*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR 507 Week 7 Quiz Study Guide (Musculoskeletal, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine): Spring 2020 (All)
NR 507 Week 7 Quiz Study Guide (Musculoskeletal, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine): Spring 2020
Document Content and Description Below
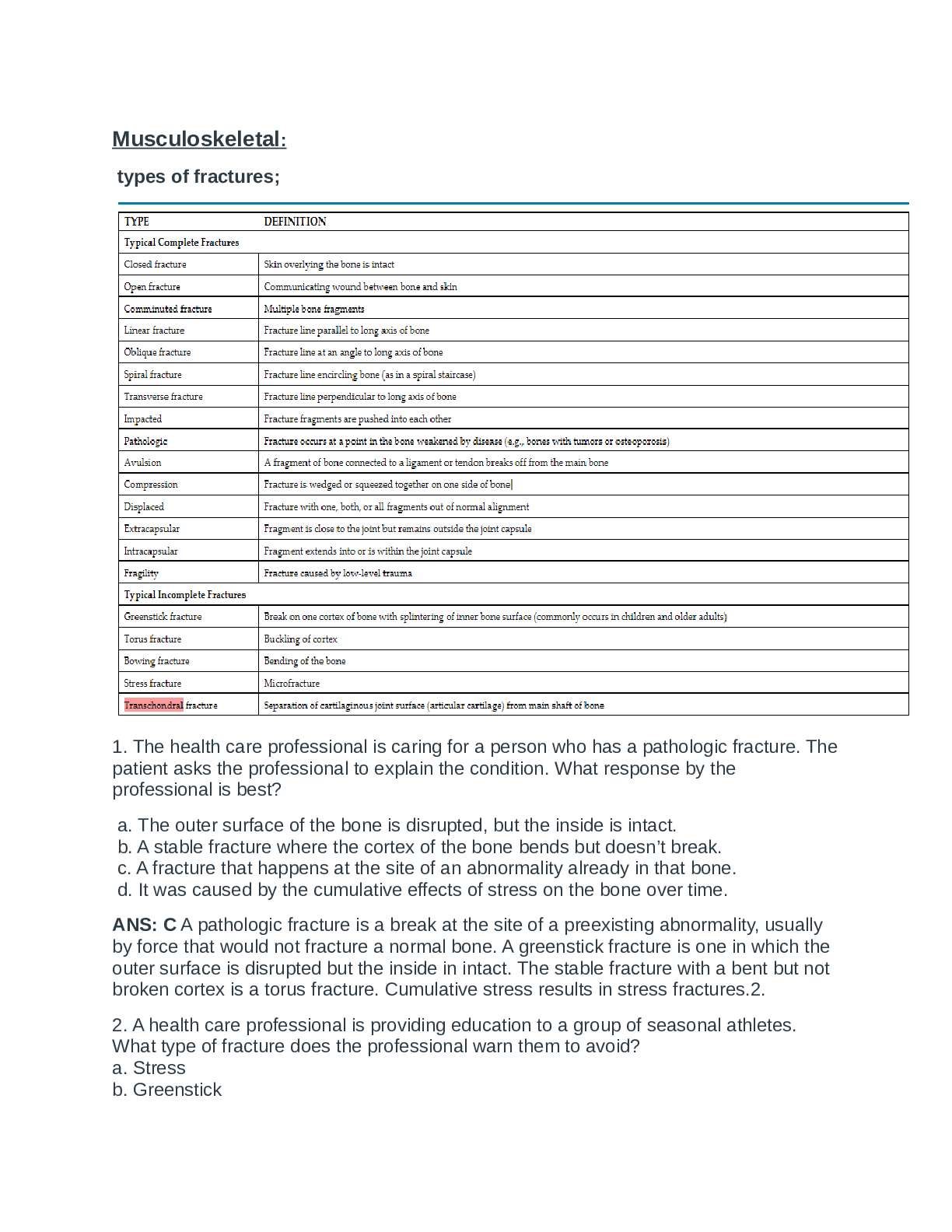
NR 507 Week 7 Quiz Study Guide (Musculoskeletal, Gastrointestinal, Endocrine): Spring 2020 (A guaranteed) Musculoskeletal: types of fractures; 1. The health care professional is caring for a p... erson who has a pathologic fracture. The patient asks the professional to explain the condition. What response by the professional is best? a. The outer surface of the bone is disrupted, but the inside is intact. b. A stable fracture where the cortex of the bone bends but doesn’t break. c. A fracture that happens at the site of an abnormality already in that bone. d. It was caused by the cumulative effects of stress on the bone over time. ANS: C A pathologic fracture is a break at the site of a preexisting abnormality, usually by force that would not fracture a normal bone. A greenstick fracture is one in which the outer surface is disrupted but the inside in intact. The stable fracture with a bent but not broken cortex is a torus fracture. Cumulative stress results in stress fractures.2. 2. A health care professional is providing education to a group of seasonal athletes. What type of fracture does the professional warn them to avoid? a. Stress b. Greenstick c. Insufficiency d. Pathologic ANS: A A stress fracture occurs in normal or abnormal bone that is subjected to repeated stress, such as repetitive and strenuous activities that occur during athletics. A greenstick fracture is one in which the outer surface of the bone is disrupted but the interior is intact. Insufficiency fractures are seen in osteoporosis and osteomalacia. A pathologic fracture is one that occurs from force that would not usually break a bone. There is usually an underlying lesion or abnormality at the site of the fracture. 3. Improper reduction or immobilization of a fractured femur can result in which outcome after cast removal? a. The muscles around the fracture site are weak. b. The fracture requires 6 to 8 weeks of physical therapy. c. The skin under the cast is dry and flaky. d. The bone is not straight. ANS: D Improper reduction or immobilization of a fractured bone may result in nonunion, delayed union, or malunion. Malunion is the healing of a bone in a nonanatomic position that could result in the bone not being straight. The other options are normal occurrences. 4. What is the tear in a ligament referred to as? a. Fracture b. Strain c. Disunion d. Sprain ANS: D Ligament tears are commonly known as sprains. A fracture is a break in a bone. A strain is an injury to a tendon or muscle. Disunion is when bones do not heal together properly after a fracture. 5. Which type of osteoporosis would a person develop after having the left leg in a cast for 8 weeks to treat fracture of the tibia and fibula? a. Iatrogenic b. Regional c. Idiopathic d. Osteoblastic ANS: B Classic regional osteoporosis is associated with disuse or immobilization of a limb because of fractures, motor paralysis, or bone or joint inflammation. 6. A patient is brought to the Emergency Department after being found by neighbors. The patient says she has been lying on the floor in the house for 3 days. What action by the health care professional is best? a. Order a serum creatine kinase (CK) level b. Obtain an x-ray of the patient’s hips c. Arrange for the patient to have a DXA scan d. Perform the Fracture Risk Assessment ANS: A Chapter 45 - Alterations of Musculoskeletal Function 440 Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis for Disease in Adults and Children 8th Edition 97803235834 This patient is at high risk of having rhabdomyolysis. The best diagnostic test for this disorder is a serum creatine kinase level. The patient may well have a hip fracture, but other bones may be broken as well and the patient may well have rhabdomyolysis. A DXA scan and Fracture Risk Assessment are useful tools for osteoporosis. 7. The health care professional teaches a group of seniors that the most common clinical manifestation of osteoporosis is which of these? a. Bone deformity b. Bone pain [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 22 pages
Instant download
Instant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 17, 2020
Number of pages
22
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 17, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
37





.png)

.png)