*NURSING > EXAM > NR 507 - Week 4 Midterm Study Guide, Possible Questions & Answers (2019/20). Verified 100% Correct. (All)
NR 507 - Week 4 Midterm Study Guide, Possible Questions & Answers (2019/20). Verified 100% Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
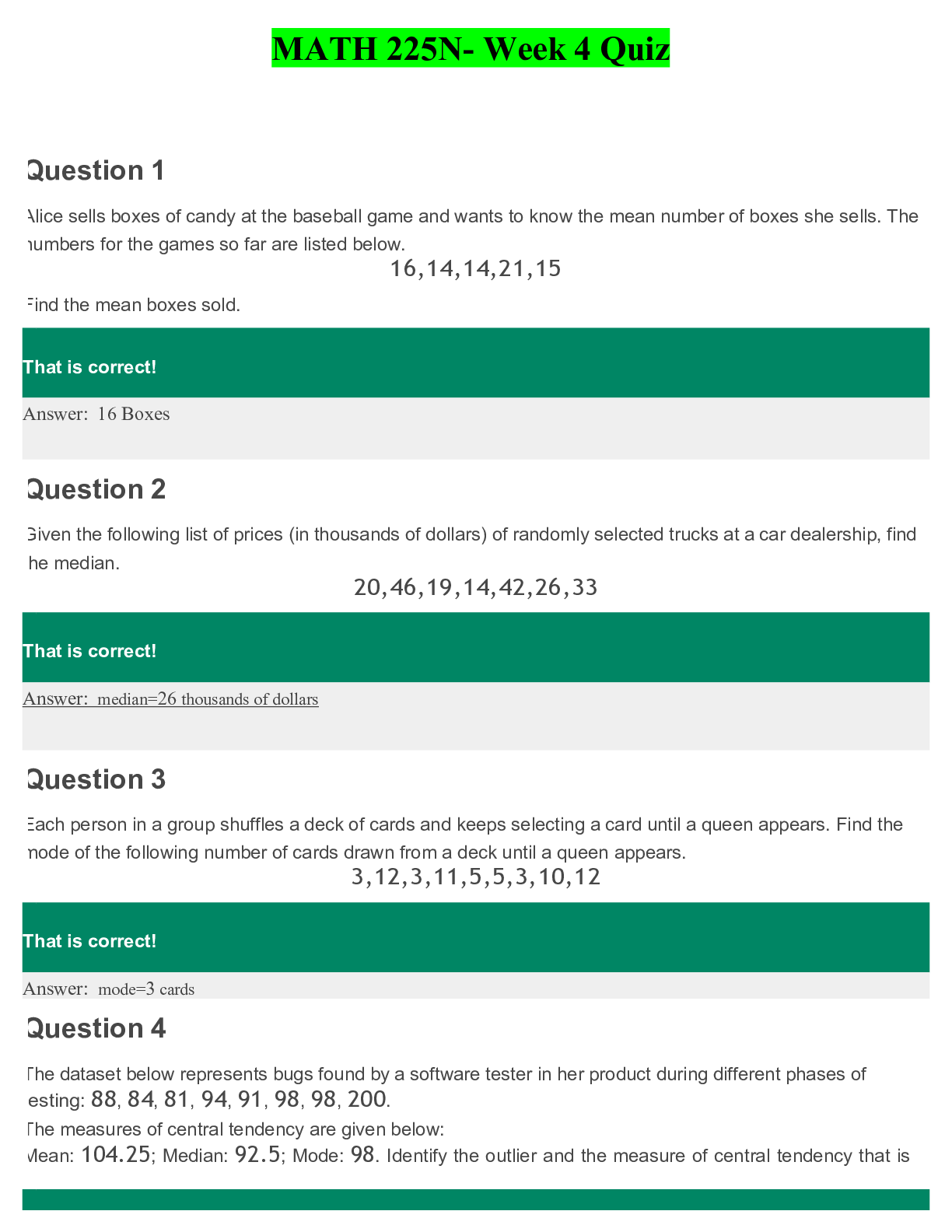
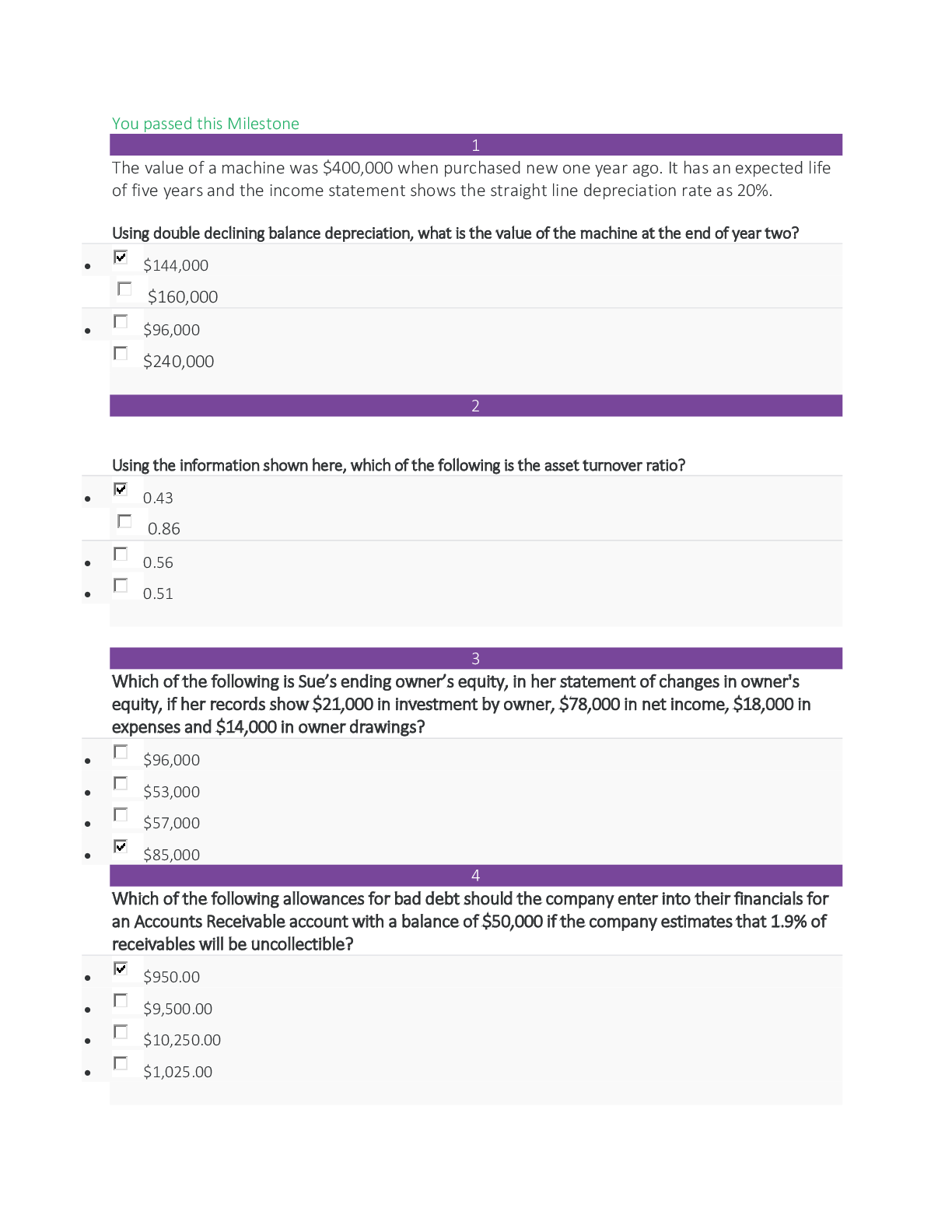
NR 507 Week 4 Midterm Chamberlain College of Nursing. Epigenetics Defects in the encoding of histone-modifying proteins 1. Question: Housekeeping Genes are vital to the function and maintenance o... f all the body’s cells. What characteristic is associated with these genes? 2. Question: Mutations in the encoding of histone-modifying proteins have been shown to influence the development of what congenial condition? 3. Question: Epigenetics refers to chemical modification that are made to what? 4. Question: Signals to change or modify epigenetic tags are received from where? 5. Question: What sort of molecule is responsible for transferring signals into cells to gen regulatory proteins? Epigenetics and its role on human development 1. Question: Research has provided support for the theory that epigenetic modification can result from deficient in utero nutrition causing? Select all that apply 2. Question: During which stage of human development does the role of epigenetics have the greatest impact on the development of epigenetic abnormalities? 3. Question: The difference between DNA sequence mutations and epigenetic modifications is? Totipotent cells and its ability to differentiate into any type of cell 1. Question: Which embryonic stem cell characteristic is referred to as a totipotent? 2. Question: Examples of two totipotent cells are? 3. Question: What is a Totipotent cell? 4. Question: Are all cells Totipotent cells? Prader-Willi syndrome and Angelman syndrome? 1. Question: What characteristic of Prader-Willi syndrome is not a characteristic of Angelman syndrome? 2. A child with Prader-Willi syndrome has been hospitalized. Which assessment findings does the nurse expect with this syndrome? 3. Question: The nurse is examining an 8-year-old boy with chromosomal abnormalities. Which sign or symptom suggests the boy has Angelman syndrome? Cellular Proliferation 5-Azacytidine and the treatment of cancer 1. Question: What is 5-azacytidine? Nucleoside analog able to … incorporated into RNA & DNA 2. Question: 5- Azactytide has demonstrated promise in the treatment of which form of cancer? The role of inactive MLH1 in the development of some forms of inherited colon cancer 1. Question: What is the role of inactive MLH1 in the development of some forms of inherited colon cancer? Effects of ethanol on neural stem cells ability to differentiate into functional neurons- 1. Question: Research has demonstrated that neural stem cells have an impaired ability to differentiate into functional neurons when subjected to? Inflammation as an etiology for cancer-note conditions in which this may occur 1. Question: What chronic inflammatory conditions can increase risk for cancer? HIV, hepatitis, h-pylori, bronchitis, pancreatitis Cancer In terms of epigenetic modifications, the role of environmental stressors associated with development of cancer 1. Question: When considering abnormal epigenetics modifications, what factor is currently being viewed as strongly associated with the development of some cancers? Environmental Stressors Defects in Mechanism of Defense Hemolytic defects in the newborn 1. Question: To explain hemolytic disorders in the new born to new parents, the nurse who cares for the new born population must be aware of the physiologic characteristics related to these conditions. What is the most common cause of pathologic hyperbilirubinemia? 2. Question: Which infant is most likely to express Rh incompatibility? 3. Question: Rh hemolytic disease is suspected in a mother’s second baby, a son. Which factor is important in understanding how this could develop? 4. Question: The nurse is caring for an infant with hemolytic disease. Which medication should the nurse anticipate to be prescribed to decrease the bilirubin level? 5. Question: A newborn is found to have hemolytic disease. Which combination would be found related to the blood types of this newborn and the parents of the newborn? 6. Question: The nurse is caring for a newborn with hemolytic disease of the newborn who is receiving phototherapy. Which nursing intervention would be the most appropriate for the nurse to do? Understand the meaning of infectivity Most effective treatment for HIV 1. Question: A patient diagnosed with acute primary HIV infection is in the clinic. What treatment should initiated for this patient? Defected cells of HIV 1. Question: A patient has human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A nurse realizes the HIV will attack: 2. Question: The nursing instructor is discussing the development of human immunodeficiency disease (HIV) with the students. What should the instructor inform the class about helper T cells? Signs of T-Lymphocyte deficiency- 1. Question: T-cell defects 2. Question: A patient has DiGeorge syndrome. Which assessment findings should the nurse monitor for in this patient? 3. Question: A nurse is caring for a client who is deficient in T cells. Which result of this T cell deficiency does the nurse anticipate? Select all that apply: Pulmonary Alterations Pulmonary function tests 1. Question: Identify purposes for preforming PFT’s? 2. Question: What is the role of pulmonary function testing? 3. Question: What do PFT screening do? 4. Question: A 15-year-old female is diagnosed with restrictive lung disease caused by fibrosis. The patient had a pulmonary functions test. Which of the following findings is expected? Relationship of lung compliance and residual volume 1. Question: A nurse is teaching about the functions of the pulmonary system. Which information should the nurse include? 2. Question: One of the functions of the pulmonary system is the: 3. Question: An 80-year-old male presents to his primary care provider reporting difficulty breathing. Pulmonary function tests reveal that he has increased residual volume. A nurse suspects the most likely cause of this disorder is? Shifts in the oxyhemoglobin dissociation 1. Question: In a patient with acidosis or a fever, the nurse would expect the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to shift: 2. Question: What factors affect oxyhemoglobin dissociation? 3. Question: In a normal person, as PaO2 drops from 100 to 80 to 60, there is ________ in how tightly Hgb is holding onto its 02 (90-100% saturation). But when the PaO2 approaches 50, the s-curve begins to __drop sharply_, and as it does it means that _ 4. Question: For a right shifted curve, for the same PaO2 there will … a lower ______ when compared to a normal curve 5. Question: What causes a R shift? 6. Question: In both healthy and pathological conditions, the signs of a R shift are? 7. Question: What causes a L shift? CO2 transport in the blood 1. Question: Most carbon dioxide in the blood is transported? 2. Question: If an individual with respiratory difficulty were retaining too much carbon dioxide, which of the following compensatory responses would the nurse expect to be initiated? 3. Question: A patient wants to know how carbon dioxide is transported in the body. How should the nurse respond? Carbon dioxide (CO2) is mainly transported in the blood: Characteristics of alveoli 1. Question: Air passage between alveoli is collateral and evenly distributed because of? 2. Question: Changes in the alveoli that cause an increase in alveolar surface tension, alveolar collapse and decreased lung expansion are a result of? 1. Question: Students in a histology class are assigned to identify regions of the lung. The slide shows a basement membrane, capillary lumen, and macrophages. The students are looking at the: 2. Question: While auscultating a patient’s lungs, a nurse recalls the alveoli in the apexes of the lungs are _____ than alveoli in the bases. 3. Question: The nurse is caring for a client who is now 2 days post near-drowning. The focused assessment would involve which of the following areas of the lung involved in gas exchange? Arterial perfusion pressure and alveolar gas pressure in the lung base 1. Question: A consequence of alveolar hypoxia is: 2. Question: The pressure required to inflate an alveolus is inversely related to: 3. Question: The nurse is describing the movement of blood into and out of the capillary beds of the lungs to the body organs and tissues. What term should the nurse use to describe this process? 4. Question: A pulmonologist is discussing the base of the lungs with staff. Which information should be included? 5. Question: When the pulmonologist discusses the condition in which a series of alveoli in the left lower lobe receive adequate ventilation but do not have adequate perfusion, which statement indicates the nurse understands this condition? When this occurs in a patient it is called: How do determine the partial pressure of oxygen given the percentage of oxygen in the air and the barometric pressure 1. Question: What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the lung given the following conditions? Percentage of oxygen in air: 20 Barometric pressure: 700 mm Hg 2. Question: What would the partial pressure of oxygen equal if the barometric pressure was 600 mm Hg? Results of increased work of breathing 1. Question: An 80-year-old male presents to his primary care provider reporting difficulty breathing. Pulmonary function tests reveal that he has increased residual volume. A nurse suspects the most likely cause of this disorder is _____ in lung compliance. Know terms: Vital capacity (VC), 1. Question: While reviewing the results of the pulmonary functions test, the nurse is aware that the maximum amount of gas that can be displaced from the lung is called: Vital Capacity Total lung capacity 1. Question: What would happen to TLC and VC of your lungs become stiff and less elasticity Can’t take in as much air because elasticity is reduced Functional capacity Residual volume,- Functional residual capacity (FRC) 1. Question: Which of the following terms should the nurse use when there is a balance between outward recoil of the chest wall and inward recoil of the lungs at rest? Renal Alterations Types of nephrons and their functions 1. Question: The nephrons that determine the concentration of the urine are _____ nephrons. 2. Question: Which of the following renal structures is not a component of the nephron? 3. Question: At which of the following locations in the nephron would a nurse practitioner first expect blood to be largely free of plasma proteins? 4. Question: Which of the following substances is most likely to be reabsorbed in the tubular segments of the nephron using passive transport mechanisms? 5. Question: What is the function of nephron? 6. Question: The nephrons are the functional units of the kidney, responsible for the initial formation of urine. The nurse knows that damage to the area of the kidney where the nephrons are located will affect urine formation. Identify that area. Overall renal physiology Substances that are actively secreted by the renal tubules 1. Question: Which of the following substances are actively secreted by the renal tubules? 2. Question: Which of the following comprises the kidney’s transport system? Activation of the renin-angiotensin system 1. Question: Which of the following statements correctly describes a direct end-effect of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system? 2. Question: What does the reduced perfusion of the kidney activate that causes constriction of peripheral arterioles? Glomerular filtration rate 1. Question: The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is directly related to the 2. Question: A nurse educator is orientating anew nurses to a renal unit of a hospital. Which of the follow teaching points should the nurse include as a part of a review of normal glomerular function? Mesangial cells 1. Question: A urologist is discussing the phagocytic cells that lie between the layers of the renal corpuscle 2. Question: Lying between the layers of the renal corpuscle is a population of phagocytic cells called? Renal system anatomy 1. Question: When the renal system secretes rennin, it causes the direct activation of? Why plasma proteins should … absent from the urine 1. Question: The fluid formed in the capillary cluster of the nephron is the same as blood plasma except for the absence of? 2. Question: Which of the following substances does not normally get filtered in the kidneys? Effects of urinary tract obstruction- hydronephrosis and a decreased glomerular filtration rate 1. Question: A 25-year-old female is diagnosed with urinary tract obstruction. while planning care, the nurse realizes that the patient is expected to have hydronephrosis and a decreased glomerular filtration rate caused by? 2. Question: Which of the following changes will result in a decreased glomerular filtration rate? Effect of urinary retention 1. Question: A 55-year-old male presents reporting urinary retention. Tests reveal that he has a lower urinary tract obstruction. Which of the following is of most concern to the nurse? 1. Question: A group of students are reviewing information about disorders of the bladder and urethra. The students demonstrate understanding of the material when they identify which of the following as a voiding dysfunction? 2. Question: A client presents at the clinic with complaints of urinary retention. What question should the nurse ask to obtain additional information about the client’s complaint? 3. Question: The nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about acute glomerulonephritis genitourinary conditions. A student asks the about a condition that occurs when there is a decreased volume of urine output. The condition the student is referring to is which of the following? Most common type of renal stone 1. Question: When a patient asks what the most common type of renal stones is composed of, how should the nurse respond? The most common type of renal stone is composed of: 2. Question: The nurse recognizes that a referral for genetic counseling is inappropriate for the client with: 3. Question: Because a client’s renal stone was found to be composed of uric acid, a low-purine, alkaline-ash diet was ordered. Incorporation of which of the following food items into the home diet would indicate that the client understands the necessary diet modifications? Epispadias 1. Question: The optimal time for surgical repair of the Hypospadias and epispadias is 2. Question: What gender has predominance for exstrophy-epispadias complex? 3. Question: What 4 considerations must be addressed when performing the epispadias repair? 4. Question: What are 2 anomalies noted with epispadias? 5. Question: List 3 goals of surgical treatment of epispadias 6. Question: What is the most important indicator of successful continence with epispadias repair? 7. Question: What are the 3 types of female epispadias? PIC: A=normal, B=clitoris altered, C and D=varying degree of urethral defect 1. Question: What are other aspects of female epispadias? Glomerulonephritis 1. Question: A 15-year-old male was … with pharyngitis. Eight days later he developed acute glomerulonephritis. While reviewing the culture results, which of the following is the most likely cause of this disease? 2. Question: When a nurse observes post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis as a diagnosis on a patient, which principle will the nurse remember? Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is primarily caused by? 3. Question: A 30-year-old male is demonstrating hematuria with red blood cell casts and proteinuria exceeding 3 to 5 g/day, with albumin being the major protein. The most probable diagnosis the nurse will see documented on the chart is? 4. Question: A 15-year-old female presents with flank pain, irritability, malaise, and fever. Tests reveal glomerulonephritis. When the parents ask what could have caused this, how should the nurse respond? 5. Question: Which of the following clusters of symptoms would make a clinician suspect a child has developed glomerulonephritis? 6. Question: A 5-year-old male was … with glomerulonephritis. History reveals that he had an infection 3 weeks before the onset of this condition. The infection was most likely located in the 7. Question: A 30-year-old male is demonstrating hematuria with red blood cell casts and proteinuria exceeding 3 to 5 g/day, with albumin being the major protein. The most probable diagnosis the nurse will see documented on the chart is? 1. Question: A 45-year-old male presents with oliguria. He is … with chronic glomerulonephritis. The nurse knows oliguria is related to? [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 11, 2019
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 11, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
128















.png)
.png)



.png)