary prevention of stress. Which interventions would be the most appropriate for the nurse to recommend to the public, in order to reduce stress levels? Select all that apply. A. Finding a source of pleasure. Correct B. Developing a positive attitude. Correct C. Counseling for chronic anxiety. Correct D. Engaging in stressful situations. E. Learning relaxation and deep breathing exercises. Correct Rationale: Primary prevention refers to activities that prevent or decrease the probability of occurrence of an injury, physical or mental illness, or health- threatening situation in an individual or family, or an event or illness in the population by combating harmful forces and by strengthening the capacity of individuals to withstand these forces. It would be most appropriate for the nurse to suggest finding a source of pleasure, whether it is spending time with family or talking a walk each day. Developing a positive attitude, seeking counseling for chronic anxiety and utilizing relaxation and deep breathing exercises are also ways to combat stress. The nurse should recommend that individuals stay away from stressful situations, in order to decrease their overall levels of stress. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate”. In this scenario, the most appropriate action is to assist the public in reducing stress levels. Eliminate option 4, because this would lead to an increase in stress levels. Review: Stress reduction. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Leadership/Management Giddens Concepts: Health Promotion, Stress HESI Concepts: Teaching and Learning/Patient Education, Stress and Coping Reference: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for nNursing Practice. (1st ed., p 354). St. Louis: Mosby. Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 92-94). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 14.ID: 9476805564 The nurse is assisting a family with end-of-life care for their child. Which actions by the nurse would be the most appropriate? Select all that apply. A. Acknowledging the emotions of the family members. Correct B. Taking time to listen to the family talk about their child. Correct C. Limiting communication with the family, to allow grieving. D. Reminding the family that their feelings and emotions are normal. Correct E. Gently reminding the family that they must focus on their remaining children. Rationale: Chronic and terminal conditions involve the loss of health and result in grief. Grief is a normal psychophysiological process that occurs in response to a specific loss. As adjustment to the condition progresses, many parents experience chronic sorrow related to the unending nature of the child's condition and the ongoing feelings of loss. It is important that the nurse take the time to listen to the family as they talk about their child. The nurse should also acknowledge the emotions of the family members and remind them that their feelings and emotions are normal. Not acknowledging the family members feelings are often triggers for grief. It would be inappropriate, or even hurtful, to the family if the nurse limited communications or suggested that the family focus on the remaining children. During this time, family members need therapeutic and caring support from the nurse. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate”. Determine which nursing actions would be the most beneficial to the family in their time of need. Eliminate options 3 and 5, because these actions may be upsetting to the family and may not provide the support that the family needs. Review: End-of-life Care. Priority Nursing Tip: The grief experience is unique to each person. Be supportive to the client and family at all times. Prepare by practicing therapeutic communication. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Leadership/Management Giddens Concepts: Communication, Palliation. HESI Concepts: Reference: Hockenberry, M, & Wilson, D. (2015). Wong’s nursing care of infants and children (10th ed. pp. 807-809). St Louis: Mosby. Awarded 2.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 15.ID: 9476797841 A pregnant client has a history of depression and has been noncompliant with treatment in the past. What actions by the nurse would be the most appropriate? Select all that apply. A. Respect the client's decisions. Correct B. Maintain a hopeful, caring relationship with the client. Correct C. Discuss the noncompliance with the client, if the client brings it up. D. Provide education to the client about depression and treatment options. Correct E. Ask the client what methods of managing the depression have worked in the past. Correct Rationale: Women are at risk for developing a psychiatric disorder between the ages of 18 and 45 years—the childbearing years. Women who have serious mental disorders may be engaging in sexual activities that can result in pregnancy. The pregnant woman may have a history of disorder in mood, anxiety, substance use, schizophrenia, personality, or development and may be noncompliant with treatment for the disorder. Assessment throughout pregnancy and the postpartum period is critical to the mother's and the baby's health. The nurse should strive to maintain respect for the client's decisions at all times, even though the nurse may not agree with the client's decisions. Maintaining a hopeful and caring relationship with the client, allows for the establishment of trust. The nurse should provide education when the client is open to learning, and utilize teachable moments whenever possible. In order to create a plan of care that works, the nurse should ask the client what methods of depression management have been successful in the past. It would not be effective for the nurse to avoid discussion of depression unless the client's brings up the topic. The nurse should recognize the need for education and begin assessing the client's readiness to learn. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate.”Think about the components of a therapeutic relationship and methods to deal with noncompliance. Determine which actions by the nurse would be the most appropriate to maintain a therapeutic relationship with the client. Eliminate option 3, because this action would not be beneficial to the client. Review: Depression. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Adherence, Caregiving, HESI Concepts: Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 748-749). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 16.ID: 9476807900 The nurse is caring for a client who is in labor and preparing for birth. The nurse has been advised that the pregnancy is the result of a rape. Which statements by the nurse would be the most appropriate? Select all that apply. A. "You are safe here." Correct B. "We have done this many times before." Incorrect C. "Just relax; we know what we are doing." D. "You are in labor and preparing to give birth to your baby." Correct E. "You do not need to be concerned about anything because your baby is ok." Correct Rationale: In order to create a comfortable environment for the client, the nurse should maintain a calm environment and use words that will comfort the client. The nurse should let the client know that the environment is safe and that safety will be maintained at all times. The client should be updated on what is happening, and letting the client know what to expect, what examinations are occurring, and the reason why. The nurse should refrain from making vague statements, and instead should personalize care to the needs of the client. If the pregnancy is a result of rape, the woman may be extremely ambivalent about the baby. If the rape occurred some time ago, the experience of pregnancy with prenatal examinations can trigger memories of the original trauma. It is important to know that she may avoid prenatal examinations because of the anxiety triggered by bodily touch and vaginal examinations. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate.” Use therapeutic communication techniques. Eliminate options 2 and 3, because these statements could increase the anxiety level of the client and are nontherapeutic. Review: rape syndrome. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Maternity Giddens Concepts: Communication, Professionalism HESI Concepts: Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 742-743). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 17.ID: 9476793873 The nurse is attending an educational session on substance abuse during pregnancy. Which statements by the nurse indicate that the education has been effective? Select all that apply. A. "Substance abuse generally has no effect on the fetus." Incorrect B. "Social stigma, labeling, and guilt are barriers to treatment." Correct C. "Pregnant women often do not seek help for fear of losing their child." Correct D. "Most pregnant women end up receiving treatment for their addictions." Incorrect E. "In some states, pregnant women who abuse substances may face criminal charges." Correct Rationale: Substance abuse refers to the continued use of substances despite related problems in physical, social, or interpersonal areas. Recurrent abuse results in failure to fulfill major role obligations, and there may be substance- related legal problems. Any use of alcohol or illicit drugs during pregnancy is considered abuse. There are serious damaging effects of alcohol and illicit drugs on pregnant clients and their fetuses. Alcohol and other drugs easily pass from a mother to her fetus through the placenta. Therefore it is important for pregnant clients to seek treatment. It is important that the nurse have a clear understanding of the effects of substance abuse during pregnancy. The nurse should understand the barriers that prevent treatment, such as social stigma, labeling, and guilt. The nurse should know that many pregnant clients avoid treatment out of fear of losing their child. In some states, pregnant clients may face criminal charges for their use of drugs while pregnant. Nurses should recognize that substance abuse has a direct effect on the health and well-being of both the mother and fetus, and that less than 10% of pregnant substance abusers actually receive treatment for their addiction. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word, “effective” and the subject, education was effective. Determine which statements by the nurse indicate that the nurse has an understanding of the effect of substance abuse during pregnancy. Eliminate options 1 and 4, because these statements are incorrect, meaning that the nurse needs more education. Review: Substance abuse during pregnancy. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluation Content Area: Maternity Giddens Concepts: Addiction, Reproduction HESI Concepts: Addiction, Sexuality/Reproduction Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 751-752). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded -1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 18.ID: 9476793860 The nurse is assessing a client who is two days post-partum, and preparing to be discharged from the health care facility. Which interventions would be the most appropriate for the nurse to perform? Select all that apply. A. Assess the client for risk factors of depression. Correct B. Determine if a follow-up after discharge is necessary. C. Provide a listing of community resources to the client and family. Correct D. Spend time observing the interactions between the client and infant. Correct E. Educate the client and family on the signs of post-partum depression. Correct Rationale: Even though the prevalence of post-partum depression is fairly well established, it often remains undetected because women are hesitant to report symptoms of depression to their health care providers or to seek help from a mental health provider. It is important that the nurse take time to adequately assess the client and prepare the family for discharge. The nurse should always plan to follow-up with the client after discharge, whether by discharge phone calls or home visit. The nurse should also assess the client for risk factors of depression before discharge, so that proper interventions can be made. Providing a list of community resources to the client and family may help in decreasing the the client and family’s anxiety in obtaining help when needed. The nurse should educate the client and family on signs of post-partum depression and where to get help. The nurse should also spend some time observing interactions between the client and infant, and performing any interventions that may be necessary. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate”. Determine which interventions would be the most appropriate, or most likely to help the client. Eliminate option 2 because follow-up after discharge is always necessary. Review: Nursing interventions for post-partum depression. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Maternity Giddens Concepts: Caregiving, Client Education HESI Concepts: Caregiving, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 749, 751). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 19.ID: 9476812010 The nurse on a post-partum floor is assessing a client for signs of post-partum depression. Which statements would be the most appropriate for the nurse to make, in order to assess the client for depression? Select all that apply. A. "How are things going for you today?" Correct B. "Do you have anyone to help you at home?" Correct C. "Can you tell me how you are feeling today?” Correct D. "I'm sure you're so happy with your new baby". E. "It is not very common to feel sad after giving birth". Rationale: To recognize symptoms of post-partum depression as early as possible, the nurse should be an active listener and demonstrate a caring attitude. Nurses cannot depend on women volunteering unsolicited information about their depression or asking for help. The nurse should observe for signs of depression and ask appropriate questions to determine moods, appetite, sleep, energy, and fatigue levels, and ability to concentrate. The nurse should make an effort to engage in conversation with the client, in order to gain an understanding of how the client is feeling. Asking if the client feels sad, how things are going, and inquiring if the client has help at home, are good ways to engage the client in conversation and determine if there is evidence of depression. Assuming that the client feels happy or making general statements are not ways that the nurse can effectively assess for post-partum depression. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate”. Determine which statements would assist the nurse in assessment of the post- partum client. Eliminate option 4 because it makes an assumption about the client. Eliminate option 5, because this is a general statement and not a question aimed at assessing the client. Options 4 and 5 are non-therapeutic statements. Review: Nursing assessment for post-partum depression. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Maternity. Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Communication HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Communication Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 747-748). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 2.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 20.ID: 9476797870 The nurse manager is educating a group of nursing students on the educational needs of bariatric clients post-surgery. Which statement by one of the nursing students indicates that the teaching has been effective? Select all that apply. A. "The client should be encouraged to keep follow-up appointments." Correct B. "During weight loss, the client may become depressed or even anxious." Correct C. "Clients should be provided with a list of available community resources." Correct D. "It is not necessary for clients to adhere to a community-based treatment plan." E. "Clients are followed by a surgeon and dietician for a few months after the surgery." Incorrect Rationale: Obesity is a chronic, lifelong problem. Diets, medication therapy, exercise, and behavior modification can produce short-term weight losses with reasonable safety. However, most who do lose weight often regain the weight. Treatment of obesity should focus on the long-term reduction of health risks and medical problems associated with obesity, improving quality of life, and promoting a health-oriented lifestyle. The nurse manager knows that teaching has been effective when the student states that post-surgical clients should keep follow-up appointments. The client may also become depressed or anxious during this time, and experience a "hibernation period." Clients should receive a list of community resources that are available specifically to them. Clients should be educated about the importance of adhering to a community- based treatment plan, which will give them access to information and support. The client should understand that they will be followed by both a surgeon and dietician for a few years after surgery. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word, “effective.” Determine which statements are correct, indicating that the student has an understanding of the topic. Eliminate options 4 and 5, because these statements are not correct regarding the educational needs of bariatric clients. These statements indicate that further education is needed. Review: Education of the bariatric client Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluation Content Area: Adult Health Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Health Promotion HESI Concepts: Health, Wellness, and Illness – Health Promotion, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 1356). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 21.ID: 9476810150 The nurse is monitoring a client who is receiving a blood transfusion. The blood has been infusing for 15 minutes. The nurse interprets which assessment findings as a possible allergic reaction? Select all that apply. A. Increased pallor Correct B. New onset of hypertension Incorrect C. The client reports feeling nervous D. Palpation of a rapid, thready pulse Correct E. A change in the client’s level of fatigue Rationale: Nursing actions during transfusions aim at prevention or early recognition of transfusion reactions. Reactions include palpation of a rapid thready pulse, and increased pallor or cyanosis. These findings should alert the nurse to a possible reaction. It is important that the nurse immediately stop the blood infusion if a reaction is suspected. Findings such as hypertension, nervousness, or a change in fatigue level do not typically indicate an allergic reaction. However, the nurse should continue to monitor these symptoms and intervene as necessary. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “possible allergic reaction to blood.” Determine which assessment findings indicate the possibility of an allergic reaction. Think about how the client might react in a reaction. and use knowledge of the assessment findings in a reaction to answer correctly. Review: Blood Administration. Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Blood Administration Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., p. 823). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 0.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 22.ID: 9476812018 The nurse is assessing the client for placement of a midline catheter. Which factors would prompt the nurse to select a different type of catheter for this client? Select all that apply. A. Dialysis fistula on the right arm Incorrect B. The use of vesicant medications Correct C. The need for long-term antibiotics Incorrect D. Client history of bilateral mastectomy with lymphedema Correct E. The need for parenteral therapy with osmolarity greater than 600 mOsm/L (600 mmol/kg) F. Correct Rationale: An infusion catheter, also known as a vascular access device (VAD), is a plastic tube placed in a blood vessel to deliver fluids and medications. The specific type and purpose of the therapy determine whether the infusion can be given safely through peripheral veins or if the large central veins of the chest are needed. Midline catheters are placed in the peripheral circulation. Fluids and medications infused through a midline catheter should have a pH between 5 and 9 and a final osmolarity of less than 600 mOsm/L(600 mmol/kg). The pH and osmolarity outside these parameters increase the risk for complications like nurse would choose another type of catheter if the client will be given any vesicant medications, because leakage of these medications could damage surrounding tissue. The nurse should also avoid use of a midline catheter if the client has had a bilateral mastectomy with lymphedema, or if the client requires parenteral therapy that has an osmolarity greater than 600 mOsm/L (600 mmol/kg). Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “contraindications for use of a midline catheter.” Think about the anatomical location of this type of catheter to answer correctly. Review: Use of midline catheters. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Intravenous Therapy Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., pp. 192-193). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded -1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 23.ID: 9476793868 The nurse is caring for a client who has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. The health care provider has just started the client on methotrexate, to manage symptoms. When creating the plan of care for this client, which adverse effects should the nurse monitor for? Select all that apply. A. Increased thirst Incorrect B. Elevated blood pressure C. Elevation of liver enzymes Correct D. A decrease in the platelet count E. An increase in white blood cells (WBC) Rationale: Methotrexate, an immunosuppressive medication, administered in a low, once-a-week dose (generally 25 mg or less per week) is a possible treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. When creating the plan of care, the nurse should monitor for certain adverse effects, and be prepared to treat them. The nurse should assess for an elevation in liver enzymes and a decrease in platelet count. Increased thirst and elevated blood pressure are not adverse effects of methotrexate. The client would experience a decrease in the WBC count, not an increase, during methotrexate therapy. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “adverse effects of methotrexate.” Recalling that this medication is an immunosuppressant will assist in answering correctly. Review: adverse effects of methotrexate Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Pharmacology Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Clinical Judgment HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., p. 308). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded -1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 24.ID: 9476793878 The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client with chronic pain. Which alternative therapies should the nurse add into the plan, to increase the client’s comfort? Select all that apply. A. Providing therapeutic massage Correct B. Play soft music during rest times Correct C. Assist with a warm, soothing bath Correct D. Educate the client to plan for rest time Correct E. Increase the client’s dosage of pain medication Rationale: With chronic pain, the client cannot depend solely on medications for relief. The nurse should offer alternative therapies to the client when appropriate. These treatments include using therapeutic massage, a warm soothing bath and soft music during rest times. The client should be educated to plan for rest times in between activities. Increasing the client’s pain medication may be appropriate, but it is not considered an alternative treatment. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “using alternative therapies in client care. ” Determine which treatments are considered alternative. Eliminate option 5, because this is a pharmacological therapy and not considered an alternative therapy. Review: Alternative therapies for pain Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Pain Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Pain HESI Concepts: Teaching and Learning/Patient Education, Pain References: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., pp. 48, 294-295). St. Louis: Saunders. Perry, A., Potter, P., & Ostendorf, W. (2014). Clinical nursing skills & techniques (8th ed., p. 366). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 25.ID: 9476805542 The nurse is caring for a client who has had a myocardial infarction. After administering intravenous morphine sulfate, which interventions should the nurse take? Select all that apply. A. Monitor the client’s blood pressure Correct B. Monitor the client’s respiratory rate Correct C. Determine the client’s oxygen saturation Correct D. Ask the client to obtain a urine specimen Incorrect E. Prepare the client for cardiac catheterization Rationale: Intravenous morphine sulfate (1 to 2 mg) is often prescribed to reduce myocardial oxygen demand by triggering blood vessel dilation. The nurse should be prepared to monitor the client’s status. After administering morphine sulfate, the nurse should monitor the client’s respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure. The nurse would not prepare the client for the cardiac catheterization unless specifically indicated by the health care provider. While a urine specimen may be needed, it is not the most important intervention after administration of the medication. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, nursing interventions after the administration of morphine sulfate. Think about the physiological action and adverse effects of morphine to answer correctly. Review: morphine sulfate Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Pharmacology Giddens Concepts: Caregiving, Safety HESI Concepts: Caregiving, Safety Reference: Gahart, B., & Nazareno, A. (2015). 2015 Intravenous medications (31st ed., pp. 841-842). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 26.ID: 9476801235 The nurse is caring for a client with known chronic kidney disease (CKD), who is taking digoxin. When assessing the client, which signs/symptoms would alert the nurse to the possibility of digoxin toxicity? Select all that apply. A. Anorexia Correct B. Muscle aches Incorrect C. Visual changes Correct D. Sudden ear pain E. Nausea and vomiting Correct Rationale: Clients with CKD are particularly at risk for digoxin toxicity because the medication is excreted by the kidneys. The symptoms include confusion, visual changes, gastrointestinal (GI) disturbances such anorexia, nausea, and vomiting. Muscle aches and sudden ear pain is not indicative of digoxin toxicity. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “signs/symptoms of digoxin toxicity.” It is necessary to know what these manifestations are in order to answer correctly. Remember that GI disturbances and visual disturbances are manifestations. Review: digoxin toxicity. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Pharmacology-Cardiovascular Medications Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient- centered collaborative care. (8th ed., pp. 661-662). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 27.ID: 9476807913 The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client who was admitted with an infection. The nurse has been informed that the client will need a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line placed, and in the next few days will be discharged home. Which information about the PICC line should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply. A. Avoid heavy lifting once Correct B. Keep the extremity immobile C. How to care for the PICC line Correct D. Reason for PICC line placement Correct E. How to get dressed with the PICC line Correct Rationale: A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) is a catheter inserted through a vein of the antecubital fossa (inner aspect of the bend of the arm) or the middle of the upper arm. PICCs should be inserted early in the course of therapy before the veins of the extremity have been damaged from multiple venipunctures and infusions. The nurse should plan to educate the client on how to care for the PICC line, how to get dressed and perform other activities of daily living, and the reason for the PICC line placement. The nurse should also educate the client to avoid heavy lifting because this can lead to muscle contraction, which can cause catheter dislodgment. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “client education about a PICC line.” Think about the anatomical location of a PICC line and what is important for a client to know. Noting the word “immobile” in option 2 will assist in elimination this option because immobility of the extremity is unnecessary. Review: PICC Lines. Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Intravenous Administration Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Teaching and Learning HESI Concepts: Teaching and Learning/Patient Education, Safety References: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., pp. 193-194). St. Louis: Saunders. Perry, A., Potter, P., & Ostendorf, W. (2014). Clinical nursing skills & techniques (8th ed., p. 708). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 28.ID: 9476810136 On assessment of a client with a normal saline intravenous (IV) infusion, the nurse notes that the IV site has infiltrated. Which actions by the nurse would be appropriate? Select all that apply. A. Stop the IV infusion Correct B. Elevate the extremity Correct C. Apply a warm compress to the IV site Correct D. Apply a sterile dressing if weeping occurs Correct E. Restart a new IV below the current IV site Rationale: Complications from IV therapy can be minor and limited or life- threatening. It is important for the nurse to frequently monitor the client’s IV site for signs of complications such as infiltration. If infiltration occurs, there are steps the nurse can take to prevent further damage to the tissue involved. These steps include stopping the IV infusion immediately, elevating the extremity to reduce swelling, and applying a warm compress to the IV site after the IV has been removed (per agency procedure). If weeping occurs from the IV site, the nurse can apply a sterile dressing to control the weeping and prevent infection. If the client requires a new IV, the nurse should place the IV in the opposite extremity. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “interventions for IV infiltration.” Think about what the effects on skin integrity are when infiltration occurs. Determine which actions are appropriate to prevent further damage to skin tissue. Eliminate option 5, because this action may increase the risk of damage to tissue. Review: IV Infiltration. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Intravenous Administration Giddens Concepts: Health Care Quality, Tissue Integrity HESI Concepts: Quality Improvement/Health Care Quality, Tissue Integrity Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., p. 204). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 29.ID: 9476810110 The nurse has been assigned a client who is receiving enalapril therapy. After receiving report and looking at the client’s chart, which action should the nurse take first? A. Obtain a blood pressure Correct B. Perform a full physical assessment C. Administer the client’s morning medications D. Order the client’s breakfast tray to be delivered at 0800 Incorrect Rationale: Enalapril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor that is used to treat hypertension. Therefore, after receiving report and gathering information from the client’s chart, the nurse should first obtain a blood pressure on the client. This will enable the nurse to make decisions about which step to take next, in order to provide safe client care. All other actions can safely wait until the nurse has obtained the client’s blood pressure. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word, “first” and focus on the name of the medication. Recalling that medications that end with the letters –pril are ACE inhibitors and that these medications are used to trest hypertension will assist in answering correctly. The remaining options can safely wait until the blood pressure has been obtained. Review: enalapril Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Leadership/Management: Prioritizing Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety Reference: Lilley, L., Rainforth Collins, S., Harrington, S., & Snyder J. (2014). Pharmacology and the nursing process (7th ed., pp. 356, 362-363). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 30.ID: 9476801260 The nurse is preparing to administer bumetanide to a client. What information is the priority for the nurse to obtain prior to administering this medication? A. The client’s current weight B. The client’s potassium level Correct C. The time of the client’s last meal D. The time of the last bumetanide administration Rationale: Bumetanide is a loop diuretic that causes the kidneys to excrete potassium, which can lead to hypokalemia. Therefore it should be the nurse’s highest priority to obtain the client’s potassium level prior to administering the potassium. While the other options are important in the care of the client, the potassium level is the highest priority for client safety and well-being. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic word, priority. Recalling that bumetanide is a diuretic will assist in answering the question. Remember that most diuretics cause hypokalemia. Review: bumetanide Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiology Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Leadership/Management: Prioritizing. Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Fluid and Electrolyte Balance HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Fluids and Electrolytes Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2016). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (8th ed., p. 165). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 31.ID: 9476801299 Which clients are at high risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE)? Select all that apply. A. A 35 year-old with intractable nausea B. A 88 year-old admitted with confusion Correct C. A 28 year-old recovering from a paralytic ileus Incorrect D. A 45 year-old recovering from a total hysterectomy Correct E. A 45 year-old in a motor vehicle accident who sustained multiple fractures Correct Rationale: Clients at risk for VTE include those with prolonged immobility such as those with multiple fractures, those recovering from a surgical procedure, such as a total hysterectomy, obese clients, and those with advancing age. Nausea and paralytic ileus alone do not increase the risk for VTE. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject of the question, clients at risk for a VTE. Think about the pathophysiology associated with VTE and about conditions that could impact circulation and blood flow to answer this question correctly. Review: Venous thromboembolism Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment Content Area: Adult Health: Cardiovascular Giddens Concepts: Clotting, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Clotting, Perfusion References: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 663). St. Louis: Saunders. Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 848). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 32.ID: 9476801214 The nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client just brought in with partial thickness burns to 50% of the body. What actions should the nurse implement as part of the care plan? Select all that apply. A. Elevate extremities Correct B. Administer tetanus vaccine for prophylaxis Correct C. Assess airway patency and provide oxygen as needed Correct D. Provide the client with a large glass of water to stay hydrated Incorrect E. Keep burns uncovered to allow for cooling air to reach the wounds Rationale: Immediate care for a burn is critical. Ensure in the first hour after a burn that the client’s extremities are elevated to prevent edema. Administer a prophylactic dose of tetanus, assess the airway to ensure patency, and administer oxygen as needed. Water should not be provided to the client because the client should remain NPO; initiate fluid rehydration with IV fluids instead. Lastly, cover he client with a blanket to help maintain body temperature. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, care for the client with burns. Also, use the ABC – airway, breathing, circulation strategy to include activities that support the airway and promote circulation. Review: immediate burn care Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Planning Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Thermoregulation, Tissue Integrity HESI Concepts: Thermoregulation, Tissue Integrity Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 520). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 33.ID: 9476805536 The nurse caring for an 8 month old child at the pediatrician’s office is reviewing medication instructions with the father. The client has otitis media and has been prescribed amoxicillin 250 mg three times daily. The medication comes as a liquid suspension of 500 mg/10 mL. The nurse would advise the father to give how many milliliters per dose? Fill in the blank and round answer to the nearest whole number. milliliters Correct Correct Responses A. 5 Rationale: First, calculate the dose needed, which is 250 mg or 5 mL. The father should administer 5 mL of medication three times daily. Desired x Volume = milliliters per dose Available 250 X 10 = 5 500 Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, a medication calculation. Use the appropriate formula to determine the correct dose. Once you have performed the calculation, ensure it makes sense and check your answer with a calculator. Review: Medication Calculations Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamental of Care: Medication/IV calculations Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety Reference: Hockenberry, M, & Wilson, D. (2015). Wong’s nursing care of infants and children (10th ed. pp. 914-915). St Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 34.ID: 9476797881 The nurse is instructing a postoperative client how to use a demand-only patient controlled analgesia (PCA) pump. What statements made by the client would indicate teaching was effective? Select all that apply. A. “This machine will deliver pain medication when I push the button.” Correct B. “I should push the button as many times as I want if I have any pain at all.” C. “Itching is a normal side effect and I do not need to worry if I experience this.” Incorrect D. “If I fall asleep, my wife can push the button for me so I continue to get pain medication.” E. “My oxygen and breathing will be monitored while using this machine to prevent being over medicated.” Correct Rationale: A patient controlled analgesia (PCA) pump allows the client to feel more empowered in the treatment of pain. A demand-only PCA will only deliver medication when the button is pushed. Oxygen levels and breathing should be assessed frequently to prevent respiratory sedation. Inform the client that pain should be tolerable, but may not be completely gone and to notify the nurse if any adverse side events develop such as itching, nausea or trouble breathing occurs. Instruct the client that no other individual, including the nurse, should push the button. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word ‘effective’ to select correct statements made by the client. A correct statement indicates learning has occurred and teaching was effective. Eliminate option 2 because of the closed-ended words “at all.” Recalling the adverse effects of pain medications and the guidelines related to PCA pumps will assist in eliminating the remaining incorrect options. Review: Pain management Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Evaluation Content Area: Fundamental of Care: Pain Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Pain HESI Concepts: Pain, Teaching and Learning/Patient EducationReference: Perry, A., Potter, P., & Ostendorf, W. (2014). Clinical nursing skills & techniques (8th ed., pp. 356- 357). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 0.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 35.ID: 9476801274 The nurse is caring for a client with Addison’s disease in acute crisis. What priority actions should the nurse implement into the care plan? Select all that apply. A. Apply telemetry monitoring Correct B. Monitor strict intake and output Correct C. Administer spironolactone as prescribed Incorrect D. Rapidly infuse normal saline as prescribed Correct E. Administer oxygen via non-rebreather mask Incorrect Rationale: Acute adrenal insufficiency as seen in Addison’s disease is a life- threatening emergency. Because of the rapid decrease in sodium and elevation of potassium, cardiac monitoring is essential along with intravenous normal saline. Intake and output are closely monitored due to blood volume depletion, rapid electrolyte imbalances, rehydration, and diuretic use. Oxygenation should be assessed, but supplemental oxygen may not be required. Diuretics are used as part of the treatment plan, however, due to elevated potassium levels, potassium-retaining diuretics should be avoided. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word ‘priority’ to select options that must occur for the client with acute crisis in Addison’s disease. Recall the role of the adrenal glands, think about the pathophysiology associated with Addison’s disease, and consider the implications of adrenal insufficiency. Review: Adrenal insufficiency Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Fluids & Electrolytes Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Fluid and Electrolyte Balance HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Fluids and Electrolytes Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 1382). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded -2.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 36.ID: 9476805582 A client asks the nurse what can be done to prevent colon cancer as his father passed away from it. What information would be appropriate for the nurse to include in the teaching? Select all that apply. A. Limit alcohol consumption and avoid smoking Correct B. Screening for colon cancer should begin at age 60 C. A diet high in fat can increase your risk of colon cancer Correct D. Fiber can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and should be limited E. Notify your healthcare provider of any changes in your bowel habits Correct Rationale: Individuals with a family history of colon cancer should discuss their risk with their healthcare provider. Risk factors for colon cancer include a diet high in alcohol and fat, and smoking. The health care provider should be notified of any changes in bowel habits such as constipation, diarrhea, or blood in stools. Screening for colon cancer should begin at age 50, or earlier if a strong family history exists. Fiber is helpful for gastrointestinal health, and a diet high in fiber is recommended. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject of the question, risk factors for colon cancer. Consider the gastrointestinal tract and what may be helpful and hurtful to the tract. Review: Colon cancer prevention Level of Cognitive Ability:Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Adult Health: Gastrointestinal Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Health Promotion HESI Concepts: Health Promotion, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 986-987). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 3.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 37.ID: 9476805576 The nurse on the labor and delivery unit notes the following fetal heart rate pattern on the fetal monitoring strip (refer to figure). What is the priority nursing action? A. Assist client to the supine position B. Increase oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion C. Administer oxygen via face mask at 8 to 10 L Correct D. Continue to monitor fetal heart rate patterns Rationale: Late decelerations are a drop in fetal heart rate after the peak of contraction. They are generally a sign of impaired placental exchange and therefore, the nurse should administer oxygen to the client to increase maternal blood oxygenation and increase available oxygen to the fetus. Repositioning the client may be helpful, but the supine position is not recommended as this could decrease perfusion to the fetus. Uterine stimulants such as oxytocin should be stopped. Continued monitoring of the fetal heart rate pattern is important, but late decelerations are a non-reassuring sign requiring intervention. Test Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, the fetal heart rate pattern and the action to take. Recall that late decelerations are nonreassuring and require intervention. Also use the ABCs, airway, breathing, and circulation to direct you to the correct option. Review: Late decelerations Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Maternity/Intrapartum Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Perfusion Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., p. 422). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 38.ID: 9476801257 A 22-year-old African American woman is 28 weeks pregnant. She is concerned about pre-term labor and asks the nurse what she should look out for. What statements made by the client would indicate the need for further teaching? Select all that apply. A. “I should stay well hydrated.” B. “I am at a higher risk because of my race.” Incorrect C. “Stress levels can impact my chance of preterm labor.” D. “My age puts me at a higher risk of having the baby early.” Correct E. “As long as I’m not obese, my weight does not increase my risk.” Correct Rationale: Preterm labor is defined as delivery between 20 to 37 weeks gestation. A woman aware of the possibility, risk factors, and signs and symptoms of preterm labor may be more likely to take action and prevent it. Age impacts the risk for preterm labor. Less than 18 or over the age of 40 increases the risk. Obesity increases the risk of preterm labor, as does being underweight for height. Hydration is important, and non-whites have a greater risk for preterm labor. Test Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words ”need for further teaching.” Focus on the client’s age, ethnicity, and weeks of pregnancy. Then think about the risk factors associated with pre-term labor to answer correctly. Review: risks for preterm labor Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Maternity/Intrapartum Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Health Promotion HESI Concepts: Health Promotion, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., p. 760). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 0.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 39.ID: 9476797818 The nurse on a medical surgical telemetry unit notes an abnormal cardiac rhythm. After quickly assessing the client, which cardiac rhythm would indicate the need for immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)? Refer to figures 1-4. A. Correct B. C. D. Rationale: Cardiac monitoring is an important aspect of care for the hospitalized client. Frequent assessment of the rhythm and client is critical. Ventricular fibrillation is a life threatening emergency and CPR should begin immediately after quickly assessing the client. Option 2 denotes normal sinus rhythm with premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), Option 3 demonstrates atrial fibrillation, and option 4 shows sinus tachycardia. While all abnormal, options 2, 3, and 4 are not life-threatening. Test Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, a cardiac rhythm requiring CPR. Recall that complexes that make up a normal ECG consist of a P wave, a QRS complex, a T wave, and possibly a U wave. Use your previous knowledge of cardiac conditions to identify life-threatening conditions. Review: Cardiac monitoring. Level of Cognitive Ability: Synthesizing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Perfusion Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 790-791). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 40.ID: 9476805593 A client with diabetes mellitus, heart failure, and hypertension is being seen by the health care provider. The health care provider prescribes lispro insulin pens at mealtime. The client asks the nurse how to store the insulin pens. The nurse should include what information in the teaching? Select all that apply. A. Once opened, insulin pens are good for one month. Correct B. When traveling, do not store the insulin pens in a warm car. Correct C. The insulin pens should be stored in the refrigerator at all times. Incorrect D. Keep the insulin pens away from children, for example on a high windowsill. Incorrect E. Unopened insulin pens may be stored in the freezer to lengthen the shelf life. Rationale: Lispro is a rapid acting insulin used to treat hyperglycemia. Opened pens are good for one month, and when storing insulin it should be protected from extreme temperatures. It should be kept in the refrigerator until opened. The client needs to be taught to avoid exposure to direct sunlight or warm temperatures, so the client should avoid using a windowsill for storage or a warm vehicle. Insulin should never be frozen. Test Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject of the question, storage of insulin. Eliminate option 3 because of the closed-ended word, all. Next eliminate options 4 and 5 because they address extremes in temperature. Also, remember the mechanism of action of insulin to help answer the question correctly. Review: Insulin Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Pharmacology: Endocrine Medications Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Safety HESI Concepts: Safety, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Rosenjack Burchum, Rosenthal (2016) pp. 698-699 Awarded -1.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 41.ID: 9476793849 The nurse is discharging an older client who was admitted for dehydration. Which instructions would be the most appropriate for the nurse to include in the discharge teaching? Select all that apply. A. Drink caffeine in moderation. Correct B. Avoid drinking water right before bed. C. Eliminate juice drinks totally from the diet. Incorrect D. Understand how prescribed medications work. Correct E. Be sure to drink 6 to 8 glasses of water each day. Correct Rationale: People older than 65 years are also at risk for dehydration because they have less body water content than younger adults. In severe cases, they require emergency department visits or hospital stays. It is important that the client receive education to prevent dehydration. The nurse should educate the client to drink caffeine in moderation. Juice drinks are appropriate and provide extra vitamins. The client should understand how prescribed medications work, especially diuretics. The client should be encouraged to drink 6 to 8 glasses of water each day. The nurse should not tell the client to avoid drinking water before bed; the client should drink when thirsty. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most appropriate.” Determine which instructions would assist the client in maintaining independence in care, prevent dehydration, and maintain quality of life. Eliminate options 2 and 3, because these options do not assist in meeting that goal. Also note the closed-ended word “totally” in option 3. Review: Dehydration. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity. Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Fluids & Electrolytes Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Health Promotion HESI Concepts: Health, Wellness, and Illness, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 17). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 42.ID: 9476801290 The nurse is working at a health fair, educating the public on how to prevent heat-related illnesses. Which information would be the most appropriate for the nurse to provide? Select all that apply. A. Avoid alcohol and caffeine Correct B. Wear sunscreen of at least SPF 30 Correct C. Limit activity at the hottest time of day Correct D. Wear clothing suited to the environment Correct E. Heat illnesses only occur to those who work outside Incorrect Rationale: High environmental temperature (above 95° F [35° C]) and high humidity (above 80%) are the most common environmental factors causing heat-related illnesses. These illnesses include heat exhaustion and heat stroke. The nurse should educate the public to avoid caffeine and alcohol, and explain that these can lead to dehydration. The best fluid to consume in high heat weather is water. The public should also be educated to wear sunscreen every day, reapplying as needed, which includes an SPF of at least 30 with UVA and UVB protection. The nurse should also advise the public to limit activity at the hottest time of day and wear clothing that is suitable to the environment. The nurse should stress that heat illnesses can happen to anyone, not just those who work outside. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words “most appropriate” and focus on the subject, preventing heat-related illnesses. Determine which actions would prevent a heat-related illness. Eliminate option 5, because this statement is inaccurate and also note the closed-ended word, only in this option. Review: causes of heat-related illness. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Safety Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Thermoregulation HESI Concepts: Teaching and Learning/Patient Education, Thermoregulation Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 137). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 43.ID: 9476801206 The nurse is working in the emergency department when a client is brought in by ambulance. The client reports being bitten by a North American pit viper. Upon assessment, the nurse notices a bite mark on the client’s left leg. Which actions should the nurse to take? Select all that apply. A. Apply ice to the bite mark B. Initiate cardiac monitoring Correct C. Prepare to administer oxygen Correct D. Start two large-bore intravenous (IV) lines Correct E. Measure the circumference of the bitten extremity every 15 to 30 minutes Correct Rationale: When providing emergency care to a victim of snakebite, determine if the venom has been injected into the body. The primary functions of venom are to immobilize, kill, and aid in digestion of prey. Therefore venom causes local and systemic toxic effects. The enzymes in venom break down human tissue proteins, alter membrane integrity, and impair blood clotting. The pathophysiologic effects of pit viper envenomation can lead to local tissue necrosis, massive tissue swelling, intravascular fluid shifts and hypovolemic shock, pulmonary edema, renal failure, hemorrhagic complications from disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), and death. The nurse should take action to prevent further injury to the client. The nurse should initiate cardiac monitoring to determine the presence of cardiac ischemia as a result of the venom. Establishing two large bore IV line is a priority in the care of this client for the administration of fluids and possible antidotes, as well as preparing to administer oxygen. The nurse should measure the bitten extremity every 15 to 30 minutes, and document the size and assess the site. The nurse should refrain from applying ice to the bite mark; ice can promote tissue necrosis. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, treatment for a snake bite. Thinking about the effects of ice and that tissue necrosis is a concern will assist in eliminating option 1. Review: treatment for snake bites Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Perfusion, Tissue Integrity HESI Concepts: Perfusion, Tissue Integrity Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 140). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 44.ID: 9476793898 The emergency department nurse has just received a client who was struck by lightning. On initial assessment, the nurse notes a pulse and that the client is breathing. Which actions should the nurse to take? Select all that apply. A. Monitor for rhabdomyolosis. B. Prepare the client for discharge. C. Assess for occult traumatic injuries. D. Request a creatinine kinase measurement. Correct E. Perform a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). Correct Rationale: Lightning produces injury by directly striking a victim, by splashing off a nearby object, or by traveling through the ground. Although few people die after a lightning strike, many survivors are left with permanent disabilities. The nurse should be prepared to deliver quick and effective care to the client. After the initial assessment, the nurse should perform a 12-lead ECG to detect any cardiac abnormalities. The nurse should continually assess for rhadomyolosis, along with occult traumatic injuries, and intervene if necessary. The nurse should collaborate with the health care provider to request a creatinine kinase measurement, in order to monitor closely for rhabdomyolosis. The nurse should not prepare the client for discharge at this time. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, care to the client who was struck by lightening. Recall the seriousness of this type of injury and how it affects the body physiologically. This will assist in eliminating option 2. Review: Lightning strike injuries. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Caregiving, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Caregiving, Perfusion Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., pp. 147, 148). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 45.ID: 9476801228 The nurse is at a local pool when alerted of a near drowning event. Which actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply. A. Send a by-stander to call for help Correct B. Obtain client history from a family member C. Initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Correct D. Maintain spinal immobilization immediately E. Handle the client gently to prevent ventricular fibrillation Correct Rationale: Drowning occurs when a person suffers primary respiratory impairment from submersion or immersion in a liquid medium (usually water). The drowning process is considered a continuum with outcomes that range from survival to death. The nurse should take immediate action when alerted to a drowning or near drowning, which includes: sending a by-stander to call for help and initiating CPR. If the nurse suspects hypothermia, the client should be handled with care to prevent ventricular fibrillation. The nurse should not spend time obtaining the client’s history, but rather spend that time in life-saving efforts to the victim. The nurse should initiate spinal immobilization on clients who are suspected to have a spinal cord injury. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “life-saving actions in a near- drowning.” Note that this is an emergency situation. Therefore, the nurse needs to take actions. Therefore option 2 can be eliminated. Next eliminate option 4 because there is no data that indicates a spinal injury occurred. Review: Near- drowning. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/Gas Exchange, Perfusion Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 1687). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 2.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 46.ID: 9476801245 The nurse is caring for a client with urinary calculi, who is preparing for a surgical procedure to remove the stones. Which action by the nurse is a priority for maintaining the client’s psychosocial integrity? A. Administer pain medications upon the client’s request B. Teach the client actions to take after the procedure if problems arise Correct C. Prepare the client’s consent form and chart to transport to the surgical area D. Explain to the client that the surgeon will provide education on the procedure Rationale: Urolithiasis is the presence of calculi (stones) in the urinary tract. Stones often do not cause symptoms until they pass into the urinary tract, where they can cause excruciating pain. Once the nurse has made the client comfortable, it is important to give attention to the client’s psychosocial integrity. Psychosocial preparation is enhanced when clients know what to expect and what actions to take if problems develop. It is a priority for the nurse to educate the client on the surgical procedure, as well as what actions to take after the procedure if problems arise. While administering pain medications it is important for the client’s physical comfort, it is not the nurses priority when maintaining psychosocial integrity for the client. Once the client’s needs have been met, the nurse can prepare the consent form. The nurse should also be well educated about the surgical procedure so that the client’s questions can be answered. Review: measures to maintain psychosocial Integrity. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word, “priority” and focus on the subject, psychosocial integrity. Determine which action would benefit the client’s psychosocial integrity the most. This will direct you to the correct option. Review: preoperative psychosocial preparation Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Perioperative Care Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Health Care Quality HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Quality Improvement/Health Care Quality Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 1507). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 47.ID: 9476805547 The nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has been diagnosed with cystitis. The nurse has been notified that the client does not have health care insurance. Which instruction from the nurse would be the most important for the client to complete in order to continue treatment? A. Follow up with a health care provider within one week. B. Call the case manager, in order to arrange payment for care. C. Fill the prescriptions that have been provided by the health care provider. Incorrect D. Review the provided list of available community resources and initiate contact. Correct Rationale: Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder. It can be caused by irritation or, more commonly, by infection from bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. It is important that the client receive proper treatment, and is properly educated about how to manage care at home. For the client without health care insurance, the nurse should focus on assisting the client to obtain needed resources, such as follow-up and medications, at a low cost. Otherwise, the client may need to return to the hospital for repeat treatment. The nurse should provide the client with a listing of available community resources, such as a free clinic, and instruct the client in how to initiate contact. Once the client has made contact with the resources, the nurse should instruct the client to receive follow- up care and contact the case manager. Prior to discharge the nurse should assist the client in obtaining the medication needed to continue treatment. This can be completed by contacting a case manager for assistance. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic words, “most important” and the subject, that the client does not have health insurance. Determine which needs the client has and which action should be done in order to reach the client’s goal of continuing treatment. Eliminate options 1, 2, and 3 because these options cannot be completed until the client is able to utilize community resources to assist in continuing treatment. Review: Cystitis and home care support Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Safety Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Health Care Quality HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Quality Improvement/Health Care Quality Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., p. 1072). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 0.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 48.ID: 9476793894 The nurse in an assisted living facility is providing care to an older client, who has just moved to the facility. Which actions should the nurse include in the plan of care to decrease relocation stress, and help the client adjust to the new environment? Select all that apply. A. Take the time to assess the client’s usual lifestyle. Correct B. Explain each procedure to the client as they occur. Correct C. Allow the client to participate in decision making activities. Correct D. Establish a trusting relationship with the client as soon as possible. Correct E. Ask the client’s family to refrain from bringing special keepsakes to the facility. Incorrect Rationale: Older adults live in the community at home, in assisted-living facilities, or in retirement or independent living complexes. Being admitted to a hospital or nursing home is a particularly traumatic experience. Older adults often suffer from relocation stress syndrome, also known as relocation trauma. Relocation stress syndrome is the physical and emotional distress that occurs after the person moves from one setting to another. The nurse can take several actions to help decrease this distress in the client. The nurse should take time to assess the client’s usual lifestyle, taking note of favorite foods or preferred bathing schedule. The nurse should explain each procedure to the client as they occur. The client should be allowed to participate in the decision making process, if the client is able to make decisions. These actions will allow the nurse to establish a trusting relationship with the client, which will be helpful in the future care of the client, and interaction with the family. The nurse should not ask the family to refrain from bringing personal keepsakes in to the client. These items may be comforting to the client and should be allowed in the facility. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “decreasing relocation stress.” Determine which actions by the nurse would help the client adjust to the new environment. Eliminate option 5, because prohibiting personal items that may be comforting would not be helpful to the client, and would not help decrease relocation stress. Review: Relocation stress. Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Developmental Stages: Early Adulthood to Later Adulthood Giddens Concepts: Stress, Coping. HESI Concepts: Caregiving, Stress and Coping Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., pp. 16, 19). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 49.ID: 9476793854 The nurse is caring for a client with chronic pain. Which actions should the nurse take, in order to assess the client’s quality of life? Select all that apply. A. Withhold pain medications to determine the client’s need. B. Ask if the client has difficulty sleeping or eating due to pain. Correct C. Ask the client about the side effects of prescribed medication. Correct D. Ask the client to describe how the pain has affected the daily routine. Correct E. Ask the client if there are activities that are no longer possible due to pain. Correct Rationale: The American Pain Society (APS) defines pain as “an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage.” This definition describes pain as a complex phenomenon with multiple components that impact a person's psychosocial and physical functioning. In order to assess the client’s quality of life, the nurse should ask questions that determine how pain has interfered with the client’s daily activities. The nurse should assess the sleep patterns, appetite, side effects, and if the client is unable to perform certain activities because of the presence of pain. The nurse should not withhold pain medications to a client with chronic pain, rather assess the need for medication and how well the client can function with the medication. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “assessing a client with chronic pain”. Determine which actions would assist the nurse in gathering information to evaluate the client’s quality of life. This will help the nurse plan interventions, if needed, to help the client. Eliminate option 1, because withholding pain medications will result in increased pain for the client, and will not assist the nurse in obtaining an accurate assessment of the client’s pain management program. Review: Chronic Pain. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing. Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity. Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment. Content Area: Fundamental Skills: Pain Giddens Concepts: Pain, Sensory Perception HESI Concepts: Pain, Sensory Perception References: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for Nursing Practice. (1st ed., pp. 270, 272). St. Louis: Mosby. Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 119- 120). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 50.ID: 9476797872 The nurse is caring for a client with severe anxiety. What should the nurse include when creating the care plan for this client? Select all that apply. A. The client will understand when to seek treatment. Correct B. The client will be able to perform deep breathing exercises. Correct C. The client will state where to obtain support group information. Correct D. The client will state when it is appropriate to ignore the symptoms. E. The client will understand how medication helps stop panic attacks. Correct Rationale: Anxiety is a normal adaptive response to stress that occurs across the lifespan. Anxiety is a subjective experience, with biological and psychodynamic dimensions. When creating a care plan, the nurse should focus on outcomes that will help the client function better. The nurse should create a plan that includes: teaching the client when to seek treatment, how to perform deep breathing exercises, how to obtain support group information and how medication works to stop panic attacks. The nurse should stress the importance of acknowledging symptoms and taking steps to prevent a panic attack, such as deep breathing. The nurse should not teach the client to ignore symptoms. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “creating a care plan.” Focus on activities that would enable the client to better manage anxiety. Eliminate option 4, because this does not allow the client to be in charge of the anxiety disorder. Review: Anxiety. Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Psychosocial Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Mental Health Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Client Education. HESI Concepts: Care Coordination, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Giddens, J. (2013). Concepts for Nursing Practice. (1st ed., pp. 310, 314, 315, 316). St. Louis: Mosby. Varcarolis, E. (2013). Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: A communication approach to evidence-based care. (revised reprint)) (2nd ed. p. 188). St. Louis: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 51.ID: 9476807975 The nurse reviewing the surgeon’s prescriptions in preparation for the client’s surgery. Which of the Surgical Care Improvement Project (SCIP) core measures does the nurse identify as appropriate? Select all that apply. A. Electric clippers are used to remove hair Correct B. Indwelling catheter will be removed on post-operative day 4 Incorrect C. Prophylactic antibiotic will be initiated 15 minutes prior to surgical incision D. Prophylactic antibiotics discontinued within 24 hours after surgery end time Correct E. Temperature will be measured 15 minutes after the end of anesthesia administration Correct Rationale: Perioperative nursing places special emphasis on safety, advocacy, and client education, and ensuring a safety is the responsibility of all health care team members. The nurse should be familiar with the SCIP core measures and be prepared to incorporate them into client care. The nurse should identify the core measures as using electric clippers to remove excess hair, instead of using razors which can irritate the skin; discontinuing prophylactic antibiotics within 24 hours after the surgical end time, and measuring the client’s temperature 15 minutes after anesthesia administration has ended. The nurse should recognize that indwelling catheter should be removed no later than 48 hours after placement, and that prophylactic antibiotics should be initiated no later than 1 hour prior to the surgical incision. Review: SCIP Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “identifying SCIP core measures.” Think about the complications associated with surgery to assist in answering correctly. This will assist to determine which actions are SCIP core measures. Review: SCIP core measures Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Analysis. Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Safety Giddens Concepts: Health Care Policy, Safety HESI Concepts: Health Policy/Systems, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 241). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 52.ID: 9476797812 The emergency department nurse is caring for a client at risk for respiratory failure. Which nursing actions are important in the care of this client? Select all that apply. A. Listen to breath sounds Correct B. Evaluate chest expansion Correct C. Assess for trauma to the chest Correct D. Look for physical abnormalities Correct E. Request a needle decompression Rationale: After the airway is secured or determined to be patent, the nurse should assess the client’s breathing. The nurse should listen to breath sounds, evaluate chest expansion and assess the client for chest wall trauma and any physical abnormalities. It would be inappropriate to request a needle decompression; these are typically performed on clients with a tension pneumothorax. In addition this is not a nursing action. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “a client at risk for respiratory failure and nursing actions.” Eliminate option 5, because this is not within the scope of nursing practice. Review: care of the client at risk for respiratory failure Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/Management Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Gas Exchange HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Gas Exchange Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 133). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 4.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 53.ID: 9476810166 The nurse works in a busy emergency department and would like to reduce the potential for adverse events. Which actions can the nurse take to accomplish this? Select all that apply. A. Wash hands frequently Correct B. Utilize automated electronic track systems Correct C. Look through the client’s belongings for medication bottles D. Obtain an accurate medical history from the client or family Correct E. Look for the presence of medical alert bracelets or necklaces Correct Rationale: A significant risk for all clients who enter the emergency care environment is the potential for medical errors or adverse events, especially those associated with medication administration. The episodic and often chaotic nature of emergency management in an environment with frequent interruptions can easily lead to errors. However, there are actions that the nurse can take to reduce the potential for adverse events. These include frequent hand washing to prevent infection, use of automated tracking systems to prevent errors or duplication of treatments, obtaining an accurate medical history, and looking for medical alert bracelets or necklaces on each client. Looking through a client’s belongings is an invasion of privacy but if this needs to be done then is should be done with another staff member present. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “reducing the potential for adverse events.” Read each option and determine which actions can prevent adverse events. Eliminate option 3, because although this seems like a reasonable action, it is an invasion of privacy and if done, the nurse should check client belongings with a second person. Review: Adverse event prevention Level of Cognitive Ability: Applying Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Safety Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Safety HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 125). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 54.ID: 9476807941 The nurse is counseling a client who has been diagnosed with the human immune deficiency virus (HIV). In creating a plan of care, which interventions should the nurse include? Select all that apply. A. Instruct the client not to share towels Incorrect B. Discuss options for medication therapy Correct C. Educate the client about proper condom use Correct D. Provide education about needle exchange programs Correct E. Discuss the client’s HIV status and ensure understanding Correct Rationale: The nurse has an important role when counseling the client who has been diagnosed with HIV. The nurse should educate the client on ways to treat the disease and reduce the risk of spreading the disease to others. These include medication therapy that will halt the growth of the virus, proper condom use and needle exchange programs to prevent the spread of infection, and ensuring that the client has an adequate understanding of HIV. Sharing towels does not lead to the spread of HIV. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “interventions when counseling a client with HIV.” Think about the pathophysiology associated with HIV to assist in selecting the interventions to include when counseling a client and those that will prevent the spread of infection. Review: HIV. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Safe and Effective Care Environment Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Adult Health: Immune Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Infection HESI Concepts: Infection, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., pp. 361-363). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 55.ID: 9476807993 The nurse is providing education to the client who is receiving external radiation therapy to the face. Which statements by the client indicate understanding? Select all that apply. A. “It is okay to wash off the ink or dye markings.” B. “I should not use soap at all when washing my face.” C. “I need to avoid exposing the irradiated area to the sun.” Correct D. “I should use my hands to wash my face, rather than a washcloth.” Correct E. “I can use lotions or powders that are prescribed by the radiation oncology department.” Correct Rationale: The immediate and long-term side effects of all types of radiation are limited to the tissues exposed to the radiation. When educating the client, the nurse should evaluate the client’s understanding. Education has been successful when the client states understanding of the need to avoid sun exposure, use hands rather than a washcloth when washing the skin, and only using lotions and powders that are prescribed. These actions will help protect the integrity of the skin. The nurse should also educate the client to avoid washing off the ink or dye markings until radiation is complete, and that it is ok to use a mild soap to wash. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “the client’s understanding of skin care when receiving external radiation therapy.” Eliminate option 2 because of the closed-ended words “at all.” Next eliminate option 1 because the skin markings provide a guide for the therapy. Also thinking about maintaining skin integrity will assist in answering correctly. Review: External radiation therapy. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluating Content Area: Adult Health: Oncology Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Tissue Integrity HESI Concepts: Teaching and Learning/Patient Education, Tissue Integrity Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 413). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 56.ID: 9476797845 The nurse is caring for a client with cancer who has just been diagnosed with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). On assessment, the client complains of weakness, muscle cramps, and loss of appetite. Which specific actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? Select all that apply. A. Check for peripheral edema Correct B. Monitor the client for a bounding pulse Correct C. Monitor the client for neck vein distention Correct D. Assess for the presence of crackles in the lungs Correct E. Observe urine for changes in color or characteristic Rationale: The treatment modality for a client with SIADH focuses on safety, maintaining fluid balance, and supportive care. This includes preventing fluid overload, which could lead to pulmonary edema and heart failure. It is important to monitor for increasing fluid overload (bounding pulse, neck vein distention, crackles in the lungs, and peripheral edema). Specific to SIADH is to monitor the amount of urine output specifically for a decrease. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “interventions for a client with SIADH.” Think about the pathophysiology associated with SIADH to assist in answering correctly. Eliminate option 5, because the nurse should observe and measure urine to determine if there has been a decrease in urine output that can occur with SIADH. Review: SIADH Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Adult Health: Oncology Giddens Concepts: Cellular Regulation, Clinical Judgment HESI Concepts: Cellular Regulation, Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 431). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 57.ID: 9476807966 The nurse is listening to an information presentation on the new objectives for Healthy People 2020. Which statements by the nurse indicate an understanding of the objectives? Select all that apply. A. “One of the objectives is to increase the 1 year survival rates for infants with Down Syndrome.” Correct B. “Healthy People 2020 will aim to increase the percentage of women ages 18 to 44 who have impaired fecundity.” C. “An objective of Healthy People 2020 is to increase the percentage of employers who have worksite lactation programs.” Correct D. “Healthy People 2020 will strive to increase the percentage of newborns to receive formula supplementation during the first two days of life.”Correct E. “Healthy People 2020 aim to increase the percentage of live births that occur in facilities that provide recommended care to lactating mother and their babies.” Incorrect Rationale: Healthy People 2020 provides science-based 10-year national objectives for improving health and preventing disease in the United States. (www.healthypeople.gov/hp2020). Some objectives for Healthy People 2020 include: increasing the survival rates for infants born with Down Syndrome; increasing the percentage of employers with worksite lactation programs; and increasing the percentage of live births that occur in facilities that provide recommended care to lactating mothers and their babies. Healthy People 2020 aim to decrease the percentage of women ages 18 to 44 who have impaired fecundity and strive to increase the percentage of newborns to be breast-fed during the first two days of life. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “Healthy People 2020 objectives.” It is necessary to know these objectives to answer this question correctly. Review: Healthy People 2020 objectives. Level of Cognitive Ability: Evaluating Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Evaluation Content Area: Leadership/Management: Prioritizing Giddens Concepts: Health Promotion, Health Care Quality HESI Concepts: Health Promotion, Quality Improvement/Health Care Quality Reference: Lewis, S., Dirksen, S., Heitkemper, M., & Bucher, L. (2014). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems (9th ed., pp. 19-20). St. Louis: Mosby. Healthy People 2020. (2014). www.healthypeople.gov/hp2020. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 58.ID: 9476805508 The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client who is planning to become pregnant. What should the nurse include in the plan to help the client have a good pregnancy outcome? Select all that apply. A. Eat a healthy diet Correct B. Avoid the use of alcohol and tobacco Correct C. Prevent sexually transmitted infections Correct D. Refrain from exercising during preconception E. Take the recommended amount of folic acid each day Correct Rationale: In recent years the concept of preconception care has been recognized as an important contributor to good pregnancy outcomes. The nurse should emphasize the importance of good health including exercise during this time. When creating a plan of care the nurse should include activities such as eating a healthy diet, avoiding the use of alcohol and tobacco, and preventing sexually transmitted infections. The nurse should also direct the client in choosing foods that are rich in folic acid, or recommend an appropriate prenatal vitamin that contains folic acid. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “creating a plan of care for good pregnancy outcome.” Determine what actions should be included to help the client reach this goal. Eliminate option 4, because clients do not have to refrain from exercise during the preconception period. Review: measures to promote a healthy pregnancy Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Maternity Giddens Concepts: Client Education, HESI Concepts: Health Promotion, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 89, 309-311). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 59.ID: 9476793841 The nurse is caring for a client in labor. During assessment, the nurse notes that the client is hypotensive and that the fetus has an abnormal heart rate pattern. Which interventions should the nurse take? Select all that apply. A. Prepare the client for a cesarean section B. Encourage the client to ambulate in the room C. Place the client in a lateral or trendelenburg position Correct D. Prepare the client for induction of labor with oxytocin E. Increase the rate of the primary intravenous (IV) infusion Correct Rationale: Nurses who care for women during childbirth are responsible for correctly interpreting FHR patterns, initiating appropriate nursing interventions based on those patterns, and documenting the outcomes of those interventions. The nurse should notify the health care provider and should increase the rate of the primary infusion and place the client in a lateral or trendelenburg position to increase blood flow to the fetus. At this time, the nurse does not need to prepare the client for a cesarean section. The client should not be allowed to ambulate in the room due to the increased risk of falling and because of the abnormal heart rate pattern. Labor induction would not be done; this is not an appropriate intervention. In addition, the client is unstable. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “client hypotension and abnormal fetal heart rate pattern.” Determine which actions the nurse should take to correct these problems. Eliminate options 1, 2, and 4 because these options are not appropriate for correcting the abnormal findings. Review: Maternal hypotension in labor and delivery Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs:Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Critical Care: Emergency Situations/ManagementGiddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Perfusion References:Lowdermilk, D., Perry, S., Cashion, K., & Alden, K. (2016). Maternity & Women’s Health Care (11th ed., pp. 439-440). St. Louis: Elsevier. McKinney, E., James, S., Murray, S., Nelson, K. & Ashwill, J. (2013). Maternal-child nursing (4th ed., p. 398). St. Louis: Elsevier. Awarded 2.0 points out of 2.0 possible points. 60.ID: 9476801265 The nurse is caring for a client with neutropenia. To monitor for infection, which action by the nurse is a priority? A. Listen to lung sounds Correct B. Encourage a nutritious diet Incorrect C. Take the client’s vital signs every shift Incorrect D. Place the client in a room close to the nurse’s station E. Rationale: The priority nursing interventions for the client with neutropenia are protect the client from infection within the health care system and teach the client and family how to reduce infection in the home. To monitor for infection, the priority action for the nurse is to listen to the client’s lung sounds to monitor for an infectious process. Hospitalized clients are susceptible to hospital- acquired pneumonia, which could be life-threatening to the client with neutropenia. The remaining options are not interventions that will monitor for infection. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the strategic word, “priority.” Also note the subject, the action that will monitor for infection. Eliminate options 2, 3, and 4 because these actions do not monitor for infection. Review: Neutropenia Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Leadership/Management: Prioritizing Giddens Concepts: Clinical Judgment, Infection HESI Concepts: Clinical Decision-Making/Clinical Judgment, Infection Reference: Ignatavicius, D & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 420). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded -2.0 points out of 1.0 possible points. 61.ID: 9476805525 The nurse is providing care to a client following thoracentesis. Which actions should the nurse add to the client’s plan of care, in order to promote health and safety? Select all that apply. A. Monitor vital signs as prescribed Correct B. Assess the dressing for bleeding Correct C. Ensure that a chest x-ray is obtained Correct D. Instruct the client to avoid deep breathing Incorrect E. Auscultate breath sounds for absent or reduced sounds Correct Rationale: The client should be monitored closely following a thoracentesis. The nurse should adjust the plan of care as needed based on the client’s needs. The nurse should plan to monitor vital signs as prescribed to detect changes that could indicate bleeding or pneumothorax, assess the dressing for bleeding and intervene as necessary. A chest x-ray should be obtained right away to rule out a pneumothorax or mediastinal shift from the procedure. Breaths sounds should be assessed for absent or reduced sounds indicating pneumothorax. The nurse should encourage the client to take deep breaths to promote the expansion of the lung. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “caring for the client following thoracentesis.” Think about what the procedure entails and the possible complications. Eliminate option 4 because of the word “avoid” and because the client should practice deep breathing technique to expand the lung. Review: Post-thoracentesis care Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of Care: Diagnostic tests Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety HESI Concepts: Collaboration/Managing Care, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., pp. 559-560). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 62.ID: 9476797802 The nurse is preparing the client for a bronchoscopy. Which actions should the nurse take to ensure client safety? Select all that apply. A. Explain the procedure to the client B. Clarify and document the client’s allergies C. Verify the client using two types of identifiers Correct D. Keep the client NPO for 2 hours prior to the test E. Ensure that pre-procedure laboratory studies are drawn Correct Rationale: A bronchoscopy is the insertion of a tube in the airways, usually as far as the secondary bronchi, for the purpose of viewing airway structures and obtaining tissue samples for biopsy or culture. It is used to diagnose and manage pulmonary diseases. Safety is a priority in nursing care. In order to ensure safety for the client, the nurse should explain the procedure to the client, ensure that pre-procedure laboratory studies are drawn and results are reviewed to detect any abnormalities, clarify and document the client’s allergies, and verify the client using two different identifiers. The client should be kept NPO 4-8 hours prior to the exam to reduce the risk of aspiration. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, preparing the client for a bronchoscopy. Think about the procedure and how it is performed. Determine which actions promote client safety. Recalling that aspiration is a concern with this procedure will assist in eliminating option 4. Review: Bronchoscopy Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Fundamentals of care: Diagnostic tests Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety HESI Concepts: Collaboration/Managing Care, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 559). Philadelphia: Saunders. Pagana, K., & Pagana, T. (2013). Mosby’s diagnostic and laboratory tests reference (11th ed., pp. 193-194). St. Louis: Mosby. Awarded 4.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 63.ID: 9476807933 The nurse is providing care to a client who has a tracheostomy. Which actions should the nurse take to prevent a tube obstruction? Select all that apply. A. Provide inner cannula care Correct B. Suction the tube as needed Correct C. Humidify the oxygen source Correct D. Assess the client every shift for tube patency Incorrect E. Teach the client how to cough and deep breathe Correct Rationale: Tube obstruction can occur as a result of secretions or by cuff displacement. The nurse can take actions to prevent tube obstruction with interventions such as: providing inner cannula care to keep the tube clean of secretions, suctioning the tube as needed, humidify the oxygen source to keep secretions thin, and teaching the client how to cough and deep breathe. The client should be assessed at least hourly for tube patency. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, preventing a tube obstruction. Think about what can cause a tube obstruction to assist in answering correctly. Read each option carefully and noting the words “every shift” in option 4 will assist in eliminating this option. Review: Tracheostomy care Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Adult Health: Respiratory Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Gas Exchange HESI Concepts: Collaboration/Managing Care, Gas Exchange Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 571). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 64.ID: 9476801209 The nurse is creating a plan of care for a client with a chest tube. Which actions should the nurse include to promote client safety? Select all that apply. A. Position the drainage tubing to prevent kinks Correct B. Strip the chest tube as needed to improve suction C. Check the system every 4 hours to ensure patency Incorrect D. Tape tubing junctions to prevent accidental disconnections Correct E. Keep sterile gauze and padded clamps (per agency procedure) at the bedside Correct Rationale: A chest tube is a drain placed in the pleural space to restore intra- pleural pressure, and allow re-expansion of the lung. When creating a plan of care for a client with a chest tube, the nurse should consider which actions will promote safety for the client. These actions that promote safety include: positioning the chest tube so that there are no kinks, keeping a sterile gauze and padded clamps (per agency procedure) at the bedside in case the chest tube is dislodged from the client, and taping tubing junction to prevent accidental disconnections in the system. Striping the chest tube should be avoided, as this can create negative pressure and damage lung tissue. The tube system should be checked hourly to ensure sterility and patency. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “chest tube care.” Read each option carefully. Eliminate option 2, because stripping the chest tube can create negative pressure and damage lung tissue. Eliminate option 3, because the chest tube should be checked more frequently than every 4 hours. Review: Chest tube care Level of Cognitive Ability: Creating Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Adult Health: Respiratory Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Safety HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/Gas Exchange, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 637). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 0.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 65.ID: 9476812024 A client will be started on peritoneal dialysis. The nurse should consider which statements in planning care for the client? Select all that apply. A. Bowel perforation is very rare. B. The client may experience respiratory distress. Correct C. The client will require a diet that is high in protein. Correct D. A complication of peritoneal dialysis is hyperglycemia. Correct E. The client will experience few hemodynamic complications. Correct Rationale: Peritoneal dialysis (PD) allows exchanges of wastes, fluids, and electrolytes to occur in the peritoneal cavity. PD is slower than hemodialysis (HD), however, and more time is needed to achieve the same effect. Complications of peritoneal dialysis include: bowel perforation, respiratory distress, protein loss, and hyperglycemia. An advantage of peritoneal dialysis is that client’s experience few hemodynamic complications. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “peritoneal dialysis.” Think about this method of dialysis and how it is performed. Recalling that a catheter is inserted into the peritoneal cavity will assist in answering correctly. Therefore, eliminate option 1, because bowel perforation is a complication of peritoneal dialysis. Review: complications of peritoneal dialysis. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Adult health: Urinary and Renal Giddens Concepts: Care Coordination, Safety HESI Concepts:. Collaboration/Managing Care, Safety Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., pp. 1558, 1564). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 66.ID: 9476797854 A client with left-sided heart failure has arrived on the cardiac unit. Which actions should the nurse initially include in the care plan for this client? Select all that apply. A. Take the apical heart rate for one minute Correct B. Toilet the client every hour and as needed Correct C. Teach the client how to regulate breathing Correct D. Allow the client rest time between activities Correct E. Allow the client to walk in the hallway a few times a day as desired Rationale: Manifestations of heart failure depend on the type of failure, the ventricle involved, and the underlying cause. The nurse should develop the care plan around the needs of the client. Actions to include are taking the apical heart rate for one minute to detect abnormalities in rate or rhythm, toileting the client every hour and as needed since the client will be most likely treated with diuretics, teaching the client how to regulate breathing for adequate oxygenation. and allowing rest time between activities. Initially, the client should not be allowed to walk in the hallways. Treatment should be initiated and then progressive activity planned. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic word, “initially.” Focus on the subject, “planning care for a client with left-sided heart failure.” Also note that the client was just admitted. This will assist in answering and in eliminating option 5. Review: Care to the client with left-sided heart failure. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Planning Content Area: Adult Health: Respiratory Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/ Gas Exchange, Perfusion Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 748). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 67.ID: 9476801249 Upon assessment of a client with heart failure, the nurse notes that the client is dyspneic. Which actions should the nurse take initially? Select all that apply. A. Prepare the client for intubation Incorrect B. Place the client in the Trendelenburg position C. Place pillows under each of the client’s arms Correct D. Assist the client with deep breathing exercises Correct E. Administer oxygen to keep O2 saturation greater than 90% Correct Rationale: The nurse should be prepared to intervene for the client with heart failure who is experiencing dyspnea. Interventions include placing the client in a high fowler’s position (not Trendelenburg) with pillows under each of the client’s arms. This position maximizes chest expansion and improves oxygenation. The nurse should also assist the client with deep breathing exercises to improve oxygenation, and administer oxygen to keep O2 saturation greater than 90%. The nurse should try these interventions before preparing the client for intubation. These actions will help the client have the best outcome. Test-Taking Strategy: Note the strategic word, initially. Focus on the subject, “caring for the dyspneic client.” Eliminate option 1 because this intervention should be considered if the initial interventions fail. Eliminate option 2 because the client should be placed in a high fowler’s position to aid in breathing. Review: initial interventions for the client who is dyspneic. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Implementation Content Area: Adult Health: Cardiovascular Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Perfusion. HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/ Gas Exchange, Perfusion Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 750). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 3.0 possible points. 68.ID: 9476807923 The home care nurse is providing care to a client with heart failure. Which assessment findings should alert the nurse to worsening heart failure? Select all that apply. A. Pallor Correct B. Confusion Correct C. Chest pain Correct D. Warm extremities Incorrect E. Activity intolerance Correct Rationale: The focus of the home care nurse's interventions is assessment and health teaching. During assessment of the client, the nurse should look for signs of worsening heart failure. These include pallor, confusion, complaints of chest pain, and activity intolerance, which indicate hypoxia. The nurse would expect to find cool extremities in a client with worsening heart failure. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, assessment findings indicating worsening heart failure. Think about the pathophysiology associated with heart failure. Heart failure causes a lack of oxygenation to body tissues resulting in cool extremities rather than warm extremities. Review: Heart failure and signs of complications Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Adult Health: Catdiovascular Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/Gas Exchange, Perfusion Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 757). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 1.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 69.ID: 9476801223 The nurse is assessing a client with mitral valve regurgitation. Which manifestations should the nurse expect to note? Select all that apply. A. Fatigue Correct B. Orthopnea Correct C. Chronic weakness Correct D. Low blood pressure E. Atypical chest pains Correct Rationale: The fibrotic and calcific changes occurring in mitral valve regurgitation (insufficiency) prevent the mitral valve from closing completely during systole, which allows backflow of blood into the left atrium when the left ventricle closes. During assessment the nurse should anticipate findings such as: fatigue, orthopnea, chronic weakness, and atypical chest pains. Blood pressure is often normal in clients with mitral valve regurgitation. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “manifestations of mitral valve regurgitation.” Think about the pathophysiology associated with regurgitation to assist with answering correctly. Remember that blood pressure is often not affected in this disorder. Review: manifestations of mitral valve regurgitation. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity Integrated Process: Nursing Process/Assessment Content Area: Adult Health: Cardiovascular Giddens Concepts: Gas Exchange, Perfusion HESI Concepts: Oxygenation/Gas Exchange, Perfusion Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 759). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 3.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. 70.ID: 9476797885 The nurse is caring for a client with infective endocarditis, who is preparing to be discharged home. Which self-management techniques should the nurse teach the client? Select all that apply. A. Brush teeth once a day, with a soft toothbrush. Incorrect B. Take prescribed antibiotics exactly as directed. Correct C. Follow instructions for care for the infusion site. Correct D. Clean open sores and apply prescribed antibiotic ointment. Correct E. Ask the health care provider for prophylactic antibiotics prior to invasive procedures. Correct Rationale: Care of the client with endocarditis usually includes antimicrobials, rest balanced with activity, and supportive therapy. If these interventions are successful, surgery is usually not required. The nurse should teach the client self-management techniques to reduce the risk of complications and re- hospitalization. These interventions include cleaning any open sores and applying prescribed antibiotic ointment, taking prescribed antibiotics and caring for the infusion site. The nurse should also teach the client to request prophylactic antibiotics prior to invasive procedures. The client should brush teeth at least twice a day with a soft toothbrush, rinsing the mouth afterwards. Test-Taking Strategy: Focus on the subject, “self-management techniques for infective endocarditis.” Select options 2 and 4 because of the word “prescribed” and option 3 because of the words “follow instructions.” For the remaining options think about the pathophysiology associated with infective endocarditis. Also, eliminate option 1, because the client should brush teeth more than once a day. Review: client instructions for infective endocarditis. Level of Cognitive Ability: Analyzing Client Needs: Physiological Integrity. Integrated Process: Teaching and Learning Content Area: Adult Health: Cardiovascular Giddens Concepts: Client Education, Infection HESI Concepts: Infection, Teaching and Learning/Patient Education Reference: Ignatavicius, D., & Workman, M. (2013). Medical-surgical nursing: Patient-centered collaborative care. (7th ed., p. 765). Philadelphia: Saunders. Awarded 2.0 points out of 4.0 possible points. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 61 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 03, 2021
Number of pages
61
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
58






.png)


















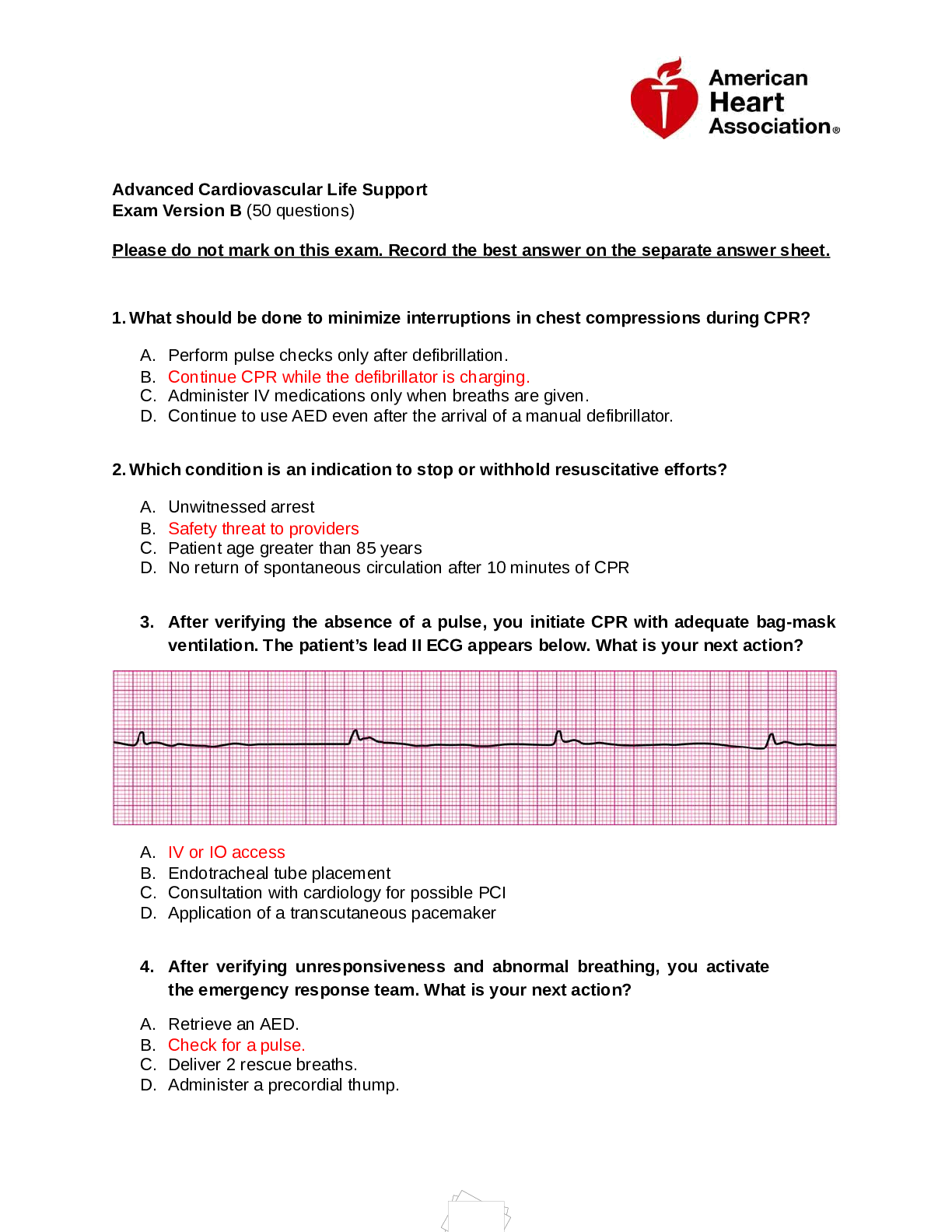
 (1).png)
 (1).png)
 (1).png)
.png)