*NURSING > EXAM > NURS6551 / NURS 6551: Primary Care of Women Final Exam Latest Update Walden University (All)
NURS6551 / NURS 6551: Primary Care of Women Final Exam Latest Update Walden University
Document Content and Description Below
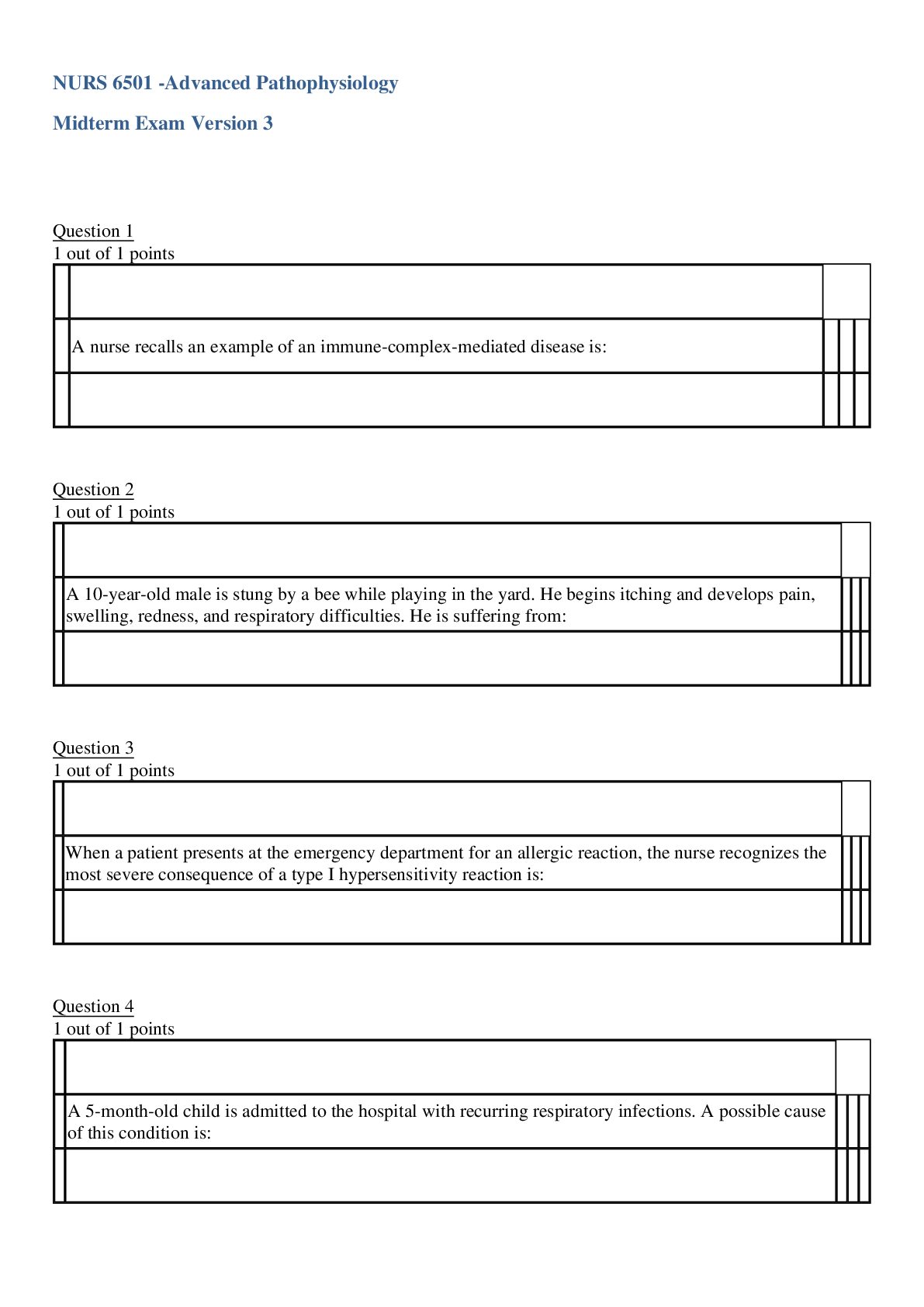
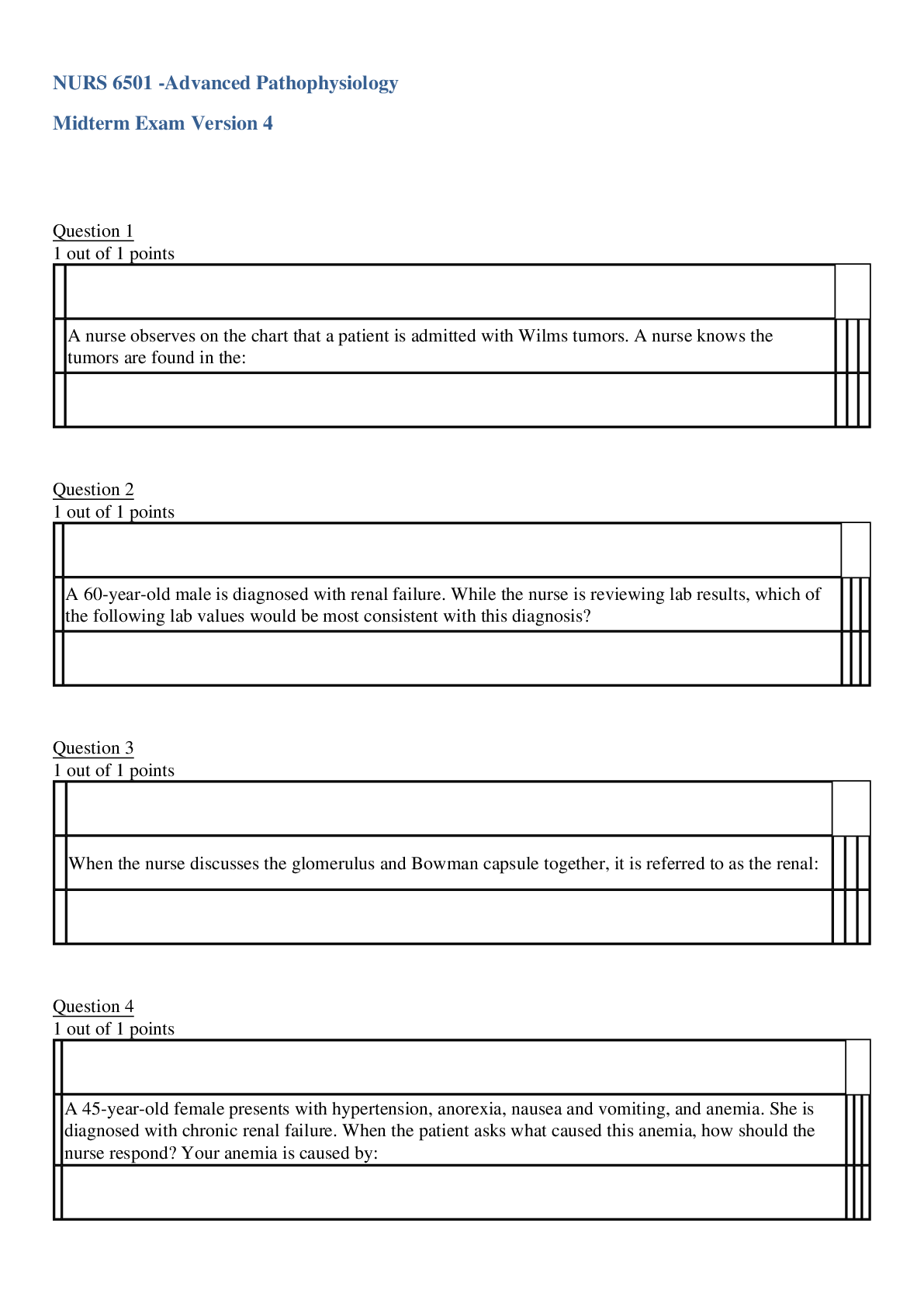
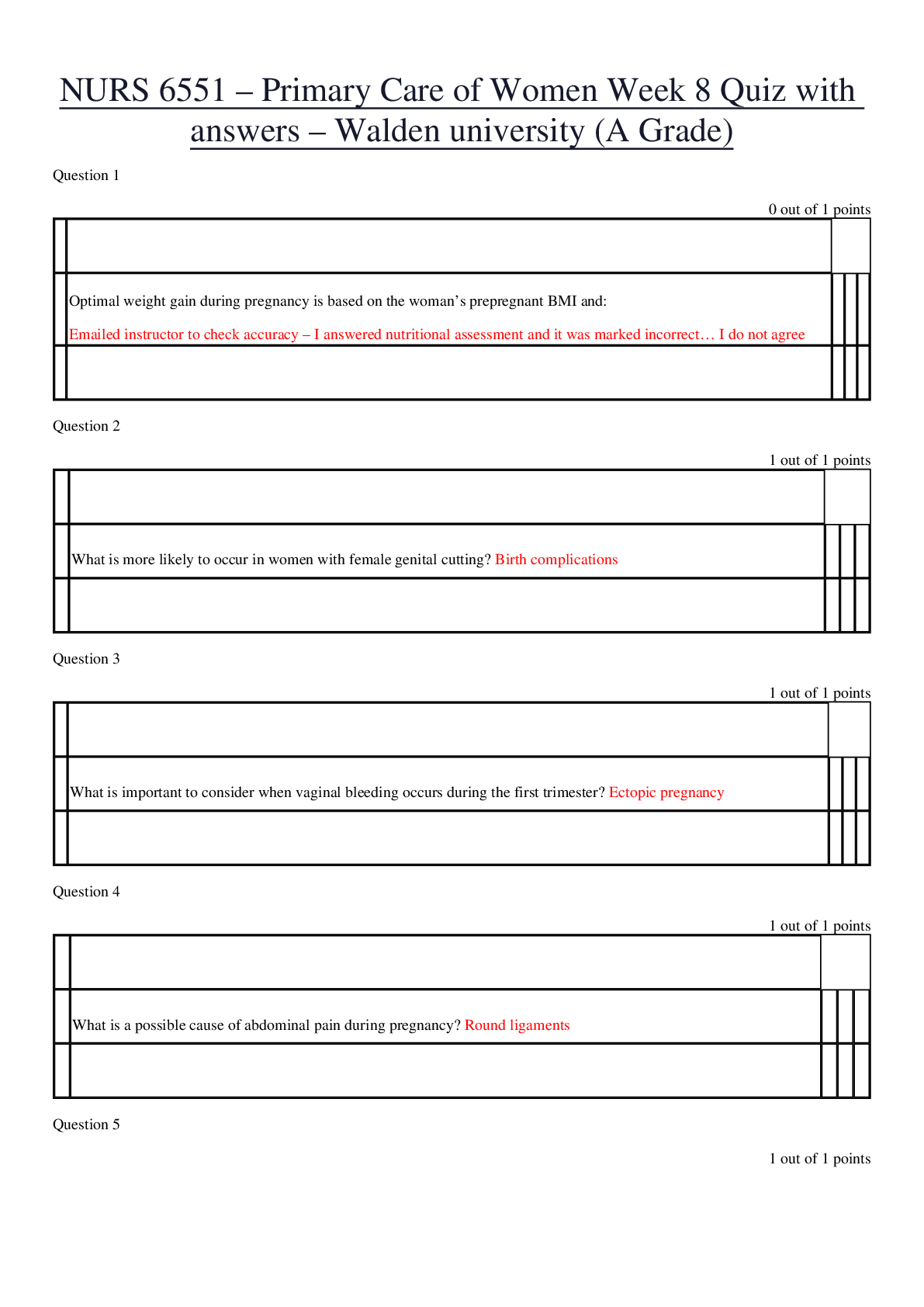
NURS 6551: Primary Care of Women Final Exam Question 1 An example of an X-linked recessive condition or trait is a. Sickle cell anemia b. Hemophilia c. Muscular dystrophy d.... Cystic fibrosis 2 points Question 2 Where does edema tend to occur in the pregnant woman’s body? a. Hands b. Face c. Feet d. Abdomen 2 points Question 3 What is the leading cause of first-trimester maternal death? a. Ectopic pregnancy b. Complications from prior gynecologic surgeries c. Abortion d. Complications from unresolved STIs 2 points Question 4 To prevent breast trauma during the breastfeeding, the nurse practitioner should stress the importance of a. Keeping the nipples dry b. Positioning of the infant c. Prenatal breast care d. Using breast shields 2 points Question 5 What components make up the biophysical profile? a. Nonstress test, amniotic fluid composition, fetal breathing, and fetal tone. b. Fetal tone, breathing, motion, and contraction stress test. c. Amniotic fluid composition, contraction challenge test, fetal breathing, and motion. d. Fetal tone, breathing, motion, amniotic fluid volume, and nonstress test. 2 points Question 6 Optimal weight gain during pregnancy is based on the woman’s prepregnant BMI and: a. Age b. Height c. Nutritional assessment d. Caloric intake 2 points Question 7 When can relief from pregnancy induces nausea and vomiting be expected? a. 6–8 weeks’ gestation b. 12–14 weeks’ gestation c. 20–22 weeks’ gestation d. after 24 weeks’ gestation 2 points Question 8 The treatment(s) with demonstrated effectiveness relieving symptoms of dysmenorrhea in women with premenstrual syndrome is (are): a. Nutrition therapy with vitamin E b. The NSAIDs c. Antihypertensive agents d. Antipsychotic medication 2 points Question 9 Which of the following dietary changes would you recommend Heather, who is experiencing nausea during her first’s trimester? a. A bland diet taken frequently in small amounts b. An increase in fat intake c. Restriction of fluid intake after 7:00 pm d. A decrease in carbohydrate intake 2 points Question 10 Without treatment shortly after birth, as many as 90 percent of infants born to hepatitis B–infected mothers will: a. Develop HIV b. Have cognitive difficulties c. Need blood transfusions d. Become infected 2 points Question 11 Mindy, age 42, is pregnant for the first time She wants a chorionic villus sampling (CVS) performed for genetic testing. Which statement is true regarding CVS? a. CVS detects only chromosomal abnormalities and not anatomical aberrations such as open neural tube defects. b. CVS may be offered only at 11-14 weeks' gestation. c. CVS is extremely safe. d. CVS can be done in the physician's office. 2 points Question 12 After 28 weeks' gestation, all women should perform fetal movement counts (FMCs). Which of the following statements regarding FMCs is true? a. Ten movements should be obtained in 2 hours. b. Counts should be done as the woman is going about her work. c. If decreased activity is perceived, a nonstress test (NST) should be performed at the next obstetric visit. d. Ten movements should be obtained in 1 hour. 2 points Question 13 At what time during pregnancy does nausea typically occur? a. At 3–6 weeks’ gestation b. At 6–8 weeks’ gestation c. At 12–15 weeks’ gestation d. At 1–3 weeks’ gestation 2 points Question 14 An autosomal recessive disorder such as cystic fibrosis is expressed in the offspring when: a. Neither parent carries the gene b. 1 parent has the disease c. 1 parent carries the gene d. Both parents carry the gene 2 points Question 15 The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear report on a 36-year-old female patient indicates atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS). Which of the following constitutes appropriate care for this patient? a. Prescribe estrogen cream b. Refer the patient to a gynecologist c. Perform a hysteroscopic examination d. Repeat the pap smear in 4 months 2 points Question 16 Carrie is due to deliver her second baby. During your work-up, you note that she hemorrhaged after delivering her first baby 2 years ago, has always had menorrhagia, and bruises easily. Her lab work reveals a normal blood work-up, including a normal prothrombin time and activated partial thromboplastin time. What do you suspect? a. Unfortunate coincidences b. Hemophilia c. Von Willibrand's disease d. Sickle cell anemia 2 points Question 17 What is the recommended timing for gestational diabetes screening? a. 12-16 weeks' gestation b. 24-28 weeks' gestation c. 30-34 weeks' gestation d. 34-38 weeks' gestation 2 points Question 18 According to Naegele's rule, if a woman's last normal menstral period (LNMP) was September 23, what is her estimated date of delivery? a. June 16 b. June 1 c. May 30 d. June 30 2 points Question 19 You see G5P4015 on a client's history form. You surmise that a. The woman has five living children, including a set of twins, and she has had one abortion. b. The woman has four living children and had one abortion, for a total of five pregnancies. c. The woman is pregnant now and has five living children, including a set of twins. d. The woman has been pregnant five times and has five living children. 2 points Question 20 Karen is taking oral contraceptive pills for fertility control. Karen calls the clinic and reports the presence of chest pain and shortness of breath. You instruct Karen to: a. Eat smaller meals more frequently to prevent gastric distention. b. Stop taking the pills and use a nonhormonal contraceptive method. c. Wait for the physician to return a telephone call to the client. d. Go to the nearest emergency room immediately to be evaluated. 2 points Question 21 What is the most common cause of death in women in the United States? a. Breast cancer b. Cardiovascular disease c. Cervical cancer d. Lung cancer 2 points Question 22 It is imperative that the nurse practitioner teach patients taking an oral contraceptive to report any of the danger signs of complications. Which of the following would be of least concern to the nurse practitioner? a. Weight gain b. Upper abdominal pain c. Lower leg pain d. Chest pain 2 points Question 23 When is a pregnant woman at risk for developing congenital rubella syndrome? a. Anytime during the pregnancy. b. During the first 16 weeks of pregnancy. c. During the first 4 weeks of pregnancy. d. During the last trimester. 2 points Question 24 In order to maintain continence bladder pressure must be a. higher than urethral pressure. b. equal to the pressure of the urethral sphincter. c. higher than the pressure of the levator ani. d. lower than urethral pressure. 2 points Question 25 After how many weeks’ gestation is a pregnancy loss considered a fetal death or stillbirth? a. 18 weeks b. 30 weeks c. 20 weeks d. 24 weeks 2 points Question 26 Allie, who has asthma, just found out that she is pregnant. She is wondering whether she should continue taking her asthma medications. Which of the following is true regarding asthma and pregnancy? a. All medications may be used except for theophylline. b. In the event of an acute exacerbation, glucocorticoids should not be used. c. Management differs little from management in nonpregnant women. d. Only inhaled (rather than oral) medications should be used. 2 points Question 27 Spontaneous abortion refers to the loss of a fetus of less than a. 12 weeks' gestation b. 18 weeks' gestation c. 26 weeks' gestation d. 22 weeks' gestation 2 points Question 28 Which of the following maternal situations is considered an absolute contradiction to breastfeeding? a. History of tuberculosis medication b. History of breast cancer c. Hepatitis C infection d. Early HIV infection 2 points Question 29 A 40-year-old female presents for a routine well woman exam. On examination, the nurse practitioner notes a scant nipple discharge, absence of a palpable mass, and absence of lymph node enlargement. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? a. Fibrocystic breast disease b. Breast cancer c. Chest wall syndrome d. Intraductal papilloma 2 points Question 30 When is round ligament pain most likely to occur in pregnant women? a. Between 6–8 weeks’ gestation b. Between 24–28 weeks’ gestation c. Between 10–12 weeks’ gestation d. Between 16–20 weeks’ gestation 2 points Question 31 What is the most typical schedule of prenatal care in the first 28 weeks of pregnancy? a. Visits scheduled every 2 weeks b. Visits scheduled every 3 weeks c. Visits scheduled every week d. Visits scheduled every 4 weeks 2 points Question 32 A 30-year-old female patient is seeking advice from the nurse practitioner about becoming pregnant. She is currently taking an oral contraceptive. She gives a history of having a hydatidiform molar pregnancy 2 years ago. The appropriate plan of care for this patient should include: a. Discontinuing the oral contraceptive b. Recommending hysterectomy c. Measuring serum chrionic gonadropinc level d. Delaying pregnancy for 1 more year. 2 points Question 33 A 25-year-old obese female has a history of frequent candida vaginal infections in the past year. She is in a monogamous sexual relationship and uses and intrauterine device (IUD) for contraception. Of the following, which is the most likely underlying condition predisposing her to recurring candida vaginitis? a. Tampon use b. Diabetes mellitus c. Pregnancy d. Trichomoniasis 2 points Question 34 What is the best description of Bishop's score? a. It is an assessment of the cervix's readiness for elective induction. b. It is a series of four maneuvers to determine fetal position. c. It is a multiparameter evaluation of fetal condition following a nonreactive nonstress test. d. It is an evaluation of fetal lung maturity and readiness for birth. 2 points Question 35 Which of the following laboratory tests is useful in the diagnosis of spontaneous abortion? a. Qualitative plasma estradiol levels b. Qualitative plasma human chrionic gonadotropin levels c. Serial quantitative beta-HCG levels d. Plasma dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) levels 2 points Question 36 According to the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Guide, screening for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) should be done on which of the following clients: a. Women who report hypoglycemic symptoms b. Women age 40 or over c. All pregnant women at 24-28 weeks. d. All women with threatened miscarriage 2 points Question 37 What distinguishes pyelonephritis from cystitis? a. The infection has descended to the bladder. b. The infection has ascended to the kidneys. c. The infection is caused by E. coli bacteria. d. The infection occurs only in pregnant women. 2 points Question 38 What is the presumptive symptom of pregnancy that involved tingling or frank pain of the breasts? a. Colostrum secretion b. Montgomery's tubercles c. Mastodynia d. Melasma 2 points Question 39 What was the reason that prenatal care began in the early 1900s? a. To screen for preeclampsia b. To predict preterm births c. To assess women’s nutritional needs d. To test women for disease 2 points Question 40 Which of the following instructions should be included in the discharge teaching plan to assist the postpartal woman in recognizing early signs of complications? a. Call the office to report any decrease in the amount of brownish-red lochia. b. Notify your health-care provider of a return to bright red vaginal bleeding. c. Palpate the fundus daily to make sure it is soft. d. The passage of clots as large as an orange is expected. 2 points Question 41 A 28-year-old pregnant patient, at 18 weeks gestation, complains of feeling lightheaded when standing. which of the following is an appropriate response by the nurse practitioner? a. Blood pressure normally decreases during pregnancy and can cause this symptom. b. The lightheadedness is a concern. A CBC should be ordered to check for anemia. c. Low blood sugar may be causing this problem. An oral glucose tolerance test is indicated. d. Lightheadedness may be caused by an abnormal elevation in blood pressure during pregnancy. 2 points Question 42 In evaluating a mother-and-infant breastfeeding situation, signs of an effective latch at the breast are a. Infant's lips flanged out; cheeks full b. Maternal nipple discomfort throughout the feeding c. Infant's cheeks sucked in and slow, shallow sucking d. Rapid, short, nonrhythmic sucking by infant 2 points Question 43 What is a possible cause of abdominal pain during pregnancy? a. Round ligament pain b. Diabetes c. Anemia d. Cytomegalovirus 2 points Question 44 Pregnant women should know that folic acid can help to prevent neural tube defects. To be most effective, women should take folic acid: a. During the second trimester. b. Soon after a positive pregnancy test. c. Before becoming pregnant. d. During the third trimester. 2 points Question 45 Which of the following should the nurse practitioner encourage pre-conceptually to decrease the risk of neural tube defect in the fetus? a. Folic acid 0.4 mg/day b. Rubella vaccine today c. Vitamin E 400 IU daily d. Maternal alpha-fetoprotein level 2 points Question 46 Sarah, who just found out she is pregnant, is taking prenatal vitamins with extra daily supplements of iron. She may be a candidate for a. Vaginal spotting during the second trimester. b. Premature delivery. c. Excessive skin bruising. d. A high-birth-weight baby. 2 points Question 47 Which of the following diseases is not acquired transplancentally? a. Varicella b. Tuberculosis c. Ruboela d. Toxoplasmosis 2 points Question 48 During nursery rounds, you examine a 12-hour-old newborn. The infant has a yellow tint to the skin and sclera. What lab test will you order to further evaluate this infant? a. Direct Combs’ test b. Blood cultures c. Blood glucose d. Arterial blood gas 2 points Question 49 What is a fetus's gestational age when its mother's uterus is palpable just above the pubic symphysis? a. 12 weeks b. 4 weeks c. 16 weeks d. 8 weeks 2 points Question 50 Jack and Jill present for a preconception health counseling session. Jack is 34, Jill is 33, and they have a 5-year-old son, Jake. Jake is the product of an uncomplicated pregnancy and labor. At birth, Jake had an open neural tube defect and now has spina bifida with a loss of function of his lower extremities. Jack and Jill want another child and ask if there is anything they can do to prevent the recurrence of a neural tube defect in future pregnancies. What is your best response to this couple? a. "Take 60 mg a day of an iron supplement to enhance stores to support fetal development." b. "Have a CVS performed at 12-14 weeks' gestation to determine the health of the fetus." c. "Take 4 mg/day of folic acid, beginning before conception. d. "It is a matter of genetics, and there is nothing you can do." [Show More]
Last updated: 11 months ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 10, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 10, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
25



.png)