*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > Chamberlain College Of Nursing:NR 511 Week 1 Study Guide 2022, Definitions and Answers;Already Grade (All)
Chamberlain College Of Nursing:NR 511 Week 1 Study Guide 2022, Definitions and Answers;Already Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
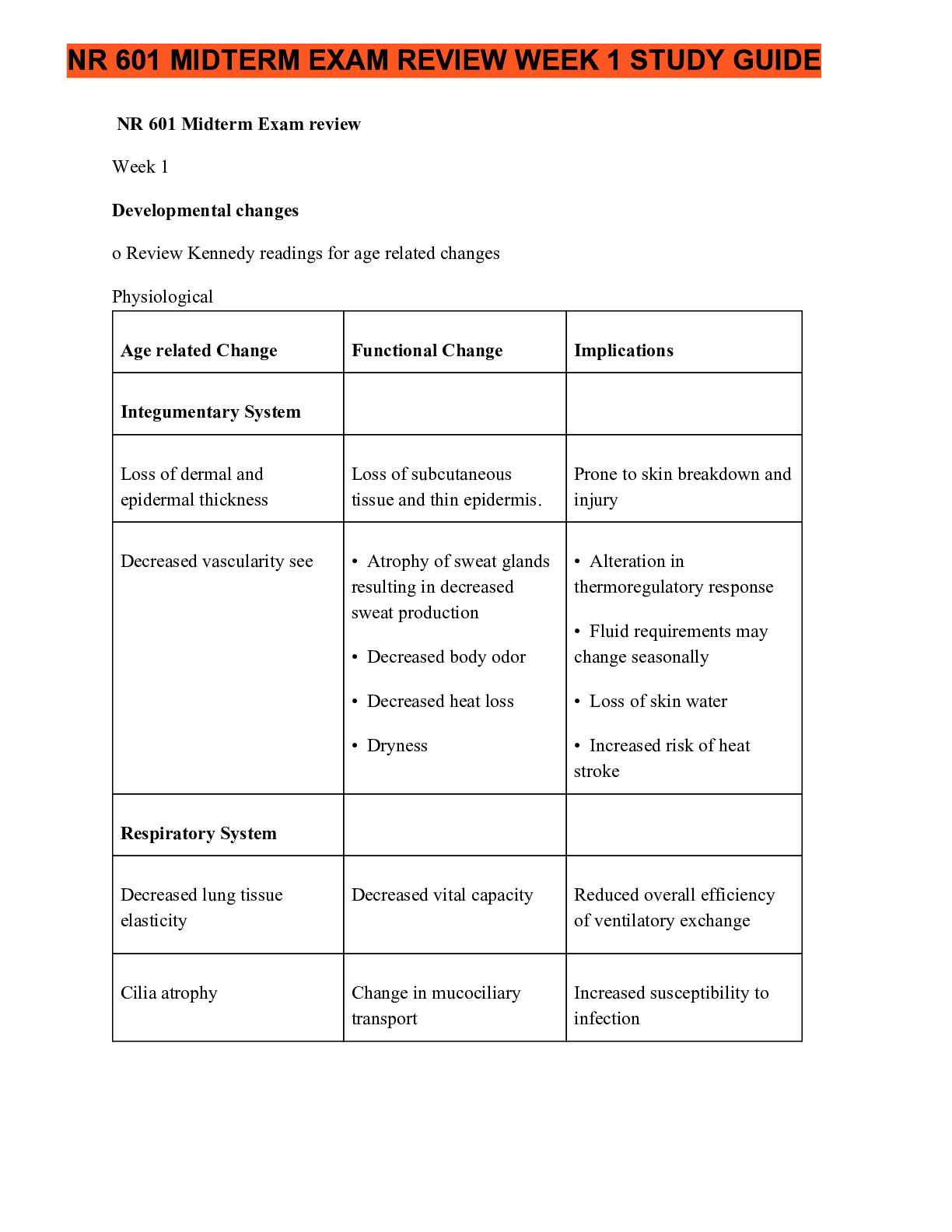
NR 511-Week 1 Exam Study Guide Week 1 1. Define diagnostic reasoning Reflective thinking because the process involves questioning ones thinking to determine if all possible avenues have been e... xplored and if the conclusions that are being drawn are based on evidence. Seen as kind of critical thinking. 2. Discuss and identify subjective & objective data Subjective-What the patient tells you, complains of, etc. Chief complaint, HPI, Review of systems Objective- What YOU can see, hear, or feel as part of your exam. Includes lab data, diagnostic test results. 3. Discuss and identify the components of the HPI Specifically related to the chief complaint only. Detailed breakdown of chief complaint. OLDCART ONSET LOCATION DURATION CHARACTERISTICS AGGRAVATING RELIEVING TIMING 4. Describe the differences between medical billing and medical coding Medical billing- Process of submitting and following up on claims made to a payer in order to receive payment for medical services rendered by a healthcare provider. Medical coding- The use of codes to communicate with payers about which procedures were performed and why. 5. Compare and contrast the 2 coding classification systems that are currently used in the US healthcare system ICD: International classification of disease codes are used to provide payer info on necessity of visit or procedure performed. Shorthand for patient’s diagnosis. CPT: Common procedural terminology codes offer the official procedural coding rules and guidelines required when reporting medical services and procedures performed by physician and non-physician providers. Must have corresponding ICD. 6. Discuss how specificity, sensitivity & predictive value contribute to the usefulness of the diagnostic data Specificity-The ability of the test to correctly detect a specific condition. If a patient has a condition but the test is negative, it is a false negative. If a patient does NOT have a condition but the test is positive, it is a false positive. Sensitivity- Test that has few false negatives. Ability of a test to correctly identify a specific condition when it is present. The higher the sensitivity, the lesser the likelihood of a false negative. Predictive value- The likelihood that the patient actually has the condition and is, in part, dependent upon the prevalence of the condition in the population. If a condition is highly likely, the positive result would be more accurate. This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-03-2022 03:54:06 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/36085533/NR511-Week-1-Exam-Study-Guide-docx/ Diagnostic tests can be used to confirm or rule out hypothesis and may be used to screen for conditions. Diagnostic test may also be used to monitor the progress in managing a chronic condition. 7. Discuss the elements that need to be considered when developing a plan Patient’s preferences and actions, research, evidence, clinical state or circumstances, and clinical expertise. 8. Describe the components of Medical Decision Making in E&M coding Risk, data, and diagnosis. The more time and consideration involved in dealing with a patient, the higher the reimbursement from the payer. Documentation must reflect MDM! 9. Correctly order the E&M office visit codes based on complexity from least to most complex New Patient: 1. Minimal/RN visit: 99201 2. Problem focused: 99202 3. Expanded problem: 99203 4. Detailed: 99204 5. Comprehensive: 99205 Established Patient 1. Minimal/RN visit: 99211 2. Problem focused: 99212 3. Expanded problem: 99213 4. Detailed: 99214 5. Comprehensive: 99215 10. Discuss a minimum of three purposes of the written history and physical in relation to the importance of documentation Important reference document that gives concise information about the patient’s history and exam findings. Outlines a plan for addressing issues that prompted the visit. Info should be presented in logical fashion and prominently features all data relevant to the patient’s condition. Is a means of communicating info to all providers involved in the patient’s care. Is a medical-legal document. Is essential in order to accurately code and bill for services. 11. Accurately document why every procedure code must have a corresponding diagnosis code Diagnosis code explains the necessity of the procedure code. Insurance won’t pay if they don’t correspond. 12. Correctly identify a patient as new or established given the historical information If the patient has never been seen in that clinic or by that group of providers OR if the patient has not been seen in the past three years, they are considered a new patient. The patient is considered an established patient if they have received a professional service from provider in same group within last three years. 13. Identify the 3 components required in determining an outpatient, office visit E&M code 1. Place of service 2. Type of service 3. Patient status This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 05-03-2022 03:54:06 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/36085533/NR511-Week-1-Exam-Study-Guide-docx/ 14. Explain what a “well rounded” clinical experience means Includes seeing kids from birth through young adult visits for well child and acute visits, as well as adults for wellness or acute/routine visits. Seeing a variety of patients, including 15% of peds and 15% of women’s health of total time in the program. 15. State the maximum number of hours that time can be spent “rounding” in a facility No more than 25% of total practicum hours in the program 16. State 9 things that must be documented when inputting data into clinical encounter 1. Date of service 2. Age 3. Gender/ethnicity 4. Visit E&M code 5. Chief Complaint 6. Procedures 7. Tests performed/ordered 8. Diagnosis 9. Level of involvement (mostly student, mostly preceptor, together, etc.) 17. Identify and explain each part of the acronym SNAPPS S-Summarize-present the patient’s H&P findings N-Narrow-based on the H&P findings, narrow down to the top 2-3 differentials A-Analyze-analyze the differentials. Compare and contrast H&P findings for each of the differentials and narrow it down to the most likely one P-Probe-ask the preceptor questions of anything you are unsure of P-Plan-come up with an specific management plan S-Self-directed learning-an opportunity to investigate more about any topics that you are uncertain of [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 03, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 03, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
80