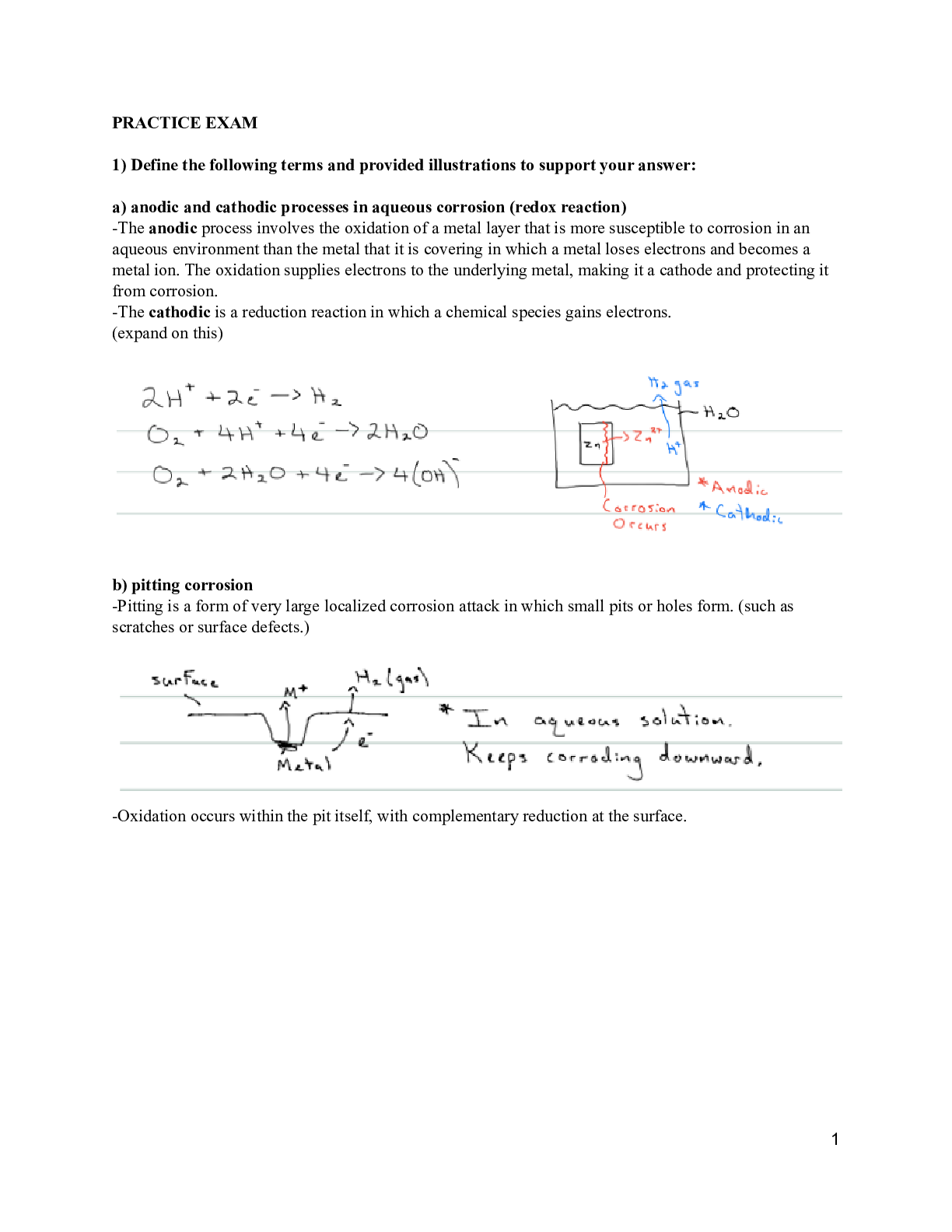
*NURSING > Final Exam Review > Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507 Final Exam Possible Questions A-Z (All)
Chamberlain College of Nursing - NR 507 Final Exam Possible Questions A-Z
Document Content and Description Below
NR 507 Final Exam Possible Questions A-Z 1. Acid base imbalance While checking arterial blood gas results, a nurse finds respiratory acidosis. What does the nurse suspect is occurring in the pa... tient? reduced tidal volumes A 20-year-old male is in acute pain. An arterial blood gas reveals decreased carbon dioxide (CO2 ) levels. Which of the following does the nurse suspect is the most likely cause? Hyperventilation The nurse is assessing a client with suspected respiratory acidosis. Which assessment items are priority for the nurse to collect? Rate and depth of respirations, Skin color and temperature, Appearance of the optic nerve o The nurse is administering sodium bicarbonate to the client with respiratory acidosis. The nurse understands that which is the primary goal of treatment for this client? Removing excess acids in blood The student nurse is assisting in the care for a client with acute respiratory acidosis. The nurse explains to the student nurse that the client's blood pH initially falls in the development of acute respiratory acidosis because of which process? Hypoventilation 2. ACTH The nurse is preparing a client for testing to determine if the client has Cushing syndrome. What tests are included in the screening process 24-hour urine secretion of cortisol Dexamethasone suppression test Plasma levels of ACTH A client comes to the clinic with fatigue and muscle weakness. The client also states she has been having diarrhea. The nurse observes the skin of the client has a bronze tone and when asked, the client says she has not had any sun exposure. The mucous membranes of the gums are bluish-black. When reviewing laboratory results from this client, what does the nurse anticipate seeing? Increased levels of ACTH A client is diagnosed with adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency (ACTH) and is to begin replacement therapy. Regarding which type of replacement will the nurse educate the client? Cortisol replacement therapy Following destruction of the pituitary gland, ACTH stimulation stops. Without ACTH to stimulate the adrenal glands, the adrenals' production of cortisol drops. This is an example of which type of endocrine disorder? Secondary The nurse is preparing a client for a test that will measure negative feedback suppression of ACTH. Which medication will the nurse administer in conjunction for this test? Dexamethasone ACTH deficiency results in secondary hypocortisolism ACTH deficiency is most commonly caused by? glucocorticoid withdrawal 6 symptoms of an ACTH deficiency tiredness weakness anorexia N/V hypoglycemia orthostatic hypotension interpretation of ACTH levels requires simultaneous assessment of plasma cortisol levels ACTH levels are normal to high in primary adrenal insufficiency ACTH levels are low to absent in secondary adrenal insufficiency The client has been taking an oral cortisol preparation for 2 years to manage an autoimmune disease. What effects does the nurse expect this therapy to have on this client's circulating levels of ACTH and aldosterone? Decreased ACTH, decreased aldosterone A nurse checks lab results as both Cushing syndrome and Addison disease can manifest with elevated levels of: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 3. Acute epiglottitis A caregiver calls the pediatrician's office and reports to the nurse that her 4-year-old, who was fine the previous day, complained of a sore throat early in the morning and now has a temperature of 102.6° F (39.2° C). The caregiver has tried to get the child to nap but the child gets panicky, immediately sits back up, and leans forward with her mouth open and tongue out when the caregiver encourages her to lie down. The nurse suspects the child has which of the following conditions? Epiglottitis The caregivers of a child report that their child had a cold and complained of a sore throat. When interviewed further they report that the child has a high fever, is very anxious, and is breathing by sitting up and leaning forward with the mouth open and the tongue out. The nurse recognizes these symptoms as those seen with which of the following disorders? Epiglottitis The nurse is caring for a 5-year-old girl who shows signs and symptoms of epiglottitis. The nurse recognizes a common complication of the disorder is for the child to: be at risk for respiratory distress. A 5-year-old child is brought to the clinic by his father because the child developed a high fever over the past 2 to 3 hours. The nurse suspects epiglottitis based on which signs and symptoms? • Difficulty speaking • Drooling • Sitting with neck extended • Frightened appearance 4. AIDS A 36-year-old man enters the hospital in an extremely debilitated condition. He has purple-brown skin lesions (a symptom of Kaposi's sarcoma) and a persistent cough. A physical examination reveals swollen lymph nodes, and laboratory tests find a very low lymphocyte count. Information taken during the personal history reveals that he has multiple sex partners with whom he frequently engages in unprotected sex. What is likely to be the man's problem and what is his prognosis? He is probably suffering from AIDS. His outlook is poor once the disease has progressed to this advanced stage. There is no cure, and drug therapy has had limited short-term success. Why does nursing care of a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) include monitoring of T lymphocyte counts? A decrease in the number of T cells would make the patient more susceptible to infection and unusual cancers. What is the length of time from infection with the AIDS virus to seroconversion? Up to six months A 21-year-old woman diagnosed with HIV/AIDS 4 years ago now presents with cytomegalovirus. The nurse explains to the woman that the infection is caused by a common organism that normally does not cause infection in someone with a healthy immune system. This type of infection is called what? Opportunistic infection The nurse is caring for a client who has just been diagnosed with AIDS. The client asks the nurse, "How long will I live?" Which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse? "AIDS is considered to be a chronic illness today." Which of the following clients is at the greatest risk for developing an intracellular pathogen infection? An AIDS client with a decreased CD4+ TH1 count 5. Alveolar ventilation/perfusion A consequence of alveolar hypoxia is: Pulmonary artery vasoconstriction The pressure required to inflate an alveolus is inversely related to: Alveolus radius The nurse is describing the movement of blood into and out of the capillary beds of the lungs to the body organs and tissues. What term should the nurse use to describe this process? Perfusion A pulmonologist is discussing the base of the lungs with staff. Which information should be included? At the base of the lungs: Arterial perfusion pressure exceeds alveolar gas pressure When the pulmonologist discusses the condition in which a series of alveoli in the left lower lo be receive adequate ventilation but do not have adequate perfusion, which statement indicates the nurse understands this condition? When this occurs in a patient it is called: Alveolar dead space Which of the following conditions should the nurse monitor for in a patient with hypoventilation? hypercapnia A nurse is describing the pathophysiology of emphysema. Which information should the nurse include? Emphysema results in: the destruction of alveolar septa and air trapping. 6. Alzheimer’s disease A patient is admitted to the unit in the middle stages of Alzheimer's disease. How would the nurse expect to find the patient's state of mind? Unable to perform simple tasks When teaching the children of a patient who is being evaluated for Alzheimer's disease (AD) about the disorder, the nurse explains that a diagnosis of AD can be made only when other causes of dementia have been ruled out. The patient has been diagnosed with the mild cognitive impairment stage of Alzheimer's disease. What nursing interventions should the nurse expect to use with this patient? Use a calendar and family pictures as memory aids. A patient with Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia has manifestations of depression. The nurse knows that treatment of the patient with antidepressants will most likely do what? Improve cognitive function The wife of a patient who is manifesting deterioration in memory asks the nurse whether her husband has AD. The nurse explains that a diagnosis of AD is usually made when what happens? All other possible causes of dementia have been eliminated 7. Angiotensin-renin system The nurse recognizes that the action of angiotensin II is what? Vasoconstriction The nurse understands that aldosterone secretion is increased when the patient has what? Hyperkalemia With what does the nurse correlate the release of renin? Decreased renal perfusion What are the 2 most common causes that activate the RAAS system? Low cardiac output or low renal perfusion The goal of the RAAS system is to increase BP to thus help restore perfusion pressure to the kidneys 8. Antibodies, IgG, IgA, etc A patient has a parasite. Which lab report should the nurse check to help confirm this diagnosis? IgE If a patient has a typical secondary immune response, which antibody is most predominant? IgG. A mother is breastfeeding her infant. The nurse realizes the main antibody being transferred from the mother to her infant through the breast milk is: IgA When a person has a life-threatening hypersensitivity/allergic reaction to bee stings, which lab result will the nurse check IgE Which immunity principle should guide the nurse when caring for an infant? At birth, IgG levels in newborn infants are: near adult levels. While reviewing a patients' immunological profile, which immunoglobulin does the nurse expect to see elevated if the patient has a type I hypersensitivity reaction? IgE The antibody that becomes bound to mast cells and basophils and causes the cells to release histamine and other chemicals is IgE In teaching a patient with SLE about the disorder, the nurse knows that the pathophysiology of SLE includes the production of a variety of autoantibodies directed against components of the cell nucleus A patient is diagnosed with a hypersensitivity reaction mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. For which type of hypersensitivity reaction should the nurse plan care for this patient? Type 12 9. Autosomal dominant diseases A nurse is assessing a patient with an autosomal-dominant inherited condition. When discussing the risk of transmission to the patient's offspring, which of the following would the nurse include? Each child has a 50% risk of inheriting the gene. A client has an autosomal-dominant disorder. His wife is unaffected. When explaining the risk for inheritance of the disorder in their offspring, which statement by the nurse would be most appropriate? There is a 50% chance that each of your children will have the condition The daughter of a patient with Huntington disease has requested that she be tested for the disease even though she has no symptoms at this time. What type of test does the nurse anticipate the physician will order? Presymptomatic testing Which of the following risk factors have been linked to ovarian cancers? Select all that apply. Gene mutations BRCA-1 and BRCA-2, Nulliparity A late acting dominant disorder is: Huntington's chorea Huntignton's chorea is characterised by Disordered muscle movement and mental disorientation Dancing gait and bizarre grimacing are characteristics of: Huntignton's disease The RN is reading the chart of a new pt. at the genetic clinic. The chart notes that the pt., her brother, and her mother all have inherited a particular condition. The RN plans care for a condition with which of the following type of inheritance pattern? autosomal dominant 10. Bartholin glands A woman visits her primary care provider with a complaint of pain and swelling in the vagina area. The pain is present when she sits and walks intercourse is painful. The nurse prepares the patient for an examination. The nurse and health care provider suspect that the patient may have an inflammation or infection of the? Bartholin glands A patient has been diagnosed with a Bartholin gland cyst. The nurse expects the patient may experience which symptoms if this becomes infected? Pain, tenderness, and dyspareunia The female external genitalia are made up of several components. What is in the vestibule of the female external genitalia? Bartholin glands When performing a pelvic examination, the nurse observes a red swollen area on the right side of the vaginal orifice. The nurse would document this as enlargement of which of the following? Bartholin's gland 11. Bile salt deficiencies Clinical manifestations of bile salt deficiencies are related to poor absorption of: Fats and fat-soluble vitamins 12. Candidiasis exacerbation Samantha Velasquez, a 24-year-old preschool teacher, is being seen by the physician in the primary care group where you practice nursing. Over the past 2 months, she has been receiving treatment for multiple ear infections and tonsillitis. She reports a curdy white vaginal discharge and burning with urination. What is the most likely cause of her symptoms? Candida albicans A nurse is counseling a client about risk factors for yeast infections. Which of the following should the nurse list as a risk factor for an overgrowth of Candida albicans? Impaired immune system Decrease in amount of bacterial flora Antibiotic therapy 13. Carbuncles Localized skin infection involving hair follicles: carbuncles 14. Carcinoma A nurse is conducting a session on education about cancers of the reproductive tract and is explaining the importance of visiting a health care professional if certain unusual symptoms appear. Which should the nurse include in her list of symptoms that merit a visit to a health care professional for further evaluation Irregular vaginal bleeding, persistent low backache not related to standing, and elevated or discolored vulvar lesions are some of the symptoms that should be immediately brought to the notice of the primary health care provider The postmenopausal woman who has bleeding and spotting and cannot tolerate a endometrial biopsy in the office would expect to have which of the following tests done to rule out endometrial cancer? transvaginal ultrasound The nursing student correctly identifies which of the following to be the treatment of choice for endometrial cancer? hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy The nursing student correctly identifies which of the following age group to be when ovarian cancer occurs more frequently? 55-75 years of age Treatment for Stage IA (Microinvasive Carcinoma) is? Ia1: Vaginal hysterectomy. Cervical conization if the patient desires to maintain her fertility. An aide asks the nurse what is the most common cause of elevated levels of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion. How should the nurse respond? Cancer The nurse working with oncology clients understands that interacting factors affect cancer development. Which factors does this include? Genetic predisposition, Exposure to carcinogens, Immune function A nurse is providing community education on the seven warning signs of cancer. Which signs are included a sore that does not heal, indigestion or trouble swallowing, obvious changes in a mole. changes in bowel or bladder habbits, unusual bleeding or discharge, thickening of lump in breast or elsewhere, nagging cough or hoarseness The nursing instructor explains the difference between normal cells and benign tumor cells. What information does the instructor provide about these cells? Growing in the wrong place or time is typical of benign tumors. The nursing student learning about cancer development remembers characteristics of normal cells. Which characteristics does this include? Nonmigratory, Specific morphology, Differentiated function The student nurse caring for clients who have cancer understands that the general consequences of cancer include which client problems? reduced immunity and blood-producing functions, altered GI structure and function, decreased respiratory function, motor and sensory deficits 15. Cervical dysplasia The nurse is caring for a woman who has dysplasia (disordered growth of abnormal cells). The nurse educates her on dysplasia progression that is high-grade. Which of the following information is important for the nurse to include? With cervical cancer, lesions start as dysplasia and progress over a period of time. Progression of a high-grade dysplasia takes about 2 years to develop into an invasive cancer Prime etiologic factor in the development of dysplasia Human Papilloma Virus Cervical dysplasia and cancer is relatively rare before .... years of age, and the mean age is about .... years. Rare before 25, mean age is 47. After speaking with the RN, Mrs. Sailor understands that the endocervical biopsy will be done by cervical conization to allow for microscopic examination of the cervical tissue. She is scheduled for cervical conization in 2 day. How should the RN respond to the client? Ask the client about her understanding of the abnormal pap smear result How often should a Pap and HPV be done All women begin screening for cervical cancer at 21 ->21-29 Pap test every 3 years, HPV unnecessary unless needed following an abnormal Pap test ->30-65 Pap and HPV every 5 years ->Older than 65 May discontinue testing if regular screenings have been negative, If diagnosed with cervical pre-cancer, continue to screen. 16. Cervical immunoglobulin A woman who is 22 weeks pregnant has a vaginal infection. She tells the nurse that she is afraid that this infection will hurt the fetus. The nurse knows that which of these statements is true? A thick mucus plug forms that protects the fetus from infection. 17. Chicken pox An older adult client tells the nurse that her granddaughter has chickenpox. The client is afraid to visit because she is afraid of getting shingles from her granddaughter. What is the nurse's best response? "If you already had chickenpox, you can safely visit your granddaughter." The nurse counsels the parent of a 12 year old diagnosed with chickenpox about when the child can return to school. The nurse determines that teaching is effective if the parent makes which statement? My child can return to school when the lesions are crusted A parent calls the clinic to report that the child has been exposed to varicella zoster (chicken pox). The nurse should tell the parent that the incubation period for chickenpox is which length of time? 2-3 weeks 18. Chronic inflammatory joint disease In assessing the joints of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis, the nurse understands that the joints are damaged by bony ankylosis following inflammation of the joints invasion of pannus into the joint causing a loss of cartilage Assessment data in the patient with osteoarthritis commonly include joint pain that worsens with use The nurse is working with a 73-year-old patient with osteoarthritis (OA). In assessing the patient's understanding of this disorder, the nurse concludes teaching has been effective when the patient describes the condition as which of the following Degeneration of articular cartilage in synovial joints A 60-year-old woman has pain on motion in her fingers and asks the nurse whether this is just a result of aging. The best response by the nurse includes the information that changes in the cartilage and bones of joints may cause symptoms of pain and loss of function in some people as they age The basic pathophysiologic process of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an immune response that activates complement and produces inflammation of joints and other organ systems During the physical assessment of the patient with moderate RA, the nurse would expect to find spindle-shaped fingers After teaching a patient with RA about the prescribed therapeutic regimen, the nurse determines that further instruction is needed when the patient says, I should perform most of my daily chores in the morning when my energy level is highest A 70-year old patient is being evaluated for symptoms of RA. The nurse recognizes that a major problem in the management of RA in the older adult is that drug interactions and toxicity are more likely to occur with multidrug therapy 19. Clonal selection When a nurse uses the term clonal diversity, what is the nurse describing? The ability of the population of lymphocytes to recognize almost any antigenic molecule Which of the following statements indicates the nurse has a good understanding of clonal selection? Lymphocytes that can recognize and react to a specific antigen proliferate. Cytokines that stimulate bone marrow pluripotent stem and progenitor or precursor cells to produce large numbers of platelets, erythrocytes, lymphocytes, neutrophils, and monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, and dendritic cells are known as: Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) 20. Complications of gastric resection surgery Care for the postoperative client after gastric resection should focus on which of the following problems? Nutritional needs Which of the following complications of gastric resection should the nurse teach the client to watch for? Dumping syndrome 21. Concept of pain The nurse is using the neuromatrix theory when determining a patient's pain. What should the nurse consider when assessing a patient's pain? cultural and genetic factors The patient complaining of pain has been waiting for medication to relieve the pain. What should the nurse understand about this patient? The patient's pain is real. The nurse is assessing a patient's pain perception. What should the nurse use to make this assessment? PQRST guide A patient is being treated for chronic pain. What should the nurse keep in mind when assessing this patient's level of pain? The pain rating may be inconsistent with the underlying pathology. A patient is seen talking and laughing in the clinic's waiting room yet complains of excruciating pain. What should the nurse realize this patient is demonstrating? inconsistent behavioral response to pain 22. Congenital heart defects The comment made by a parent of a 1-month-old that would alert the nurse about the presence of a congenital heart defect is: "He tires out during feedings." The nurse explains that which congenital cardiac defect(s) cause(s) increased pulmonary blood flow? Atrial septal defects (ASDs), Patent ductus arteriosus, Ventricular septal defects (VSDs) A newborn is diagnosed with a congenital heart defect (CHD). The test results reveal that the lumen of the duct between the aorta and pulmonary artery remains open. This defect is known as patent ductus arteriosus or PDA. Congenital heart defects (CHDs) are classified by which of the following? Defects with increased pulmonary blood flow, Defects with decreased pulmonary blood flow., Mixed defects, Obstructive defects. Hypoxic spells in the infant with a congenital heart defect (CHD) can cause which of the following? Polycythemia, Blood clots, Cerebrovascular accident, Developmental delays, Brain damage. A 6-month-old who has episodes of cyanosis after crying could have the congenital heart defect (CHD) of decreased pulmonary blood flow called tetalology of fallot or TOF While looking through the chart of an infant with a congenital heart defect (CHD) of decreased pulmonary blood flow, the nurse would expect which laboratory finding? Polycythemia. In which congenital heart defect (CHD) would the nurse need to take upper and lower extremity BPs? Coarctation of the aorta (COA). 23. Congenital intrinsic factor deficiency A newborn is diagnosed with congenital intrinsic factor deficiency. Which of the following types of anemia will the nurse see documented on the chart? Pernicious anemia A 35-year-old female is diagnosed with vitamin B12 deficiency anemia (pernicious anemia). How should the nurse respond when the patient asks what causes pernicious anemia? A decrease in intrinsic factor is the most likely cause. 24. Congenital murmurs While assessing a newborn with respiratory distress, the nurse auscultates a machine-like heart murmur. Other findings are a wide pulse pressure, periods of apnea, increased PaCO2, and decreased PO2. The nurse suspects that the newborn has: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). A 2-day-old infant was just diagnosed with aortic stenosis. What is the most likely nursing assessment finding? Heart murmur A newborn develops a murmur and cyanosis shortly after birth. She is diagnosed with pulmonic stenosis (PS) after an echocardiogram revealed narrowing of the pulmonary: Valve orifice 25. Consanguinity- most common types of relationships in a family 1.consanguineous 2. affinal 3. family of origin blood relationship: consanguineous What specific consequences are there for consanguinity 1. increased risk for AR disorders 2. increased risk of SB 3. increased risk for multifactorial and complex inheritance (ie., birth defects) 26. Croup The 3-year-old child is seen in the local clinic for croup. The child's parents ask the nurse what to do for the child at home to alleviate symptoms. Which suggestions by the nurse is most appropriate? "Stand with your child in front of an open freezer" The nurse is assessing a child with croup in the emergency department. The child has a sore throat and is drooling. Examining the child's throat using a tongue depressor might precipitate what condition? Complete obstruction The mother of a 20-month-old boy tells the nurse that he has a barking cough at night. His temperature is 37° C (98.6° F). The nurse suspects mild croup and should recommend which intervention? Provide fluids that the child likes and use comfort measures. A 3-year-old child woke up in the middle of the night with a croupy cough and inspiratory stridor. The parents bring the child to the emergency department, but by the time they arrive, the cough is gone, and the stridor has resolved. What can the nurse teach the parents with regard to this type of croup? A cool mist vaporizer at the bedside can help prevent this type of croup. 27. Dermatologic conditions e.g. pityriasis rosea The physician instructs a mother to take her child out in the sun for approximately an hour or until the skin turns red (not sunburned). This is a common medical treatment for Pityriasis Rosea The patient has a rash on her back that began about 10 days ago with a raised, scaly border and a pink center. Now she has similar eruptions on both sides of her back. From these signs, the nurse would determine the rash to be Pityriasis Rosea A 28-year-old client comes to the office for evaluation of a rash. At first there was only one large patch, but then more lesions erupted suddenly on the back and torso; the lesions itch. Physical examination reveals that the pattern of eruption is like a Christmas tree and that various erythematous papules and macules are on the cleavage lines of the back. Based on this description, what is the most likely diagnosis? Pityriasis rosea 28. Dermatology terminology-macules, nevi, etc The nurse's assessment shows that the patient has a solid, elevated, circumscribed lesion that is less than 1 cm in diameter. In the documentation the nurse would chart this as a Papule While waiting to see the physician, a patient shows the nurse skin areas that are flat, nonpalpable, and have had a change of color. The nurse recognizes that the patient is demonstrating what? macule A young student comes to the school nurse and shows the nurse a mosquito bite. As the nurse expects, the bite is elevated and has serous fluid contained in the dermis. How would the nurse classify this lesion? A wheal is a primary skin lesion that is elevated and has fluid contained in the dermis 29. Endogenous antigen When a patient asks what activates the immune response, how should the nurse respond? Molecules that are capable of inducing an immune response are called: antigens. A nurse is discussing an endogenous antigen. Which example indicates the nurse has a good understanding? The body's own tissue A nurse recalls the major histocompatibility class I (MHC I) antigens are found on which of the following cells? Red blood cells B lymphocytes and macrophages only Liver, heart, and bone marrow cells only While the nurse is discussing the immune system, which information should the nurse include? Plasma cells have the capacity to produce antibodies during an immune response. o Which cell is a patient missing if the patient's immune system cannot ingests microorganisms for the purposes of presenting their antigen to the immune system and activating an immune response? Macrophage A nursing student comes to the nurse with some questions about receptors. The student asks about the location of CD8 receptors. The nurse tells the student that these are located on: cytotoxic T cells. Which class of MHC proteins presents exogenous antigens? class II MHC proteins Class II MHC proteins are found on which of the following cell types? antigen-presenting cells Class I MHC proteins are recognized by which of the following cell types (that are destined to become T cells)? CD8 Which major class of lymphocytes become cytotoxic T cells? CD8 30. Folate deficiency The nurse recognizes that patients with which disorder are at greatest risk for folate deficiency? Alcoholism The nurse teaches the breastfeeding patient that the recommended daily allowance for folic acid is what? 500 mcg The nurse reviews the medications of a patient taking folic acid. The nurse notes that the patient is concurrently taking vitamin B12. This concerns the nurse because of the fact that folic acid may mask the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency. A person has an inadequate intake of folic acid (folate) what wil happen to this persons RBCs. impaired dna synthesis A 2-year-old malnourished child has vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies. A blood smear suggests the deficiency is macrocytic and normochromic. The nurse would expect the hemoglobin to be: Normal When a patient wants to know why vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies cause anemia, how should the nurse respond? Red blood cells have a shorter life span 31. Gastroesophageal reflux disease A patient comes to the clinic complaining of heartburn after meals and is diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Which dietary instructions should the nurse include in teaching? The patient should limit caffeinated foods and drinks, decrease fat intake, eat four to six small meals per day, and remain upright for 1 to 2 hours after each meal. Which of the following terms refers to the symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) which is characterized by a burning sensation in the esophagus? Pyrosis A patient describes a burning sensation in the esophagus, pain when swallowing, and frequent indigestion. What does the nurse suspect that these clinical manifestations indicate? Gastroesophageal reflux disease A 50-year-old male is experiencing reflux of chyme from the stomach. He is diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux. This condition is caused by: Loss of muscle tone at the lower esophageal sphincter 32. General adaptation syndrome Increased blood volume, heart rate, blood glucose levels, and increased mental alertness occur during which part of the general adaptation syndrome (GAS)? ALARM STAGE While assessing a person for effects of the general adaptation syndrome, the nurse should be aware that: Glucose level increases during the alarm reaction stage A client with cancer has recovered from tumor removal surgery and is now stable while undergoing a chemotherapy treatment schedule. She is not having any symptoms at this time and is continuing to work and enjoy social events. What stage of the general adaptation syndrome (GAS) would you place her in? Resistance 33. Genetic disorders such as Down Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, etc Which type of genetic test would be used to detect the possibility of Down syndrome? Chromosomal analysis The nurse is obtaining health history from a client with a genetic disorder. Which of the following would be most appropriate for the nurse to establish the pattern of inheritance? Construct a pedigree of the client's family. The nurse is assessing a child with Turner syndrome. The nurse anticipates which of the following findings? Short stature The nurse is working with a mother whose unborn child was diagnosed as having Down syndrome. The nurse explains to the mother that Down syndrome occurs due to which of the following? Chromosome nondisjunction Parents request that a test be done to determine if the fetus has Down syndrome. What type of test does the nurse anticipate the physician will order? Prenatal screening Nondisjunction of a chromosome results in which of the following diagnoses? Down syndrome Match the condition with chromosomal abnormlity or linkage. Klinfelter's syndrome-- 44 + XXY Trisomy 21 is otherwise called: Down's syndrome Down's syndrome is due to: An extra chromosome In Down's syndrome, the chromosome number in each cell is: 47 The risk of Down's syndrome in offsprings is high to mothers at the age of: 35 years Persons with Klinfelter's syndrome have chromosomes: 47 Turner's syndrome is characterised by chromosomes: 45 A person having Klinfelter's syndrome is characterised by: Male with some secondary sexual characters of female 34. Genital warts During an external genitalia examination of a woman, the nurse notices several lesions around the vulva. The lesions are pink, moist, soft, and pointed papules. The patient states that she is not aware of any problems in that area. The nurse recognizes that these lesions may be: human papillomavirus (HPV), or genital warts. A woman has just been diagnosed with HPV, or genital warts. The nurse should counsel her to receive regular examinations because this virus makes her at a higher risk for cervical During a health history, a 22-year old woman asks, "Can I get that vaccine for HPV? I have genital warts and I'd like them to go away!" What is the nurse's best response? "The vaccine cannot protect you if you already have an HPV infection." a patient with an STD who is most likely to have a nursing diagnosis of disturbed image that hinders future sexual relationships is the patient with genital warts it is most important for the nurse to teach the female patient with genital warts to have an annual Pap smear A female client has just been diagnosed with condylomata acuminata (genital warts). What information is appropriate to tell this client? This condition puts her at a higher risk for cervical cancer; therefore, she should have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear annually 35. GI symptoms of conditions such as pyloric stenosis, hiatal hernia, ulcerative colitis The nurse explains to the patient with gastroesophageal reflux disease that this disorder: often involves relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach contents to back up into the espophagus The client with a hiatal hernia chronically experiences heartburn following meals. The nurse planc to teach the client to avoid which action because it is contraindicated with hiatal hernia? Lying recumbent following meals The client is diagnosed with an acute exacerbation of ulcerative colitis. Which inter- vention should the nurse implement? Monitor intravenous fluids. Which of the following factors would most likely contribute to the development of a client's hiatal hernia? . The client asks the nurse whether he will need surgery to correct his hiatal hernia. Which reply by the nurse would be most accurate? "Hiatal hernia symptoms can usually be successfully managed with diet modifications, medications, and lifestyle changes." A client with ulcerative colitis (UC) has stage 1 of a restorative proctocolectomy with ileo-anal anastomosis (RPC-IPAA) procedure performed. The client asks the nurse, "How long do people with this procedure usually have a temporary ileostomy?" How does the nurse respond? "It is usually ready to be closed in about 1 to 2 months." The nurse is caring for a patient with fulminant ulcerative colitis. The nurse would be alert for which of the following symptoms associated with severe fulminant ulcerative colitis? Toxic megacolon, 10 or more bowel movements per day, Bowel perforation,Anemia Which of the following clients would the nurse suspect to have pyloric stenosis? A 5-week-old infant with projectile vomiting A 3-week-old infant diagnosed with pyloric stenosis is admitted to the hospital during a vomiting episode. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate? position on right side Which of the following conditions can cause a hiatal hernia? Weakness of the diaphragmic muscle 36. GI symptoms resulting in heart burn The nurse is performing an admission assessment on a client diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Which signs and symptoms would indicate GERD? Pyrosis, water brash, and flatulence The male client tells the nurse he has been experiencing "heartburn" at night that awakens him. Which assessment question should the nurse ask? What have you done to alleviate the heartburn? The nurse is obtaining a health history from a client who has a sliding hiatal hernia associated with reflux. The nurse should ask the client about the presence of which of the following symptoms? Heartburn. Which of the following symptoms is common with a hiatal hernia? Esophageal reflux 37. Glaucoma A client has just been diagnosed with early glaucoma. During a teaching session, the nurse should: demonstrate eyedrop instillation The nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client with glaucoma. Which of the following would alert the nurse to suspect that the client was at increased risk for this disorder? Prolonged use of corticosteroids Which of the following types of glaucoma presents an ocular emergency? acute angle-closure glaucoma The nurse is performing an assessment of the visual fields for a patient with glaucoma. When assessing the visual fields in acute glaucoma, what would the nurse expect to find? Marked blurring of vision A 52-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a follow-up examination after being diagnosed with glaucoma. The client states, "I'm hoping that I don't have to use these drops for very long." Which response by the nurse would be most appropriate? You'll need to use the drops for the rest of your life to control the glaucoma A patient visits a clinic for an eye examination. He describes his visual changes and mentions a specific diagnostic clinical sign of glaucoma. What is that clinical sign? The presence of halos around lights 38. Glomerulonephritis A 15-year-old male was diagnosed with pharyngitis. Eight days later he developed acute glomerulonephritis. While reviewing the culture results, which of the following is the most likely cause of this disease? Group A B-hemolytic streptococcus When a nurse observes post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis as a diagnosis on a patient, which principle will the nurse remember? Acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis is primarily caused by? antigen –antibody complex deposition in the glomerular capillaries and inflammatory damage A 30-year-old male is demonstrating hematuria with red blood cell casts and proteinuria exceeding 3 to 5 g/day, with albumin being the major protein. The most probable diagnosis the nurse will see documented on the chart is? Acute glomerulonephritis A 15-year-old female presents with flank pain, irritability, malaise, and fever. Tests reveal glomerulonephritis. When the parents ask what could have caused this, how should the nurse respond? Post streptococcal infection Which of the following clusters of symptoms would make a clinician suspect a child has developed glomerulonephritis? Gross hematuria, flank pain and hypertension A 5-year-old male was diagnosed with glomerulonephritis. History reveals that he had an infection 3 week before the onset of this condition. The infection was most likely located in the Pharynx A 30-year-old male is demonstrating hematuria with red blood cell casts and proteinuria exceeding 3 to 5 g/day, with albumin being the major protein. The most probable diagnosis the nurse will see documented on the chart is? acute glomerulonephritis A 45-year-old male presents with oliguria. He is diagnosed with chronic glomerulonephritis. The nurse knows oliguria is related to? thickening of the glomerular membrane and decreased renal blood flow Which assessment finding is most important in determining nursing care for a client with acute glomerulonephritis? Blurred vision. Visual disturbances can be indicative of rising blood pressure in a client with acute glomerulonephritis. The nurse is assessing a child with acute post streptococcal glomerulonephritis. Which of the following would the nurse expect to assess? fatigue, lethargy, abdominal pain, hypertension, crackles, and anorexia. A 10-year-old child is diagnosed with glomerulonephritis. Test reveal the disposition of immunonoglobin IgA in the glomerular capillaries. The nurse will monitor for recurrent: Hematuria Glomerulonephritis is an autoimmune disease that severely impairs renal function. When reviewing laboratory results, the nurse should immediately notify the health care provider about which finding? Glomerular filtration rate of 20 mL/min 39. Glycoprotein ( this is the only one I COULD NOT FIND!!! 40. Gonococcal disease When counseling a woman who is having difficulty conceiving, the nurse will be most concerned about a history of infection with N. gonorrhoeae. When a patient returns to the clinic for follow-up after treatment for nongonococcal urethritis, a purulent urethral discharge is still present. When trying to determine the reason for the recurrent infection, which question is most appropriate for the nurse to ask the patient? "Were your sexual partners treated with antibiotics? A woman in the STD clinic tells the nurse that she is concerned she may have been exposed to gonorrhea by her partner. To determine whether the patient has gonorrhea, the nurse will plan to obtain a cervical specimen for an enzyme immunoassay (EIA). The nurse assesses a client in the family planning clinic. Which of the following statements, if made by a client, suggests to the nurse that the client has been exposed to gonorrhea? My boyfriend has a drip a female patient with a purulent vaginal discharge is seen at the outpatient clinic. The nurse would expect a diagnosis of gonorrhea to be treated with cefixime (Suprax) and doxycycline (Vibramycin) A 22-year-old male is being treated at a college health care clinic for gonorrhea. Which of the following teaching points should the nurse include in patient teaching? "While you're taking your antibiotics, you will need to abstain from participating in sexual activity or drinking alcohol." The client is single, admits to not using condoms during sexual intercourse, and has had multiple partners over the past year. Which of the following symptoms would alert the nurse to a possible gonorrheal infection? Dysuria, Abnormal uterine bleeding, Mild sore throat, Abnormal vaginal discharge A newborn is diagnosed with ophthalmic neonatorum. The nurse understands that this newborn was exposed to which infection? Gonorrhea 41. Guillain-Barre Syndrome patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome has experienced a sharp decline in vital capacity. What is the nurse's most appropriate action? prepare to assist with intubation. mechanical ventilation is required if the vital capacity falls, making spontaneous breathing impossible and tissue oxygenation inadequate nurse caring for a patient diagnosed with Guillain-Barré syndrome is planning care with regard to the clinical manifestations associated this syndrome. The nurse's communication with the patient should reflect the possibility of what sign or symptom of the disease Vocal paralysis Guillain-Barré syndrome is a disorder of the vagus nerve The nurse caring for a patient in ICU diagnosed with Guillain-Barré syndrome should prioritize monitoring for what potential complication Autonomic dysfunction potential complications that may develop include respiratory failure and autonomic dysfunction. nurse is teaching a patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome about the disease. patient asks how he can ever recover if demyelination of his nerves is occurring. the nurse's best response Guillain-Barré spares the Schwann cell, which allows for remyelination in the recovery phase of the disease." The nurse recognizes which pathophysiologic feature as a hallmark of Guillain-Barré syndrome? The immune system destroys the myelin sheath. The nurse correlates which clinical manifestation of Guillain-Barré syndrome as the most common? Progressive, ascending weakness and paresthesia In reviewing laboratory data on a client, the nurse correlates which findings with Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS)? Increased cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) protein level without increased cell count A nurse is caring for a client with Guillain-Barré syndrome who has been admitted to the intensive care unit. During the last 2 hours, the nurse notes that the client's vital capacity has declined to 12 mL/kg, and the client is having difficulty clearing secretions. Which is the nurse's priority action? Preparing the client for elective intubation A patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome asks the nurse what has caused the disease. In responding to the patient, the nurse explains that Guillain-Barré syndrome is due to an immune reaction that attacks the covering of the peripheral nerves. A 29 -year-old patient is hospitalized with the onset of Guillain-Barré syndrome. During this phase of the patient's illness, the most essential assessment for the nurse to carry out is performing constant evaluation of respiratory function Guillain-Barré syndrome is an autoimmune attack on the peripheral myelin sheath. Which of the following is an action of myelin? Speeds nerve impulse transmission 42. Hormonal regulation of calcium When evaluating the laboratory findings of a patient with decreased function of the anterior pituitary gland, the nurse would expect to find normal serum calcium levels. When teaching a patient with hypoparathyroidism about the disorder, the nurse explains that blood calcium levels are altered because the role of parathyroid hormone is to stimulate bone resorption and increase the calcium in the blood when blood calcium levels fall. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) has which effects on the kidney? Stimulation of calcium reabsorption and phosphate excretion Which serum laboratory result should the nurse monitor in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism? Calcium 43. Hypersensitivity reaction A patient had a hypersensitivity reaction involving the formation of antibodies against tissue-specific antigen. Which type of hypersensitivity reaction did the patient experience? type II A patient has a hypersensitivity reaction mediated by Tc cells. A nurse recalls that this type of hypersensitivity reaction is called: type IV The patient is having a reaction to a bee sting. Which type of hypersensitivity reaction does the nurse expect to see documented in the patient's chart? type I Which type of hypersensitivity reaction is characterized by the formation of antigen-antibody complexes deposited on vessel walls or in extravascular tissues? type III The nurse is interpreting a patient's positive tuberculin skin test. This finding is consistent with which type of hypersensitivity reaction? type IV A nurse is conducting a physical assessment on a patient. Which symptoms would indicate to the nurse that the patient experienced a type I hypersensitivity reaction? Rhinorrhea, watery eyes, and pruritus The nurse is concerned about the patient having tissue injury during type II hypersensitivity. Which mechanism provides the rationale for this concern? Autoantibody mediation of neutrophils with detoxication of their toxic substances contributes to tissue injury. The patient has a type IV hypersensitivity reaction. In planning care for this patient, the nurse should consider that this type of reaction is related to: delayed response Type IV hypersensitivity tissue effects are initiated by: the stimulation of cytotoxic T cells. Allergy is the most common type of immediate hypersensitivity. 44. Kidney stones A client presents to the emergency department complaining of a dull, constant ache along the right costovertebral angle along with nausea and vomiting. The most likely cause of the client's symptoms is: renal calculi. The nurse reviews a client's history and notes that the client has a history of hyperparathyroidism. The nurse would identify that this client most likely would be at risk for which of the following? Kidney stones Which of the following are appropriate interventions in the care of a patient diagnosed with renal calculi? Straining the client's urine • Addressing the client's pain • Keeping track of intake and output A nurse is administering medications to a patient with a kidney stone. Which medication does the nurse administer that will lower urinary calcium by increasing tubular reabsorption to decrease the amount of calcium in the urine? Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) Which of the following is a nonsurgical method of treatment for renal calculi (kidney stones)? Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) A patient is being treated with colchicine (Colcrys) for pain in the big right toe. The patient begins to complain of severe right flank pain and is diagnosed with kidney stones. Which of the following types of kidney stones does the nurse recognize this patient is most likely affected by? Uric acid A patient has chronic hyperparathyroidism. Which complication should the nurse monitor for in the patient? Renal calculi (stones) While planning care for a patient with renal calculi, the nurse remembers the most important factor in renal calculus formation is: urine PH 45. Lactose intolerance During the nursing assessment a patient reveals that he has diarrhea and cramping every time he has ice cream. He attributes this to the cold nature of the food. However, the nurse begins to suspect that these symptoms are associated with: Lactose intolerance. A client receiving enteral feedings develops abdominal distention and diarrhea shortly after initiation of the feedings. In review of the nursing history for this client, which of these notations indicates the need to notify the health care provider? Lactose intolerance since childhood The nurse is working with a client with lactose intolerance. What can this nurse suggest to this client to increase tolerance to small amounts of milk? Consume milk with food. People who have lactose intolerance suffer from bloating, gas, and diarrhea. What type of diarrhea is caused by lactose intolerance? Osmotic diarrhea 46. Large bowel obstruction The nurse is taking a health history of a newly admitted patient with a diagnosis Rule/out bowel obstruction. Which of the following is the priority question to ask the patient? When was the last time you moved your bowels You are admitting a patient with complaints of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. A bowel obstruction is suspected. You assess this patient for which anticipated primary acid-base imbalance if the obstruction is high in the intestine? Metabolic alkalosis 47. Loss of language and/or comprehension-such as terms-aphasia, etc. The nurse is planning health teaching for a 65-year-old woman who has had a cerebrovascular accident (stroke) and has aphasia. Which of these questions is most important to use when assessing mental status in this patient? Please point to articles in the room and parts of the body as I name them. The nurse discovers speech problems in a patient during an assessment. The patient has spontaneous speech, but it is mostly absent or is reduced to a few stereotypical words or sounds. This finding reflects which type of aphasia? Global The nurse is caring for a patient with dysphagia. Which of the following interventions would be contraindicated while caring for this patient? Placing food on the affected side of mouth The nurse is caring for a patient with aphasia. Which of the following strategies will the nurse use to facilitate communication with the patient? Establishing eye contact A patient has been diagnosed as having global aphasia. The nurse recognizes that the patient will be unable to do which of the following actions? Form words that are understandable or comprehend the spoken word A patient with a cerebrovascular accident (stroke) has left-sided flaccidity and is unable to speak but seems to understand everything the nurse says. Which term should the nurse use to document the patient's communication impairment Expressive aphasia A patient tells the nurse that at times it seems like the mouth muscles do not want to work and the patient's speech is slurred. What should the nurse realize that the patient is describing? Dysarthria 48. Lupus A 26-year-old woman has been diagnosed with early systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) involving her joints. In teaching the patient about the disease, the nurse includes the information that SLE is a(n): Disorder of immune function, but it is extremely variable in its course, and there is no way to predict its progression. A patient with polyarthralgia with joint swelling and pain is being evaluated for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The nurse knows that the serum test result that is the most specific for SLE is the presence of: Anti-Smith antibody (Anti-Sm). A client is suspected of having systemic lupus erythematous. The nurse monitors the client, knowing that which of the following is one of the initial characteristic sign of systemic lupus erythematous? Rash on the face across the bridge of the nose The nurse is assigned to care for a client with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The nurse plans care knowing that this disorder is: An inflammatory disease of collagen contained in connective tissue 49. Male and female sex hormone production The nurse is conducting a prenatal class for expectant parents on conception. The nurse provides additional teaching when a parent states which of the following? Reproductive cells are formed through mitosis A human male produces sperms with genotypes AB, Ab, aB, and ab in equal proportions. What is the genotype of the person? Aa Bb Females seldom become bald as they lack: Male sex chromosome A 30-year-old female patient was brought to the emergency department (ED) after a seizure at work. During the assessment she mentions hair loss and menstrual irregularities. What diagnostic tests would be helpful to determine if endocrine problems are a cause of her problem Luteinizing hormone (LH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head Which hormone is best described by "tropic hormone that stimulates the gonads to secrete sex hormones"? luteinizing hormone The external and internal female reproductive organs develop and mature in response to what hormones? Estrogen and progesterone Ovarian hormones include which of the following? Estrogens, progesterone, testosterone The nurse working with pediatric clients knows that the primary hormone secretions that induce puberty include which of the following? Follicle-stimulating hormone Leuteinizing hormone Gonadotropin-releasing hormones 50. Maternal immune system If a patient has a typical secondary immunity response, which antibody is most predominant IgG A mother is diagnosed with a bacterial infection and is worried that her newborn infant will also contract the infection. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching plan for the client? Your newborn has maternal IgG antibodies that were transferred through the placenta before birth, providing some protection from infection. The laboratory finds IgA in a sample of cord blood from a newborn infant. This finding is important because it signifies what? Fetal reaction to exposure to an intrauterine infection A woman experiences a viral infection while pregnant. Which of the following types of immunity does an infant have at birth against this infection? Passive The nurse is aware that the only class of immunoglobulins to cross the placenta is: IgG 51. Nephrotic syndrome A urologist is discussing nephritic syndrome. Which information should be included? If nephrotic syndrome is not caused initially by kidney disease, it is termed ____ nephrotic syndrome?Secondary A 4-year-old male is diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following assessment findings accompanies this condition? Proteinuria A 7-year-old female is diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following should the nurse ask the parents if they or the child has noticed recently? Frothy urine Nephrotic syndrome occurs when there is loss of _____ in the urine. Protein Secondary forms of nephrotic syndrome are associated with all of the following conditions except: Hyperthyroidism Which of the following diseases is a glomerular disorder? Nephrotic syndrome Which assessment finding is common in children diagnosed with nephrotic syndrome? Periorbital edema A child is getting a diagnostic work-up for nephrotic syndrome. Which of the following lab results would the nurse expect to see? Proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and hypercholesterolemia are diagnostic of a child with nephritic syndrome. The child will also present symptomatically with a sudden onset of edema. Hematuria is typically seen with glomerulonephritis. 52. Neural tube defect The nurse clarifies to the parents of a child with spina bifida that their child has a portion of the spinal cord in the sac in addition to the meninges. This type of spina bifida is known as a(n) meningomyelocele How are neural tube defects detected before delivery? 1. AFP (maternal alpha fetoprotein) levels 2. Level II Ultrasound 3. Amniocentesis How are neural tube defects prevented? Folic Acid Where do neural tube defects occur? occur anywhere in the brain or spinal cord How are neural tube defects detected? via a ultra sound 53. Obstructive sleep apnea When assessing a client for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), the nurse understands the most common symptom is: Excessive daytime sleepiness The nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing sleep apnea. The nurse understands that which elements occur when a client has sleep apnea? Carbon dioxide retention will cause the pH to decrease and respiratory acidosis to develop. The patient is diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. Identify the symptoms you would expect the client to exhibit. Daytime fatigue, Snoring The nurse knows the following risk factors are associated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) Deviated septum, recessed chin, alcohol use, large neck 54. Pancreatic enzymes The nurse understands which of the following is the principal reason for the use of enzyme inhibitors (Diamox) in a patient with pancreatitis? Pancreatic enzymes escape into interstitial tissue The nurse is administering a pancreatic enzyme to the client diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis. Explain the rationale for this. In pancreatitis, the enzymes become activated while still in the pancreas. This causes the enzymes to irritate the cells of your pancreas, causing inflammation and the signs and symptoms associated with pancreatitis. Of the following enzymes, which one is responsible for the breakdown of starch? Amylase The nurse is reviewing with a client the digestive pathway. The steps involved in the digestive pathway are in random order. The nurse asks the client to place them in the correct sequence. Which does the client say are the correct sequences of steps involved in the digestive pathway? The physical breakdown of food is accomplished by the process of mastication The process of churning the food takes place in the pylorus of the stomach The chemical breakdown of food occurs by the release of various enzymes Dilution of the food entering the digestive tract is accomplished by water and various enzymes. Absorption of the dissolved molecules occurs in the small intestine. The molecules are then taken into circulation Most digestive processes occur in the small intestine. The nurse is reviewing with a client who has had gastrointestinal surgery that these intestinal enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, which promote and speed up chemical reactions. Based on this information, which enzyme would be the best response from the client about the enzymes that are responsible for facilitating the formation of proteins into amino acids- pepsin and trypsin Which of the following processes breaks up food into absorbable nutrients? Digestion Which of the following begins the digestive process? Saliva An instructor is describing the action of pancreatic enzymes on substances. Which of the following would the instructor include as being acted on by these enzymes? Sugars Proteins Fats After reviewing the process of secretion, a group of students demonstrate understanding when they identify which pancreatic enzyme as being secreted to break down sugars? Amylase High levels of acid in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract decrease the secretion of which of the following enzymes? Gastrin A 22-year-old male exercises by swimming laps. Which organ secretes enzymes responsible for the digestion of carbohydrates to provide energy? Pancreas 55. Pancreatic insufficiency A nurse has admitted a client suspected of having acute pancreatitis. The nurse knows that mild acute pancreatitis is characterized by: Edema and inflammation student nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client with chronic pancreatitis. What nursing diagnosis related to the care of a client with chronic pancreatitis is the priority? Impaired nutrition: less than body requirements Increased appetite and thirst may indicate that a client with chronic pancreatitis has developed diabetes melitus. Which of the following explains the cause of this secondary diabetes? Dysfunction of the pancreatic islet cells The nurse, interviewing a patient with acute pancreatitis, expects what finding in the patient's history? Diabetes mellitus 56. Parts of the heart in terms of function, such as pericardium How does the nurse differentiate a pleural friction rub from a pericardial friction rub? Have the patient hold his or her breath; if the rub persists, it is pericardial A 52-year-old female is admitted to the cardiac unit with a diagnosis of pericarditis. She asks the nurse to explain where the infection is. In providing an accurate description, the nurse states that the pericardium is: A membranous sac that encloses the heart A nurse is explaining the function of the heart. Which is a correct response by the nurse? A function of the pericardium is to: Provide a barrier against extracardial infections. A nurse is teaching about the heart. Which information should the nurse include? The chamber of the heart that generates the highest pressure is the: Left ventricle A nurse recalls the chamber that receives blood from the systemic circulation is the: Right atrium Which statement indicates the nurse understands blood flow? Oxygenated blood flows through the: Pulmonary veins While viewing the electrocardiogram, the nurse recalls the bundle of His conducts action potentials down the atrioventricular septum. 57. Pituitary hormone secretion Which hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland? Prolactin, growth hormone, gonadotropic hormone, melanocyte- stimulating hormone, TSH, ACTH When educating a group of students about the pituitary hormones, which should the nurse identify as the function of vasopressin? Stimulates contraction of blood vessels The nurse is explaining to the nursing students the relationship between "releasing" hormones and "inhibiting" hormones. What is the best answer by the nursing students of which part of the body is responsible for releasing hormones that either inhibit release or promote release of other hormones from the anterior lobe of the pituitary? Hypothalamus A 22-year-old patient is being seen in the clinic with increased secretion of the anterior pituitary hormones. The nurse would expect the laboratory results to show Increased urinary cortisol. A client thought to have a problem with the pituitary gland is given a stimulation test using insulin. A short time later, blood analysis reveals elevated levels of growth hormone (GH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Which is the nurse's interpretation of this finding? A normal pituitary response to insulin 58. Process of muscle contraction The nurse encourages the patient to do his own activities of daily living such as bathing, eating, dressing, and toileting activities. How do these activities promote physical conditioning: These activities are isotonic exercises in which muscle tension is constant and then shortens to produce muscle contraction and movement. Because the muscles contract, the shape, size, and strength of the muscles are maintained as well as joint mobility A patient is admitted for electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). The physician orders the neuromuscular blocking agent succinylcholine to reduce trauma by relaxing skeletal muscles. Explain the process of muscle contraction and how a neuromuscular blocking agent such as succinylcholine would interfere with muscle contraction. Muscle contraction begins with a stimulus to the nerve. When the impulse reaches the neuromuscular junction, depolarization occurs, resulting in an influx of calcium ions from the extracellular fluid into the terminals, which then release a neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), into the cleft. The ACh combines with receptor sites on the postjunctional muscle cell membrane, depolarizing it and facilitating the entry of sodium. Neuromuscular blocking agents act at the motor end plate by competing with the ACh for the receptor sites, or by blocking depolarization. While assessing a patient, the patient tells the nurse that she is experiencing rhythmic muscle contractions when the nurse performs passive extension of her wrist. What is this pattern of muscle contraction referred to as? Clonus 59. Pulmonary terminology such as dyspnea, orthopnea, etc A patient has dyspnea upon lying down. What term should the nurse use to document this finding? orthopnea A patient has dyspnea. Which of the following typical findings will the nurse observe during the assessment? difficulty breathing A 10-year-old female develops pneumonia. Physical exam reveals subcostal and intercostal retractions. She reports that breathing is difficult and she feels she cannot get enough air. What term should the nurse use to document this condition? Dyspnea 60. Risk factors for hypertension What target cultural population is a priority for the nurse to educate about prevention of hypertension? African Americans An older African-American client with hypertension is admitted to the hospital. Which data from the client's history and diagnostic workup represent risk factors for hypertension Occasional cocaine use African-American heritage What significant risk factor for hypertension does the student nurse identify for Mr. Dunn according to this health history? Alcohol consumption The student nurse continues to talk with Mr. Dunn about hypertension. Mr. Dunn states he feels physically and does not see why he needs to see his healthcare provider. How should the student nurse respond? While often there are no symptoms, high blood pressure does cause damage to many organs What information obtained during the assessment supports this diagnosis (stage 2, primary [essential] hypertension)? Blood pressure of 184/98 He asks, "shouldn't the healthcare provider find out why I have hypertension?" How should the nurse respond to Mark's question? 90-95% of all cases of hypertension are without an identified cause, so unless there is some indicator in you health history, the healthcare provider does not look for one A nurse takes an adult patient's blood pressure and determines it to be normal. What reading did the nurse obtain? Systolic pressure less than 120 mm Hg and diastolic pressure less than 80 mm Hg Most cases of combined systolic and diastolic hypertension have no known cause and are documented on the chart as primary hypertension. 50-year-old obese male with hypertension and coronary artery disease visits a nutritionist for food counseling. He has an elevated level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and a low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Which of the following should the nurse advise him to avoid? Trans fats A 65-year-old male with a history of untreated hypertension is now experiencing left heart failure. A nurse recalls his untreated hypertension led to: Myocardial hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling A 30-year-old Caucasian female was recently diagnosed with primary hypertension. She reports that she eats fairly well, usually having red meat and potatoes daily. She also reports that her father has hypertension as well. A nurse determines which of the following risk factors is most likely associated with this diagnosis? Genes A 52-year-old male is diagnosed with primary hypertension. He has no other health problems. Present treatment would cause the nurse to anticipate administering which drug to the patient? A diuretic A 55-year-old female has undiagnosed hypertension. She presents to her primary care provider reporting impaired vision and chronic edema. Lab tests reveal that she also has renal insufficiency. While planning care, the nurse realizes the most likely cause for these findings is: End-organ damage A nurse monitors the patient for encephalopathy when rapid onset of malignant hypertension results. A nurse is teaching an adolescent about primary hypertension. Which statement made by the adolescent indicates an understanding of primary hypertension? Primary hypertension may be treated with weight reduction. 61. Signs of breast cancer A client is at risk for breast cancer. Which of the following would reflect the client's genotype for this disorder? carrier of BRCA1 mutation A 32-year-old patient has just been told that she has the BRCA1 hereditary breast cancer gene mutation. What is her risk of developing cancer by the age of 65 years? 80% The nurse is reviewing statistics regarding breast cancer. Which woman, aged 40 years in the United States, has the highest risk for development of breast cancer? African-American The nurse is preparing for a class in early detection of breast cancer. Which statement is true with regard to breast cancer in African-American women in the United States? African-American women are more likely to die of breast cancer at any age. The nurse is reviewing risk factors for breast cancer. Which of these women have risk factors that place them at a higher risk for breast cancer? 65-year-old whose mother had breast cancer A 43-year-old woman is at the clinic for a routine examination. She reports that she has had a breast lump in her right breast for years. Recently, it has begun to change in consistency and is becoming harder. She reports that 5 years ago her physician evaluated the lump and determined that it "was nothing to worry about." The examination validates the presence of a mass in the right upper outer quadrant at 1 o'clock, approximately 5 cm from the nipple. It is firm, mobile, nontender, with borders that are not well defined. The nurse's recommendation to her is: "Because of the change in consistency of the lump, it should be further evaluated by a physician. A 54-year-old man comes to the clinic with a "horrible problem." He tells the nurse that he has just discovered a lump on his breast and is fearful of cancer. The nurse knows that which statement about breast cancer in males is true? One percent of all breast cancer occurs in men. The nurse is assessing the breasts of a 68-year-old woman and discovers a mass in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. When assessing this mass, the nurse keeps in mind that characteristics of a cancerous mass include which of the following? Nontender mass Hard, dense, and immobile Irregular,poorly delineated border A 26-year-old female presents to the health care clinic for a yearly pap & physical exam. She tells the nurse that she has felt a few tender areas in the left breast that are only occasionally palpable. She drinks about 3 cups of coffee daily and an occasional soft drink with caffeine. Family history reveals a maternal aunt with breast cancer at age 75 years. Which nursing diagnosis can be confirmed from this data? Ineffective health maintenance While interviewing a client, a nurse asks the client whether she has ever noticed any lumps or swelling in the breasts. What other area associated with the possible risk for breast cancer should she ask about regarding the presence of lumps or swelling? Underarm During the physical examination of a female client, the nurse notes that the client's axillary lymph nodes are enlarged, hard, and fixed. The nurse recognizes that these findings are consistent with what disease process? Malignancy A 63-year-old nurse comes to the office upset because she has found an enlarged lymph node under her right arm. She states she found it last week while taking a shower. She isn't sure if she has any breast lumps because she doesn't know how to do self-breast examinations. She states her last mammogram was 5 years ago and it was normal. Her past medical history is significant for high blood pressure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. She quit smoking 2 years ago after a 55-pack a year history. She denies any illegal drugs and drinks alcohol rarely. Her mother died of a heart attack and her father died of a stroke. She has no children. Examination shows an older woman appearing her stated age. Visual inspection of her right axilla reveals nothing unusual. Palpation reveals a 2-cm hard fixed lymph node. She denies any tenderness. Visualization of both breasts is normal. Palpation of her left axilla and breast is unremarkable. On palpation of the right breast, the nurse detects a nontender 1-cm lump in the tail of Spence. What disorder of the axilla is most likely responsible for her symptoms? Breast cancer A client comes to the clinic for a routine evaluation. During the physical examination, the nurse palpates the client's breast and finds a small lump. Which of the following would lead the nurse to suspect possible breast cancer? the lump is irregularly shaped. A nurse is reviewing a client's history for possible risk factors associated with breast cancer. Which of the following would the nurse identify as increasing the client's risk? First full-term pregnancy at age 34 years 62. Skin cancer nurse is participating in a health promotion campaign that has the goal of improving outcomes related to skin cancer in the community. What action has the greatest potential to achieve this goal? Educating participants about the early signs and symptoms of skin cancer A patient complains that he has basal cell carconima and is going to die. The nurse knows that Basal cell carcinoma is rarely terminal. Which patient would be more likely to have the highest risk of developing malignant melanoma? A fair-skinned woman who uses a tanning booth regularly In teaching a patient with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) about this disorder, the nurse considers that which statement about this skin cancer is true? BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. When studying the incidence of skin cancers in a population, a nurse finds that a greater number of skin cancer cases have been reported in white patients than in African American patients. What could be the most likely cause of such an occurrence? Whites have less melanin content in their skin than African Americans. The nurse, preparing educational information about types of skin cancer, recalls that which type has a higher risk for metastasis and poor prognosis unless it is treated early? Melanoma 63. Skin cancer lesions A patient is scheduled for Mohs' microscopic surgery for removal of a skin cancer lesion on his forehead. The nurse knows to prepare the patient by explaining that this type of surgery requires: Removal of the tumor, layer by layer A patient with squamous cell carcinoma has been scheduled for treatment of this malignancy. The nurse should anticipate that treatment for this type of cancer will primarily consist of what intervention? Surgical excision A patient has just been told that he has malignant melanoma. The nurse caring for this patient should anticipate that the patient will undergo what treatment? Wide excision A patient with a suspected malignant melanoma is referred to the dermatology clinic. The nurse knows to facilitate what diagnostic test to rule out a skin malignancy? A skin biopsy is done to rule out malignancies of skin lesions. While performing an initial assessment of a patient admitted with appendicitis, the nurse observes an elevated blue-black lesion on the patient's ear. The nurse knows that this lesion is consistent with what type of skin cancer? Malignant melanoma 64. Small patent ductus arteriosus An infant is experiencing dyspnea related to patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). The nurse understands dyspnea occurs because blood is: circulated through the lungs again, causing pulmonary circulatory congestion. The nurse assessing a premature newborn infant auscultates a continuous machinery-like murmur. This finding is associated with which congenital heart defect? Patent ductus arteriosus Before preparing a teaching plan for the parents of an infant with ductus arteriosus, it is important that the nurse understands this condition. Which statement best describes patent ductus arteriosus? Patent ductus arteriosus involves a defect in which the fetal shunt between the aorta and the pulmonary artery fails to close 65. Sympathetic/parasympathetic nervous system By which of these ways does the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) help to regulate body temperature? Sympathetic nerves to sweat glands promotes secretion of sweat Piloerection induced by sympathetic nerves causes heat conservation The nurse is teaching a patient about the functions of the sympathetic nervous system related to a prescribed medication. What should the nurse tell the patient about the functions of this system? It maintains the body temperature. It regulates the cardiovascular system. It implements the "fight-or-flight" reaction. The nurse is reviewing the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) effects on the heart and blood vessels. Which statement is correct regarding the effect of SNS stimulation? Stimulation of sympathetic nerves to veins causes vasoconstriction. A patient is experiencing symptoms of the fight-or-flight response. Which autonomic process stimulates this response? Sympathetic system The nurse is teaching a group of coworkers about the functions of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). Which statement by a coworker would require correction? "The SNS regulates control of vision." Cholinergic (parasympathomimetic) drugs that stimulate muscarinic receptors are indicated for which situation? Producing miosis in certain eye diseases A nurse is preparing to give a drug that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system. Which patient response is an expected outcome of this drug? Heart rate decreases to 60 beats per minute. A patient is experiencing symptoms of the fight-or-flight response. Which autonomic process orchestrates this response? Stimulation of the sympathetic system Which organs are controlled primarily by the parasympathetic system? Gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, skin & salivary glands 66. Terms such as hypochromic, macrocytic, microcytic, etc A patient is admitted with a 2-month history of fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and dizziness. The patient is diagnosed with idiopathic autoimmune hemolytic anemia. On reviewing the laboratory results, the nurse notes which of the following that confirms this diagnosis? RBC fragments the client is an average-sized adult and has abnormal microcytic hypochromic red blood cells due to a long-term, chronic disease. Which of the following complete blood count (CBC) results is characteristic of her type of anemia? Hemoglobin 8 g/dL A patient's anemia is described as having erythrocytes that demonstrate anisocytosis. The nurse would recognize the erythrocytes would be: Able to assume various shapes A 5-year-old male was diagnosed with normocytic-normochromic anemia. Which of the following anemias does the nurse suspect the patient has? Hemolytic anemia A 45-year-old male is diagnosed with macrocytic, normochromic anemia. The nurse suspects the most likely cause of this condition is: Defective DNA synthesis A patient has microcytic hypochromic anemia. Which of the following pathogenic mechanisms may cause anemia in this patient? Decreased erythrocyte life span, Failure of mechanisms of compensatory erythropoiesis, Disturbances of the iron cycle 67. The inflammatory process upon injury A nurse will be teaching about body defenses. Which information should the nurse include? The body's first line of defense against microorganisms is comprised of the: skin and mucous membranes. While planning care for a patient with an infection, which principle should the nurse remember? In contrast with the inflammatory response, the immune response recognizes specific invaders The nurse assesses clients for the cardinal signs of inflammation. Redness, edema and warmth A client has a leg wound that is in the second stage of the inflammatory response. For what manifestation does the nurse assess? Purulent drainage Which event in the inflammatory response would the nurse correlate with the action of bradykinin? Pain A nurse recalls if the surface barriers such as the skin or mucus membranes are breached, the second line of defense in innate immunity is the: inflammatory response. A nurse is teaching about inflammation. Which information should be included? The first vascular response in inflammation is: vasoconstriction. When a nurse is asked about the purpose of vasodilation and increased vascular permeability during inflammation, how should the nurse respond? To bring white blood cells to the area of injury When a nurse is asked which of the following inhibits the inflammatory response, what is the nurse's best answer? Eosinophils While reviewing lab results, which finding would alert the nurse to a patient with acute inflammation? Increased sedimentation rate While planning care for a patient with acute inflammation and pain, which principle should the nurse remember? The inflammatory chemicals responsible for inducing pain during inflammation are: Bradykinin and prostaglandins While planning care for a patient, which principle should the nurse use to guide care? The first line of defense against pathogens is the: skin and mucous membranes. 68. Type 2 diabetes What characterizes type 2 diabetes b- CELL EXHAUSTION, INSULIN RESISTANCE, GENETIC PREDISPOSITION, altered production of adipokines, inappropriate glucose production by liver The nurse is teaching the patient with prediabetes ways to prevent or delay the development of type 2 diabetes. What information should be included Maintain a healthy weight, monitor for polyuria, polyphagia and polydipsia A client with Type II diabetes has an order for regular insulin 10 units SC each morning. The client's breakfast should be served within: 30 minutes A patient diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus is admitted to the medical unit with pneumonia. The patient's oral antidiabetic medication has been discontinued and the patient is now receiving insulin for glucose control. Which of the following statements best explains the rationale for this change in medication? Stress-related states such as infections increase risk of hyperglycemia The healthcare provider is assessing the glucose level of a patient with a diagnosis of diabetes. Which of these is most helpful in evaluating this patient's long-term glucose management? Hemoglobin A1c A 54 year old patient admitted with type 2 diabetes asks the nurse what "type 2" means. What is the most appropriate response by the nurse? "With type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion is decreased, and insulin resistance is increased." The nurse is assigned to the care of a 64-year-old patient diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In formulating a teaching plan that encourages the patient to actively participate in management of the diabetes, what should be the nurse's initial intervention? Assess patient's perception of what it means to have diabetes. The nurse is evaluating a 45-year-old patient diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which symptom reported by the patient is considered one of the classic clinical manifestations of diabetes? Excessive thirst The nurse is teaching a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus about exercise to help control his blood glucose. The nurse knows the patient understands when the patient elicits which exercise plan? I will take a brisk 30-minute walk 5 days per week and do resistance training 3 times a week. 69. Types of anemia The nurse is collecting data on a patient with suspected pernicious anemia. Which of these signs or symptoms would the nurse expect to find for this patient? Glossitis Megaloblastic anemia is a result of insufficient folic acid or vitamin B12, affecting which of the following? Rapidly turning over cells A patient with anemia who is given iron salts could expect to show a therapeutic increase in hematocrit within 6 to 10 months. After reviewing the major types of anemia, students demonstrate understanding of the info when they identify which of the following as an example of a hemolytic anemia? Sickle cell anemia Which of the following would the nurse encourage a pt. to consume to prevent folic acid anemia? broccoli milk liver A pt. is receiving ferrous sulfate as treatment for iron deficiency anemia. After teaching the pt., which statement indicates the need for additional teaching? "i need to take an antacid with the pill to prevent an upset stomach" An 82-year-old client has pernicious anemia and has been receiving treatment for several years. What is she lacking that results in pernicious anemia? Intrinsic factor An 82-year-old client has pernicious anemia and has been receiving treatment for several years. Which symptom may be confused with another condition in older adults? Dementia A nurse is caring for a client admitted with pernicious anemia. Which set of findings should the nurse expect when assessing the client? Pallor, tachycardia, and a sore tongue During the review of morning lab values on a patient complaining of severe fatigue and a red, swollen tongue, the nurse suspects chronic, severe iron deficiency anemia based on which of the following findings? Low ferritin level You are caring for an 87-year-old female who has been admitted to your unit with iron-deficiency anemia. What would you suspect? Blood loss from the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract A patient is brought to the ER complaining of fatigue, large amounts of bruising on the extremities, and abdominal pain localized in the left upper quadrant. A health history reveals the patient has been treated three times in the past 2 months for a sore throat. Lab tests indicate severe anemia, significant neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. Based on the symptoms, with what could the patient be diagnosed? Aplastic anemia. The nurse understands which is the most common type of anemia? Iron-deficiency anemia THE NURSE CARES FOR A CLIENT DIAGNOSED WITH POLYCYTHEMIA VERA. THE NURSE EXPECTS TO MAKE WHICH OBSERVATION? DARK, FLUSHED FACE A 57-year-old male presents to his primary care provider for red face, hands, feet, ears, and headache and drowsiness. A blood smear reveals an increased number of erythrocytes, indicating: Polycythemia vera (PV) The nurse understands that the client with pernicious anemia will have which distinguishing laboratory findings? intrinsic factor absent Which type of anemia is associated with normochromic and macrocytic red blood cells (RBCs)? Megaloblastic anemia What is the genetic disorder that is associated with excessive red blood cell (RBC) destruction? Sickle cell anemia A patient's anemia is described as having erythrocytes that demonstrate anisocytosis. The nurse would recognize the erythrocytes would be: Able to assume various shapes A newborn is diagnosed with congenital intrinsic factor deficiency. Which of the following types of anemia will the nurse see documented on the chart? Pernicious anemia A 70-year-old male is brought to the emergency department, where he dies shortly thereafter. Autopsy reveals polycythemia vera (PV). His death was most likely the result of: Cerebral thrombosis A 67-year-old male was diagnosed with polycythemia vera (PV) but refused treatment. His condition is at risk for converting to: Acute myeloid leukemia A 20-year-old female undergoes lab testing for anemia. Results show high iron, bilirubin, and transferrin and low hemoglobin and hematocrit. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis to be documented on the chart? Sideroblastic anemia How should the nurse prepare a patient who is to receive a Schilling test for pernicious anemia? Administer radioactive cobalamin and measure its excretion in the urine. A 67-year-old female has chronic gastrointestinal bleeding. A nurse recalls the primary cause of her anemia is: Iron deficiency A 34-year-old male presents in the emergency room with extreme fatigue and shortness of breath. His skin and sclera appear to have a yellowish discoloration. These assessment findings are consistent with which type of anemia? Hemolytic anemia A nurse is preparing to teach the staff about aplastic anemia. Which information should the nurse include? Aplastic anemia is caused by: Stem cell deficiency A 50-year-old female was diagnosed with sideroblastic anemia. Which of the following assessment findings would most likely occur? Bronze colored skin 70. Types of fractures The human body is designed to protect its vital parts. A fracture of what type of bone may interfere with the protection of vital organs? Flat bones A patient has sustained a long bone fracture. The nurse is preparing a care plan for this patient. Which intervention should the nurse include in the care plan to enhance fracture healing? Monitor color, temperature, and pulses of the affected extremity The nurse is writing a care plan for a patient admitted to the Emergency Department (ED) with an open fracture. The nurse will assign priority to what nursing diagnosis for a patient with an open fracture of the radius? Risk for infection While caring for a patient with a hip fracture, the nurse will instruct the patient to do what to prevent the most common complication associated with a hip fracture? Increase fluid intake Radiographs were ordered for a 10-year-old boy who had his right upper arm injured. The radiographs show that the humerus appears to be fractured on one side and slightly bent on the other. What type of fracture is this an example of? Green stick A 76-year-old female was diagnosed with osteoporosis by radiologic exam. She is at high risk for: Pathologic bone fractures A 65-year-old Hispanic female is admitted to the hospital with a pathologic, compound, transverse fracture of the femur. Which of the following statements best describes this type of fracture? The fracture line is straight across the bone. A 70-year-old female with osteoporosis fractures her leg at a location of preexisting abnormality. She reports that the fracture occurred following a minor fall. Which of the following best describes the Pathologic fracture A 32-year-old obese male begins a jogging routine. A week after beginning, he fractures his leg. This is referred to as a what type of fracture? fatigue What does prolonged bed rest put the older adult at risk for Pathologic fractures A nurse is describing the pathophysiology of a torus fracture. Which information should the nurse include? A torus fracture is a type of: incomplete fracture. A patient has a fracture that broke into several fragments. Which type of fracture did the patient sustain? Comminuted fracture A torus fracture occurs when: The cortex of the bone buckles While teaching a group of student nurses about different types of fractures, the nursing instructor says, "This fracture is characterized by the crushing of cancellous bone." Which type of fracture is the nursing instructor describing? Compression A client sustained multiple fractures in a motor vehicle accident. The nurse determines that the client is at a high risk for osteomyelitis due to which type of fracture? Open A patient has a fracture line at an angle to the long axis of the bone. Which type of fracture did the patient sustain? Oblique transchondral fractures are most prevalent in Adolescents An adolescent patient has sustained a fracture that involves fragmentation of the articular cartilage. Which type of fracture did the adolescent sustain? Transchondral The orthopedic nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with a fracture of the radius. When the nurse is considering all of the various types of bone fractures, which bone type is most anticipated? Cancellous Radiographic evaluation of a client's fracture reveals that a bone fragment has been driven into another bone fragment. The nurse identifies this as which type of fracture? Impacted The nurse understands which of the following are considered the key components of the musculoskeletal system? Bones, muscle, joints, and ligaments A patient has a fracture in a bone that does not have the ability to recover. The nurse will be caring for which type of fracture? Insufficiency 71. Types of gastric ulcers-signs and symptoms, characteristics The nurse understands that most cases of peptic ulcer disease is caused by what? Infection with Helicobacter pylori Which are pathologic changes associated with acute gastritis? Vascular congestion, severe mucosal damage and ruptured vessels, edema & acute inflammatory cell infiltration Which are possible complications of chronic gastritis? Pernicious anemia, gastric cancer, decreased gastric acid secretion, peptic ulcer disease What is true regarding duodenal ulcers? More common in men than in women, typically develop between the ages of 30 and 55. More common in individuals who smoke A client with a duodenal ulcer asks the nurse why antibiotics are a part of the treatment plan. Which information should the nurse include in the explanation? Most duodenal ulcers are caused by Helicobacter pylori. When obtaining a nursing history from a client with suspected gastric ulcer, which signs and symptoms should the nurse assess? Vomiting, weight loss & anemia 72. Types of hormones A nurse is teaching staff about protein hormones. Which information should the nurse include? One of the protein hormones is: Insulin -A patient has high levels of hormones. To adapt to the high hormone concentrations, the patient's target cells have the capacity for: Down regulation -A patient has researched lipid-soluble hormones on the Internet. Which information indicates the patient has a good understanding? Lipid-soluble hormone receptors cross the plasma membrane by: Diffusion Hormones are effective communicators because they: decrease their secretion in response to rising plasma hormone levels Which of the following is a protein hormone that is water soluble? insulin From where is the hormone glucagon secreted? α-Cells of the islets of Langerhans Which endocrine gland secretes cortisol? Adrenal cortex What accurately demonstrates that hormones of one gland influence the function of hormones of another gland? Increased atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) levels inhibit the secretion of aldosterone. 73. Types of immunity-e.g. innate, active, etc A student nurse asks the clinician which cells are most primary in a patient's immunity. What is the clinician's best answer? Lymphocytes. A nurse recalls humoral immunity is generated through the process of: producing antibodies. While taking a health history, if a person has resistance to a disease from natural exposure to an antigen, how would the nurse document this form of immunity? Active acquired What type of immunity will the nurse expect in an individual who is given a vaccine? Active acquired immunity A new mother asks the nurse about immunity of her newborn as she is breastfeeding. The nurse's response should include a discussion on which type of immunity? Passive The nurse has been explaining to a student nurse about the different types of immunity. Which response indicates that the student nurse has a good understanding of adaptive immunity? Both the humoral and cell-mediated immunity develop memory cells Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of adaptive immunity by natural killer cells The primary immune response ________. has a lag period while B cells proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells Which of the following is true about the number of binding sites per functional antibody unit? IgM contains 10 binding sites. Which cell of the immune system is absolutely required for an adaptive immune response? Helper T cell The adaptive immune system involves three major cell types: antigen-presenting cells, T cells, which constitute cell- mediated immunity, and B cells, which govern humoral immunity. The nurse understands that the function of IgG is as what? A bond with target cells and a promoter of phagocytosis The nurse understands that which type of immunity is the longest acting? Natural active Natural killer cells are specialized lymphocytes that are one of the major parts of which immunity? Innate 74. Urinary tract obstruction A patient is admitted with lower urinary tract obstruction and stasis. Which of the following is the primary intervention? Urinary catheterization The nursing students have learned in class that causes of urinary obstruction and urinary incontinence include which of the following? Impairment of neurologic control of bladder function, Structural changes in the urethra & Structural changes in the bladder An elderly client has just been admitted for urinary tract obstruction and retention. Which of the following are symptoms that the nurse should suspect this client to demonstrate? Bladder distention• Hesitancy • Small stream • Overflow incontinence Which of the following individuals are displaying identified risk factors for the development of lower urinary tract obstruction? 68 year-old man who has been diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). • 30 year-old woman who has been diagnosed with gonorrhea. • 74 year-old woman who has developed a lower bowel obstruction following several weeks of chronic constipation. • 20 year-old man who has spina bifida and consequent impaired mobility. If obstructed, which component of the urination system would cause peristaltic waves? Ureters The nurse is planning care for a patient with a urinary tract obstruction. The nurse includes assessment for which of the following possible complications? Increased blood pressure 75. Vaginal candidiasis During a vaginal examination of a 38-year-old woman, the nurse notices that the vulva and vagina are erythematous and edematous with thick, white, curdlike discharge adhering to the vaginal walls. The woman reports intense pruritus and thick white discharge from her vagina. The nurse knows that these history and physical examination findings are most consistent with which of these conditions? Candidiasis A patient undergoing treatment for vaginitis is also counseled about measures to prevent its recurrence. Which patient statement best indicates effective counseling? "My sexual partner will also need to be treated." A nurse is reviewing a client's medical history. Which factor indicates the client is at risk for candidiasis? Use of corticosteroids A nurse who works in a gynecologist's office frequently cares for patients who are diagnosed with vulvovaginal candidiasis. The nurse should teach the patients how to manage and treat the most common symptom of: Vulvar pruritus. A patient with HIV has recently completed a 7-day regimen of use of antibiotics. She reports vaginal itching and irritation. In addition, the patient has a white, cottage cheese-like vaginal discharge. Which of the following is the patient most likely suffering? Vulvovaginal candidiasis A woman complains to the nurse that she has developed a yeast infection. The woman does not understand how she could get a yeast infection since she has been on antibiotics for a urinary tract infection. What is the rationale for this patient's complaint? Destroying one type of resident flora (bacteria) can allow over proliferation of another competing type (yeast). 76. Ventilation/perfusion ratio A nurse recalls a high ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) ratio can be caused by: obstruction to pulmonary blood flow. A nurse is teaching about the functions of the pulmonary system. Which information should the nurse include? One of the functions of the pulmonary system is the: Exchange of gases between the environment and blood Which of the following terms should the nurse use when there is a balance between outward recoil of the chest wall and inward recoil of lungs at rest? Functional residual capacity (FRC) is reached. The nurse is describing the receptors in the lung that decrease ventilatory rate and volume when stimulated. Which receptors is the nurse discussing? Stretch receptors While reviewing the results of the pulmonary functions test, the nurse is aware that the maximum amount of gas that can be displaced (expired) from the lung is called: Vital capacity (VC) While auscultating a patient's lungs, a nurse recalls the alveoli in the apexes of the lungs are larger than alveoli in the bases. 77. Vitamin B-12 therapy The nurse knows the Vitamin B12 is found naturally in many foods. Which foods contain the LEAST amount of B12? Chocolate. B12 is found in meats, seafood, fermented cheeses. A patient had a portion of stomach removed and must take vitamin B12. Which of the following statements should be included in the patient teaching? "Pernicious anemia is a complication of this surgery, so you must take vitamin B12." After teaching a patient with pernicious anemia about vitamin B12, therapy, which patient statement would indicate that the teaching was successful? I need to inject this drug intramuscularly every 5 to 10 days. When describing the function of vitamin B12, which of the following would be appropriate to include? Maintenance of myelin sheath A patient has vitamin B12 deficiency following a subtotal gastrectomy. The nurse understands the patient has which type of anemia? megaloblastic The nurse is teaching a patient with B12 deficiency caused by a previous gastrectomy and lack of intrinsic factor. Which statement by the nurse is the most appropriate to include in the teaching plan? "You may be prescribed a high dose of oral vitamin B12." The nurse is preparing the patient for a test to determine the cause of vitamin B12 deficiency. The patient will receive a small oral dose of radioactive vitamin B12 followed by a large parenteral dose of nonradioactive vitamin B12. What test is the patient being prepared for? Schilling test A client with pernicious anemia is receiving parenteral vitamin B12 therapy. Which client statement indicates effective teaching about this therapy? "I will receive parenteral vitamin B12 therapy for the rest of my life." The nurse would instruct the client to eat which of the following foods to obtain the best supply of vitamin B12? Meats and dairy products The nurse recognizes that which patient is at the greatest risk for pernicious anemia or vitamin B12 deficiency? 60-year-old woman who has undergone a total gastric resection In monitoring a patient for early signs of vitamin B12 deficiency, the nurse correlates which clinical manifestation with this disorder? Paresthesia in hands and feet A 2-year-old malnourished child has vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies. A blood smear suggests the deficiency is macrocytic and normochromic. The nurse would expect the hemoglobin to be: Normal Which of the following individuals should the nurse assess first for a vitamin B12 deficiency anemia? 47-year-old male who had a gastrectomy procedure (removal of the stomach) ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ A patient with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP) asks the nurse at the doctor's office what causes all the nosebleeds that have been occurring. The nurse's best response would be the presence of which of the following? Immune cells that destroy the platelets A hospital laboratory technologist is analyzing the complete blood count (CBC) of a hospital patient. Which of the following statements best reflects an aspect of the platelets that would constitute part of the CBC? The half-life of a platelet is typically around 8-12 days. How many days do erythrocytes live in circulation? 120 days Mature red blood cells have a life span of approximately how many days? 120 A patient with a history of acquired idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) arrives at the emergency department complaining of fatigue, shortness of breath, and multiple nosebleeds during the previous week. The platelet level is 10,000/μL, and the hemoglobin is significantly below normal. The nurse would anticipate which of the following interventions? Immune globulin infusion A client tells the nurse that the doctor told her she has too many red blood cells accompanied by elevated white cells and platelet counts. The nurse recognizes this as: Polycythemia vera The parent of a 5 year old who was admitted with a sudden onset of purpura following the flu and who was diagnosed with acute idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is very concerned that the child will have ITP for the rest of his life. The best response for the nurse to make is which of the following? "It is usually self-limiting." Which disorder does the nurse know is considered to be an autoimmune disease? Myasthenia gravis The nurse is completing a health assessment of a 42-year-old female with suspected Graves' disease. The nurse should assess this client for: tachycardia. A client visits the physician's office complaining of agitation, restlessness, and weight loss. The physical examination reveals exophthalmos, a classic sign of Graves' disease. Based on history and physical findings, the nurse suspects hyperthyroidism. Exophthalmos is characterized by: protruding eyes and a fixed stare. Propylthiouracil (PTU) is prescribed for a client with Graves' disease. The nurse should teach the client to immediately report: sore throat [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 07, 2020
Number of pages
38
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 07, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
76