Pathophysiology > EXAM > NURS 231 Pathophysiology Exam Reviews -Questions And Answers,.Top score (All)
NURS 231 Pathophysiology Exam Reviews -Questions And Answers,.Top score
Document Content and Description Below
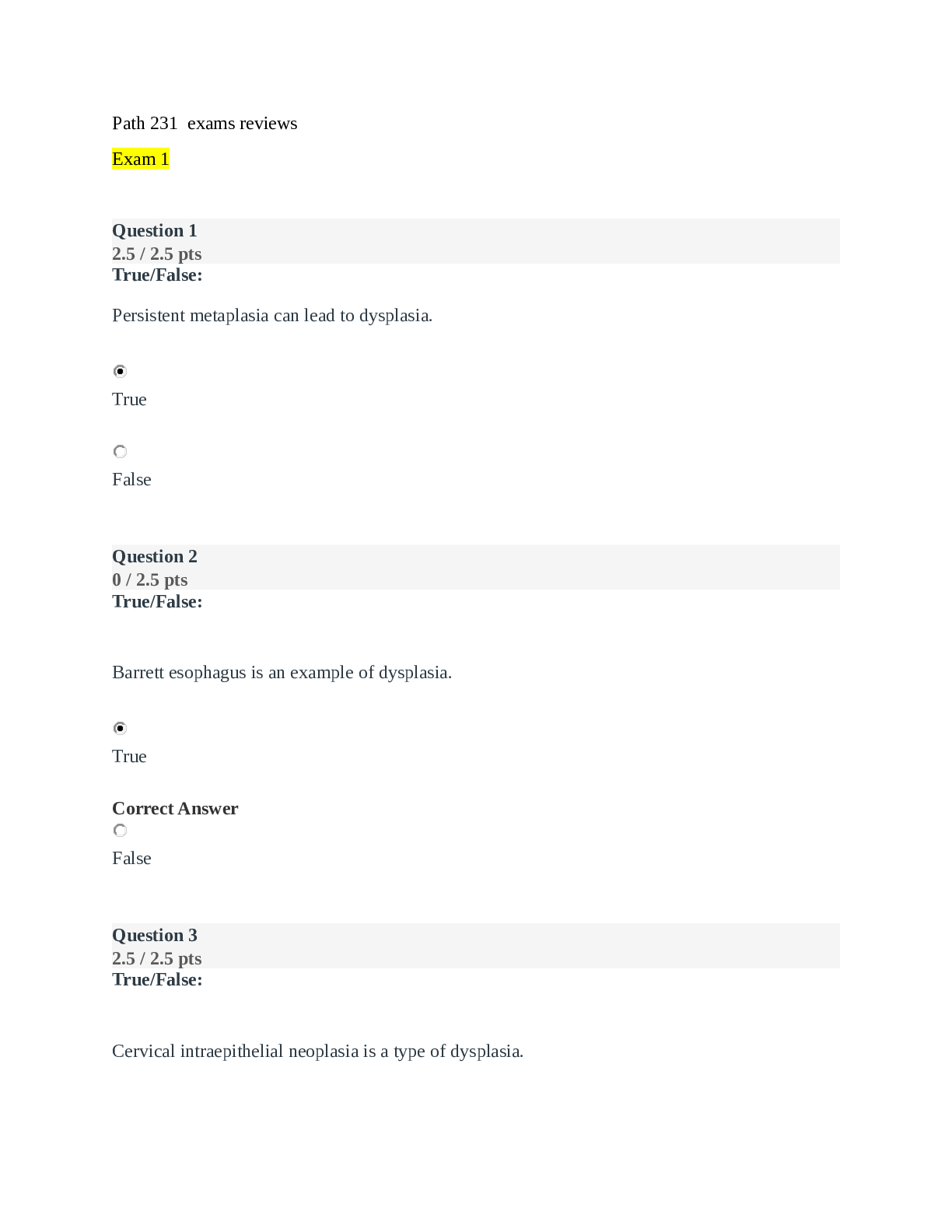
Path 231 exams reviews Exam 1 Question 1 2.5 / 2.5 pts True/False: Persistent metaplasia can lead to dysplasia. Correct! True False Question 2 0 / 2.5 pts True/False: Barrett esophagus is an example o... f dysplasia. You Answered True Correct Answer False Question 3 2.5 / 2.5 pts True/False: Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia is a type of dysplasia. Correct! True False Question 4 0 / 2.5 pts True/False: Endometrial hyperplasia is a normal physiologic occurrence. You Answered True Correct Answer False Question 5 10 / 10 pts Match the following: 1. Proportion of people with a disease who are positive for that disease a. Validity 2. How likely the same result will occur if repeated b. Reliability 3. How a tool measures what it is intended to measure c. Sensitivity 4. People without the disease who are negative on a given test d. Specificity Correct! Proportion of people with a disease who are positive for that disease c. Sensitivity Correct! How likely the same result will occur if repeated Correct! How a tool measures what it is intended to measure Correct! People without the disease who are negative on a given test Question 6 1.25 / 2.5 pts Multiple Choice Which are true of the mitochondria? Select all that apply. Correct! It is involved in cellular respiration You Answered They are found far from the site of energy consumption Correct! They play a role in apoptosis They control free radicals Question 7 1.25 / 2.5 pts Which of the following are true regarding cell communication? Select all that apply. b. Reliability a. Validity d. Specificity You Answered Paracrine signaling depends on hormones Correct! Neurotransmitters act through synapses Enzyme linked receptors act through an on-off switch Correct! Autocrine signaling releases a chemical into the extracellular fluid that affects its own activity Question 8 2.5 / 2.5 pts Multiple Choice Which of the following are false of the cell? Proteins carry out the functions of the cell membrane. Lysosomes are the digestive system of the cell. Correct! The rough ER is the site for lipid synthesis. Microfilaments are thin, threadlike cytoplasmic structures. Question 9 2.5 / 2.5 pts Which is true of the cytoskeleton? Select all that apply. Correct! It controls shape and movement Correct! Cilia and flagella are microtubule-filled cellular extensions It includes peroxisomes and proteasomes Question 10 1.88 / 2.5 pts What factors are used by epidemiologic methods? Select all that apply. Correct! How disease is spread Correct! How to control disease Correct! How to prevent disease Correct! How to eliminate disease You Answered How to treat disease All of the above None of the above Question 11 2.5 / 2.5 pts Multiple Choice A patient complains of a sore throat and headache. What are these examples of? Signs Correct! Symptoms Both A & B Question 12 0 / 2.5 pts Multiple Choice Which of the following is NOT helpful to the clinician to make a diagnosis? You Answered Detailed history Physical exam Correct Answer Evidence based practice Laboratory tests Question 13 0 / 2.5 pts Multiple Choice Chemical agents (poison, alcohol) are examples of which of the following? You Answered Risk factors Clinical manifestations Pathogenesis Correct Answer Etiologic factors Question 14 10 / 10 pts Define primary prevention and give an example: Your Answer: when the risk factors has to be remove to stop the disease from occurring example-eathing healthy / exercising to stay in shape or prevent heart disease.Giving vaccination to pervent disease in children The goal of primary prevention is to remove risk factors to prevent disease from occurring. Examples include taking folic acid while pregnant to prevent neural tube defects, vaccinating children to prevent communicable disease, eating healthy and exercising to prevent heart disease, and wearing seatbelts or helmets. Question 15 10 / 10 pts Explain apoptosis and why it is necessary: Your Answer: apoptosis is the programmed of cell death.this process is necessary for cell dividing because it is removing unwanted cells to make way for new cell. Apoptosis is programmed cell death. This process eliminates cells that are worn out, have been produced in excess, have developed improperly, or have genetic damage. Apoptosis is also responsible for several normal physiologic processes, like replacing cell in the intestinal villi and removing aging red blood cells. Question 16 10 / 10 pts Explain what necrosis is and give an example and description of one type of necrosis. Your Answer: necrosis is when cell dies in an organ/tissues that is still alive .this process can interferes with the tissue regeneration and how cell can be replace. one type of necrosis is gengrenouse necrosis which can bowel or the lower extremities that may causes changes in tussue and it functions Necrosis refers to cell death in an organ or tissues that is still part of a living person. It often interferes with cell replacement and tissue regeneration. Coagulative necrosis results most often from a sudden cutoff of blood supply to an organ (ischemia), particularly the heart and kidney. Liquefactive necrosis occurs when some of the cells die but their catalytic enzymes are not destroyed. It is commonly seen with brain infarcts or abscesses. Caseous necrosis occurs as part of granulomatous inflammation and is most often associated with tuberculosis. Gangrenous necrosis most often affects the lower extremities or bowel and is secondary to vascular occlusion. The term gangrene is applied when a considerable mass of tissue undergoes necrosis. In dry gangrene the affected tissue becomes dry and shrinks, the skin wrinkles, and its color changes to dark brown or black. The spread of dry gangrene is slow. It results from a cut off in arterial blood supply and is a form of coagulation necrosis. In wet gangrene, the affected area is cold, swollen, and pulseless. The skin is moist, black, and under tension. Blebs form on the surface, liquefaction occurs, and a foul odor is caused by bacterial action. The spread of tissue damage is rapid. Question 17 9 / 10 pts Match the type of cell injury to the cause. Some answers may be used more than once. (1 point each) 1. Sunburn a. Physical agents 2. Obesity b. Radiation injury 3. Reactive oxygen species c. Chemical injury 4. Low oxygen to tissues d. Biologic agents 5. Fractures e. Nutritional imbalances 6. OTC drugs f. Free radical injury 7. Hypothermia g. Hypoxic cell injury 8. Radiation treatment 9. Lead toxicity 10. Bacteria Correct! Sunburn Correct! Obesity You Answered Reactive oxygen species Correct Answer f. Free radical injury Correct! Low oxygen to tissues Correct! Fractures Correct! OTC drugs Correct! Hypothermia Correct! b. Radiation injury e. Nutritional imbalances c. Chemical injury g. Hypoxic cell injury a. Physical agents c. Chemical injury a. Physical agents Radiation treatment Correct! Lead toxicity Correct! Bacteria Question 18 5 / 10 pts List the 4 types of tissue found in the body. Pick 2 and give a description and example of each. Your Answer: nervours tissue-can be find throughout the body and it's used for communication. muscle tissue connective tissue epithelial-(covers the outer surface of the body and lines the inner surfaces. Epithelial tissue covers the body’s outer surface, lines the inner surfaces, and forms glandular tissue. Epithelial tissue has three distinct surfaces and the basal surface is attached to an underlying basement membrane. It is avascular, meaning without blood vessels. It receives oxygen and nutrients from the capillaries of the connective tissue on which it rests. Connective or supportive tissue is the most abundant tissue in the body. It connects and binds or supports the various tissues. Its cells produce the extracellular matrix that support and hold tissues together. Connective tissue is divided into two types: connective tissue proper and specialized connective tissue (cartilage, bone, and blood cells). The four types of connective tissue proper are loose (areolar), adipose, reticular, and dense connective tissue. The function of muscle tissue is to move the skeletal structures, pump blood through the heart, and contract the blood vessels and visceral organs. Muscle tissue can accomplish this by contraction. The two types of fibers that contract are called thin and thick filaments. Thin filaments are called actin, and the thick filaments are myosin. The three types of muscles tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Nervous tissue is distributed throughout the body for communication. It provides the means for controlling body function and for sensing and moving about the environment. b. Radiation injury c. Chemical injury d. Biologic agents The two types of cells are neuron and glial cells. Neurons function is communication. Glial (meaning glue) cells support the neurons. Question 19 2.5 / 2.5 pts What term means “cell eating” and engulfs and then kills microorganisms or other particulate matter? Your Answer: cell eating is refered to phagocytosis Phagocytosis Question 20 2.5 / 2.5 pts What term means “cell drinking,” and engulfs small solid or fluid particles, as seen with proteins and electrolytes? Your Answer: cell drinking is refrered to pinocytosis Pinocytosis Question 21 2.5 / 2.5 pts Give one function of a membrane potential: Your Answer: membrane potential can causes music contractions Generate nerve impulse, muscle contractions, or cause hormone secretion Question 22 2.5 / 2.5 pts What is the term that best describes the following process? A transport protein aiding a lipid insoluble or large molecule across the cell membrane that would otherwise not be able to pass through on its own. Your Answer: Facilitated diffusion facilitated diffusion Exam 2 Question 1 3 / 3 pts True/False: Blood tests for tumor markers can make a diagnosis of cancer. Why or why not? Your Answer: false,because tumor are usually elevated in benign conditions ,and in the early stages of malignancy they can't be elevated. False, only tissue can diagnose. Tumor markers are helpful to assess response to therapy or reoccurrence. Question 2 3 / 3 pts What is the most important procedure in diagnosing the correct cancer and histology? Your Answer: tissue biopsy because they play a critical role in dignosing the right cancer and histology tissue biopsy Question 3 4 / 4 pts Explain the TNM system: Your Answer: is a staging system that was created by AJCC for the help study cancer.It is also very effective in classifieng cancers tumor componments. Classification goes as such: T relates to the local spread of the primary of the tumor and the size N relates to the involvement of the regional/location of the lymph nodes M is the extent of the metastatic invilvement T is the size and local spread of the primary tumor. N is the involvement of the regional lymph nodes. M is the extent of the metastatic involvement. Question 4 10 / 10 pts 1. List two signs or symptoms a patient may present with that might indicate a cancer diagnosis: 2. What are two side effects commonly experienced by cancer patients? Your Answer: 1) Bleeding and weight loss 2) hair loss and sleep disturbances 1. Bleeding; sore that doesn’t heal; fluid in the pleural, pericardial, or peritoneal spaces; chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, abdominal discomfort or swelling. Other possible answers can include a mass or lump, pain (need to be specific), fatigue, fevers, weight loss 2. Weight loss, wasting of body fat and muscle tissue, weakness, anorexia, and anemia, fatigue, sleep disturbances Question 5 10 / 10 pts 1. What are the three possible goals of cancer treatment? 2. How does radiation kill cancer cells? Your Answer: 1) the three goal is to curative,control and palliative 2) radiation kill cancer cells by using high energy/waves particles to destroy/damage cancer cells.However this treatment can sometimes interrupt the cells cycle by killing good cells or damaging DNA cells 1. Curative, control, palliative 2. Radiation therapy uses high-energy particles or waves to destroy or damage cancer cells. This leads to the creation of free radicals, which damage cell structures. Radiation can interrupt the cell cycle process, kill cells, or damage DNA in the cells. Question 6 2.5 / 2.5 pts True/False: Cell proliferation is the process in which proliferating cells become more specialized cell types. True Correct! False False, cell differentiation Question 7 0 / 2.5 pts True/False: Cell differentiation is the process in which proliferating cells become more specialized cell types. Correct Answer True You Answered False Question 8 2.5 / 2.5 pts This type of cell remains incompletely differentiated throughout life: Your Answer: stem cell stem cell Question 9 2.5 / 2.5 pts These are cells of the same lineage that have not yet differentiated to the extent that they have lost their ability to divide: Your Answer: they are progenitor progenitor or parent cells Question 10 4 / 4 pts What is angiogenesis? Why do tumors need it? Your Answer: angiogenesis is the delovement of new blood vessels with a tumor and tumorns need angiogenesis to grow development of new blood vessels within the tumor. They need it to continue to grow. Question 11 3 / 3 pts What are normal genes called that become cancer-causing if mutated? Your Answer: proto-oncogenes protooncogenes Question 12 3 / 3 pts What is a tumor suppressor gene? Give one example. Your Answer: they're gene that are associated with gene underactivity because of this it slows down cell division or may tell cell when to die. Tumor suppressor genes are associated with gene underactivity. These genes slow down cell division, repair DNA mistakes, or tell cells when to die. BRCA1 or 2, TP53 Question 13 10 / 10 pts A 40-year-old woman has experienced heavy menstrual bleeding. She was told she has a uterine tumor called a leiomyoma. She is worried she has cancer. What do you tell her? Explain at least 2 differences between a benign and malignant tumor. Your Answer: I will tell her not to worry because leiomyoma is a non-cancerous tumor and it can be surgically remove and to always have a regular doctor visit two differences between a benign and malignant tumor is that has a well-differentiated cells and have slow progressive growth rate.Malignant tumor is more aggressive because it destroy tissue,grows rapidly and spread to other body parts and lacks well defined margins Leiomyoma is a benign tumor. (Leiomyosarcoma is malignant) Student can add any of the following: Benign tumors are well-differentiated cells, resemble the cells of tissues of origin, and have a slow, progressive rate of growth. They grow by expansion and remain localized to their site of origin, not capable of metastasizing. They develop a rim of connective tissue around the tumor called a fibrous capsule, which aids in surgical removal. Benign tumors are less of a threat unless they interfere with vital functions Malignant neoplasms invade and destroy tissue. They grow rapidly, spread to other parts of the body, and lack well-defined margins. They can compress blood vessels and outgrow their blood supply, causing ischemia and tissue injury. Surgery can be more difficult if it has spread. Question 14 10 / 10 pts A 62-year-old man with a 30-pack year smoking history is diagnosed with small cell lung cancer with metastasis to the bone. (1) Explain the process of how cancer spreads metastatically. (2) What symptoms might he have presented with? (3) Which screening test would he have benefited from? Your Answer: 1) cancern that are spreads by metastatically is loose from the primary tumor that have extracellular matrix from the surrounding tumor,or has gain access to the blood vessle which it can grow and establish a blood supply. 2 some symptoms that may be presented are shortness of breath,chest or bone pain and cough 3) hw benefited from low dose chest CT that could be done yearly (1) Metastasis- a cancer cell must break loose from the primary tumor, invade the surrounding extracellular matrix, gain access to a blood vessel, survive its passage in the bloodstream, emerge at a favorable location, invade the surrounding tissue, begin to grow, and establish a blood supply. (2) Chest pain, shortness of breath, cough, bone pain. (3) Yearly low-dose chest CT. Question 15 1.5 / 3 pts Malignant tumors have which of the following characteristics? Select all that apply. Correct! Variable rate of growth Correct! Spreads by metastasis Well-differentiated cells You Answered Fibrous capsule Question 16 0 / 3 pts What are molecular and cellular mechanisms in genes that increase susceptibility to cancer? Select all that apply. Correct Answer Lack of cellular senescence Correct! Angiogenesis You Answered Ability to undergo apoptosis Correct! Mutations in growth factor signaling pathways You Answered Intact DNA repair genes Question 17 4 / 4 pts List 4 of the 7 risk factors linked to cancer as stated in the module. Your Answer: 1)obesity 2)hormonal factors 3)environmental agents 4) cancer causing viruses Heredity, hormonal factors, obesity, immunologic mechanisms, environmental agents such as chemicals, radiation, and cancer-causing viruses. Question 18 10 / 10 pts List three characteristics of cancer cells and briefly explain what it means: Your Answer: cancer cells grow in an altered cell differentiation and growth which can also be called neoplasia they can have a neoplasm growth where normal tissue lacks regulatory controls cancer cells also have genetic abnormalities that causes uncontrollble proliferation and can cause normal call or benign tumors into malignant tumors Answer: Any of the following Anaplasia is the loss of cell differentiation in cancerous tissue. Genetic instability means they have a high frequency of mutations. Growth factor independence means cancer cells can proliferate even in the absence of growth factors. Cell density-dependent inhibition means cancer cell don’t stop growing when they come into contact with each other. Cell cohesiveness and adhesion means they don’t stick together. Anchorage dependence means cancer cells aren’t anchored to neighboring cells or the underlying matrix to live and grow. Cell-to-cell communication in cancer cells is poor, which interferes with intercellular connections and responsiveness to membrane-derived signals. Life span is unlimited – cancer cells are immortal. Antigen expression -cancer cells contain several cell surface molecules or antigens that are immunologically identified as foreign. Cancer cells can produce enzymes, hormones, and other substances that the tissues of origin either does not produce or produces in much smaller amounts. Cancer cells can show cytoskeletal changes or abnormalities. This includes abnormal intermediate filament types or changes in actin filaments and microtubules that help with invasion and metastasis. Question 19 3.5 / 3.5 pts Which of the following is not a risk factor for developing cancer? Correct! Sunscreen Obesity HPV High red meat intake Question 20 3.5 / 3.5 pts All of the following viral agents are correctly paired with the associated lesion except: Human papillomavirus (HPV): genital warts Correct! Epstein-Barr virus: carcinoma of the cervix Epstein Barr is linked to Burkitt lymphoma and nasopharyngeal cancer. Cervical carcinoma is linked to HPV. Hepatitis B virus: hepatocellular carcinoma Human herpes virus-8: Kaposi sarcoma Question 21 3 / 3 pts List one example of screening for each method: observation, palpation, and lab test/procedure: Your Answer: observation-external genitalia palpation-lymph nodes lab test/procedure-pap smear Observation: skin, mouth, external genitalia Palpation: breast, thyroid, rectum and anus, prostate, lymph nodes Laboratory tests and procedures: Pap smear, colonoscopy, mammography Exam 3 Question 1 5 / 5 pts Short answer Explain the challenges of diagnosing autoimmune disorders. Your Answer: since there are too many autoimmune disorder,diagnosing is made by serological finding,history or physical testing.blood testing could have been a good way to test but since some blood are more generic can be elevated to show other diseases therefore it best go by finding that are listed. There are over 80 identified, many with overlapping presentations. Many manifestations are nonspecific and are seen in other non-autoimmune diseases. Blood testing isn’t perfect either, as some tests are more generic and can be elevated in the presence of other diseases [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 109 pages
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 07, 2022
Number of pages
109
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
15












 (1).png)
 (1).png)
 (1).png)