Pharmacology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 508 Pharmacology Midterm Exam(Questions with Answers) (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 508 Pharmacology Midterm Exam(Questions with Answers)
Document Content and Description Below
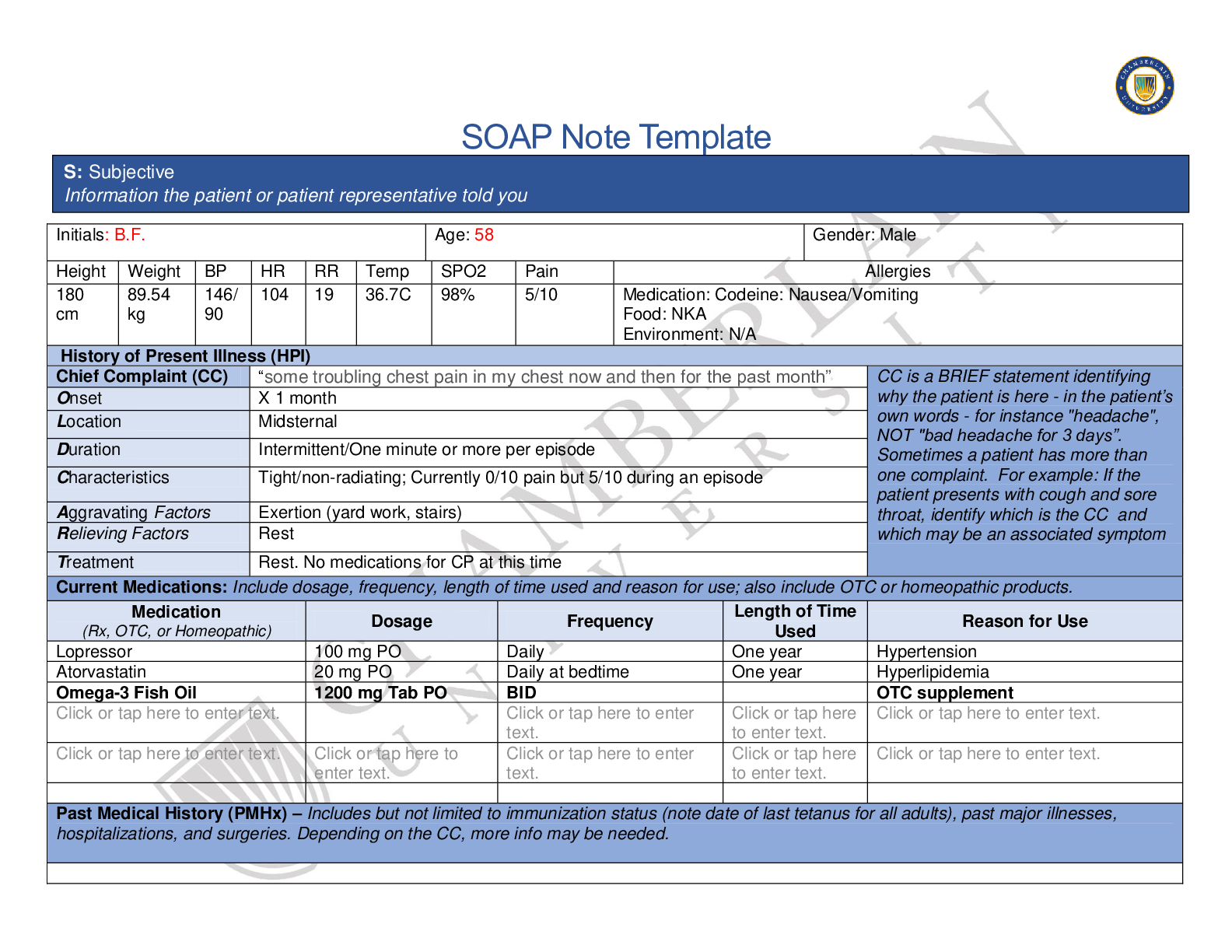
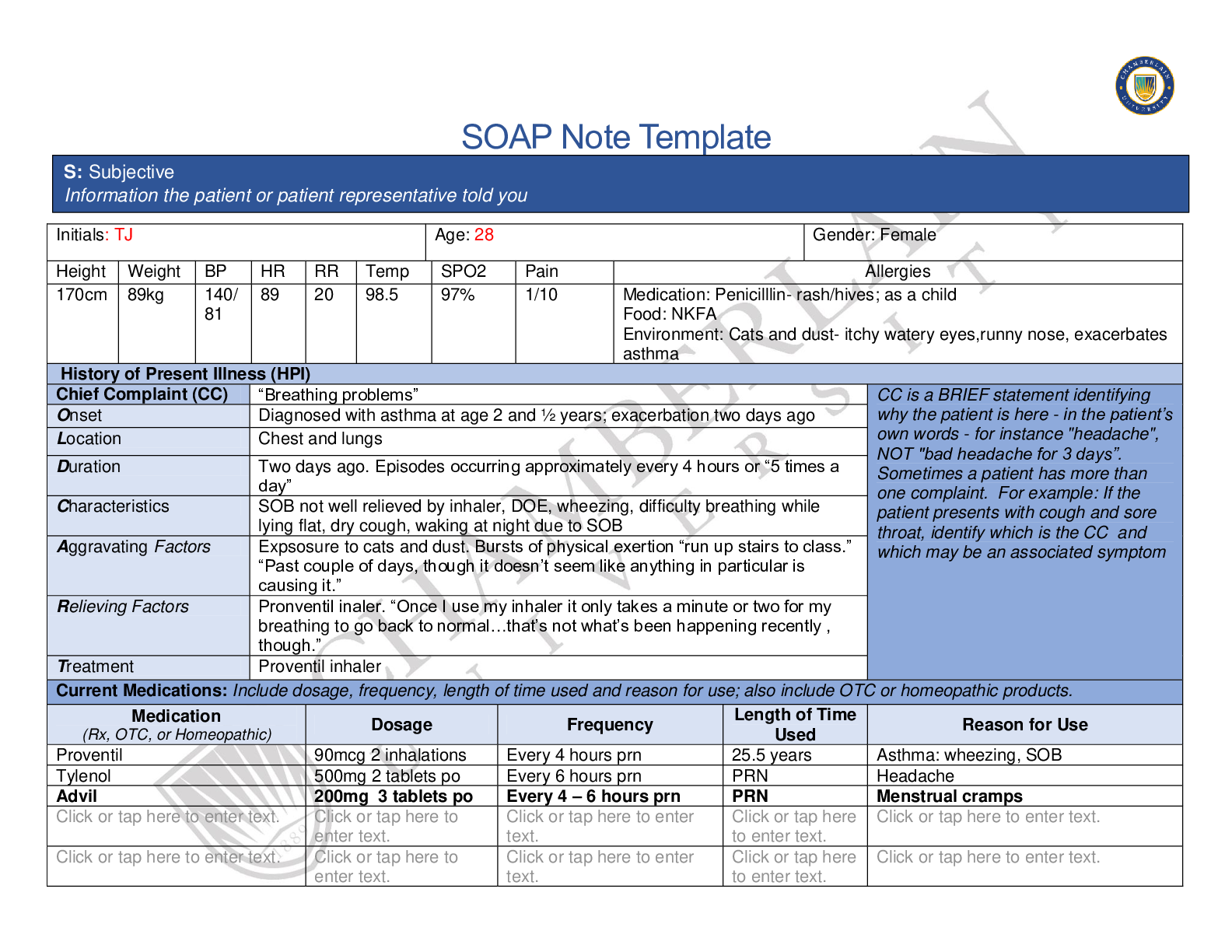
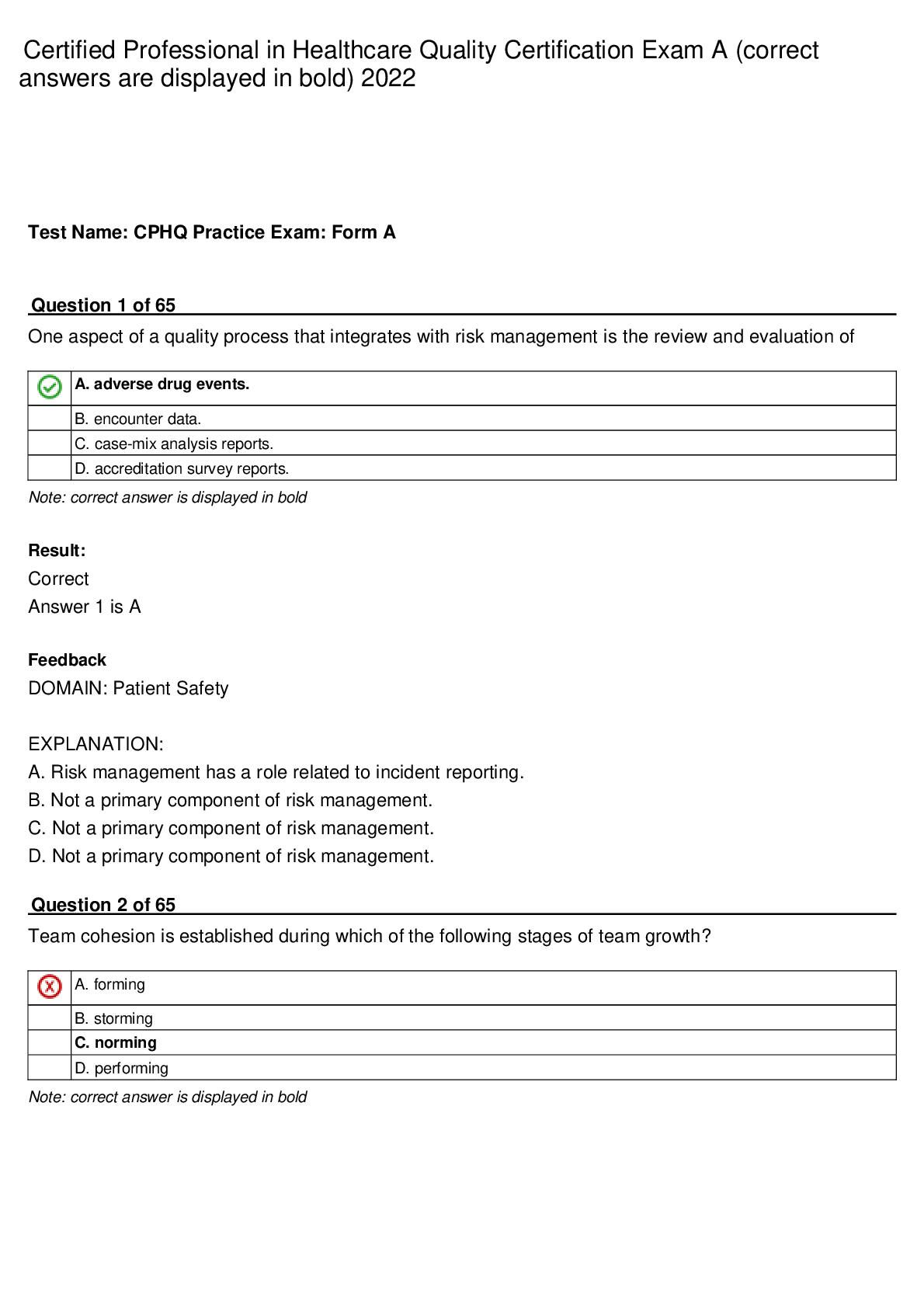
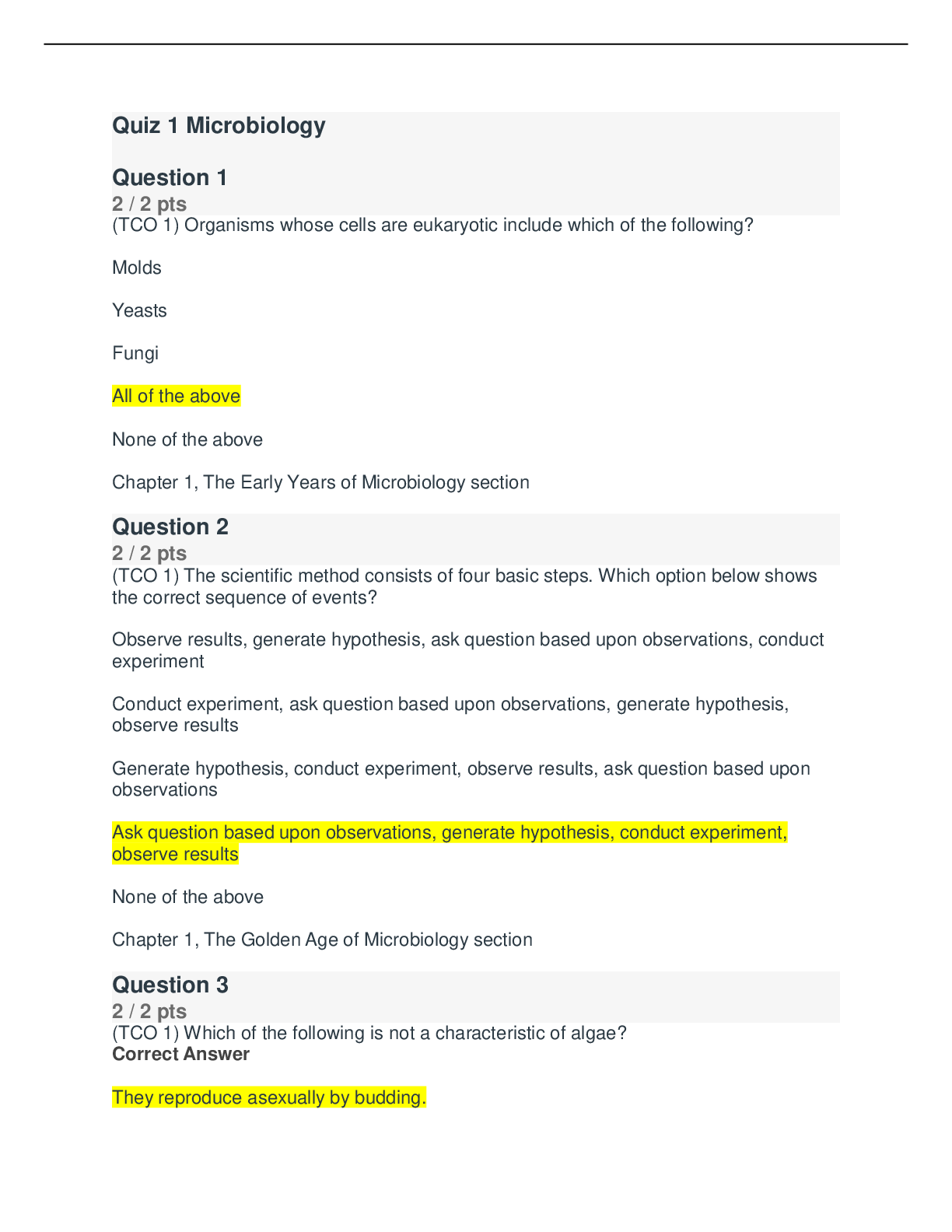
A patient who has primary hyperlipidemia and who takes atorvastatin (Lipitor) continues to have LDL cholesterol of 140 mg/dL after 3 months of therapy. The primary care NP increases the dose from 10 ... mg daily to 20 mg daily. The patient reports headache and dizziness a few weeks after the dose increase. The NP should: change the atorvastatin dose to 15 mg twice daily. change the patient’s medication to cholestyramine (Questran). Correct! add ezetimibe (Zetia) and lower the atorvastatin to 10 mg daily. recommend supplements of omega-3 along with the atorvastatin. When used in combination with a low-dose statin, ezetimibe has been noted to produce an additional 18% reduction in LDL. Because this patient continues to have elevated LDL along with side effects of the statin, the NP should resume the lower dose of the statin and add ezetimibe. Atorvastatin is given once daily. Cholestyramine and omega3 supplements are not indicated. Question 2 2 / 2 pts A patient who has hyperlipidemia has been taking atorvastatin (Lipitor) 60 mg daily for 6 months. The patient’s initial lipid profile showed LDL of 180 mg/dL, HDL of 45 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 160 mg/dL. The primary care NP orders a lipid profile today that shows LDL of 105 mg/dL, HDL of 50 mg/dL, and triglycerides of 120 mg/dL. The patient reports muscle pain and weakness. The NP should: order liver function tests (LFTs). Correct! order a creatine kinase-MM (CK-MM) level. change atorvastatin to twice-daily dosing. add gemfibrozil (Lopid) to the patient’s medication regimen. Hepatotoxicity and muscle toxicity are the two primary adverse effects of greatest concern with statin use. Patients who report muscle discomfort or weakness should have a CK-MM level drawn. LFTs are indicated with signs of hepatotoxicity. It is not correct to change the dosing schedule. Gemfibrozil is not indicated. Question 3 2 / 2 pts A patient comes to the clinic with a 4-day history of 10 to 12 liquid stools each day. The patient reports seeing blood and mucus in the stools. The patient has had nausea but no vomiting. The primary care NP notes a temperature of 37.9° C, a heart rate of 96 beats per minute, and a blood pressure of 90/60 mm Hg. A physical examination reveals dry oral mucous membranes and capillary refill of 4 seconds. The NP’s priority should be to: obtain stool cultures. Correct! begin rehydration therapy. consider prescribing metronidazole. administer opioid antidiarrheal medications. Acute diarrhea is usually mild and self-limited. Nonpharmacologic measures, especially bowel rest and adequate hydration, are helpful and should be a priority. Stool cultures may be ordered after hydration therapy is begun. Metronidazole is indicated if C. difficile is present. Opioid antidiarrheals may prolong symptoms. Question 4 2 / 2 pts A perimenopausal woman tells the primary care NP that she is having hot flashes and increasingly severe mood swings. The woman has had a hysterectomy. The NP should prescribe: Correct! estrogen-only HT. low-dose oral contraceptive therapy. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor therapy until menopause begins. estrogen-progesterone HT. Estrogen-only regimens are used in women without a uterus and may be initiated to treat perimenopause symptoms if needed. Low-dose oral contraceptive pills are used to treat irregular menstrual bleeding in perimenopausal women. Question 5 2 / 2 pts A primary care NP prescribes a nitroglycerin transdermal patch, 0.4 mg/hour release, for a patient with chronic stable angina. The NP should teach the patient to: change the patch four times daily. use the patch as needed for angina pain. use two patches daily and change them every 12 hours. Correct! apply one patch daily in the morning and remove in 12 hours. To avoid tolerance, the patient should remove the patch after 12 hours. The transdermal patch is not changed four times daily or used on a prn basis. The patch is applied once daily. Question 6 2 / 2 pts A parent calls a clinic for advice about giving an over-the-counter cough medicine to a 6-year-old child. The parent tells the NP that the medication label does not give instructions about how much to give a child. The NP should: order a prescription antitussive medication for the child. Correct! ask the parent to identify all of the ingredients listed on the medication label. calculate the dose for the active ingredient in the over-the-counter preparation. tell the parent to approximate the dose at about one third to one half the adult dose. Over-the-counter cough medications often contain dextromethorphan, which can be toxic to young children. It is important to identify ingredients of an over-the-counter medication before deciding if it is safe for children. A prescription antitussive is probably not warranted until the cough is evaluated to determine the cause. Until the ingredients are known, it is not safe to approximate the child’s dose based on only the active ingredient. Question 7 2 / 2 pts A patient who has disabling intermittent claudication is not a candidate for surgery. Which of the following medications should the primary care NP prescribe to treat this patient? Correct! Cilostazol (Pletal) Warfarin (Coumadin) Pentoxifylline (Trental) Low-dose, short-term aspirin Patients with disabling intermittent claudication who are not candidates for surgery or catheter-based intervention should be treated with cilostazol rather than pentoxifylline. Warfarin is not indicated. Patients with chronic limb ischemia are treated with lifelong aspirin therapy. Question 8 2 / 2 pts The primary care NP prescribes an extended-cycle monophasic pill regimen for a young woman who reports having multiple partners. Which statement by the patient indicates she understands the regimen? “I have to take a pill only every 3 months.” Correct! “I should expect to have only four periods each year.” “I will need to use condoms for only 7 more days.” “This type of pill has fewer side effects than other types.” The extended-cycle pills have fewer pill-free intervals, so women have only four periods a year. Patients take pills every day. Because this patient has multiple partners, she should continue to use condoms. This type of pill has the same side effects as other types. Question 9 2 / 2 pts The primary care NP prescribes an inhaled corticosteroid for a patient who has asthma. The third-party payer for this patient denies coverage for the brand that comes in the specific strength the NP prescribes. The NP should: provide pharmaceutical company samples of the medication for the patient. inform the patient that the drug must be paid for out of pocket because it is not covered. Correct! order the closest formulary-approved approximation of the drug and monitor effectiveness. write a letter of medical necessity to the insurer to explain the need for this particular medication. The second step of medical decision making takes into account benefits versus costs along with an understanding that it is impossible to do everything because of limited resources. The NP should prescribe what is covered and evaluate its effectiveness; if it does not work, the third-party payer may be approached about the need for the other medication. Providing samples is not always possible, and this practice is being discouraged, so it is not a viable solution. Asking patients to pay out of pocket ultimately may be necessary but carries risks that the patient will not obtain the medication. Writing a letter of medical necessity may be indicated if the available drugs are not effective but is not the initial step. Question 10 2 / 2 pts A primary care NP prescribes levothyroxine for a patient to treat thyroid deficiency. When teaching this patient about the medication, the NP should: counsel the patient to take the medication with food. Correct! tell the patient that changing brands of the medication should be avoided. instruct the patient to stop taking the medication if signs of thyrotoxicosis occur. tell the patient that the drug may be stopped when thyroid function tests stabilize. Patients should be told not to change brands of the medication; there is potential variability in the bioequivalence between manufacturers. The medication should be taken at approximately the same time each day before breakfast or on an empty stomach. Patients should be instructed to contact the provider if signs of thyrotoxicosis are present. Thyroid replacement medications are usually given for life. [Show More]
Last updated: 10 months ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages

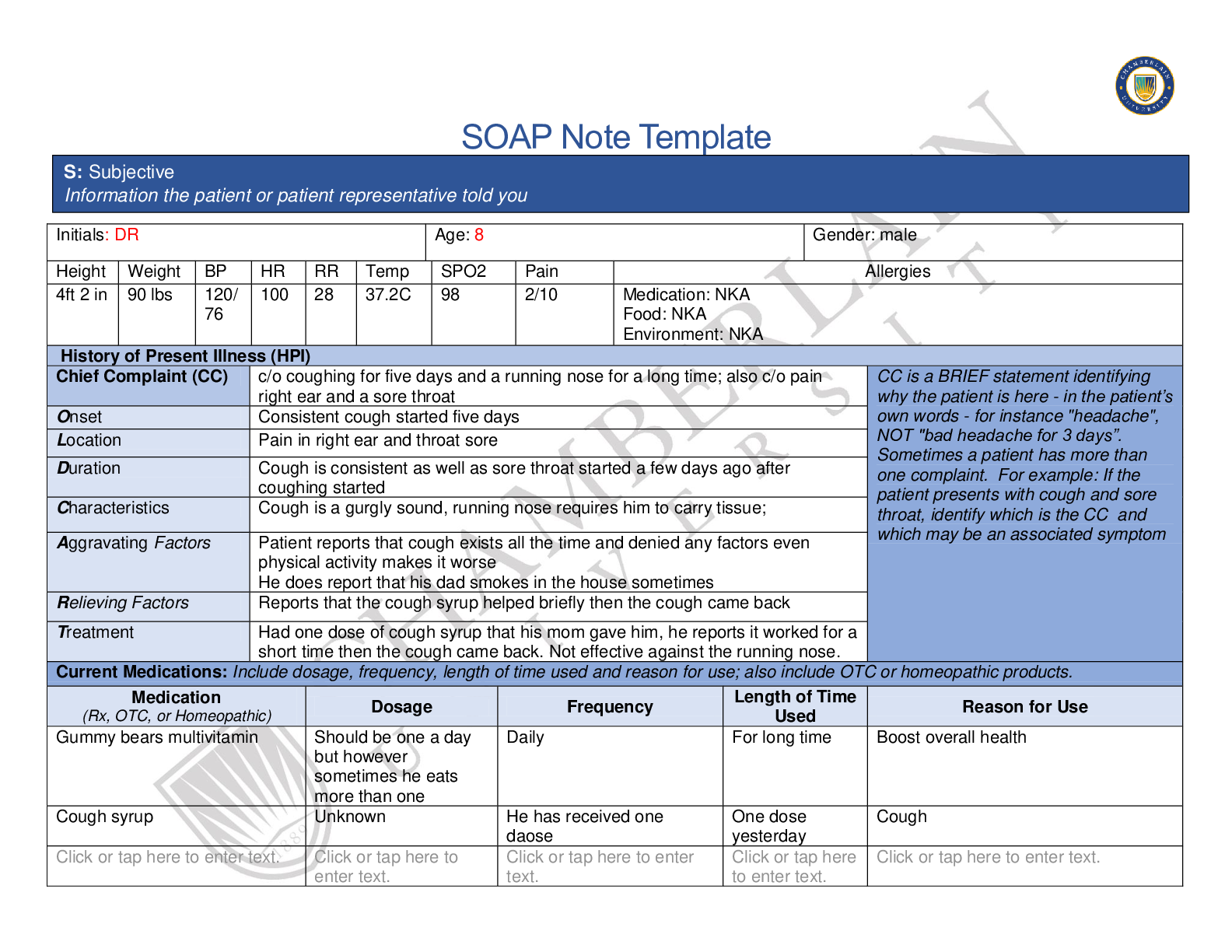
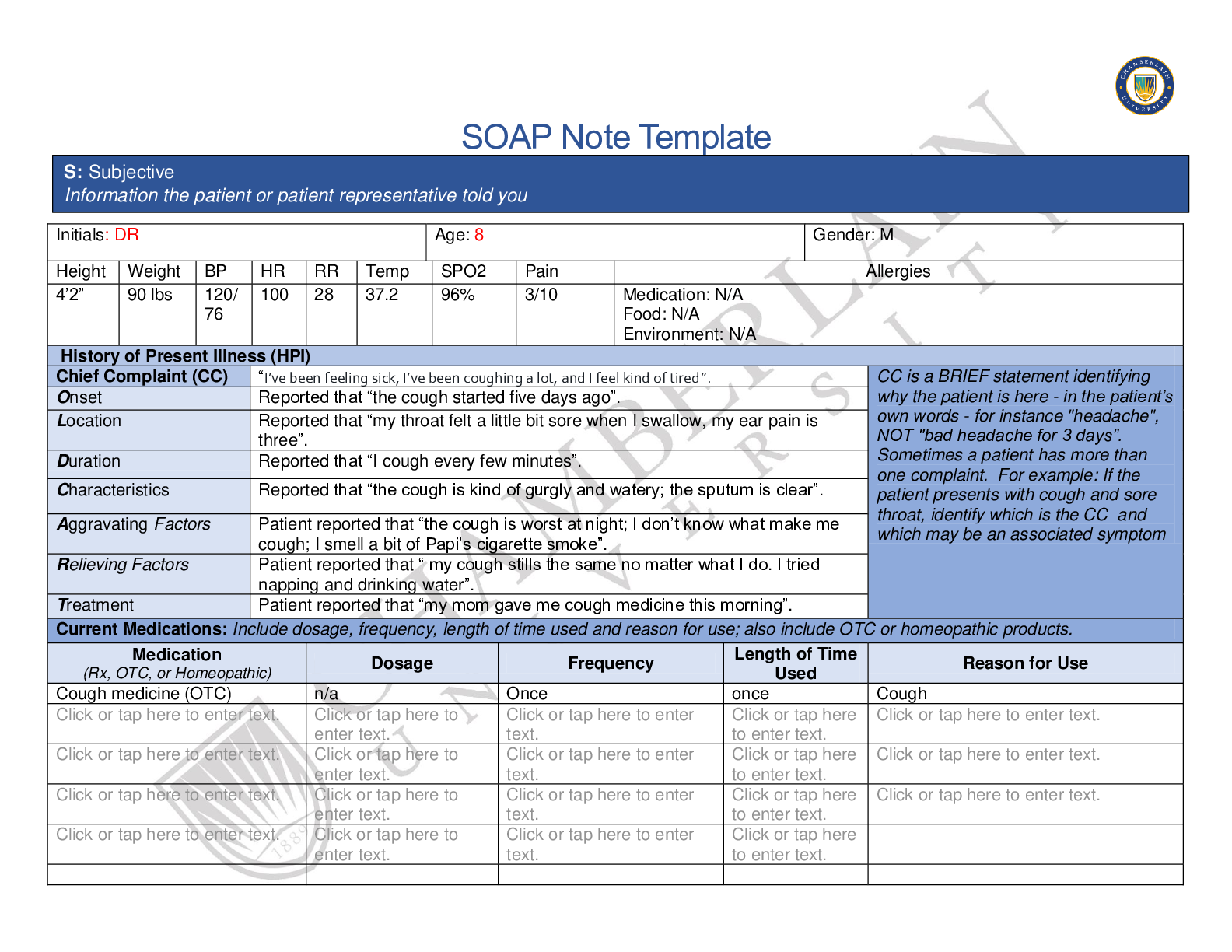
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 29, 2020
Number of pages
27
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 29, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
55









 (1).png)

 A+ Guide.png)



.png)