Portage Learning; Nursing Fundamentals Week 1 Latest and Complete
Document Content and Description Below
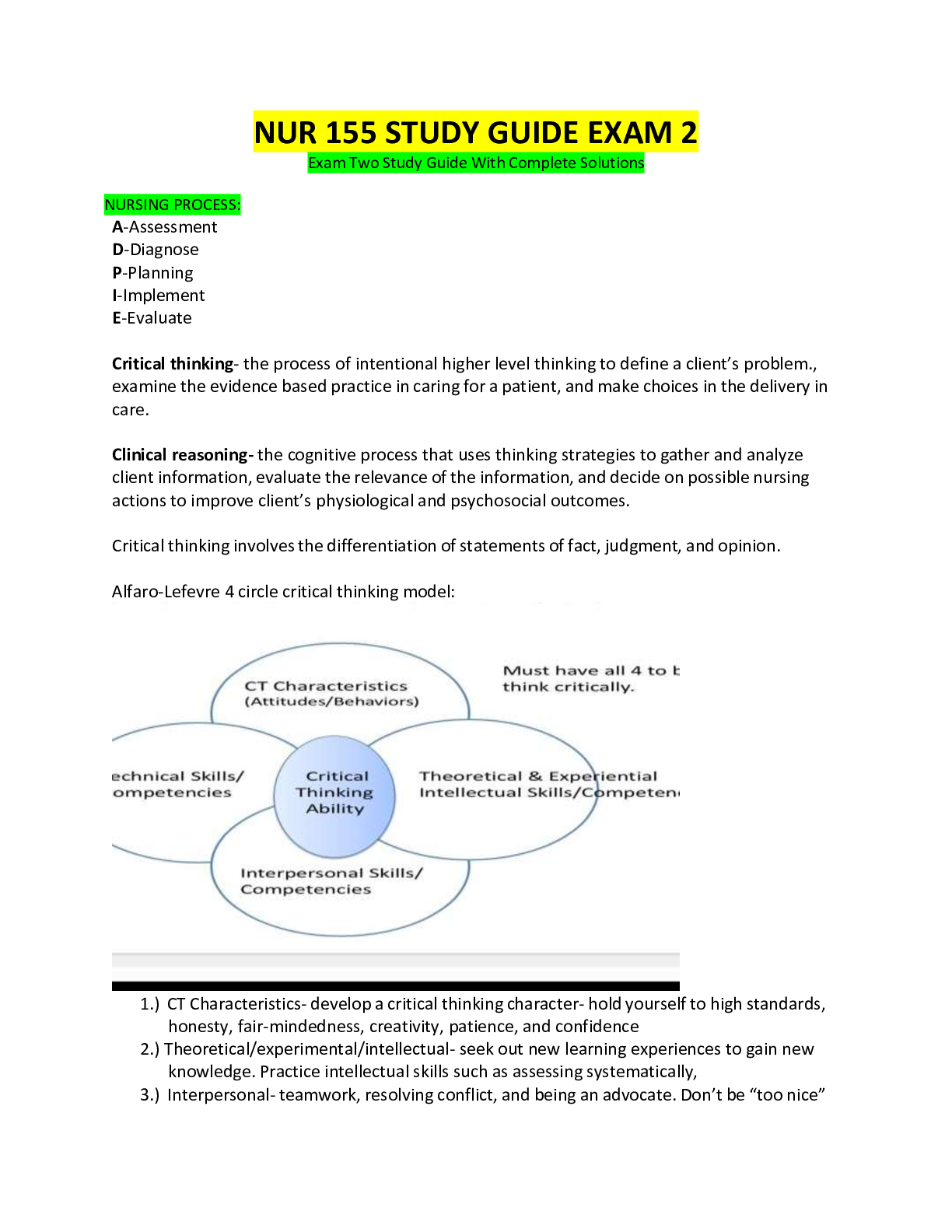
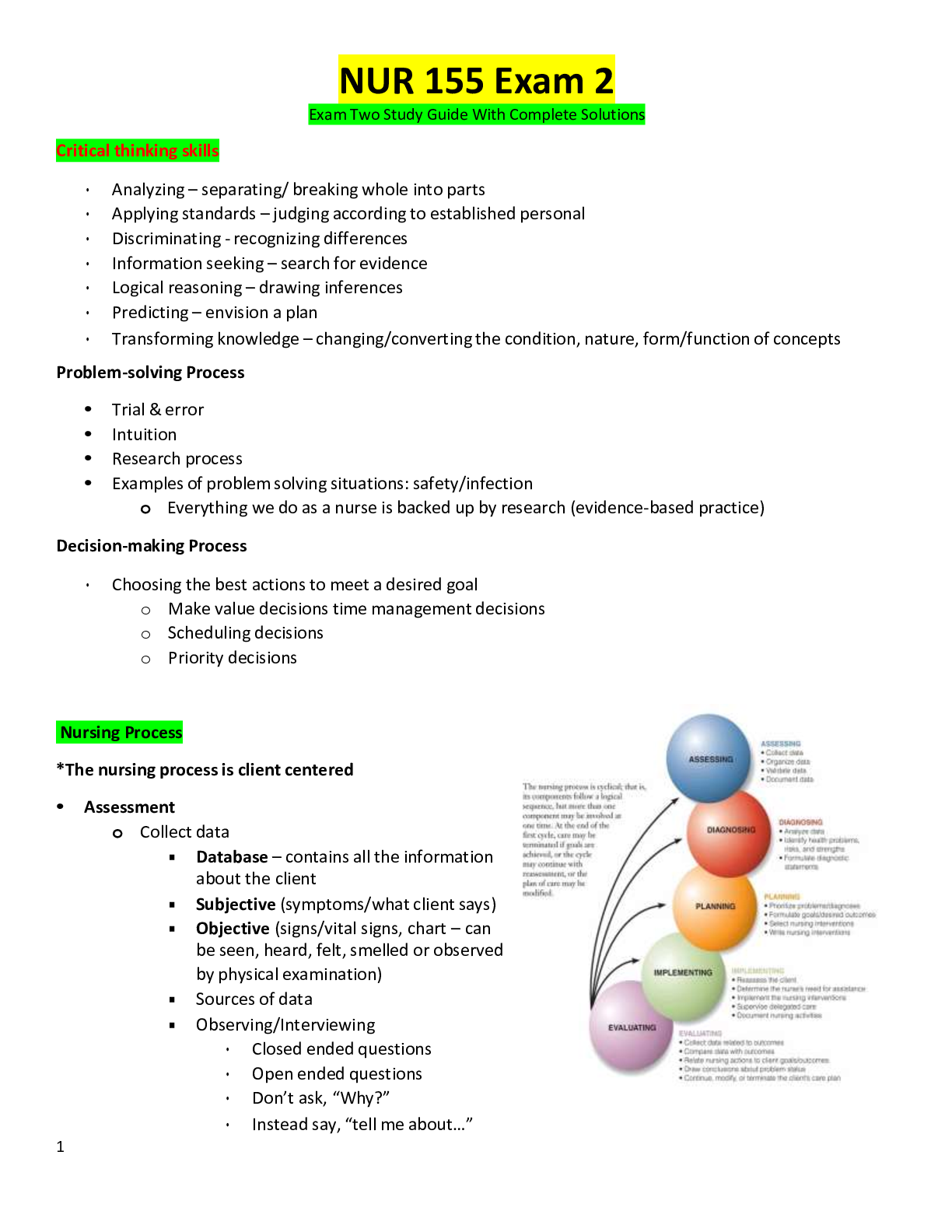
1. Without Fever: Afebrile 2. Substance or procedure that reduces fever: Antipyretic 3. Disappearance of sound when obtaining a blood pressure; typically oc- curs between the first and second Korotk... off sounds: Auscultatory Gap 4. Amount of energy used in a unit of time by a fasting, resting subject to maintain vital functions: Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) 5. Force exerted on the walls of an artery by the pulsing blood under pressure from the heart: Blood Pressure 6. Slower-than-normal heart rate; heart contracts fewer than 60 times/min: - Bradycardia 7. Also known as end titled CO2 monitoring, it provides instant information about how effectively CO2 is eliminated by the pulmonary system, how effectively it is transported through the vascular system, and how effectively CO2 is produced by cellular metabolism. Capnography is measured near the end of exhalation: Capnography 8. Volume of blood expelled by the ventricles of the heart, equal to the amount of blood ejected at each beat multiplied by the number of beats in the period of time used for computation (usually 1 minute): Cardiac Output (CO) 9. The transfer of heat from one object to another with direct contact: Con- duction 10. The transfer of heat away by air movement. A fan promotes heat loss through convection. The rate of heat loss increases when moistened skin comes into contact with slightly moving air: Convection 11. Temperature of deep structures of the body: Core Temperature 12. Secretion of sweat, especially profuse secretion associated with an ele- vated body temperature, physical exertion, or emotional stress: Diaphoresis 13. Pertaining to diastole, or the blood pressure at the instant of maximum cardiac relaxation: Diastolic 14. Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to one of lower concentration: Diffusion 15. Deviation from the normal pattern of the heartbeat: Dysrhythmia 16. Normal respirations that are quiet, effortless, and rhythmical: Eupnea 17. The transfer of heat energy when a liquid is changed to a gas. The body continuously loses heat by evaporation: Evaporation 18. Pertaining to or characterized by an elevated body temperature: Febrile 19. Elevation in the hypothalamic set point so body temperature is regulated at a higher level: Fever 20. Refers to a fever with an undetermined cause: Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO) 21. Occurs when the body is exposed to subnormal temperatures. Ice crys- tals form inside the cells, and permanent circulatory and tissue damage occurs: Frostbite 22. Abnormal condition caused by depletion of body fluid and electrolytes resulting from exposure to intense heat or the inability to acclimatize to heat: Heat Exhaustion 23. Continued exposure to extreme heat that raises the core body tempera- ture to 40.5° C (105° F) or higher: Heatstroke 24. Percentage of red blood cells in the blood, determines blood viscosity: - Hematocrit 25. Disorder characterized by an elevated blood pressure persistently ex- ceeding 120/80 mm Hg: Hypertension 26. Situation in which body temperature exceeds the set point: Hyperthermia 27. Abnormal lowering of blood pressure that is inadequate for normal per- fusion and oxygenation of tissues: Hypotension 28. Abnormal lowering of body temperature below 35° C, or 95° F, usually caused by prolonged exposure to cold: Hypothermia 29. Arterial blood oxygen level less than 60 mm Hg; low oxygen level in the blood: Hypoxemia 30. Autosomal-dominant trait characterized by often fatal hyperthermia in affected people exposed to certain anesthetic agents: Malignant hyperthermia 31. Occurs primarily in neonates. Because neonates cannot shiver, a limited amount of vascular brown adipose tissue present at birth can be metabolized for heat production: Nonshivering thermogenesis 32. Abnormally low blood pressure occurring when a person stands: Ortho- static hypotension 33. Amount of hemoglobin fully saturated with oxygen, given as a percent value: Oxygen saturation 34. (1) Passage of a fluid through a specific organ or an area of the body. (2) Therapeutic measure whereby a drug intended for an isolated part of the body is introduced via the bloodstream. (3) Relates to the ability of the cardiovascular system to pump oxygenated blood to the tissues and return deoxygenated blood to the lungs.: Perfusion 35. Abnormally low blood pressure occurring when an individual assumes the standing posture; also called orthostatic hypotension: Postural hypoten- sion 36. Condition that exists when the radial pulse is less than the ventricu- lar rate as auscultated at the apex or seen on an electrocardiogram. The condition indicates a lack of peripheral perfusion for some of the heart contractions: Pulse deficit 37. Difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures, normally 30 to 40 mm Hg: Pulse pressure 38. Abnormal elevation of the temperature of the body above 37° C (98.6° F) because of disease; same as fever: Pyrexia 39. Substances that cause a rise in body temperature, as in the case of bacterial toxins: Pyrogens 40. The transfer of heat from the surface of one object to the surface of another without direct contact between the two. As much as 85% of the surface area of the human body radiates heat to the environment: Radiation 41. Involuntary body response to temperature differences in the body. The skeletal muscle movement during shivering requires significant energy. Shivering sometimes increases heat production 4 to 5 times greater than normal: Shivering 42. Device for measuring the arterial blood pressure that consists of an arm or leg cuff with an air bladder connected to a tube, a bulb for pumping air into the bladder, and a gauge for indicating the amount of air pressure being exerted against the artery: Sphygmomanometer 43. Pertaining to or resulting from ventricular contraction: Systolic pressure 44. Rapid regular heart rate ranging between 100 and 150 beats/min: Tachy- cardia 45. Internal control of body temperature: Thermoregulation 46. Respiratory process by which gases are moved into and out of the lungs: Ventilation 47. Temperature, pulse, respirations, and blood pressure: Vital signs 48. Activities that depend on the patient's motivation to adopt a specific health program: Active Strategies of Health Promotion 49. Illness characterized by symptoms that are of relatively short duration, are usually severe, and affect the functioning of the patient in all dimensions- : Acute illness 50. Illness that persists over a long time and affects physical, emotional, intellectual, social, and spiritual functioning: Chronic illness 51. Dynamic state in which individuals adapt to their internal and external environments so there is a state of physical, emotional, intellectual, social, and spiritual well-being: Health 52. Understanding the process of changing behaviors will help you support difficult health behavior changes in patients: Health Behavior Change 53. Because health and illness are complex concepts, models explain the relationships between these concepts and a patient's attitudes toward health and health behaviors: Health Behaviors 54. Conceptual framework that describes a person's health behavior as an expression of his or her health beliefs: Health Belief Model 55. Activities such as routine exercise and good nutrition that help patients maintain or enhance their present level of health and reduce their risk of developing certain diseases: Health Promotion 56. Comprehensive view of the person as a biopsychosocial and spiritual being: Holistic Health Model 57. (1) Abnormal process in which any aspect of a person's functioning is diminished or impaired compared with his or her previous condition. (2) The personal, interpersonal, and cultural reaction to disease: Illness 58. Ways in which people monitor their bodies, define and interpret their symptoms, take remedial actions, and use the health care system: Illness Behavior 59. Health education programs or activities directed toward protecting pa- tients from threats or potential threats to health and minimizing risk factors- : Illness prevention 60. Activities that involve the patient as the recipient of actions by health care professionals: Passive Strategies of Health Promotion 61. First contact in a given episode of illness that leads to a decision regard- ing a course of action to prevent worsening of the health problem: Primary Prevention 62. Any internal or external variable that makes a person or group more vulnerable to illness or an unhealthy event: Risk Factor 63. Level of preventive medicine that focuses on early diagnosis, use of referral services, and rapid initiation of treatment to stop the progress of disease processes: Secondary Prevention 64. Activities directed toward rehabilitation rather than diagnosis and treat- ment: Tertiary Prevention 65. Dynamic state of health in which an individual progresses toward a higher level of functioning, achieving an optimum balance between internal and external environments: Wellness 66. Abnormal lung sounds heard with auscultation: Adventitious Sounds 67. Partial or complete loss of hair; baldness: Alopecia 68. Abnormal neurological condition in which language function is defective or absent; related to injury to speech center in cerebral cortex, causing receptive or expressive aphasia: Aphasia 69. (1) Heartbeat as listened to with the bell or diaphragm of a stethoscope placed on the apex of the heart (2) Point where the heartbeat can most easily be palpated through the chest wall. This is usually the fourth intercostal space at the midclavicular line: Apical impulse or point of maximal impulse (PMI) 70. Opaque ring, gray to white in color, that surrounds the periphery of the cornea. The condition is caused by deposits of fat granules in the cornea. Occurs primarily in older adults: Arcus Senilis 71. Wasted or reduced size or physiological activity of a part of the body caused by disease or other influences: Atrophied 72. Method of physical examination; listening to the sounds produced by the body, usually with a stethoscope: Auscultation 73. Audible abdominal sounds produced by hyperactive intestinal peristal- sis: Borborygmi 74. Abnormal sound or murmur heard while auscultating an organ, gland, or artery: Bruit [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 41 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 14, 2022
Number of pages
41
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 14, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37