Statistics > SOPHIA Milestone > STAT 200 Sophia learning Introduction to Statistics Unit 3 Milestone 3 _Passed The Milestone (All)
STAT 200 Sophia learning Introduction to Statistics Unit 3 Milestone 3 _Passed The Milestone
Document Content and Description Below
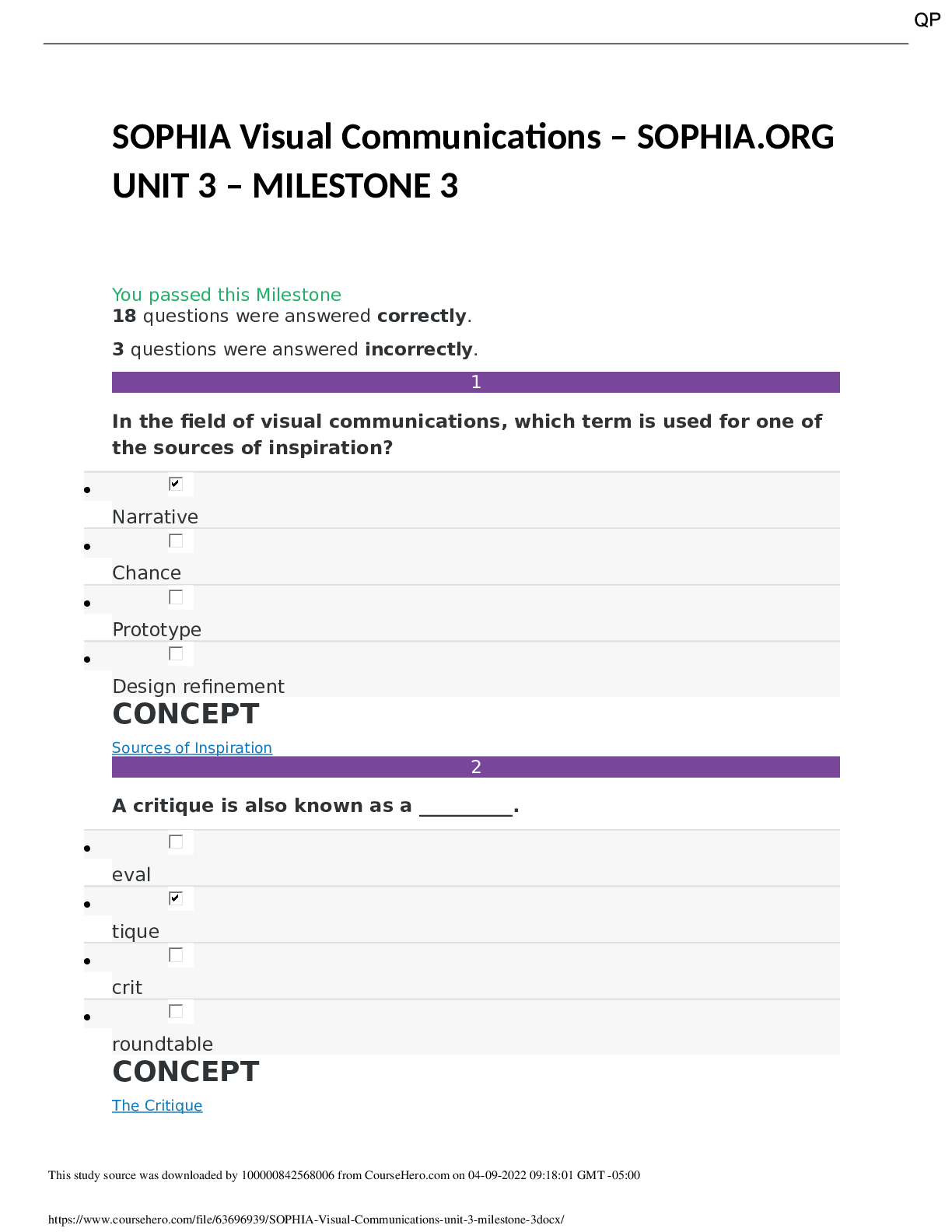
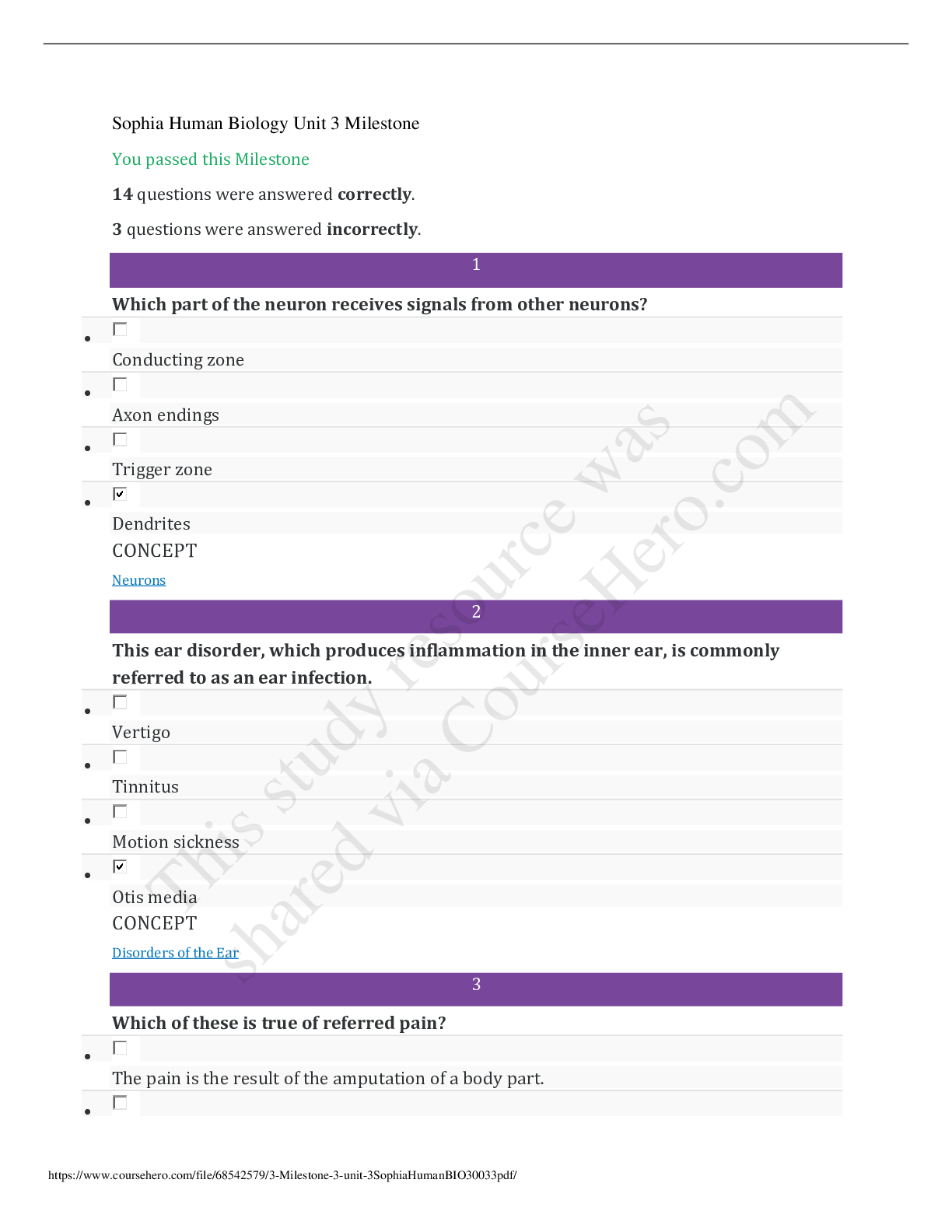
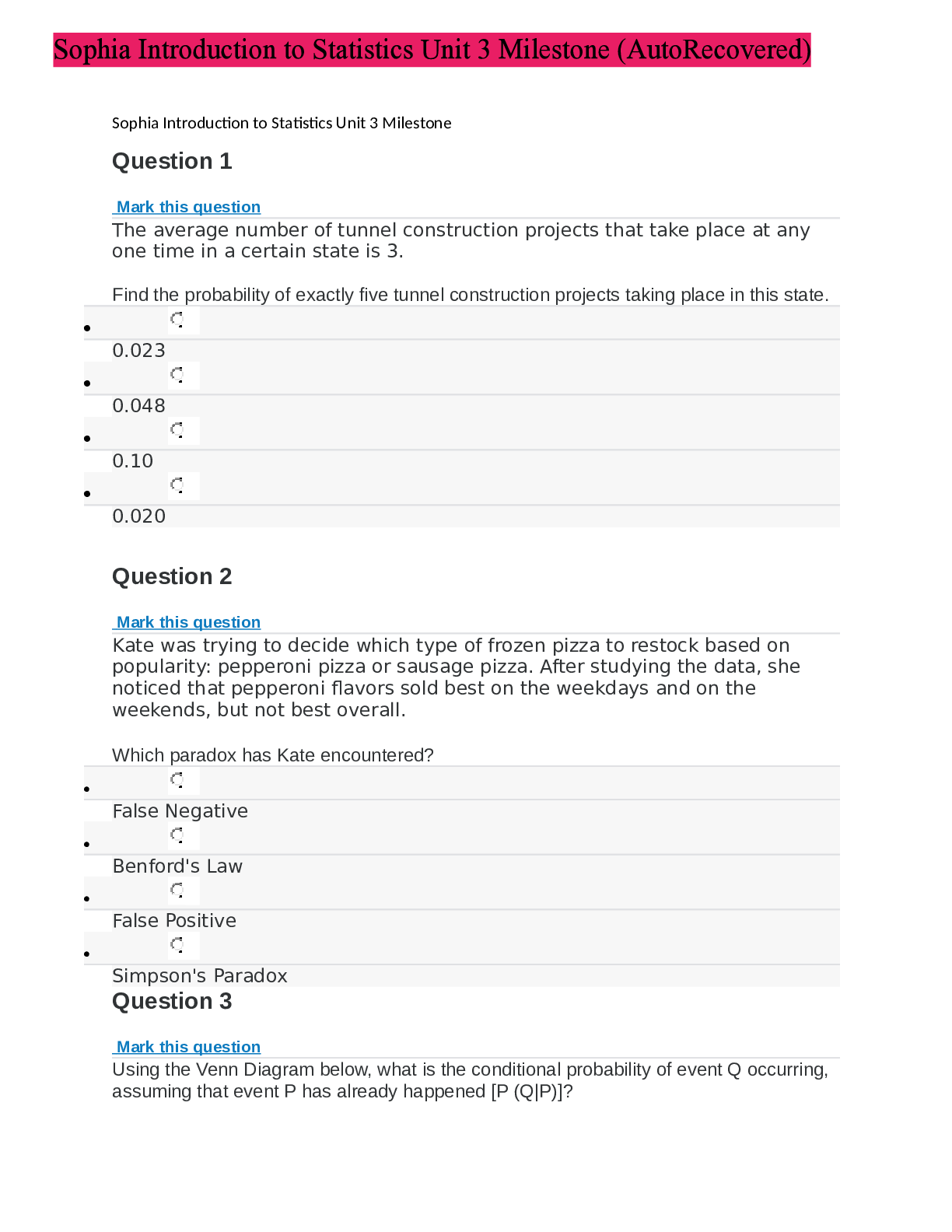
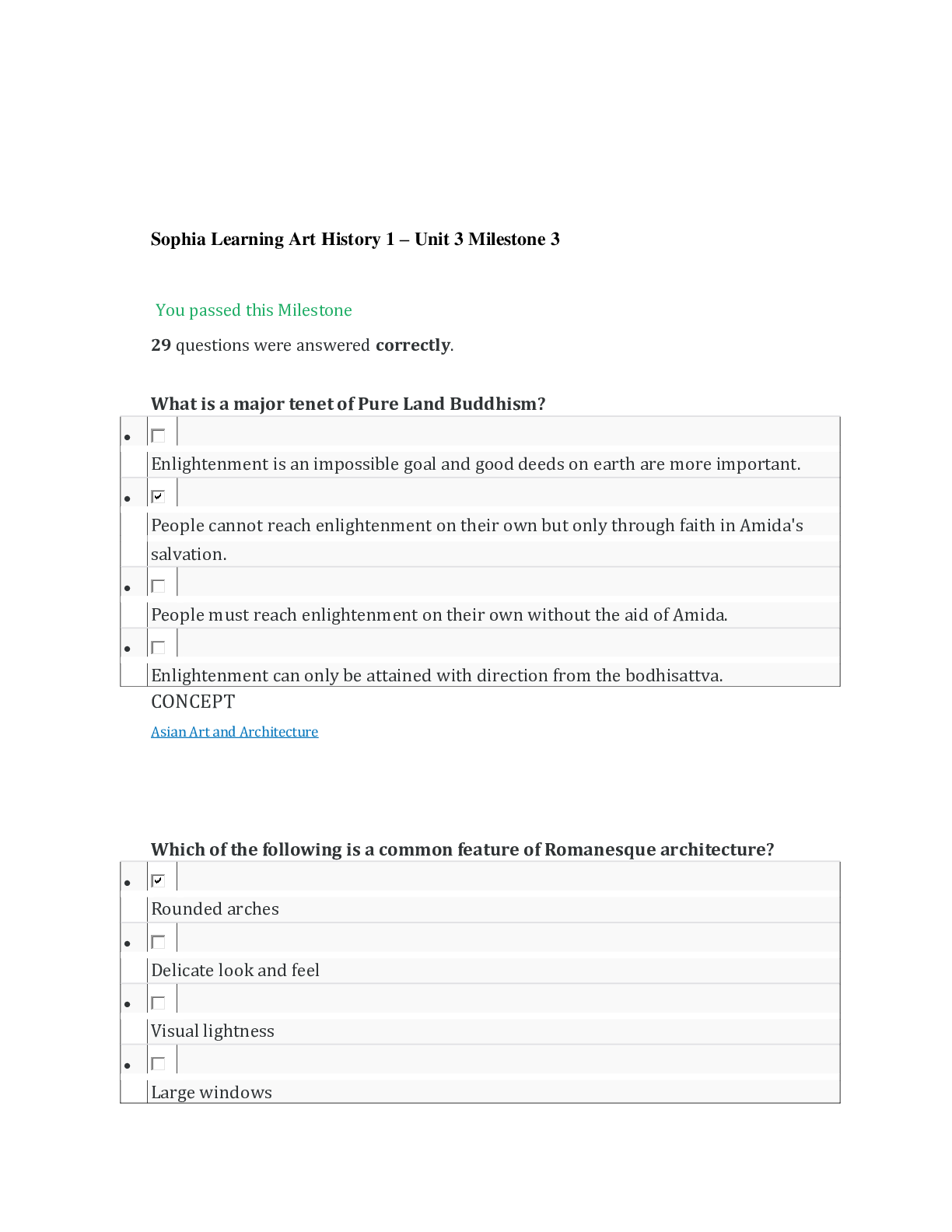
STAT 200 Sophia learning Introduction to Statistics Unit 3 Milestone 3 You passed this Milestone 21 questions were answered correctly. 6 questions were answered incorrectly. 1 Which of the follow... ing is a property of binomial distributions? All of the observations made are dependent of each other. There are exactly four possible outcomes for each trial. The expected value is equal to the number of successes in the experiment. The variable of interest is the total number of successes or failures for a given number of observations. RATIONALE Recall that for the binomial distribution we are concerned with an event occurring (successes) or not occurring (failures) in a given number of trails (n). CONCEPT Binomial Distribution 2 A survey asked 1,000 people which magazine they preferred, given three choices. The table below breaks the votes down by magazine and age group. Age Below 40 Age 40 and Above The National Journal 104 200 Newsday 120 230 The Month 240 106 If a survey is selected at random, what is the probability that the person voted for "Newsday" and is also age 40 or older? Answer choices are rounded to the hundredths place. 0.34 0.54 0.23 0.66 RATIONALE If we want the probability of people who voted for "Newsday" and are also age 40 and over, we just need to look at the box that is associated with both categories, or 230. To calculate the probability, we can use the following formula: CONCEPT Two-Way Tables/Contingency Tables 3 Zhi and her friends moved on to the card tables at the casino. Zhi wanted to figure out the probability of drawing a King of clubs or an Ace of clubs. Choose the correct probability of drawing a King of clubs or an Ace of clubs. Answer choices are in the form of a percentage, rounded to the nearest whole number. 8% 4% 2% 6% RATIONALE Since the two events, drawing a King of Clubs and drawing an Ace of Clubs, are non-overlapping, we can use the following formula: CONCEPT "Either/Or" Probability for Non-Overlapping Events 4 Which of the following situations describes a discrete distribution? A probability distribution showing the weights of newborns. A probability distribution showing the heights of children in a first grade class. A probability distribution of the quantity of babies in the intensive care unit. A probability distribution showing the average time it takes for children to walk to school. RATIONALE A distribution is discrete if the outcomes we are measuring can only take on a limited number of values. The number of babies in an intensive care unit can be 0, 1, 2, and so on, which are a limited set of values. CONCEPT Probability Distribution 5 What is the probability of NOT drawing a Queen from a standard deck of 52 cards? RATIONALE Recall that the probability of a complement, or the probability of something NOT happening, can be calculated by finding the probability of that event happening, and then subtracting from 1. Note that there are a total of 4 Queen cards in a standard deck of 52 cards. So the probability of NOT getting a Queen is equivalent to: CONCEPT Complement of an Event 6 Fifty people were asked whether they were left handed. Six people answered "yes." What is the relative frequency of left-handed people in this group? Answer choices are rounded to the hundredths place. 1.14 0.88 8.33 0.12 RATIONALE The relative frequency of a left hand is: CONCEPT Relative Frequency Probability/Empirical Method 7 Colleen has 6 eggs, one of which is hard-boiled while the rest are raw. Colleen can't remember which of the eggs are raw. Which of the following statements is true? If Colleen selected one egg, cracked it open and found out it was raw, the probability of selecting the hard-boiled egg on her second pick is 1/5. If Colleen selected one egg, cracked it open and found out it was raw, the probability of selecting the hard-boiled egg on her second pick is 1/6. The probability of Colleen selecting a raw egg on her first try is 1/6. The probability of Colleen selecting the hard-boiled egg on her first try is 1/5. RATIONALE The probability of choosing the hard-boiled egg is 1/6. If she cracks an egg and it is not the hard-boiled egg, then it becomes 1/5 on the next try because there are now only 5 eggs remaining and one has to be the hard-boiled egg as she did not pick it on the firs [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 14, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 14, 2022
Downloads
1
Views
265