Anthropology > STUDY GUIDE > RSSS 315 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE (All)
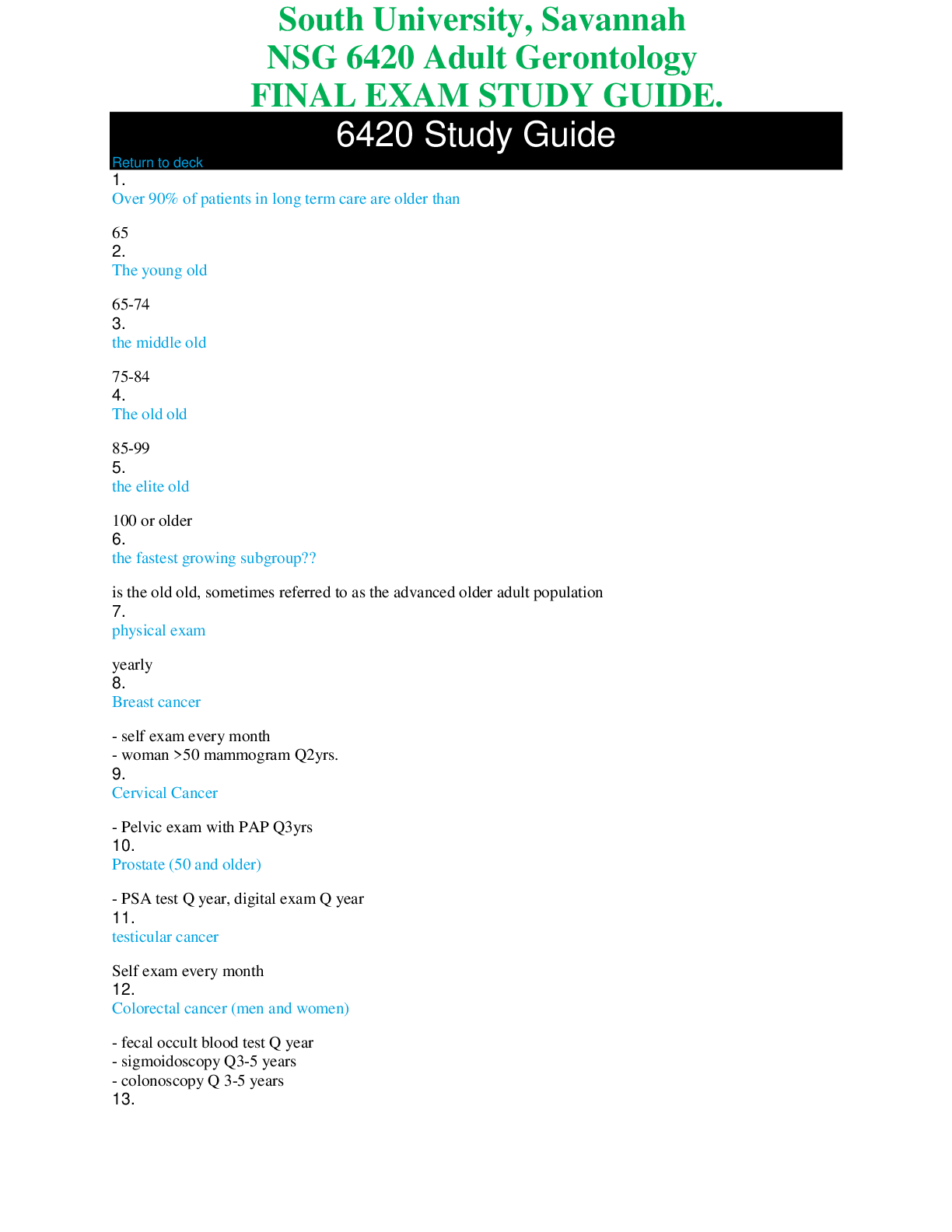
RSSS 315 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
Document Content and Description Below
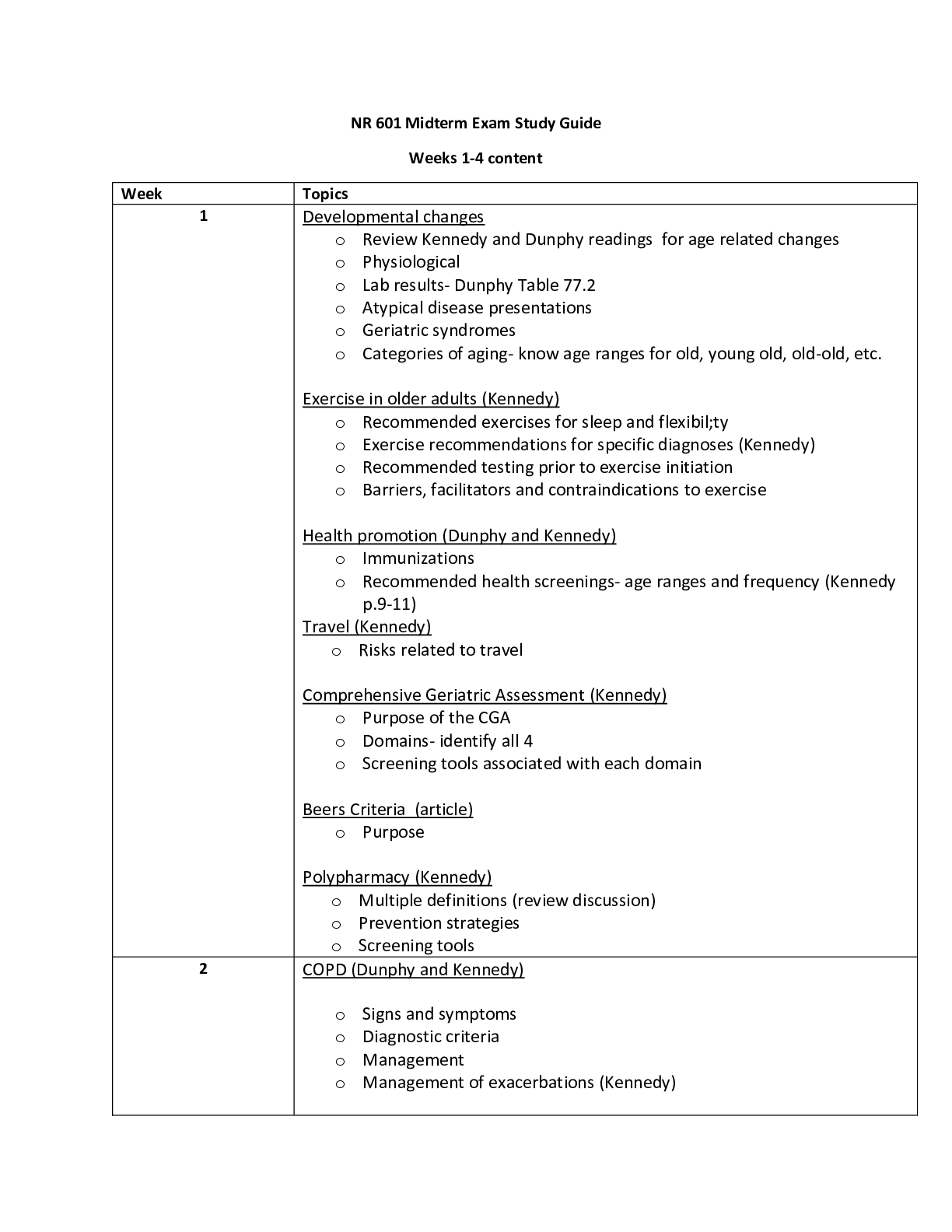
RSSS 315 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE ● Katharina Wilson and the 4 possible origins for the word "vampire," as well as which of the 4 she identifies as the true origin. ○ Turkish (uber = witch) ○... Greek (pij = drink) ○ Old Slavic (opiri) ○ Hungarian (vampire) ○ True origin- Slavic ● Various roots / forms for the word "werewolf" in English, Greek, and Slavic (Russian, Serbian); the ways some of those words might intersect with the vampire; the cultural connection between shape-shifting and the bear in some cultures ○ Old English - wer (“man”) and wulf (“wolf”) ○ Greek - likos (“wolf”) and anthropos (“human”) ■ Lycanthrope (technical term for werewolves) ○ Serbian - vuk (“wolfn”) and dlak (“hair, fur, skin”) ○ Vukodlak (slavic term) ○ Vurdalak - shares a connection with vampire (shapeshifter/bloodsucker) ○ Shapeshifting connection between werewolves and bears ■ Beowulf (bee-wolf = bear) ■ Sami rituals and bear transformation ● Who Sts. Cyril and Methodius were and why they are important in many East European cultures ○ Christian missionaries. They influenced the conversion to christianity that occured in between the 9th or 10th century. ● Slavic Paganism: Who Perun, Veles, Jarilo, and Morana were & what they represented; what "dvoeverie" is and at least one example of it. - Perun= god of sky, lightning, fire, hills (supported upper class), the thunder god; strong man, beard = power, upperlcass - Veles= god of earth, water, cattle, commerce, lowlands - shapeshifter/ trickster, but not evil, steals Perun’s cattle - Represents the ordinary person, down to earth - Jarilo= god of spring and life; kidnapped by Vales - raised in the underworld by Vales, return = spring, reunion=boutiful harvest - Morana= goddess of winter, rebirth, death, dreams - Dvoeverie= Dual Belief; coexistence of organized, canonical religion and those beliefs that have a pre-conversion, pagan character, transition or conversion - Ex: Veles → St. George (cattle, serpents) - Ex: Jarilo/ Morana → Christ ● Folk Tales: Who Vladimir Propp was and his theory of the folktale; how many "functions" are in his theory (but not each individual function); the 4 "spheres" and their titles; the 7 character types and their role; the three other highlighted approaches to folktales and their primary authors/theorists ○ Vladimir Propp the man: ■ Soviet Scholar ■ Aimed to devise science of literature ■ Published Morphology of the Folktale in 1928 ○ There are 31 functions. ○ The names, etc. may change, the actions of the characters within the plot are constant. ○ 31 functions create a recognizable fairy-tale skeleton even as the outer shape changes. ○ Tale may not contain all functions, but will appear in a similar sequence. ■ 1st Sphere: The Problems Begin ■ 2nd Sphere: The Body of the Story ■ 3rd Sphere: The Donor Sequence ■ 4th Sphere: Return of the Hero Character Type Character Role The Hero Thwart the villain, get the prize. The Villain Struggle with the hero, use trickery. The Prize/Princess The goal of the quest. The Donor Tests the hero and gives a gift to help. The Helper A person or magical entity that helps the hero on the quest. The False Hero Tries to take credit from the hero and/or get the Princess/Prize. -Also Dispatcher: Identifies the need and sends the hero Three other highlighted - gendered reading (Marcia Lieberman) - socio-political readings (Jack Zipes) - psychological (Bruno Bettelheim) ● Baba Yaga tales: identifying characteristics of her home, the two objects the cat gives the children, the reason why the animals/objects help the children, how to identify Baba Yaga - She lives in a hut on hen’s feet and a rooster’s head on top, in a forest - The cat gives the children a towel and a comb - The animals help the children because they are nice to them and do them favors, which Baba Yaga has never done for them - Baba Yaga is a witch, old grandmother, responds to ‘Izboushka’, rides a broom, found in the hut with one foot in one corner, another foot in another corner and knees close to the ridge pole ● "The Peasant and the Corpse": The object the peasant will not return until the vampire reveals his secret - the coffin lid ● "The Vampire": how Marusia is able to track the young man from the party, what object Marusia turns into after she dies, how Marusia is able to defeat the vampire. - Takes a ball of thread, loops a bit of thread on a button on his clothes. Waits until it all rolls out, then follows it. - a flower above her grave - Sprinkles him with holy water from a vial her grandmother gives her. ● "The Sorceress": what the young boy sees the princess do - take off her head, clean it, comb her hair and then reattach it ● "The Three Brothers": what the sister trades for, how the youngest brother "tracks" the sister; what animal kills the sister - Iron teeth and a stone to sharpen them - Puts water in kettle over the fire; the water turns to blood; the more it bubbles the closer she gets to his brothers, eventually the blood turns back into water so she is dead - A dog ● "The Young Man and His Vampire Brother": why the vampire helps the young man, why the young man runs away from his bride, how the vampire "cures" the young man's bride. - The young man pays off the vampire’s debt after he died and gave him a proper burial - he runs away because he lost all his money in a card game - sliced her down the middle to release the serpent inside of her ● "The She-Wolf": How the woman transforms into a wolf & how the soldier prevents her from transforming; how the son "rescues" the mother - She transforms by having a wolf’s pelt. - The soldier hides the pelt so she is stuck in human form. Nails it to the wall - The son reveals where her pelt is hidden. ● "The Werewolf's Daughter": what the father does to his daughters, the ways the youngest daughter escapes from the father, how the father frames the daughter for a crime, how the father is defeated - lures 8 of the 9 into the forest and kills them separately - the 9th daughter strips down, hits her father, and runs to a barn/haystack to hide - Dresses as a beggar, enters the castle, enters the nursery, slits the throats of his daughters two children, places the knife he used under the daughters pillow, then leaves. - He is “cast of a cliff into the sea” ● "Little Red Riding Hood": the moral of the Perrault version of the tale - pretty women should not talk to strangers ● The four types of Werewolves and their origins (i.e., punishment, demonic possession, etc.) - Literal: person actually transforms into a werewolf Sign of punishment for offending gods like ishtar, Lycaon, Actaeon, - Spiritual: may or may not physically change, but person has “spirit” of the wolf (shamanic rituals) Sign of magic power through wearing wolf skins - Demonic: person is possessed and/or the devil does the mischief while person sleeps or in a catatonic state - Medical: person suffers from a mental illness or other medical condition (believes they are a werewolf, but doesn't change) ● Lupercalia: Its date and origins - Date: Feb 15th - Roman celebration - Contemporary valentine’s day - Fertility rites to make women more fertile, matchmaking ● The key werewolf trials from St. Claude (France), their dates, and how the associations of the werewolf changed over time. - Pierre Burgot and Michael Verdun (1521) - Confessed under torture to being werewolves - Claimed to have made deal with 3 men dressed in black who would protect their sheep for rejection of god - Burgot given ointment that transformed them into wolves that killed/ate children - executed - Pierre Tornier, wife, and sister (1551) - All werewolves (15 murders) - Accused of lycanthropy and witchcraft -> burned alive at stake - 1570s - Real wolf attacks increased - “Wolves the size of small horses” - Civilians armed to defend against werewolves - The Gandillon Family (1598) - first sister killed 2 children then was killed by villagers - 3 siblings confessed to being werewolves, holding and luring children to black sabbath, having sex with the devil in the form of a goat, creating hailstorms, and eating people all as wolves - Changed by salves - Matheiu Brothers acquitted (1663) - Mistrial of brother - Werewolf gradually becomes gender neutral and generally associated with the working class of society - 80% were men at first → 50% by end - Threat from lower classes ● Peter Stubbe: the date and location of his death, how he transformed into a wolf, who helped him transform, how he was caught and executed ○ October 31st, 1589, Germany - a girdle that allows him to transform into a werewolf when he wearsz it - The devil - With the help of God, hunters gathered hunting dogs that chased after the wolf; he was captured, examined, and executed by being attached to wheel, flesh being torn off, legs and arms broken, head struck from body and burned ● Old Thiess and the Benandanti - how they differ from other werewolves in history ○ Thiess of Livonia - Admits to being a werewolf, but says he is fighting the devil and witches (werewolf as community protector) ○ Given 20 lashes and banished from town ○ Benandanti (Italy) - Men and women born with certain signs have the power to fight demons; while in a cataleptic state, their spirit takes animal form and protects area and crops ○ 100 Benandanti questioned in trial - only warning given no punishments ● Illnesses associated with Medical Werewolves ○ Clinical Lycanthropy ■ rare psychiatric syndrome, a form of schizophrenia ■ delusion of transformation (or undergoing transformation) into an animal form ● feeling of being an animal (not just a wolf, but any type) ● Crawling on all fours, growling, howling, living outdoors ○ Hypertrichosis (“werewolf syndrome”) ■ Abnormal amount of hair growth over body ■ May be congenital (incurable) or acquired (treatable) ● only 50 cases of congenital hypertrichosis recorded. ● Jan Perkowski's 4 Types of Vampires and their meaning; Perkowski's 10-point analysis ○ Folkloric ■ a supernatural creature that can be detected, warded off, and destroyed in ways prescribed by local lore and tradition ○ Psychic ■ the vampire feeds on psychic, spiritual, or emotional energy rather than blood ○ Psychotic ■ Person is not a vampire per se, but suffers from a mental illness or medical condition ○ Literary ■ a fictitious creature, possibly based on truth, that combines aspects of the other three types of vampires 10-point Analysis: o 1. Information Source — This might be a folklore or anthropological field report, a folk tale, a proverb, a court record, a newspaper article, a traveler's eyewitness account, a Christian polemic, or some other source. If the source is published, knowledge of the author's credentials and the date of publication are essential. o 2. Country and Region — Vampire belief varies not only from country to country, but even from village to village. In addition, it sometimes happens that vampire beliefs are held only by a minority group within a given country. o 3. Name — The various designations for the vampire should be carefully listed with literal English translations, since the very name frequently provides a clue to the belief structure. o 4. Origin — How did the vampire become a vampire? Is the malady endemic or epidemic? o 5. Detection — How is the vampire discovered? Can he be detected before he attacks or only after there is a victim? o 6. Attributes — What are his distinguishing characteristics? First and foremost, is he alive or dead? Does he show contamination from other daemons: werewolf, succuba, poltergeist, ghoul, etc.? o 7. Activity Pattern — How does he ply his trade? Which sort of sustenance does he require: blood, flesh, other? o 8. Precautions — Once it is known that there is a vampire, what can be done to protect oneself? o 9.Cures - Which are the final measures to be taken to rid oneself of the pest? o 10. Social/Psychological Role — Does he enfranchise anomalous members of the society? Does he anthropomorphize repressed fears and desires? ● Peter Blagojevich: when, where, activities, signs on corpse that he was a vampire ○ source: german/Austrian imperial bureaucrat ○ country/region: Serbia, 1725 ○ name: Petar Blagojevich, vampir, vukodlak, “evil”, “the dead” ○ origin: unknown ○ activity pattern: 9 people die after a brief illness. all claim Petar came to them in the night and strangled them. Petar returns to ask his wife for his shoes ○ Detection/attributes: PB’s corpse exhumed and a. no odor noticed; b. hair, beard, and nails had grown; c. fresh blood in the mouth; d. “wild signs”; e. fresh blood flows after PB is staked ● The Vrykolakas: when, where, signs of the vampire's presence, cure ○ -From Greece (1740s), revenant (came back from death) ○ -2 days after the burial the man seen walking through the night, turned off lamps and grabbed people from behind-Say mass/prayer and pull out corpses heart to stop the creature ○ -Beating people, breaking doors and worst of all drinking all the liquor in the town ○ -Heart was not enough so the towns people stabbed body over and over and took body to an island because spirits can’t cross water ○ -Written by a botanist so skeptics arised, warmth of body came from candles ● South-Slavic Vampires & The Lastovo Testimonies: the vampire's Origins, Precautions, Activities, Detection, and Cure ○ South-Slavic Vampires: Associated with death and used to explain various forms of evil that befell people; Origin- Problem with death, burial, or birth. Precautions- Place a crucifix in the coffin. Spill seeds around the grave. Pierce the corpse with thorns or stakes. Activity Pattern- Tends to attack family, friends, and others. Sheep and cattle die unexpectedly. Sudden illness or epidemics. Detection- Check the corpse for signs. Cure- Destroy the vampire with a stake to the heart. Decapitate the corpse and/or burn the body. ○ The Lastovo Testimonies: Early 18th century on the Island of Lastovo, severe epidemic swept the population; locals believed that vampires were to blame. ○ Villagers went on rampage digging up graves, 17 vampire hunters were arrested and convicted of grave desecration ○ The role of sexual relations in the accounts ● The general social/psychological roles of the vampire in the historical testimonies ○ The vampire helps explain sexual relations/ births (usually after the husband died) without having to admit the adultery within a community ○ The vampire helps to explain the natural process of death and decay ● Where the Balkans are; which country Transylvania is in ○ Balkans: Geographic region in Southeastern Europe ○ Transylvania is in Romania. ● What is orientalism and who coined it? ○ Orientalism (Edward Said 1978) -; Western prejudice against Eastern peoples/culture. Derives from Western images/ representations that reduce the East to fictional stereotypes and exotic locales. Orientalism helps the West feel “superior” and is the basis of Western imperialism throughout history ● Vlad III Dracula - date of birth, country and region associated with him, the origin / roots of the word "Dracula" ○ Date of Birth: 1428-1476 ○ Country / Region: Wallachia / Transylvania ○ “Dracula” means “Son of Dracul”, draco means “dragon” or “devil”, as Vlad Tepes’ father had the moniker “Dracul”, having been a member of The Order of the Dragon ● "The Story of Dracula: the date of Dracula's death, how Dracula supposedly died (according to this account), the "great sin" of Dracula, at least one example from the text of Dracula's cruelty, at least one example from the text of Dracula's sense of justice ○ Date of Death: Jan 1477 ○ His people trampled and killed him ○ Converts from Orthodox to Catholic ○ Killed disabled and sick people ○ Dracula believed in honesty. A merchant who lost 160 gold ducats informed Dracula. Dracula threatened to burn the city if the gold was not found and returned with one extra gold piece. The merchant counted his returned gold and realized there was one additional piece. He informed Dracula and Dracula said had he not told him of this additional piece he would have been impaled with the thief, but since he was honest he could go in peace. ● Elizabeth Bathory: country, year of birth / death, why she was put on trial and how she was punished. ○ 1560 — Born in Hungary/Slovakia ○ 1574 — Gives birth to a (peasant) baby out of wedlock ○ 1575 — Marries and manages affairs of the castle ■ punishment and torture of servants begins ■ husband joins in and teaches new tortures ○ 1604 — husband dies ○ 1609 — Elizabeth begins torturing noble women ○ 1611 — Trial and Punishment ■ names 650 victims noted in a journal, all in her handwriting ■ accomplices executed ■ bathory given solitary confinement (walled in bedroom) ○ 1614 — death ● "The Epic of Gilgamesh": who Ishtar is, how she punished her lover ○ Daughter of the gods Anu and Antum ○ Asks gods to let her seek revenge on Gilgamesh; sends The Bull of Heaven to wreak havoc on world and split the ground ● Ovid's Metamorphosis: who Lycaon is, why Lycaon was turned into a wolf ○ Lycaon: King of Arcadia, turned into a wolf ○ Tried to trick Zeus into eating human flesh. Zeus transformed him into a wolf as punishment ● Volsung Saga: how/why Sigmund and Sinfjotli became wolves ○ They found a wolf skin hanging up in the forest and when they put it on they transformed into werewolves. ● "Viy": Author, date, setting, name of lead character, what the lead character and the old woman do, how Viy "captures" the lead character, the social/psychological role of the vampire in "Viy" - 1835, by Nikolai Gogol - setting: Ukraine - Khoma Brut (protagonist) - Khoma Brut is caught in the homestead of an old woman at night, the woman jumps on his back and rides him as if he were horse along neighboring field. Khoma Brut is able to get a way and saddles the woman the woman is beaten by the woman turns into a beautiful young woman and Khoma Brut runs away. Khoma Brut is then called upon by the old woman to read the prayers. He recognizes the woman as the witch from that night. He is able to protect himself from the witch for the first two nights, but on the third night she summons a bunch of demons and Viy. - Khoma Brut can't help self and ends up looking at viy and dies. All the demons are caught in the church and parish when the sun rises. - Represents fear of looking and being seen/ not seeing. No escape from what lies below one’s conscience. - Sexual tension/ forbidden desire- “midnight rides”; corruption of motherhood (attacking baby and wife) ● "Family of a Vourdalak": Author, date, setting, social/psychological role of vampire - 1839, by Aleksey K. Tolstoy - Date: 1839 - setting: Serbia 1769 - social / psychological role of the vampire: - Sexual tension: beautiful exotic woman who brings danger or death to the male hero - Contamination of the west by the east: vampirism is contagious ● The 3 sources of the English / Western literary vampire, when the word "vampire" enters the English dictionary, when vampire bats become known in the West, who Vuk Karadzic was 3 sources of the English/Western vampire - News/scientific discussion - Slavic folklore - Gothic novel - 1734 - “Vampire” Enters the English dictionary in - 1810 - First reports of a vampire bat in Western scientific journals - Serbian who worked with the Grimm Bros. to translate and publish South Slavic epics and tales into German and other languages ● Lord Byron: date / title of literary work related to the vampire, date, name of the vampire ○ 1816/1819 “A Fragment of a Novel” ○ Augustus Darvell ● James Polidori: date / title of literary work related to the vampire, date, name of the vampire character (and who that character is based on), how Polidori's story is a pivotal transition ○ The Vampyre 1 April 1819 vampires name is Ruthven ○ Pivotal attribute: vampire no longer the lowly peasant of folklore, but now a charismatic, mysterious aristocrat ● Varney the Vampyre: Author, date, location, “cure”, and social/psychological role ○ 1847, by James Rymer, ○ England & Italy, ○ Suicide by volcano ○ sympathy ● Carmilla: Author, date, vampire hunter character’s name, how Carmilla “hides” over the course of time ○ 1872, by J. Sheridan Le Fanu, ○ General Spielsdorf (vampire killed his niece) and Baron Vordenburg (descendant of past vampire hunters) ○ Hides by changing her name into different anagrams of ‘Carmilla’; sleeps in hidden tomb for Mircalla ● The Were-Wolf: Author, date, name of werewolf character, who Cesare Lombroso is, how the book contradicts Lombroso’s theories ○ 1896, by Clemence Housman, ○ White Fell ○ Lombroso founded the process of criminal anthropology, anthropologist that believed women were of 3 types: The Normal Woman, The Prostitute, The Criminal Woman ○ Lombroso’s Criminal woman is an unstable personality and masculine, degenerative primal type. White fell is an enchanting strong woman who is kind to everyone and dotes on children, she is not a liar, but must stay safe, wears clothes that are half masculine and yet not unwomanly others desire her, kills for food, out of instinct not out of malice, chooses prey by ritual; casts voices at the door those she kisses will die. ○ ● "The Company of Wolves": Author’s name ○ 1979, by Angela Carter ● When Animals Dream: Name of the werewolf, signs of lycanthropy in the film ○ Marie, and her mother ○ she begins to grow fur and have personality changes. While having sex with someone her eyes glow green and her spine starts to change. Also, her nails begin to grow in and bleed. ● The Hunger: Date, what illness the film uses vampirism as a metaphor for (according to many) ○ 1983, ○ AIDS ● Dracula (the novel): author, date, key characters, "The New Woman" and its relation to the novel, "troeverie" and its connection with Van Helsing, how Dracula represents Orientalism, why Harker is in Transylvania, how Dracula gets to England, Renfield (his illness and connection with Dracula), what happens to Lucy and why, what happens to Mina and why, how Dracula is defeated Author: Bram Stoker ○ Date: 1897 ○ Key Characters: Jonathan Harker, Mina Murray, Lucy Westenra, Arthur Holmwood, Dr. Seward, Quincey Morris, Abraham Van Helsing, Dracula ○ The New Woman: New Woman mentioned in Chapter 8 by Mina ○ "Troeverie": How technological advances, superstition, and christianity interact with one another. From SparkNotes: Van Helsing is a doctor (technological advance), philosopher and metaphysician. versed not only in the modern methods of Western medicine, but with an unparalleled knowledge of superstitions and folk remedies.morally righteous and religiously committed. Van Helsing views his pursuit of Dracula with an air of grandiosity. He envisions his band as “ministers of God’s own wish,” and assures his comrades that “we go out as the old knights of the Cross to redeem more.” ○ Orientalism: Dracula represents western fears of infection from the East. He preys on Lucy Westenra (notice last name) and turns her into a vampire. He also represents “reverse colonization” by purchasing property in England ○ Harker: Help Dracula buy a property in England ○ Dracula gets to England by using a boat and he killed the passengers ○ Renfield: a patient at Sewards mental asylum he consumes living creatures, believing they will provide him with strength vitality and life force. From SparkNotes: Dying, Renfield admits to the other men that Dracula often visited him, promising him flies, spiders, and other living creatures from which to gain strength in return for Renfield’s obedience. Later, when Mina visited him, Renfield noted her paleness and realized that Dracula had been “taking the life out of her.” He grew angry, and when the count slipped into his room that night, Renfield attempted to seize him. The vampire’s eyes “burned” him, and he was flung violently across the room as Dracula slipped away into the asylum. ○ Lucy: gets infected by Dracula so the team has to kill her. Her fiance Arthur kills her ○ Mina: Dracula makes her drink his blood so she is tied to him / he can use her as a spy ○ Dracula’s Defeat: Morris plunges his knife into Dracula’s heart as Harker slashes his throat Dracula dies and turns to dust with a look of peace on his face ● Nosferatu: Date, country of release, director, relationship to Dracula, relationship to illness, pivotal feature of the film for the vampire tradition ○ March 4, 1922 ○ Germany ○ F.W. Murnau, ○ Loose adaptation of Dracula - could not get copyright so they changed the names ○ Spanish Flu of 1918-1920 ○ First film featuring death of vampires by sunlight. ● Blacula: Date, country of release, director, name of vampire, W.E.B. DuBois and “double-consciousness” ○ 1972 ○ USA ○ William Crain ○ Mamuwalde or Blacula ○ He has double-consciousness in that he has the identity of a vampire so he feels the desire to kill people, but he also has the identity of a human so he wants to find his love again whom he thought was his dead wife. ● Psychic vampires: qualities, The Blood of the Vampire (date, author, country, and relationship to psychic vampire) ○ One of Jan Perkowskis four types of vampire. ■ The other 3: Folkloric, literary, psychotic. ■ Psychic Vamp: Feed on variety of forces: emotions, memories, talents, ideas, creativity, energy. ■ Hide in the fabric of society much easier than traditional vampires, no constraints, traditional protections may not work. ■ MOST DANGEROUS OF ALL! ○ 1897 by Florence Marryat, UK, ● "Luella Miller": Author, date, attributes / activity pattern of the vampire, Lydia Anderson ○ 1903, by Mary Wilkins Freeman ○ Helpless, People start dying after being in contact with Luella, Psychic vampire ○ Lydia Anderson (neighbor) shielded herself from her when she realized how Luella is causing death. ● "The Transfer": Author, date, attributes / activity pattern of the vampires, Mr. Frene Sr. ○ 1912, by Algernon Blackwood ○ Activity patterns: drain others vitality within crowds ○ Mr. Frene mostly loner until entering crowd ○ Benefited from others ideas ● Transformation scenes: points of emphasis in transformation scenes - Sympathy & fear/ horror - The Observer ● American Werewolf in London: Date, country of release, director, name of main character ○ 1981 ○ USA ○ John Landis ○ David Kessler ● Let the Right One In: Date, country of release, name of the vampire, who Oskar is and how he develops a relationship with Eli ○ 2008 ○ Sweden ○ Oskar develops a relationship with Eli after he moves into Oskar’s apartment complex. Oskar befriends Eli as they are both social outcasts. Eli saves Oskar from his bullies and they run away together. ● Ginger Snaps: Date, country of release, names of the two sisters, connection of shape-shifting with adolescence / “body horror” ○ April 1st, 2000 ○ Canada ○ Sisters: Ginger & Brigitte ○ The physiological changes that teenagers go through until they can no longer be recognised is just like shape shifting in monster tales. ○ Relates to the hypersexuality of teens during puberty i.e. extremely turned on when she’s “changing” ● Vampire and economics: How/Why Marx & Engels connect capitalism to the vampire, what is "dead" labor v. "living" labor ○ They wrote the communist manifesto. Capitalism feeds off others work just like vampires feed off others blood or emotions. Living-> productive labor builds self-worth+pride" and "dead->exploitative from other’s work" labor: ● "Girl with the Hungry Eye": Date, author, country of release, how the vampire feeds / is active ○ 1949, Fritz Leiber, ○ country of release: USA, ○ how the vampire feeds / is active: she feeds off of other people’s ‘lives’ and memories and they tell her things because she has the essence of captivation that comes from her eyes ● "Mindworm": date, author, country of release, how the vampire feeds, how the vampire is defeated ○ 1950, by C.M. Kornbluth ○ country of release: USA, ○ how the vampire feeds, how the vampire is defeated: He is a psychic vampire. The Eastern Europeans had some knowledge in vampires and they recognized him and staked him to the heart. ● Genre: definition of, types of (restricted v. free), a definition for post-modernism ○ Genre: category of music, art, literature, etc., characterized by similar forms, styles, or subject matter. ○ Restricted: genres can be stifling, the idea of having to produce a “classic” could prevent growth or fresh ideas ○ Free: genres change and adapt, possibly through “pastiche” or mixing of elements ○ Post-modernism: combine multiple genres to create a unique narrative to comment on situations or art itself ● "A Werewolf Problem in Central Russia": date, author, country of release, Russian folklore (Rusalka, Leshii, Firebird, Domovoi, Nightingale the Robber) and their attributes ○ Date: 1994 ○ Author: Victor Pelevin ○ Country and Region: Konkovo, Russia ○ Rusalka: female water nymph. Leave the waters at midnight to dance and nurture crops. Undead rusalka: soul of woman who died near water and haunts the areas. Beauty seduces young men to death ○ Leshii: male wood spirit. Change height, size, form. Leads travelers astray in the woods ○ Firebird: magical glowing bird (blessing/doom). Feathers glow as flame. Often in folktales as a premonition of difficulty of a hero(ine)’s goal. ○ Domovoi: male house spirit. Lives under stove or threshold, protects house in turn for food. Causes problems if angered by dirty house or disrespect. Prophetic tough. Need to take with you in a shoe if moving houses. ○ Nightingale the Robber: Human-bird monster, flies, lives in a nest, has human hands, powerful whistle and scream is his weapon, he is captured and killed by Ilya of Murom ● "Wolfland": Date, author, how one becomes a werewolf in the story ○ 1983, by Tanith Lee. ○ One becomes a werewolf by eating/swallowing yellow flowers from the Wolfland forest, calling on the wolf-woman (with the head of a wolf and yellow hair), she’ll come and give you the “gift” until you die. ● Vampire Hunters & Hybrids: 4 Tasks of Van Helsing & how they compare with modern vampire hunters like Blade or Anton ○ The 4 tasks= Identify a group of “students”; protect others; teach students to broaden their views; prove that vampires exist. ○ Contemporary Vampire Hunters: - Work as a team - Mediate the relationship between the vampire world and the human world - A post-human hybridity - Humans + vampires must exist as enemies - Inclusivity: team working together ● Blade: Date, country of release, how Blade defeats the main vampire ○ 1998 ○ country of release: USA, ○ Blade defeats Frost by several injections of the EDTA serum, and explodes, but first he must drink Dr. Karen Jensen’s blood to regain his strength. ○ Last scene is in Moscow, Russia. Blade saves women there. ● Night Watch: date, country of release, who the Others are (generally speaking) ○ 2006 ○ Russia ○ The Others are individuals that have greater powers than ordinary humans (like shapeshifters, sorcerers, witches and vampires) ○ The others are also divided into the Forces of the Light and the Forces of the Darkness --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- DON’T FORGET YOUR ESSAY TOPICS! *this is just a little reminder in case anyone forgets, it does not need any notes because it is individually written :) Essay Topics. You will need to write a response to any TWO of the essay topics listed below. There is no set word-count minimum for the essays, but it is expected that to fully and thoughtfully answer the prompts you will likely need 3-4 paragraphs (for each response); be sure you have some sort of introductory statement and final take-away in your responses as well. The essay topics will not change and will appear on the test exactly as posted here, so you may consider your response to the various topics as you prepare your notes for the test. Topic 1. The scholar Chantal Bourgault Du Coudray writes, “like other Gothic monsters, the werewolf has been thoroughly constructed as an alien ‘other’ threatening society; [the werewolf is] the negative of a normalized social identity” (Curse of the Werewolf 50). Agree or disagree with this statement, noting in what ways the werewolf and vampire have become a means to express humanity’s fears of “others” (broadly understood). In your essay, use evidence from at least four works (texts or films) from the course materials this semester to support your opinion. You must include at least one example (each) of a werewolf and a vampire, you may not write about only one monster. Topic 2. Caitlin Giacopasi writes that “beyond the restrictions of humanity, the werewolf could publicly act and desire in ways which the average man could only dream. […] The refusal to accept a gender role and the inability to embrace a sexuality mark the monster” (“The Werewolf Pride Movement” 5-6). Discuss the way(s) in which the werewolf and vampire break or complicate traditional gender roles and/or sexual identity based on what we have seen in the course materials this semester. In your essay, discuss at least four works (texts or films) from the course materials this semester. You must include at least one example (each) of a werewolf and a vampire, you may not write about only one monster. Topic 3. Jeffrey Cohen writes that "fear of the monster is really a kind of desire." What is it about the vampire / werewolf that has captivated human imagination for centuries? How can we explain our fascination with these monstrous and (often) repulsive figures? In your essay, use evidence from at least four works (texts or films) from the course materials this semester to support your opinion. You must include at least one example (each) of a werewolf and a vampire, you may not write about only one monster. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Add to cartInstant download
Reviews( 0 )
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 17, 2019
Number of pages
23
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 17, 2019
Downloads
0
Views
88